Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Homework 5
Hochgeladen von
José Del Angel Sánchez BurgosOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Homework 5
Hochgeladen von
José Del Angel Sánchez BurgosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tópicos de Mecánica Clásica 2019
Homework 5: Ecuaciones de Hamilton
Fecha de presentación: 11.08.19
1. Consider the Atwood’s machine shown in Fig.1. Let x and y be the vertical positions of the middle mass
and right mass, respectively, with upward taken to be positive. Find the Hamiltonian in terms of x
and y and their conjugate momenta, and then write down the four Hamilton’s equations.
2m
m 2m
Figure 1
2. Two beads of mass m are connected by a spring (with spring constant k and relaxed length `) and are
free to move along a frictionless horizontal wire. Let the position of the left bead be x, and let the
stretch of the spring (relative to equilibrium) be z. Find the Hamiltonian in terms of x and z and their
conjugate momenta, and then write down the four Hamilton’s equations.
3. A mass m is connected to a wall by a horizontal spring with spring constant k and relaxed length `0.
The wall is arranged to move back and forth with position Xwall = A sin ωt. Let z measure the stretch
of the spring. Find the Hamiltonian in terms of z and its conjugate momentum, and then write down
Hamilton’s equations. Is H the energy? Is H conserved?
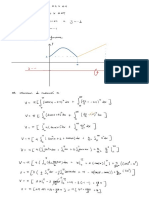
4. Consider a harmonic oscillator governed by the Hamiltonian H = p2/2m + kx2/2. If xi and pi are
the initial position and momentum, then from the results of Chapter 4, we know that x and p at a
general later time are given by
³ pi ´
(x, p) = xi cos ωt + sin ωt, −mωxi sin ωt + pi cos ωt .
mω
Consider the rectangle shown in Fig.2, with one corner at the point (x0, p0) and sides of lengths ∆x
and ∆p. Show that at any later time, the image of the rectangle is a parallelogram with area ∆x ∆p.
p
∆p
∆x
(x0, p0)
x
Figure 2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PHYS Harmonic MotionDokument34 SeitenPHYS Harmonic MotiontitinsuhartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Tensor of InertiaDokument5 SeitenThe Tensor of InertiacutieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy 421 Fall 2017 - Final ExamDokument1 SeitePhy 421 Fall 2017 - Final ExamjjwfishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Barton Zwiebach MITDokument6 SeitenAssignment 1 Barton Zwiebach MITJhon FlorezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morita EquivalenceDokument8 SeitenMorita EquivalenceANDREEA-ELENA DĂNĂȘELNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2,3 2, 1 - Sin III Xy Y, 1 2, Xy: Combined MathsDokument4 Seiten2,3 2, 1 - Sin III Xy Y, 1 2, Xy: Combined MathsSandun WanaguruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section A: Pure MathematicsDokument6 SeitenSection A: Pure MathematicsMohammed ArslaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- QFT Main2023v1Dokument146 SeitenQFT Main2023v1panzhanghiggsNoch keine Bewertungen
- RegionDokument6 SeitenRegionNersés AramianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.06x Problem Set 1Dokument5 Seiten8.06x Problem Set 1ken adamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mae 371 HW 2Dokument3 SeitenMae 371 HW 2Kevin RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture II-14, Part II: Quantum Cohomology of K Ahler ManifoldsDokument8 SeitenLecture II-14, Part II: Quantum Cohomology of K Ahler ManifoldsluisdanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- QPhys PS4Dokument2 SeitenQPhys PS4Resting BeastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 StudentDokument15 SeitenChapter 1 Studentgerearegawi721Noch keine Bewertungen
- L4 5 Path IntegralDokument19 SeitenL4 5 Path IntegralJohn KahramanoglouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthogonal SpacesDokument23 SeitenOrthogonal SpacesDeeksha BadyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201305Dokument2 Seiten201305Sachin BarthwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 5Dokument2 SeitenPs 5Henry HughesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIR - LML - Markushevich A. I. - Areas and LogarithmsDokument76 SeitenMIR - LML - Markushevich A. I. - Areas and Logarithmsavast2008100% (5)
- CE BOARD NOV 2020 Structural Analysis Set 2Dokument1 SeiteCE BOARD NOV 2020 Structural Analysis Set 2Eugenio Genesis AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9TH Differentiation Integration (32 To 55) - PHYSICSDokument24 Seiten9TH Differentiation Integration (32 To 55) - PHYSICSAashvlayan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Problems: Problems I: Introductory Problems & Collisions in One DimensionDokument4 SeitenIntroductory Problems: Problems I: Introductory Problems & Collisions in One DimensionDiego ForeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Linear Regression For Functional Data: Alain Berlinet, Abdallah Elamine, André Mas Université Montpellier 2Dokument23 SeitenLocal Linear Regression For Functional Data: Alain Berlinet, Abdallah Elamine, André Mas Université Montpellier 2الشمس اشرقتNoch keine Bewertungen
- KC SinhaDokument33 SeitenKC Sinhasai kiran50% (6)
- State Monads and Their AlgebrasDokument16 SeitenState Monads and Their AlgebrasEric HongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Two-And Higher-Dimensional Random VariablesDokument66 Seiten6 Two-And Higher-Dimensional Random VariablesViba R UdupaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGMT 221 Ch. 1Dokument13 SeitenMGMT 221 Ch. 1kebron100% (1)
- StewartCalcET7e 15 05Dokument44 SeitenStewartCalcET7e 15 05nicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 236 Midterm 2021Dokument2 Seiten236 Midterm 2021Christ CherfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GaugeTh Cours TD III 2023 24Dokument1 SeiteGaugeTh Cours TD III 2023 24Azer TyuiopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Geo HamiltonmDokument6 SeitenIntro Geo HamiltonmDiego GuillénNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monoidal - Categories Over - Operads: Elements of Higher AlgebraDokument19 SeitenMonoidal - Categories Over - Operads: Elements of Higher AlgebraKeeley HoekNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Linear Harmonic OscillatorDokument7 SeitenThe Linear Harmonic OscillatorjasmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Step Methods For Variational Inequalities On Hadamard ManifoldsDokument5 SeitenTwo Step Methods For Variational Inequalities On Hadamard ManifoldsSIDDHARTH MITRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Prob 1Dokument3 SeitenFluid Prob 1asafNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Conventions: Integration For Shear and Moment DiagramsDokument7 Seiten1 Conventions: Integration For Shear and Moment DiagramsCarl SorensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One MathsDokument11 SeitenChapter One Mathsየገጠር ልጅNoch keine Bewertungen
- Junior Inter 1b 2 Model Paper 2Dokument18 SeitenJunior Inter 1b 2 Model Paper 2Prathap Ur's MNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap1 Intro To ManifoldsDokument9 SeitenChap1 Intro To ManifoldsC FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extremal Problems - Past and Present Vladimir M. Tihomirov: Adef ABCDokument11 SeitenExtremal Problems - Past and Present Vladimir M. Tihomirov: Adef ABCmjcarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optional Problems On The Harmonic OscillatorDokument6 SeitenOptional Problems On The Harmonic OscillatorSaidWebbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harmonic Oscillator PDFDokument8 SeitenHarmonic Oscillator PDFŘoul ŤapanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes On Multivariable CalculusDokument36 SeitenLecture Notes On Multivariable CalculusAnwar ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set of Problems in Quantum MechanicsDokument4 SeitenSet of Problems in Quantum MechanicsAishwarya MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- YJCP1Dokument4 SeitenYJCP1Aloysius LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prolem Set1Dokument1 SeiteProlem Set1Dibyajyoti MohantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics: Fall Term 2009Dokument4 Seiten22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics: Fall Term 2009daniam_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Cal - W4Dokument32 SeitenBasic Cal - W4Norman LoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Theory 2019-20: Practice Problems No. IV April 17, 2020Dokument2 SeitenElectromagnetic Theory 2019-20: Practice Problems No. IV April 17, 2020DevenderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burgos de JongDokument54 SeitenBurgos de JongLong MaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SynopsisDokument13 SeitenSynopsisAaqid BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry of Warped Products As Riemannian SubmanifoldsDokument32 SeitenGeometry of Warped Products As Riemannian SubmanifoldsLinda MoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics With Mathematica Fall 2013 Exercise #1 27 Aug 2012Dokument12 SeitenPhysics With Mathematica Fall 2013 Exercise #1 27 Aug 2012Ali RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scopus Sultanov 2019Dokument10 SeitenScopus Sultanov 2019Agung Gde AgungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Time Evolution of A Coherent StateDokument7 Seiten1 Time Evolution of A Coherent StateHalloMannNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Tatjana Rack) Tomita Takesaki TheoryDokument12 Seiten(Tatjana Rack) Tomita Takesaki TheoryLUIS QUEZADANoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle of Stress-MohrDokument7 SeitenCircle of Stress-MohrArianna EstructurasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Harmonic Oscillator State Synthesis and AnalysisDokument13 SeitenQuantum Harmonic Oscillator State Synthesis and AnalysisDhakal NagendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Progress of Algebraic Geometry in JapanVon EverandRecent Progress of Algebraic Geometry in JapanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)Von EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled NotebookDokument2 SeitenUntitled NotebookJosé Del Angel Sánchez BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Seven: The Pendulum and Phase-Plane PlotsDokument15 SeitenChapter Seven: The Pendulum and Phase-Plane PlotsJosé Del Angel Sánchez BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To The Classical Three-Body Problem: From Periodic Solutions To Instabilities and ChaosDokument28 SeitenAn Introduction To The Classical Three-Body Problem: From Periodic Solutions To Instabilities and ChaosJosé Del Angel Sánchez BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wilson Loops in Large-N Theories: AbstractDokument9 SeitenWilson Loops in Large-N Theories: AbstractJosé Del Angel Sánchez BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HistoryDokument4 SeitenHistoryJosé Del Angel Sánchez BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen