Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ELEX PRBRD
Hochgeladen von
O Meter0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten12 SeitenThis document contains questions about electronics topics such as oscillators, filters, and networking. It asks about the components, characteristics, and functions of different circuit types like LC oscillators and filters. It also contains questions about networking topics like routing, IP addressing, and network device types.
Originalbeschreibung:
sample
Originaltitel
ELEX-prbrd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document contains questions about electronics topics such as oscillators, filters, and networking. It asks about the components, characteristics, and functions of different circuit types like LC oscillators and filters. It also contains questions about networking topics like routing, IP addressing, and network device types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten12 SeitenELEX PRBRD
Hochgeladen von
O MeterThis document contains questions about electronics topics such as oscillators, filters, and networking. It asks about the components, characteristics, and functions of different circuit types like LC oscillators and filters. It also contains questions about networking topics like routing, IP addressing, and network device types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 12
1. A single resistor and a single capacitor can be connected to 6.
Which types of LC oscillator uses a tickler coil in the feedback
form a filter with a roll-off rate of path?
a. -20dB/decade a. Colpitts
b. -40dB/decade b. Hartley
c. -6dB/octave c. Armstrong
d. Answer A and C d. Clapp
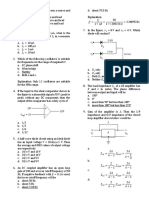
2. Identify the given figure 7. An oscillator differs from an amplifier because
a. It has more gain
b. It requires no input signal
c. It requires no dc supply
d. It always has the same output
8. Wien-bridge oscillator are based on
a. Even functions
a. Positive feedback
b. Odd functions
b. Negative feedback
c. Half-wave
c. The piezoelectric effect
d. Even Quarter-Wave
d. High gain
3. The equivalent noise temperature of the amplifier is 25 K.
9. One condition for oscillation is
What is the noise figure?
a. A phase shift around the feedback loop 180⁰
a. 1.86
b. A gain around the feedback loop of one third
b. 0.1086
c. A phase shift around the feedback loop is 0⁰
c. 1.086
d. A gain around the feedback loop of less than 1
d. 10.86
10. The frequency at which a crystal oscillator functions is
4. The number of poles in a filter affect the
determined mainly by
a. Voltage gain
a. The values of the inductor and capacitor.
b. Bandwidth
b. The thickness of the crystal
c. Center frequency
c. The amount of capacitance across the crystal
d. Roll-off rate
d. The power-supply voltage
5. A tapped coil is used in a(n):
11. A high-pass filter has R = 47Ω and C = 0.002µF, the cut-off
a. Hartley oscillator
frequency is
b. Colpitts oscillator
a. 1.694 KHz
c. Armstrong oscillator
b. 10.6 KHz
d. Clapp oscillator
c. 3.39 Hz 17. A bypass capacitor Cb across Rb provides low-pass filtering
d. None of these because:
12. An oscillator might fail to start for any of the reasons except: a. Current in the Cb branch is maximum for low frequencies
a. Low-power supply voltage b. Voltage across Cb is minimum for high frequencies
b. Low stage gain c. Voltage across Cb is minimum for low frequencies
c. In-phase feedback d. Voltage across Rb is minimum for low frequencies
d. Very low output impedance 18. For a series or parallel LC circuit, resonance occurs when
13. A series LC circuit has a Q of 100 at resonance. When 5mW is a. XL is 10 times XC or more
applied at the resonant frequency, the voltage across C equals b. XC is 10 times XL or more
a. 50µW c. XL=XC
b. 20mW d. The phase angle of the circuit is 90⁰
c. 100mV 19. A high-pass filter has R = 47Ω and C=0.002µF, the cut-off
d. 500mW frequency is:
a. 1.694KHz
14. The bipolar transistors or JFETs in a multivibrator are usually b. 10.6 KHz
connected in: c. 3.39 KHz
a. Class B d. None of these
b. A common-emitter or common-source arrangement 20. Identify the circuit
c. Class C
d. A common-collector or common-drain arrangement
15. A phase-shift oscillator has
a. Three RC circuits
b. Three LC circuits
c. A T-type circuit
d. A π-type circuit
16. The operation of a relaxation oscillator is based on
a. Charging and discharging of a capacitor
b. A highly selective resonant circuit
a. Colpitts
c. A very stable supply voltage
b. Hartley
d. Low power consumption
c. Armstrong
d. Clapp
21. At resonance, the phase angle is equals Refer to the exhibit. Which networking term describes the data
a. 0⁰ interleaving process represented in the graphic?
b. 90⁰ a. Piping
c. 180⁰ b. PDU
d. 270⁰ c. Streaming
22. A receiver connected to an antenna whose resistance is 50 d. Multiplexing
ohms has an equivalent noise resistance of 30 ohms. What is e. Encapsulation
the receiver’s noise temperature? 27. Refer to the exhibit. Which term correctly identifies the device
a. 754 K type that is included in the area B?
b. 464 K
c. 174 K
d. 293K
23. Skip
24. The maximally flat frequency response is known as
a. Chebychev
b. Butterworth
c. Bessel
d. Colpitts
25. A high-pass 2-pole filter has a cut-off frequency of 1.23 KHz.
The BW of the filter is? a. Source
a. 2.46 KHz b. End
b. 1.23 KHz c. Transfer
c. 644 KHz d. Intermediary
d. None of the choices 28.
26.
Refer to the exhibit. What type of network is shown? 31. Refer to the exhibit. Using the network in the exhibit, what
a. WAN would be the default gateway address for host A in the
b. MAN 192.133.219.0 network?
c. LAN
d. WLAN
29. Which layer encapsulates the segment into packets?
a. Physical
b. Data link
c. Network
d. Transport
30. .
a. 192.135.250.1
b. 192.31.7.1
c. 192.133.219.0
d. 192.133.219.1
32. What type of routing uses information what is manually
entered into the routing table?
a. Dynamic
b. Interior
c. Static
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only end d. Standard
devices? 33. Which process do routers use to determine the subnet
a. A, C, D network address based upon a given IP address and subnet
b. B, E, G, H mask?
c. C, D,G, H, I, J a. Binary adding
d. E, F, H, I, J b. Hexadecimal anding
c. Binary multiplication
d. Binary anding
34. Refer to the exhibit. Host A is connected to the LAN, but it 36. Which OSI layer is responsible for binary transmission, cable
cannot get access to any resources on the internet. The specification and physical aspects of network communication?
configuration of the host is shown in the exhibit. What could a. Presentation
be the cause of the problem? b. Transport
c. Data link
d. Physical
37. A network administrator is required to use media in the
network that can run up to 100 meters in cable length without
using repeaters. The chosen media must be inexpensive and
easily installed. The installation will be in a pre-existing
building with limited cabling space. Which type of media would
best meet these requirements?
a. STP
b. UTP
c. Coaxial
d. Single-mode fiber
38. What type of network cable is used between a terminal and a
console port?
a. Cross-over
b. Straight-through
a. The host subnet mask is incorrect. c. Rollover
b. The default gateway is a network address. d. Patch cable
c. The default gateway is a broadcast address. 39. Refer to the exhibit. What destination IP address will PC1 place
d. The default gateway is on a different subnet from the host. in the header for a packet destined for PC2?
35. In most business LANs, which connector is used with twisted- a. 192.168.1.1
pair networking cable? b. 192.168.2.1
a. BNC c. 192.168.2.2
b. RJ-11 d. 192.168.3.1
c. RJ-45 e. 192.168.3.54
d. Type F
40. Which option identifies the primary interface which would be a. PPM
used for initial configuration of a Cisco router? b. PWM
a. AUX interface c. PAM
b. Ethernet interface d. CODEC
c. Serial interface 46.
d. Console interface
41. Which device is used to create or divide broadcast domains?
a. Hub
b. Switch
c. Bridge
d. Router
42. It occurs when telephones, broadcasts, and computer Refer to the exhibit. All devices shown in the exhibit have
communications all use the same rules, devices, and media to factory default settings. How many collision domains are
transport their messages. represented in the topology that is shown?
a. Divergence a. 3
b. Convergence b. 4
c. Protocol c. 9
d. Network d. 10
43. What is the subnetwork address for a host with the IP address 47. It means that the internet will continue to function normally
200.10.5.68/28? even when some of the components of the network fail.
a. 200.10.5.56 a. Fault tolerance
b. 200.10.5.32 b. Scalability
c. 200.10.5.64 c. Protocol
d. 200.10.5.0 d. Quality of service(QoS)
44. Which multiplexing technique transmits analog signals? e. Security
a. WDM 48. The most common method used for sampling voice signals in
b. TDM PCM systems is
c. SDM a. Ideal sampling
d. FDM b. Natural sampling
45. It is used as an intermediate form of modulation with FSK, c. Flat-top sampling
QAM, and PCM, although it is seldom used by itself d. Sampling and holding
49. Which multiplexing technique transmits digital signals? a. Increases
a. FDM b. Stay constant
b. TDM c. Decreases
c. WDM d. Insufficient data can’t be solved
d. SDM 55. In AM Rx, Which of the following is true about the
50. It is the process of converting an infinite number of frequency of the local oscillator?
possibilities to a finite number of conditions. a. It is above the RF frequency
a. Sample and Hold b. It is below the RF frequency
b. Quantization c. It can be either above or below the RF frequency
c. Encoding d. It is fixed, typically at 455 KHz
d. Analog to digital conversion 56. What part of the AM receiver of which the primary
51. Which of the following is not used as another name for functions are amplification and selectivity?
defining modulation index? a. RF stage
a. Modulation Reliability b. Mixer stage
b. Modulation Factor c. IF stage
c. Degree of Modulation d. AM detector
d. Modulation coefficient 57. Suppose an AM receiver uses a 5-MHz IF frequency.
52. What type of modulation is used to produce FM by using Assuming High-side injection, what would be the image
PM techniques? frequency if the receiver was tuned in ….. MHz? kulang ng
a. Indirect FM given bsta gagamiting formula fimg=f+2fLO
b. Direct FM a. 40 MHz
c. Low level PM b. 45 MHz
d. High level PM c. 55 MHz
53. In AM, as the modulation index increases, what happen to d. 60 MHz
the carrier power? 58. If an AM receiver has an RF bandwidth of 20MHz and an IF
a. It increases bandwidth of 200 KHz, what is the value of NFimprovement?
b. It remains the same a. -20 dB
c. It decreases b. -40 dB
d. It varies randomly c. 20 dB BI=BRF/BIF, NFimprove=10logBI
54. In FM, as the frequency deviation decreases the modulation d. 40 dB
index
59. An AM signal in which the carrier is 70% modulated 63. If the deviation sensitivity of an FM modulator is 2KHz/V,
contains 1500W at the carrier frequency. What is the power what will be the modulation index caused by a 1-volt, 1KHz
content in each sideband when the percent modulation audio signal?
drops to 50%? a. 0.5
a. 183.75 W b. 1
b. 153.75 W c. 1.5
c. 123.75 W d. 2 mf=delta/fm
d. 93.75 W PUSB=PLSB=(m2Pc)/4 64. The FM receiver is tuned to92.3 MHz. What is the local
60. The antenna current of an AM broadcast transmitter, oscillator frequency?
modulated to a depth of 40% by an audio sine wave, is 11 a. 81.6 MHz
Amp. It increases to 12 Amp as a result of simultaneous b. 70.9MHz
modulation by another signal. What is the modulation index c. 103MHz FLO=FIF+FI , FIF=10.7MHz
due to this second signal? d. 113.7MHz
a. 0.458 65. The FM receiver is tuned to 92.3 MHz, what is the possible
b. 0.526 image frequency?
c. 0.643 IT=IC(1+(m2/2))1/2 a. 81.6 MHz
d. 0.718 b. 70.9MHz
61. The range of frequencies over which a PLL will acquire or c. 163.2MHz
recognize an input signal variations is known as the (d ko d. 141.8MHz
sure yung sagot sa dalawa) 66. If an AM transmitter puts out 100watts with no modulation,
a. Circuit Bandwidth it will pull out ____watts with 100% modulation.
b. Capture range a. 50
c. Acceptance bandwidth b. 75
d. Lock range c. 150 PT=Pc(1+m2/2)
62. If a 2-KHz audio tone causes a frequency deviation of 4 KHz d. none of the choices
in 89.1 MHz carrier, determine the FM bandwidth using 67. In AM, if the carrier power is 1000watts, what is the power
Carson’s rule. in the USB at 70.7% modulation?
a. 6 KHz a. 707 watts
b. 8 KHz b. 250 watts PT=Pc(1+m2/2), PSB=PT–PC
c. 12 KHz c. 353.5 watts
d. 16 KHz d. none of the choices
68. It is the amount of the power that flows through each 73. In wave propagation it is more …………. when the obstacle
square meter of a surface perpendicular to the direction to has sharp edges and when the surface dimensions are small
travel. in comparison to the wavelength
a. Effective Isotropic Radiated Power a. Diffraction
b. Power Density b. Reflection
c. Power Intercepted c. Refraction
d. Isotropic Received Level d. Attenuation
69. The two important characteristics of antenna are Gain an 74. What is the velocity of radio a signal in a medium with a
a. Frequency dielectric constant of 2.1?
b. Power input a. 142.66 x 106 m/s
c. Effective Area b. 182.65x 106 m/s
d. Power output c. 207.02x 106 m/s
70. If the operating frequency of a transmitter increases then its d. 215.68x 106 m/s
antenna gain will _____. 75. What is the power density at a distance of 5 km, if the
a. decreases transmitter effective isotropic radiated power is 1000
b. remain the same Watts?
c. increase a. 8.31 mW/m2
d. randomly change b. 1.83 µW/m2
71. In wave propagation, it is the ratio of the received power to c. 5.38 nW/m2
the transmitted power d. 3.18 µW/m2
a. Power Density 76. In telephone system the noise interference is comprised of
b. Free Space Attenuation the degree of annoyance to the listener and the effect on
c. Power Gain intelligibility of speech which are both functions of
d. Received Signal Level a. Amplitude
72. It governs the behavior of electromagnetic waves being b. Frequency
refracted. c. Phase
a. Inverse Square Law d. None of the choices
b. Snell’s Law 77. Which of the following cable gauge will provide a greater
c. Right Hand Rule loop length based on a certain loop loss limit?
d. Fresnel’s Law a. 26
b. 24
c. 22 c. Dialing circuit
d. 19 d. Protection circuit
78. It is the ……. ……. For measuring the quality of a speech ….. 83. It is the proportion of total calls, usually during the busy
a. Quality of Service hour that cannot be completed immediately or serve within
b. Loudness ……. a prescribed time.
c. …… a. Grade of service
d. Test level point (TLP) b. Quality of service
79. In the telephone industry, A/D conversion is referred to as: c. Blockage
a. Voice recovery d. Calls per busy hour
b. Voice sampling 84. A 0.02 Erlang per line rating would mean
c. Voice digitization a. 2 calls lost per 100 attempts
d. Voice quantization b. 2 calls connected per 100 attempts
80. In today’s Central Office, which of the following is not c. 20 calls lost per 100 attempts
implemented using digital technology? d. 20 calls connected per 100 attempts
a. Line interface 85. If the grade of service of a telephone system is ………… …
b. Signaling circuit 0.05, it means that
c. Switching circuit a. Completed calls of 5%
d. Call processor b. Lost call of 95%
81. It is consists of a ring relay, an overvoltage protection c. Lost call of 5%
circuit, a subscriber loop interface circuit, an d. Blocked calls of 95%
encoder/decoder, and a time-slot assignment circuit. 86. What are the seven functions (BORSCHT functions)
a. Central Office performed by the analog line interface?
b. Line interface a. Battery, overcurrent protection, ringing, signaling, A/D
c. Switching circuit conversion, hybrid and testing
d. Call processor b. Battery, overvoltage protection, ringing, supervision,
82. It is a part of telephone set that is consists mainly of coding, hybrid and testing
amplifiers that route the voice signal to be transmitted from c. Battery, overvoltage protection, ringing, supervision,
the handset microphone to the telephone line, and line 2W/4W conversion, hybrid and testing
received voice signal from the telephone line to the handset d. Battery, overvoltage protection, ringing, signaling,
earpiece. coding, hybrid, time division multiplexing
a. Speech circuit 87. It was found that 1KHz signal in telephone system will
b. Switchhook produce zero or negligible interference at a level of
a. -85 dBm a. 5000 n=(w/b)(M/frf)
b. -90 dBm b. 1000
c. -85 dB c. 200
d. -90 dB d. 10000
88. Noise is a problem in telephone system and one of the 93. Cellular base stations are normally using what type of
solution to minimize it is to antenna?
a. Increase the bandwidth a. Omni-directional
b. Use amplifier b. Bi-directional
c. Increase the S/N c. Sectored-directional
d. Use filter d. Hexa-directional
89. It is a power measurement unit adjusted to 0 dBm that 94. A telephone system has a 7-digit telephone directory
indicates what the power would be if the signal were numbering plan, what is the capacity of the system?
measured at a 0 TLP. a. 1,000,000 lines
a. dBmC b. 100,000 lines
b. dBmCO c. 10,000 lines
c. dBmO d. 7000 lines
d. dBa 95. A local loop has a resistance of 1KΩ, and the telephone
90. at the telephone set A which is -30 dBm TLP, the signal was connected to it has and off-hook resistance of 200Ω.
measured as -35 dBm and the noise was measured as 18 Calculate the loop current when the phone is off-hook.
dBm. What is the noise level in dBm? a. 36mA
a. -72 b. 40mA
b. -108 c. 48mA
c. -98 d. 44mA
d. -82 96. Skip
91. It is the act of changing from one channel to another. 97. Which of the following is not branded as 3G?
a. Roaming a. UMTS
b. Handover b. WCDMA
c. Paging c. GSM-EDGE
d. Switching d. HSPA
92. What is the system capacity for a 20 cells with frequency 98. Which of the following is branded as 4G?
reuse factor of 4 if the available spectrum is from 800-830 a. Zigbee
MHz and the required voice bandwidth is 30KHz? b. WI-FI
c. WI-MAX
d. HSPA
99. 2.5G is a stepping stone between 2G and 3G cellular
wireless technology. Which of the following is 2.5G?
a. EDGE
b. GPRS
c. GSM-EDGE
d. E-GPRS
100. Which of the following is a 2.75G system?
a. EDGE
b. IMT2000
c. CDMA2000
d. UMTS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Malvino Chapter 23 MCQ With AnswersDokument4 SeitenMalvino Chapter 23 MCQ With AnswersAly BueserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miller MCQ PDFDokument21 SeitenMiller MCQ PDFRafael Mappala DagasaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDC - Bit Bank 20122017Dokument29 SeitenPDC - Bit Bank 20122017VigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar Junction Transistors 1Dokument6 SeitenBipolar Junction Transistors 1APPLENoch keine Bewertungen
- Tasks 4 You Tasks 4 You: MCQ of Electrical Circuits and Networks (ECN)Dokument8 SeitenTasks 4 You Tasks 4 You: MCQ of Electrical Circuits and Networks (ECN)Manmat BiradarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ of Miller 7th Ed PDFDokument18 SeitenMCQ of Miller 7th Ed PDFJae Ar AbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ of Miller 7th EdDokument18 SeitenMCQ of Miller 7th EdmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miller 7th Ed ReviewerDokument16 SeitenMiller 7th Ed ReviewerChristian De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indiabix IIDokument60 SeitenIndiabix IISylvina Anne Conde AsiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 CIPRESDokument7 SeitenAssignment 1 CIPRESEric Paolo CipresNoch keine Bewertungen
- IndiaBIX - Analog Electronics - Section 1Dokument6 SeitenIndiaBIX - Analog Electronics - Section 1Mikaela VillalunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5Q .Wiz RLC Question Paper1Dokument5 Seiten5Q .Wiz RLC Question Paper1R.s. VenkatachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indiabix IiiDokument42 SeitenIndiabix IiiSylvina Anne Conde Asiño100% (1)
- Module 3 Aug 17Dokument3 SeitenModule 3 Aug 17rashmiameNoch keine Bewertungen
- V I V I Z I: ∈=L ΔΙ ∈=L Δι P ∈=−LDokument3 SeitenV I V I Z I: ∈=L ΔΙ ∈=L Δι P ∈=−LMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indiabix IiiDokument43 SeitenIndiabix IiiPeter ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Past Board April 2005 With AnswersDokument17 SeitenElectronics Past Board April 2005 With AnswersJose Maria ManabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Test Ch. 14. Frequency Effects SoalDokument2 SeitenSelf Test Ch. 14. Frequency Effects SoalIis SuharniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Exam Electro 212 Prepared By: CircuitsDokument11 SeitenPrelim Exam Electro 212 Prepared By: Circuitsjy marquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grainy or dull surfaceDokument4 SeitenGrainy or dull surfaceJoshua DoctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Elex PreboardDokument8 Seiten4 Elex PreboardV1NSKYNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDIABIX PART 3 ELEX MCQs 080918 PDFDokument41 SeitenINDIABIX PART 3 ELEX MCQs 080918 PDFJehuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GC-8 Basic ElectronicsDokument5 SeitenGC-8 Basic ElectronicsyihesakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Elex PreboardDokument8 Seiten9 Elex PreboardV1NSKYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pinoybix Communication: Series of MCQ Part 1. Transmission FundamentalsDokument41 SeitenPinoybix Communication: Series of MCQ Part 1. Transmission Fundamentalsmark stephen yapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Engineering Correlation 1 (Electronics 1 and 2) QuestionsDokument45 SeitenComputer Engineering Correlation 1 (Electronics 1 and 2) QuestionsNorman OcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELEX (MASTERY EXAM 1) Questions and AnswersDokument4 SeitenELEX (MASTERY EXAM 1) Questions and AnswersJoshua DoctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perc Comms 1Dokument9 SeitenPerc Comms 1Miguel BulanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTRONICSDokument5 SeitenELECTRONICSDaphnie DelantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 18Dokument11 SeitenEc 18Darshan NakawalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dsaaasdg FgdsDokument6 SeitenDsaaasdg Fgdstetimo mekutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EST Correl 2Dokument10 SeitenEST Correl 2ashlyolsemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elex Practice2334467Dokument3 SeitenElex Practice2334467AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLOYD2 32pagesDokument32 SeitenFLOYD2 32pagesCorzynill MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics MCQ Practice Test: Amplifiers, Oscillators, and Power SuppliesDokument2 SeitenElectronics MCQ Practice Test: Amplifiers, Oscillators, and Power SuppliesDurga DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece 511final Exam - Oct2017printingDokument3 SeitenEce 511final Exam - Oct2017printingLoryliza M DeiparineNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC Unit 2 Sem 2 PDFDokument2 SeitenBEC Unit 2 Sem 2 PDF19juee jamsandekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE QuestionsDokument4 SeitenECE QuestionsAnne Mary FabregasNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ's Chap 16aDokument5 SeitenMCQ's Chap 16aArham MunirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics 1Dokument14 SeitenElectronics 1Marvin LabajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Refresher 5Dokument4 SeitenElectronics Refresher 5Jonas ParreñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pinoybix WADokument28 SeitenPinoybix WAKenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOCK BOARD EXAM IN ELECTRONICS (BDokument8 SeitenMOCK BOARD EXAM IN ELECTRONICS (BCherryl Mae AlmojuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME1Dokument5 SeitenME1jj012586Noch keine Bewertungen
- Telangana ECET 2016 Model Question Paper with AnswersDokument11 SeitenTelangana ECET 2016 Model Question Paper with AnswersJammula Sivanaga Chowdary100% (1)
- Transmission LineDokument28 SeitenTransmission LineJonathan TuazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ot 2Dokument9 SeitenOt 2Eugene MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Weekly TestDokument2 Seiten1st Weekly TestJayson EbronNoch keine Bewertungen
- TH Solutions Feedback Oscillators October 2019.PDF Version 1Dokument2 SeitenTH Solutions Feedback Oscillators October 2019.PDF Version 1Nida Bagoyboy NatichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obj Electrical 2002paper IIDokument13 SeitenObj Electrical 2002paper IImuthusamyeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseDokument59 SeitenAmplifier Frequency ResponseJehuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Electricity New 1Dokument11 SeitenApplied Electricity New 1Samuel Owusu DonkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Quantum Electronics: Volume 3Von EverandAdvances in Quantum Electronics: Volume 3D. W. GoodwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma Sources for Thin Film Deposition and EtchingVon EverandPlasma Sources for Thin Film Deposition and EtchingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitor Discharges - Magnetohydrodynamics - X-Rays - UltrasonicsVon EverandCapacitor Discharges - Magnetohydrodynamics - X-Rays - UltrasonicsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Von EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Von EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- 2bit Comparator Boolean ExpressionDokument27 Seiten2bit Comparator Boolean ExpressionO MeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floyd Semicon&specialpurposediodesDokument7 SeitenFloyd Semicon&specialpurposediodesO MeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optics LectureDokument26 SeitenFiber Optics LectureJitendra MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BJT Fet Amp Op OsciDokument7 SeitenBJT Fet Amp Op OsciRaine LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework RoboticsDokument14 SeitenHomework RoboticsO Meter100% (2)
- Floyd Semicon&specialpurposediodesDokument7 SeitenFloyd Semicon&specialpurposediodesO MeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem: SolutionDokument15 SeitenProblem: SolutionbethNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS-EE2Dokument10 SeitenCNS-EE2Achilles AldaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework RoboticsDokument14 SeitenHomework RoboticsO Meter100% (2)
- Hw1 Robotics EditedDokument10 SeitenHw1 Robotics EditedO MeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johnny Mbizo DyaniDokument4 SeitenJohnny Mbizo DyaniBob ShuruncleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word Power 1Dokument36 SeitenWord Power 1nelrivera100% (1)
- Art Music 3 Baroque Era Study GuideDokument4 SeitenArt Music 3 Baroque Era Study Guidethot777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prog RockDokument23 SeitenProg Rockemschris100% (1)
- Eminem Poem AnalysisDokument3 SeitenEminem Poem Analysisapi-243178570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bronx Pastor Fired: Jamaican Artist Convicted On Drug ChargesDokument24 SeitenBronx Pastor Fired: Jamaican Artist Convicted On Drug ChargesPatrick MaitlandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feminist ViewDokument22 SeitenFeminist ViewAhmed EidNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Design of Low Noise AmplifierDokument7 SeitenRF Design of Low Noise AmplifiersubbusriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yamaha YST-MS28 Powered Speakers Owners ManualDokument7 SeitenYamaha YST-MS28 Powered Speakers Owners Manualbrett oestingNoch keine Bewertungen
- JazzTimes - June 2023Dokument54 SeitenJazzTimes - June 2023Guillermo ArriagadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whistling in The Dark by Shirley Hughes Chapter SamplerDokument40 SeitenWhistling in The Dark by Shirley Hughes Chapter SamplerCandlewick PressNoch keine Bewertungen
- LNA Design Using UMS Foundry Desig KitDokument39 SeitenLNA Design Using UMS Foundry Desig KitstepannpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 - Communication ModelsDokument12 SeitenModule 2 - Communication ModelsKwon SunooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Celebrating God's Wildly Inclusive Love at Central Presbyterian Church Advent 2013Dokument1 SeiteCelebrating God's Wildly Inclusive Love at Central Presbyterian Church Advent 2013Phillip MorganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Call Flow inDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding Call Flow inAmit RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RythmDokument2 SeitenRythmNico Montemayor100% (1)
- Certified Professionals Engineers - 201408011549472009Dokument3 SeitenCertified Professionals Engineers - 201408011549472009chanu9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pelco Endura VCD5000 Video Console Display QSG ManualDokument24 SeitenPelco Endura VCD5000 Video Console Display QSG ManualRafa Vinícius LeopoldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guitar - Tab Book - Richie Blackmore - Best of Deep Purple PDFDokument97 SeitenGuitar - Tab Book - Richie Blackmore - Best of Deep Purple PDFLoren100% (2)
- Session 4A7 Eigenfunction Expansion Based Analysis of Electromagnetic StructuresDokument11 SeitenSession 4A7 Eigenfunction Expansion Based Analysis of Electromagnetic StructuresNicoletaRebenciucNoch keine Bewertungen
- MISTYDokument6 SeitenMISTYJoanna Panayi100% (2)
- XTS DVR5616 S 59Dokument2 SeitenXTS DVR5616 S 59erazorafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halifax Comcast License Exhibit 2Dokument2 SeitenHalifax Comcast License Exhibit 2RiazboniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 905 Tower Antenna Mount CDokument4 Seiten905 Tower Antenna Mount CEhsan RohaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of a Half-Wave Dipole Antenna in CSTDokument5 SeitenDesign and Simulation of a Half-Wave Dipole Antenna in CSTali saleh100% (2)
- Elements of Art AuditoryDokument10 SeitenElements of Art AuditoryMendoza Robin I.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Writing that evokes emotionDokument11 SeitenWriting that evokes emotionManu RemakantNoch keine Bewertungen
- RadhamadhavaDokument10 SeitenRadhamadhavatadepalli patanjaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sor - Etude - Op.44 n.1Dokument20 SeitenSor - Etude - Op.44 n.1Tachka Photo 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elements and Principles of ArtsDokument9 SeitenElements and Principles of ArtsJireh LumaynoNoch keine Bewertungen