Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GCD and Sum of Cubes Formula Proof
Hochgeladen von
Mr SAQOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GCD and Sum of Cubes Formula Proof
Hochgeladen von
Mr SAQCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ID: BC180409108
Question No: 1
Solution: -
GCD(255561, 25)
Divide 255561 by 25
This gives us 255561 25 10222 11
Divide 25 by 11
This gives us 25 11 2 3
Divide 11 by 3
This gives us 11 3 3 2
Divide 3 by 2
This gives us 3 2 1 1
Divide 2 by 1
This gives us 2 1 2 0
Hence GCD 255561, 25 1 Answer
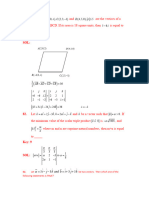
Question no: 2
Solution: -
n 2 n 1
2
1 2 3 ... n
3 3 3 3
for all positive integers
4
Let P(n) denotes the given equation
Basis Step:
P (1) is true for n 1
L.H.S of P (1) 13 1
12 (1 1) 2 4
R.H.S of P(1) 1
4 4
So L.H .S R.H .S of P 1 .Hence P 1 is true
Inductive Step:
Suppose P (k ) is true for some integers k 1
k 2 k 1
2
13 23 33 ... k 3 (i)
4
To prove P(k 1) is true
k 1 k 1 1 k 1 k 2
2 2 2 2
13 23 33 ... (k 1)3 13 23 33 ... (k 1)3
4 4
Opening powers
k 4 6k 3 13k 2 12k 4
13 23 33 ... (k 1)3 (ii)
4
Consider L.H.S of above equation ii
13 23 33 ... (k 1)3 13 23 33 ... k 3 ( k 1)3
k 2 k 1
2
(k 1)3 a b a 2 2 ab b 2 a b a 3 3a 2b 3ab 2 b3
2 3
and
4
k 2k 3 k 2
4
k 3 3k 2 3k 1
4
k 4 2k 3 k 2 4k 3 12k 2 12k 4
4
k 4 6k 3 13k 2 12k 4
4
Hence P k +1 is also true and so by Mathematical induction the given equation is true for all integers n 1.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Proofs: Zeph GrunschlagDokument36 SeitenProofs: Zeph GrunschlagElda Oktaviani100% (1)
- The Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151Von EverandThe Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151Noch keine Bewertungen
- LDPC Code BER SimulationDokument5 SeitenLDPC Code BER SimulationM A DiptoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Mathematics A Discrete Introduction 3rd EditionDokument38 SeitenSolution Manual For Mathematics A Discrete Introduction 3rd Editionguerdonnettlerph4gz100% (9)
- MTH202 Assignment SolutionDokument2 SeitenMTH202 Assignment SolutionSehar TanveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring 2019 - MTH202 - 2Dokument3 SeitenSpring 2019 - MTH202 - 2waqarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTH202 Practice Questions 23-45Dokument20 SeitenMTH202 Practice Questions 23-45Musa0% (1)
- (MAA 1.9) :PMI - SolutionsDokument14 Seiten(MAA 1.9) :PMI - SolutionsDAVIES KIPRONONoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture # 19 (Induction)Dokument32 SeitenLecture # 19 (Induction)Abdul Hannan FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Mathematical InductionDokument6 SeitenPrinciple of Mathematical InductionAmiya Kumar PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full First Course in The Finite Element Method Si Edition 6th Edition Logan Solutions Manual PDFDokument36 SeitenDwnload Full First Course in The Finite Element Method Si Edition 6th Edition Logan Solutions Manual PDFcostyrafic2100% (13)
- Full Download First Course in The Finite Element Method Si Edition 6th Edition Logan Solutions ManualDokument36 SeitenFull Download First Course in The Finite Element Method Si Edition 6th Edition Logan Solutions Manualmariputwashercy4ca97% (38)
- XI - PRINCIPLE OF MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION-Remesh-hssliveDokument7 SeitenXI - PRINCIPLE OF MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION-Remesh-hssliveChristy BinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Course in The Finite Element Method SI Edition 6th Edition by Logan ISBN Solution ManualDokument67 SeitenFirst Course in The Finite Element Method SI Edition 6th Edition by Logan ISBN Solution Manualahmed100% (25)
- Solution Manual For First Course in The Finite Element Method SI Edition 6th Edition by Logan ISBN 1305637348 9781305637344Dokument36 SeitenSolution Manual For First Course in The Finite Element Method SI Edition 6th Edition by Logan ISBN 1305637348 9781305637344ianparkerjkqtnbefrw95% (20)
- 2012 GCE H2 Maths Solutions Paper 1Dokument8 Seiten2012 GCE H2 Maths Solutions Paper 1tsoi lam chanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download First Course in The Finite Element Method 6th Edition Logan Solutions ManualDokument36 SeitenFull Download First Course in The Finite Element Method 6th Edition Logan Solutions Manualmariputwashercy4ca100% (35)
- Dwnload Full First Course in The Finite Element Method 6th Edition Logan Solutions Manual PDFDokument36 SeitenDwnload Full First Course in The Finite Element Method 6th Edition Logan Solutions Manual PDFcostyrafic2100% (10)
- Logan 6e ISM Chapter 02Dokument22 SeitenLogan 6e ISM Chapter 02leehyobeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rinciple F Ounting: BBA-103 Unit - 1Dokument13 SeitenRinciple F Ounting: BBA-103 Unit - 1Rishab Jain 2027203Noch keine Bewertungen
- TUTORIAL: Test For Convergence: 1 K 1 K 2 K 1 K 3Dokument3 SeitenTUTORIAL: Test For Convergence: 1 K 1 K 2 K 1 K 3Ahmad Haziq Bin ZamriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Is The Angle That The String Makes With The Vertical When Released From Rest Will Affect TheDokument8 SeitenAngle Is The Angle That The String Makes With The Vertical When Released From Rest Will Affect TheHidayah SakinahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usama Ahmed Assignment Mth202Dokument3 SeitenUsama Ahmed Assignment Mth202Usāmā ĀhmēdNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB M2 E02Dokument40 SeitenQB M2 E02ym5c23240% (1)
- Chapter Four: P (1) Is True If P (K) Istrue, Then P (K +1) Is Alsotrue Then, P (N) Is True For All N Element Z I N (n+1)Dokument5 SeitenChapter Four: P (1) Is True If P (K) Istrue, Then P (K +1) Is Alsotrue Then, P (N) Is True For All N Element Z I N (n+1)Ciara LadromaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET (UG) 2017 Paper Solution PDFDokument45 SeitenNEET (UG) 2017 Paper Solution PDFManickam GnanashekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUTORIAL: Test For Convergence: 1 K K 2 1 K KDokument3 SeitenTUTORIAL: Test For Convergence: 1 K K 2 1 K KEja RotiKejuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matematika InduksiDokument37 SeitenMatematika InduksiAnonymous CKmTItqNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The K-Lucas NumbersDokument11 SeitenOn The K-Lucas NumbersEraslan Şevki YilmazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft of Solution: EXAM IN COURSE TFY4220 Solid State PhysicsDokument8 SeitenDraft of Solution: EXAM IN COURSE TFY4220 Solid State Physicslyon juniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2.3Dokument7 SeitenExample 2.3fxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5Dokument19 SeitenLecture 5Tyrell WellickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rationalization and SurdsDokument90 SeitenRationalization and SurdsThe Csf CsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths HL InductionDokument10 SeitenMaths HL InductionKadar PathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical InductionDokument16 SeitenMathematical InductionHaphnia Gonzaga SalomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical induction proofsDokument9 SeitenMathematical induction proofsDane SinclairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sathis FinalDokument14 SeitenSathis FinalsathishNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Junior College 2014 - 2015 H2 Mathematics Sequences and Series Assignment SolutionsDokument3 SeitenNational Junior College 2014 - 2015 H2 Mathematics Sequences and Series Assignment SolutionsYu XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Assignments #1 - SolDokument4 SeitenHome Assignments #1 - SolMike RossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aft 2010 PDFDokument85 SeitenAft 2010 PDFRoberto CorralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control 11 3 PDFDokument14 SeitenControl 11 3 PDFMais SarayraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symetric Group 2Dokument4 SeitenSymetric Group 2Hafiz AzeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical InductionDokument17 SeitenMathematical InductionLeng Hour lengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequences & Summations: CS 1050 Rosen 3.2Dokument14 SeitenSequences & Summations: CS 1050 Rosen 3.2MOhi Ud dinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matematika MinatDokument20 SeitenMatematika MinatNathanael KennethNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5Dokument27 Seiten5SIDDPPA.SATAYMANAVAR SataymanavarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors Revision Exercise (Solutions)Dokument10 SeitenVectors Revision Exercise (Solutions)Lee Jun HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Olytechnic OF Amibia Chool OF Ealth AND Applied CiencesDokument3 SeitenOlytechnic OF Amibia Chool OF Ealth AND Applied CiencesTiofelus H. HamutenyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 PH 1 VectorsDokument12 Seiten2023 PH 1 VectorsKillerpkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 601 Num Meth Lecture 5Dokument18 SeitenCe 601 Num Meth Lecture 5Worl BossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 2Dokument3 SeitenHomework 2euler96Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1200 Assignment 3Dokument3 Seiten1200 Assignment 3Bludimir ClawgsburgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequences & Summations: Discrete Structure 1 Bscs 2Dokument14 SeitenSequences & Summations: Discrete Structure 1 Bscs 2Jan Peter PiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability DistributionDokument13 SeitenProbability DistributionLëryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Mathematical InductionDokument41 Seiten17 Mathematical InductionJohn Lloyd EnguitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Induction FormulasDokument17 SeitenMathematical Induction Formulasmita sari halawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relaxed Skolem Mean Labeling of Four Star GraphsDokument5 SeitenRelaxed Skolem Mean Labeling of Four Star GraphsVinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS3230: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Semester 2, 2020-21, School of Computing, NUSDokument3 SeitenCS3230: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Semester 2, 2020-21, School of Computing, NUSSourabh RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Pendulum (MDokument16 SeitenPhysical Pendulum (Mthathalakshman121407Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thomson Vib 5 Ech 2 P 02Dokument2 SeitenThomson Vib 5 Ech 2 P 02Salar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math WorksheetDokument4 SeitenMath WorksheetYen AduanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math III QauntumDokument240 SeitenMath III Qauntumgamer stupidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Partition Function Revisited: M. Ram MurtyDokument19 SeitenThe Partition Function Revisited: M. Ram MurtyMuhammad Andyk MaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Those Fascinating NumbersDokument452 SeitenThose Fascinating NumbersnachtjaegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- APX-BB (B.sc. Computer Science)Dokument199 SeitenAPX-BB (B.sc. Computer Science)kavirajeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Santos - Jiunior Problem Seminar - 2008 - 9-9Dokument1 SeiteSantos - Jiunior Problem Seminar - 2008 - 9-9chengpeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Structures - Assignment-01: PART 1: CountingDokument2 SeitenDiscrete Structures - Assignment-01: PART 1: CountingXYZNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Quadratic Reciprocity LawDokument178 SeitenThe Quadratic Reciprocity LawTong ZouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qbasic Programs 1: Find Prime, Capital Letters, Palindrome & MoreDokument16 SeitenQbasic Programs 1: Find Prime, Capital Letters, Palindrome & MoreArdie GucciNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-Routine For Topological Sort And Shortest Path AlgorithmsDokument3 SeitenC-Routine For Topological Sort And Shortest Path AlgorithmsSudharsan Amalraj JothirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout-1 Foundations of SetsDokument3 SeitenHandout-1 Foundations of Setsapi-253679034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 5 Computer Arithmetic: 5.1 Addition and SubtractionDokument16 SeitenUnit - 5 Computer Arithmetic: 5.1 Addition and SubtractionKeshav NaganathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Maths Chapter 6Dokument37 Seiten8th Maths Chapter 6Pradeep SreedharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Trellis Diagram and The Viterbi AlgorithmDokument12 Seiten07 Trellis Diagram and The Viterbi AlgorithmAejaz AamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harder 3u Level 3Dokument22 SeitenHarder 3u Level 3greycouncilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binary Number SystemDokument18 SeitenBinary Number SystemMuhammad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integer Answer Type-Questions OnlyDokument3 SeitenInteger Answer Type-Questions OnlyDevi PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- C4 Binomial Expansion Exam Questions: (C4 Jan 2014 (R) Q1) 1Dokument18 SeitenC4 Binomial Expansion Exam Questions: (C4 Jan 2014 (R) Q1) 1anthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Structure & Theory of Logic Exam QuestionsDokument2 SeitenDiscrete Structure & Theory of Logic Exam QuestionsKanchanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules For Significant FiguresDokument2 SeitenRules For Significant FiguresWilliam BoykeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expression & Assignment Worksheet For Java: A Ac B B XDokument1 SeiteExpression & Assignment Worksheet For Java: A Ac B B XKhanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors and MultiplesDokument9 SeitenFactors and MultipleschrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4-Decrease and Conquer & Divide and ConquerDokument13 SeitenUnit 4-Decrease and Conquer & Divide and Conquernosignal411Noch keine Bewertungen
- University of Chakwal: Department of Computer Science & Information TechnologyDokument3 SeitenUniversity of Chakwal: Department of Computer Science & Information Technologysania ejazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton'S Divided Difference Interpolating PolynomialsDokument3 SeitenNewton'S Divided Difference Interpolating PolynomialsRaffandi RolandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benson Fridrich LLDokument16 SeitenBenson Fridrich LLSergiotfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtech Cs and Crs Pcb 2024Dokument10 SeitenMtech Cs and Crs Pcb 2024Dr. Sourav DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class V Ntop-3 Worksheet-1Dokument3 SeitenClass V Ntop-3 Worksheet-1AIM Technologies Computer ScienceNoch keine Bewertungen
- COP 3502 Exam #1 Review Test Date/Time: September 24 (Thursday) 4:30-5:45pm CB2-207Dokument3 SeitenCOP 3502 Exam #1 Review Test Date/Time: September 24 (Thursday) 4:30-5:45pm CB2-207Tyrone BombaclatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backtracking - Set 6 (Hamiltonian Cycle) - GeeksforGeeksDokument10 SeitenBacktracking - Set 6 (Hamiltonian Cycle) - GeeksforGeeksAtul GargNoch keine Bewertungen