Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Day 2 Lecture Kinds of Laws
Hochgeladen von
Hassan MalaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Day 2 Lecture Kinds of Laws
Hochgeladen von
Hassan MalaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
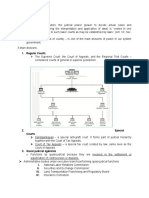
Kinds of laws:
Classification of law:
I. Natural law
- This derives its force and authority from God. Superior to other laws. It is binding upon the
whole world and in all countries.
II. Human positive law
- This law is promulgated expressly or indirectly by competent human authority for the common
good, and usually, but not necessarily, imposing sanctions in case of disobedience
Kinds of natural law
Physical law – universal rule of action that governs the conduct and movement of things which are
non-free and material.
Moral law – set of rules which establishes what is right and what is wrong as dictated by the human
conscience.
Divine law
a) Divine positive law, i.e. Ten commandments
b) Divine human positive law
- Made by church authority (i.e. Commandments of the church)
Kinds of human positive law
Accdg to force and effect:
1. Mandatory and/or prohibitory laws – those which have to be complied with, because they
are expressive of public policy: disobedience is punished either by direct penalties or by
considering an act or contract void.
2. Permissive or suppletory laws – those which may be deviated from, if the individual so
desires.
Accdg to the scope or content of the law:
1. Public law – that which governs the relations of the individual with the state or rules or
community as a whole. (This includes political law, criminal law, and law on taxation)
2. Private law – that which regulates the relations of the members or a community with one
another. (This consists of civil law, labor law, and commercial law)
Accdg to whether a right is given, or merely the procedure for enforcement is laid down:
1. Substantive law – that which establishes rights and duties
2. Remedial (or procedural or adjective law) – that which prescribes the manner of enforcing
legal rights and claims.
Political law
- That branch of public law which deals with the organization and operations of the governmental
organs of the state and defines the relations of the state with the inhabitants of the territory
It consist, among other, of:
Constitutional law I and II
Administrative law, law on public officers and election laws
Public international law
Criminal law
- That branch of law which defines offenses and specify the corresponding penalties therefor.
- It consists, among others, of:
Criminal law I
Criminal law II
Taxation
- That branch of law which deals with the imposition and collection of taxes
- It consists, among others, of:
Taxation I
Taxation II
Civili law
- That vranch of law which every particular nation or state has established peculiarly for itself.
This law concerns with civil or private rights and remedies, as contrasted to criminal law.
- It consists, among others, of:
Persons and family relations
Property
Obligations and contracts
Succession
Sales
Credit transactions
Agency, trust and partnership
Torts and damages
Transportation law
Labor laws
- That branch of law which deals with the relationship between the employer and the employee,
as well as the working conditions, wages, fringe benefits, grievances and association of
employees.
- It consists, among others, of:
Labor law I
Labor law II
Commercial law
- Body of law that applies to the rights, relations and conduct or persons and businesses engaged
in commerce, merchandising and trade.
- It consists, among others, or:
Corporation Law
Negotioable Instruments Law
Remedial law
- It refers to the means and methods of setting the courts in motion, making facts known to them
and effectuating their judgements.
- It consists, among others, of:
Civil procedure
Criminal procedure
Evidence
Special proceedings
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Classification of Law by Atty. GaleonDokument3 SeitenClassification of Law by Atty. GaleonTin AngusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 Intro to Remedial LawDokument16 SeitenWeek 1 Intro to Remedial LawAira JaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Classifications of LawDokument3 SeitenIntroduction to Classifications of LawMaria ForkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Fundamentals of LawDokument4 Seiten1 Fundamentals of LawJasmin Ann Macawili RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAW 1 Notes PrelimDokument9 SeitenLAW 1 Notes PrelimRhyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Law IIDokument2 SeitenIntro To Law IIAphelionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To LawDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To LawChristine Joy LeonardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oblicon1-Chapters 1-4Dokument24 SeitenOblicon1-Chapters 1-4Zenji Sen PaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction To LawDokument5 Seiten1 Introduction To LawJonathan Tungal100% (2)
- Organization of Courts and Legal ClassificationsDokument23 SeitenOrganization of Courts and Legal ClassificationsShantalle KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Law: Presented byDokument47 SeitenBasics of Law: Presented bygayukutty7Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Origin Nature and Development of LawDokument25 Seiten1 Origin Nature and Development of LawJhianne Mae AlbagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal System of BangladeshDokument6 SeitenLegal System of BangladeshdarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Fundamentals of LawDokument4 Seiten1 - Fundamentals of LawJlyn Coma0% (2)
- Chapter 1Dokument15 SeitenChapter 1Mark Adiel Fodra PalaruanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law Summary - First ExamDokument11 SeitenLaw Summary - First ExamROJO- Lourdes TabieresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Law Slides (Unit1-7) Edited (0) Theardyear1sem-1Dokument146 SeitenBusiness Law Slides (Unit1-7) Edited (0) Theardyear1sem-1Zerihun ReguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinds of Laws (2023) - RMGDokument16 SeitenKinds of Laws (2023) - RMGUnduwe SalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BL ChapterDokument20 SeitenBL Chapteraboood al7tamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political Law OverviewDokument31 SeitenPolitical Law OverviewEyanna Cabico100% (1)
- 1 Introduction To LawDokument16 Seiten1 Introduction To LawPearl Nathalie S. PabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law on Obligation and Contracts ExplainedDokument4 SeitenLaw on Obligation and Contracts ExplainedPAUL CLARENCE CA�ETENoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF LAWDokument4 SeitenGENERAL PRINCIPLES OF LAWvictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFBT1 - General Introduction On Law, Subject Introduction (Until Kinds of Obligations)Dokument24 SeitenRFBT1 - General Introduction On Law, Subject Introduction (Until Kinds of Obligations)Mikee RizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of LawDokument5 SeitenClassification of LawannieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ContractDokument63 SeitenTypes of Contractmanjunatha TKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obligations and Contract - de Leon, Chapter 1 SummaryDokument7 SeitenObligations and Contract - de Leon, Chapter 1 Summarynisha100% (1)
- Introduction To LawDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To LawLuna KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Ho (w1)Dokument4 SeitenAccounting Ho (w1)Maria Jessa HernaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Law CourseDokument8 SeitenNational Law CourseBrinzila ValentinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines Constitution, Legal Research, and Types of LawsDokument7 SeitenPhilippines Constitution, Legal Research, and Types of LawsPiaRuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Law and ObligationsDokument75 SeitenIntroduction to Law and ObligationsCarmina Pangan80% (5)
- Introduction To Law and Fundamental RightsDokument55 SeitenIntroduction To Law and Fundamental Rightsrita tamohNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECELAW1 DocuDokument163 SeitenECELAW1 DocuJay AlmerolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 1 Oblicon Online ClassDokument4 SeitenHandout 1 Oblicon Online ClassJosh Jozef CABERTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Law Ma. Anjiellamie MaravillaDokument45 SeitenFundamentals of Law Ma. Anjiellamie MaravillaJJ DelfinadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Law and RegDokument19 SeitenBus Law and RegLiane Dimaun-LaksamanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBLICON - Business LawDokument16 SeitenOBLICON - Business LawArlene Gwyneth AmbatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oblicontract 1Dokument6 SeitenOblicontract 1jownathanjowstarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Legal SystemDokument3 SeitenUnit 1 Legal SystemÁlvaro Vacas González de EchávarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political Law Notes and Constitutional Law IntroductionDokument19 SeitenPolitical Law Notes and Constitutional Law IntroductionEyanna CabicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Business Law NotesDokument3 SeitenEssential Business Law NotestamiratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Adjustment (Week 4)Dokument19 SeitenProfessional Adjustment (Week 4)joeljohndelamercedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction-to-LawDokument5 SeitenIntroduction-to-LawJobel SingsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Law Dme Master Class.Dokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Law Dme Master Class.Daniel MukelabaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Branches of LawDokument9 SeitenChapter 2 - Branches of LawNouran Mohamed Abd AzeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction To LawDokument14 Seiten1 Introduction To LawKimberly Anne MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oblicon Week 2Dokument3 SeitenOblicon Week 2LOMA, ABIGAIL JOY C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To LawDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To LawJomar Francis BaybayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Aspects PrelimsDokument12 SeitenLegal Aspects Prelimsdumpacc.skyyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business law basics and definitionsDokument4 SeitenBusiness law basics and definitionsDipty HiraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. General Principles: A. Effect and Application of Laws Definition of Law: Private LawDokument5 SeitenI. General Principles: A. Effect and Application of Laws Definition of Law: Private LawKim Manuel TenerifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breach of ContractDokument26 SeitenBreach of ContractAdil HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etl Chapter 3Dokument6 SeitenEtl Chapter 3Hussen RediNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction To The Irish Legal SystemDokument10 Seiten1 Introduction To The Irish Legal SystemConstantin LazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Law FundamentalsDokument101 SeitenIntroduction to Law FundamentalsKuya Em100% (1)
- Commercial Law NotesDokument56 SeitenCommercial Law NotesNyakundi Mosoti100% (1)
- Fire & Smoke: Government, Lawsuits, and the Rule of LawVon EverandFire & Smoke: Government, Lawsuits, and the Rule of LawNoch keine Bewertungen
- U.S. Department of Justice Guide to Death InvestigationDokument64 SeitenU.S. Department of Justice Guide to Death InvestigationValentin G.0% (1)
- Crime Scene InvestigationDokument58 SeitenCrime Scene Investigationreader27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Penal Code Articles 94-113Dokument14 SeitenRevised Penal Code Articles 94-113Hassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Memo and Client Letter SampleDokument3 SeitenLegal Memo and Client Letter SampleRobinson Flores100% (2)
- GlossaryDokument2 SeitenGlossaryHassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 1 Lecture Theories of LawDokument5 SeitenDay 1 Lecture Theories of LawHassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Official Rules of The 2019 Inter-Class Moot Court CompetitionDokument4 SeitenOfficial Rules of The 2019 Inter-Class Moot Court CompetitionHassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jespajo Realty Corp DigestDokument2 SeitenJespajo Realty Corp DigestTine ArenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion to Quash Information in Violation of Right to Speedy TrialDokument10 SeitenMotion to Quash Information in Violation of Right to Speedy TrialHassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion to Quash Information in Violation of Right to Speedy TrialDokument10 SeitenMotion to Quash Information in Violation of Right to Speedy TrialHassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compromis Moot Problem 2019Dokument4 SeitenCompromis Moot Problem 2019Annabelle Cubillan GuimaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shanne SpeechDokument2 SeitenShanne SpeechHassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement of QuestionsDokument1 SeiteStatement of QuestionsHassan MalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - Void, Voidable and Illegal ContractsDokument4 SeitenChapter 6 - Void, Voidable and Illegal Contractstata cocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Positioning To Print Marks With Sinamics V90 and SIMATIC S7-1200 (TO)Dokument24 SeitenPositioning To Print Marks With Sinamics V90 and SIMATIC S7-1200 (TO)Jahidul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Complaint For Unfair Sales Practice Under The Consumer Act of The PhilippinesDokument5 SeitenSample Complaint For Unfair Sales Practice Under The Consumer Act of The PhilippinesCharry Deocampo100% (1)
- Toyota Engine Warranty Prescription CaseDokument2 SeitenToyota Engine Warranty Prescription CaseOmsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence FinalsDokument21 SeitenEvidence FinalsTen De Los SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCC A-3-Mra-14-0050-9-14-1735 11-2014Dokument1.110 SeitenCCC A-3-Mra-14-0050-9-14-1735 11-2014L. A. PatersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ho 8 - Last Minute Tips (Legal & Judicial Ethics)Dokument15 SeitenHo 8 - Last Minute Tips (Legal & Judicial Ethics)J Velasco PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract Modes: Info SheetDokument4 SeitenContract Modes: Info SheetPEP Zona 7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nagpur Mumbai RFPDokument56 SeitenNagpur Mumbai RFPVinod Dakarapu0% (1)
- Example of How To Negotiate Price With SuppliersDokument9 SeitenExample of How To Negotiate Price With SuppliersVaibhav SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supreme Court Rules Against Preferred Credit Claim in Carabao Pledge CaseDokument1 SeiteSupreme Court Rules Against Preferred Credit Claim in Carabao Pledge CaseChilzia RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- United Special Watchman Agency vs. CADokument6 SeitenUnited Special Watchman Agency vs. CARona TumaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM Power Vs Capitol Industrial DigestDokument3 SeitenLM Power Vs Capitol Industrial DigesttinctNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opn Partner Toma v060917 Al EngDokument51 SeitenOpn Partner Toma v060917 Al EngIlir DakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Septo Trading (2020)Dokument23 SeitenSepto Trading (2020)Zviagin & CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter of IntentDokument2 SeitenLetter of Intentpierololli75% (4)
- Guerrero, Alpha Holy - BSTM 3-2 - CCHTM 3105 - Assignment No.3Dokument3 SeitenGuerrero, Alpha Holy - BSTM 3-2 - CCHTM 3105 - Assignment No.3ALPHA HOLY GUERRERONoch keine Bewertungen
- Transpo Spouses Perena and Zarate CaseDokument3 SeitenTranspo Spouses Perena and Zarate CaseXtine CampuPot100% (4)
- Dak PDFDokument27 SeitenDak PDFSiddarth AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Cases - Digests (30) DigestsDokument31 SeitenProperty Cases - Digests (30) DigestsSan Vicente Mps IlocossurppoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBASyll 07Dokument65 SeitenMBASyll 07seeralan balakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Warehouse Receipts LawDokument42 SeitenThe Warehouse Receipts Lawkeith105100% (1)
- Supreme Court: Wigberto E. Tañada For Petitioner. Teofilo Mendoza For RespondentsDokument10 SeitenSupreme Court: Wigberto E. Tañada For Petitioner. Teofilo Mendoza For RespondentsLance LagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract Agreement GuideDokument4 SeitenContract Agreement GuideMalyadam PadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proforma Invoice - MINI 12PSBDokument2 SeitenProforma Invoice - MINI 12PSBmkdiesel30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Republic vs. Del Monte Motors, Inc., 504 SCRA 53, G.R. No. 156956 October 9, 2006Dokument8 SeitenRepublic vs. Del Monte Motors, Inc., 504 SCRA 53, G.R. No. 156956 October 9, 2006Claudia Rina LapazNoch keine Bewertungen
- APRIL 24, 2017 Leave A Comment: Separation Pay and BackwagesDokument6 SeitenAPRIL 24, 2017 Leave A Comment: Separation Pay and BackwagesowenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04th August Labour LawDokument7 Seiten04th August Labour LawJasmine KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labrel Midterms and FinalsDokument186 SeitenLabrel Midterms and Finalsjanine nenariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saln ManualDokument29 SeitenSaln Manualscribe03Noch keine Bewertungen