Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
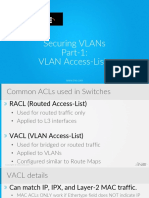
Intro To Vacl
Hochgeladen von
joseOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Intro To Vacl
Hochgeladen von
joseCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Switch1(config)# match mac address acl-name
Switch1(config)# vlan access-map ALLOWTELNET 10
Switch1(config-access-map)#action
map)#action forward
Switch1(config)#vlan filter ALLOWTELNET vlan-list
vlan 1-50
Procedure –
1. Define the standard or extended access list to be used in VACL –
An access-list
list should be defined to identify the type of traffic and the hosts on which it
is applied.
2. Define a VLAN access map –
A VLAN access-map map is defined in which hosts IP address will be matched (using the access-list
access
defined)
3. Configure an action clause in a VLAN access map ma sequence –
This will tell what action (forward or drop) should be taken on the traffic (defined in the VLAN
access-map)
4. Apply the VLAN access map to the specified VLANs –
The last step in the configuration of VACL is to create filter list specifying, on which VLAN the
access map has been applied.
5. Display VLAN access map information –
We can verify the information by using the command.
Configuration –
There is a switch named as switch1 which is connected to 3 routers named as Router1 (IP address-
192.168.1.1/24), Router2 (IP address-192.168.1.2/24)
address and Router3 (IP address-192.168.1.3/24)
192.168.1.3/24) as shown
in the figure.
In this task, we will deny traffic from Router1 to Router3 using VACL.
Configuring access-listlist on switch1 stating that all IP traffic
traffic should be allowed from host 192.168.1.1 to
192.168.1.3
switch1(config)#ip access-list
list extended My_access_list
switch1(config-ext-nacl)#permit
nacl)#permit ip host 192.168.1.1 host 192.168.1.3
Now, configuring VLAN access-map
map which states that match the IP address defined in access-list
access and take
action of drop (which means traffic should not be allowed from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.3).
switch1(config)#vlan access-map
map Mapping 10
switch1(config-access-map)#match
map)#match ip address My_access_list
switch1(config-access-map)#action
ion drop
switch1(config-access-map)#exit
In the first command, 10 is the sequence number of access-map.
access map. If we not define any sequence number
then it will automatically take 10 as sequence number.
Now, for the traffic from Router1 (192.168.1.1) to Router3 (192.168.1.3), the traffic will be dropped but
what about the traffic from Router2 to Router3?
The traffic from Router2 to Router3 will also get drop because no action is defined for this traffic (implicit
deny). Therefore, we have to define another
anot rule stating that the other traffic should be allowed.
switch1(config)#vlan access-map
map Mapping 20
switch1(config-access-map)#action forward
switch1(config-access-map)#exit
In the first command, 20 is the sequence number which means this rule will be checked after the first rule
having sequence number 10.
At last, we will assign this access-map, named as My_access_list, to a VLAN (here VLAN 1)
switch1(config)#vlan filter Mapping vlan-list 1
To verify the configuration, use the command.
switch1#show vlan access-map
This command will display the access-map. This will display the name of the access-map, sequence
number of the rule and the access-list name (that have been used).
switch1#show vlan filter
This will display the VLANs which are filtered by vlan access-map.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationVon EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkVon EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Securing VLANs Part 1Dokument5 Seiten20 Securing VLANs Part 1jdwhite9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2.9.4 Catalyst 2950 and 3550 Series Intra-VLAN Security: ObjectiveDokument5 SeitenLab 2.9.4 Catalyst 2950 and 3550 Series Intra-VLAN Security: ObjectiveKishore Reddy KandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layer 3 SwitchingDokument8 SeitenLayer 3 SwitchingKaushik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vlan Labs 1Dokument14 SeitenVlan Labs 1anurag76843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Area 0 Is Required For OSPF To Function, and Is Considered The "Backbone"Dokument8 SeitenArea 0 Is Required For OSPF To Function, and Is Considered The "Backbone"clubmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCMSN Lab - Qos Lab 8-1-10 2 enDokument6 SeitenBCMSN Lab - Qos Lab 8-1-10 2 enDaniela GFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configu Aciones Básicas de Nivel 3Dokument13 SeitenConfigu Aciones Básicas de Nivel 3Seijuurou HikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CCNA - Layer 3 SwitchesDokument3 SeitenCisco CCNA - Layer 3 SwitchesMohammed HazzaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACL Practice Lab 2Dokument7 SeitenACL Practice Lab 2LGBT Việt NamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Technology NET 272 - Lab Exercise Advanced STP - PVST+, RSTP, MST Conducted On 9/16 By: Chris OrtizDokument7 SeitenNetworking Technology NET 272 - Lab Exercise Advanced STP - PVST+, RSTP, MST Conducted On 9/16 By: Chris OrtizchrisncissNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5Dokument7 Seiten5mouradwac87Noch keine Bewertungen
- DMVPN ConfigurationDokument6 SeitenDMVPN ConfigurationSithu MawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packet TracerDokument16 SeitenPacket TracerecolemorsliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCN Lab 8Dokument4 SeitenCCN Lab 8Hamna YounisNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Procurve Advanced CLI Commands ReferenceDokument8 SeitenHP Procurve Advanced CLI Commands ReferenceSachin Damodare100% (1)
- IPSec VPN LABDokument7 SeitenIPSec VPN LABAparna Garg100% (2)
- Copy Running-Config TFTP - Send Details of Router Config To Server Copy TFTP: Running-Config - To Access Saved Data On ServerDokument24 SeitenCopy Running-Config TFTP - Send Details of Router Config To Server Copy TFTP: Running-Config - To Access Saved Data On ServerAkshay kerkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Network: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineer IEEE 802.3 Standard Coaxial, Twisted Pair, FiberDokument22 SeitenTypes of Network: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineer IEEE 802.3 Standard Coaxial, Twisted Pair, FibergokuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP3 Lab 4 1 enDokument10 SeitenCCNP3 Lab 4 1 enmanucvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4-2 Inter-VLAN Routing With An Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF FunctionsDokument13 SeitenLab 4-2 Inter-VLAN Routing With An Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF FunctionszenekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9.8.1 Managing Network Performance Using Content-Based Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ) and Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)Dokument7 SeitenLab 9.8.1 Managing Network Performance Using Content-Based Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ) and Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)Kishore Reddy KandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 8Dokument8 SeitenPractical 8riyevas163Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yeferson Sierra CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab6-1 FHRP HSRP VRRP STUDENTDokument41 SeitenYeferson Sierra CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab6-1 FHRP HSRP VRRP STUDENTSebastianBarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- T SHOOT Tickets 300 135Dokument11 SeitenT SHOOT Tickets 300 135Danilo RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Practice Certification Exam 2Dokument11 SeitenCCNA Practice Certification Exam 2Gabriel GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switch (Config) #Ip Routing: Step by Step Cisco L3 Switch ConfigurationDokument3 SeitenSwitch (Config) #Ip Routing: Step by Step Cisco L3 Switch Configurationmaheshreddy437Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8.9.2 Introduction To The Modular Qos Command-Line InterfaceDokument9 SeitenLab 8.9.2 Introduction To The Modular Qos Command-Line InterfaceCharles MorrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0317 - Configure EtherChannel and HSRP Lab - InstructionsDokument8 Seiten0317 - Configure EtherChannel and HSRP Lab - Instructionsnetgame760% (1)
- Configure InterVLAN RoutingDokument5 SeitenConfigure InterVLAN RoutingJuan Felipe Corso AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Output Drops Due To QoS On Cisco 2960 3560 3750 SwitchesDokument7 SeitenOutput Drops Due To QoS On Cisco 2960 3560 3750 Switchestang410872108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6Dokument25 SeitenLab 6RapacitorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercices ACLDokument9 SeitenExercices ACLPapa NiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hudini 2Dokument6 SeitenHudini 2Vlad PetreanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Lab Questions:: AnswerDokument27 SeitenCCNP Lab Questions:: Answerjakeandmis100% (1)
- ROUTE Chapter 5 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Dokument10 SeitenROUTE Chapter 5 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ticket 8 - Switchport VLAN 10Dokument9 SeitenTicket 8 - Switchport VLAN 10Layan Al-FantoukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comandos Avanzados de Consola para Router HP 3comDokument4 SeitenComandos Avanzados de Consola para Router HP 3comcgf_arNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Design Using Access Controls and Voip: Saurav Kumar PandeyDokument46 SeitenNetwork Design Using Access Controls and Voip: Saurav Kumar PandeyLK AnhDungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 13 CNDokument7 SeitenLab Report 13 CNjoy leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NETWORK LAB Summary GPDokument11 SeitenNETWORK LAB Summary GPعبد المهيمن احمد قصيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clase 3 VRF, PBR & IpslaDokument58 SeitenClase 3 VRF, PBR & IpslaOscar sanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tshoot Strategy by KhattakDokument10 SeitenTshoot Strategy by Khattaka_u_xNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSHOOT Strategy by KhattakDokument10 SeitenTSHOOT Strategy by KhattakMatt HoffmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 802dot1q Qinq TunnelingDokument13 Seiten802dot1q Qinq TunnelingNb A DungNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSRP Bridge ModeDokument8 SeitenHSRP Bridge ModesopencoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Command With Explanation: ExampleDokument8 SeitenCcna Command With Explanation: Examplefshahzad79Noch keine Bewertungen
- EIGRP MindmapDokument1 SeiteEIGRP MindmapJason RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksVon EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and Performance MeasurementVon EverandLTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and Performance MeasurementNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolVon EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONVon EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Von EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingVon EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPLSDokument177 SeitenMPLSChanchal Kumar BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB2Dokument13 SeitenLAB2Guyala, Mary Grace E.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Configuration Guide Strongswan: Thegreenbow Ipsec VPN ClientDokument14 SeitenConfiguration Guide Strongswan: Thegreenbow Ipsec VPN ClientRajeev KpNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZyXEL-OLT2406 Datasheet v06 6099Dokument4 SeitenZyXEL-OLT2406 Datasheet v06 6099htnlinnNoch keine Bewertungen
- P11 IEEE - 802 en SlidesDokument21 SeitenP11 IEEE - 802 en Slidesoktaviola sibaraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- gs1900 QosDokument9 Seitengs1900 QosCuong TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF Protocol CNDokument6 SeitenOSPF Protocol CNsaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNI 7390-2012 - Bioetanol Terdenaturasi Untuk Gasohol PDF - PDFDokument793 SeitenSNI 7390-2012 - Bioetanol Terdenaturasi Untuk Gasohol PDF - PDFIhsan Rafi RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBP 13 Using Windows Nps As Radius in Eduroam FinalDokument78 SeitenCBP 13 Using Windows Nps As Radius in Eduroam FinalMed TisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hunting Beacons: Bartosz JerzmanDokument52 SeitenHunting Beacons: Bartosz Jerzmanvha KyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IK2218 Homework - 2 - Solutions PDFDokument9 SeitenIK2218 Homework - 2 - Solutions PDFRonjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acterna Da 3600Dokument12 SeitenActerna Da 3600samtobias86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abb Fox System Specifications r8 RF 1khw002006Dokument68 SeitenAbb Fox System Specifications r8 RF 1khw002006Mustafa HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMG - v7.0 - Q&A.Verificar Que Es OKDokument30 SeitenFMG - v7.0 - Q&A.Verificar Que Es OKAlejandra Rodríguez Arana100% (2)
- Introduction To Ethical HackingDokument28 SeitenIntroduction To Ethical Hackingemeka ozuome0% (1)
- CobWeb - A System For Automated In-Network Cobbling of Web ServiceDokument15 SeitenCobWeb - A System For Automated In-Network Cobbling of Web Serviceolutay zoayoolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco SDWAN 20.4 What's New!Dokument33 SeitenCisco SDWAN 20.4 What's New!Salis AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ePMP™ Force 300 Series: Quick LookDokument9 SeitenePMP™ Force 300 Series: Quick LookAlex IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- d832tcs8stf2 WhatsNew NGFW 6.10Dokument16 Seitend832tcs8stf2 WhatsNew NGFW 6.10Mohamed AbdelhadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SatLink 2900 Mobile VSAT - Rev K - 0Dokument2 SeitenSatLink 2900 Mobile VSAT - Rev K - 0Christian Starchy Mimeck'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFDokument3 SeitenFFnafiyad berhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- FortiGate 7.4 Administrator Sample Questions - Attempt ReviewDokument9 SeitenFortiGate 7.4 Administrator Sample Questions - Attempt ReviewJorge Daniel100% (2)
- MP3Dokument5 SeitenMP3Kapil Kale0% (1)
- Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router MPLS Layer 3 VPNDokument142 SeitenCisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router MPLS Layer 3 VPNdexonnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ah en Modbus TCP 8294 en 03 PDFDokument32 SeitenAh en Modbus TCP 8294 en 03 PDFZH HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8Dokument98 SeitenModule 8Le Minh NgocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barracuda Web Application Firewall - FoundationDokument15 SeitenBarracuda Web Application Firewall - FoundationNiven MaharjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 01 - Implement Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMDokument10 SeitenLab 01 - Implement Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMPeter AltamiranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Datagram Protocol (Udp)Dokument22 SeitenUser Datagram Protocol (Udp)Harsh IsamaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Command Reference - Old PDFDokument2.264 SeitenCommand Reference - Old PDFjavier_domine6459Noch keine Bewertungen