Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
At The End of The Period, The Pupils Will Be Able To
Hochgeladen von
MarissOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
At The End of The Period, The Pupils Will Be Able To
Hochgeladen von
MarissCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
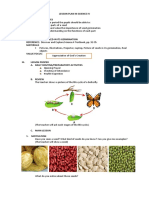
DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 4
1. LESSON OBJECTIVES
At the end of the period, the pupils will be able to:
a. Identified the parts of a seed
b. Defined GERMINATION
c. Illustrated understanding on the functions of each part
2. SUBJECT MATTER
TOPIC: PARTS OF THE SEED IN ITS GERMINATION
REFERENCE: Science for Daily Use 4 Textbook, pp. 83-84
MATERIALS: Charts, Pictures, Overhead Projector, Multimedia
VALUE COOPERATION: Cooperation
TEACHER’S ACTIVITY PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
A. PREPARATORY ACTIVITY
Opening Prayer
Checking of Attendance
Review of the Past Lesson
B. MOTIVATION
(The teacher will ask some questions)
Have you seen a seed? Yes ma’am
What kind of seeds do you know?
(Pupils will respond)
(The teacher will post a picture of a seed)
(The teacher will call one by one)
What do you notice about those seeds?
They differ in size and shape
C. ACTIVITY
Now, I have here a short story and I want
you to listen carefully and we will answer few
questions later
(The teacher will present a story in title The
Tiny Seed by: Eric Carle)
Yes ma’am!
Did you enjoy the story?
Are you ready to answer some (Pupils will respond)
Questions?
Discussion Questions:
1. Who is the main character of the Story? The Tiny Seed
2. What blows the seed?
Air
3. Did the tiny seed fell on the ground during
No ma’am!
autum?
4. What happens after the tiny seed falls into
(Pupils will respond)
the ground?
D. ANALYSIS
(The teacher will ask few more questions)
Where does seed come from?
How are you going to help the tiny
seed grow
E. ABSTRACTION
Seed have been an important
development in the reproduction and spread
of flowering plants.
Seeds - though too small, they have their
own parts, like an Ordinary living thing.
Today, we are going to learn the different
parts of a SEED
A seed only develops its part only when it
undergoes a process called SEED
GERMINATON
I have here an illustration of a seed
during Germination.”
(The teacher will post an illustration)
(The teacher will post the definition of
GERMINATION)
(The teacher will let the pupils read it aloud)
GERMINATION - is the process by which
plant, emerges from the seed and begins
to grow.
Okay, thank you!
These are the parts of a SEED during
germination
PARTS OF A SEED
EMBRYO - a very young plant which a
new plant grow under proper
conditions.
RADICLE - in a dicot is the embryonic
root.
Can you point out where is the radicle (The pupil will go in front and point out
in the illustration? Radicle in the illustration)
Within the seed, there is usually a
store of nutrients for the seeding that will
grow from the EMBRYO.
The seed has its own food supply-
Called the EPICOTYL and COTYLEDONS.
SEED COAT - develops from tissue,
originally surrounding by the OVULE.
The seed coat helps protect the
embryo.
So where’s the seed coat in the
(A pupil will respond)
Illustration?
Okay, thank you. So you see, the SEED
COAT is the outer part of the seed.
Any other question?
None, ma’am!
Did you understand the lesson?
Yes, ma’am!
Again what is the very young plant from
which a new plant grows under proper
AN EMBRYO
conditions?
What about the embryonic root in a
dicot seed? RADICLE
What do you call the seeds own food
supply? EPICOTYL and COTYLEDON
Very good!
3. APPLICATION
Group Activity
1. Arrange the process of seed Germination.
2. Identify and name the different parts of
the seed from the figure.
4. EVALUATION
(The teacher will post a chart with questions
on the board)
DIRECTION: On your answer sheet, answer
the following:
1. It Protects the embryo.
a. roots
b. Leaf
c. seed coat
2. It grows into a young plant.
a. Seed coat
b. endosperm
c. embryo
3. It has its own food supply.
a. seed coat
b. embryo
c. epicotyl
4. Which of these is not part of the seed?
a. flower
b. embryo
c. seed coat
5. The epicotyl is a part of embryo that grows
into ______________.
a. leaves
b. roots
c. stem
5. ASSIGNMENT
Answer the following questions in your
notebook
1. List down the factors that affect seed
germination and growth.
2. Where does a flowering plant start?
3. What is a primary root?
4. What are the seeds that germinate
even without soil?
5. How does seed grow into a plant?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Science Simplified: Simple and Fun Science (Book D, Grades 3-5): Learning by DoingVon EverandScience Simplified: Simple and Fun Science (Book D, Grades 3-5): Learning by DoingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Dokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4April Anacio KaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Simplified: Simple and Fun Science (Book E, Grades 4-6): Learning by DoingVon EverandScience Simplified: Simple and Fun Science (Book E, Grades 4-6): Learning by DoingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 4 Monocot and DicotDokument9 SeitenDETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 4 Monocot and DicotAngelica Fernandez Resabal Acot86% (7)
- Seed LPDokument7 SeitenSeed LPKim Rose BorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Dokument10 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Rolly Fallorina SenangeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seed Germination PartsDokument6 SeitenSeed Germination PartsJeremiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4 (Parts of A Seed)Dokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4 (Parts of A Seed)Faty Villaflor95% (102)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Garde IVDokument3 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Garde IVAlona Ramos100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Dokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Allysa Marie SilbolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4: TeacherDokument10 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4: TeacherArjay DensaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Media2747407954848197013Dokument8 SeitenLocal Media2747407954848197013Dawn Kathlia FulgencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan ScienceDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan ScienceMj ColongonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Dokument3 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4MacellyBudiongan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science Iv I. Lesson ObjectivesDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan in Science Iv I. Lesson ObjectivesKim Rose BorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Science 4Dokument4 SeitenLesson Plan in Science 4Francis DecenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Dokument8 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Repaso AlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan on FlowersDokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan on FlowersMarichu CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cot Science 3Dokument6 SeitenCot Science 3aizel suizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIDokument7 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIJeolina CuratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5e's LESSON PLAN FINALDokument4 Seiten5e's LESSON PLAN FINALEstella ゝNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP IN SCINCE 4Dokument8 SeitenDLP IN SCINCE 4Rosemarie GaringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Science 3 - EscrimadoraDokument8 SeitenLesson Plan in Science 3 - EscrimadoraMar Jen100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan on Plant Parts & FunctionsDokument8 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan on Plant Parts & FunctionsReign Jacob Andres-Salonga89% (19)
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN ON PLANT PARTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONSDokument7 SeitenDETAILED LESSON PLAN ON PLANT PARTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONSJuy Clair Pano EncarguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Technology Enhanced Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4 Designed by Panganiban, Baby Rica E. (BEED 2-2)Dokument6 SeitenA Technology Enhanced Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4 Designed by Panganiban, Baby Rica E. (BEED 2-2)Monneth DalisayNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP Science 1-17-2023Dokument7 SeitenDLP Science 1-17-2023Ser EdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenLesson Planremeceldo dagamac0% (1)
- Learn Parts of Flowering Plants and ReproductionDokument8 SeitenLearn Parts of Flowering Plants and ReproductionDanica AdobasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IiiDokument8 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Iiiangel tabarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Agriculture and Fishery Arts: Teacher's Activity Student's ActivityDokument7 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Agriculture and Fishery Arts: Teacher's Activity Student's ActivityMicah Yvonne Vilar LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7Es-DLP-TEMPLATE-ScienceDemo-JenniferNarraDokument7 Seiten7Es-DLP-TEMPLATE-ScienceDemo-JenniferNarranarrajennifer9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science DLP Parts of PlantsDokument8 SeitenScience DLP Parts of PlantsMishell AbejeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDokument11 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in ScienceMordecaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seed Parts and FunctionsDokument7 SeitenSeed Parts and FunctionsSer EdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan on Interrogative and Exclamatory SentencesDokument9 SeitenLesson Plan on Interrogative and Exclamatory SentencesLadyClyne LaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAROQUILLO LP Science 5 RevisedDokument5 SeitenBAROQUILLO LP Science 5 Revisedjason baroquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDokument8 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Sciencedeseree abendanio100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIDokument8 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIvicra rajahbuayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan IN Science V: Prepared By: Checked byDokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan IN Science V: Prepared By: Checked byJosefina Trazona100% (12)
- Lesson Plan in English III I. ObjectivesDokument9 SeitenLesson Plan in English III I. ObjectivesLadyClyne LaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan Lappay Liezl P.Dokument10 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan Lappay Liezl P.Russel Jane BaccayNoch keine Bewertungen
- DETAILED PLANT LESSON FOR GRADE 3Dokument6 SeitenDETAILED PLANT LESSON FOR GRADE 3Evita Esguerra100% (2)
- ReconstructDokument6 SeitenReconstructIan AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIDokument8 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIダイアン メルカドNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan IN Science VDokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan IN Science VJosefina TrazonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Plant PartsDokument6 SeitenIdentifying Plant PartsMaureen Kryzel BariteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Vascular PlantsDokument4 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Vascular PlantsJedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of a Seed and Germination Explained for 4th Grade ScienceDokument6 SeitenParts of a Seed and Germination Explained for 4th Grade ScienceJocelynt Tabaosares100% (4)
- 4a's Science Lesson Plan (Parts of Flower)Dokument11 Seiten4a's Science Lesson Plan (Parts of Flower)jamilkattirinaonaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIDokument16 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIJenny Anne TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IiiDokument9 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IiiDiana Louise ToribioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proper Plant Care LessonDokument6 SeitenProper Plant Care LessonTricia MorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP in ScienceDokument7 SeitenLP in ScienceAubrey Louise repilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101 Lesson PlanDokument5 Seiten101 Lesson PlanYancy MiclatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demo LPDokument5 SeitenDemo LPJenny Rose Rejano HilumNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Seeds GrowDokument6 SeitenHow Seeds GrowAdrian RamroopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade Level: I&II Learning Area: Science I. ObjectivesDokument11 SeitenGrade Level: I&II Learning Area: Science I. ObjectivesIlex Avena MasilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morphology and Anatomy of Horticultural CropsDokument5 SeitenMorphology and Anatomy of Horticultural CropsNarecom Stotomas ChapterdavaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GradesDokument2 SeitenGradesMarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolicitatonDokument2 SeitenSolicitatonMarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- English K2Dokument3 SeitenEnglish K2MarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- TQDokument3 SeitenTQMarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- At The End of The Period, The Pupils Will Be Able ToDokument5 SeitenAt The End of The Period, The Pupils Will Be Able ToMarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authorization LetterDokument1 SeiteAuthorization LetterMarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certification: To Whom It May ConcernDokument3 SeitenCertification: To Whom It May ConcernMarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Verbs For ObjectivesDokument4 SeitenAction Verbs For ObjectivesAnn Michelle TarrobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Science Lesson Plan for Grade 4Dokument1 SeiteDetailed Science Lesson Plan for Grade 4MarissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emcee King & QueenDokument8 SeitenEmcee King & QueenMaryHazelClaveBeniga100% (10)
- Class X - Reproduction in Living OrganismsDokument4 SeitenClass X - Reproduction in Living Organismsvijos16655Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Pendampingan Kesejahteraan JaninDokument6 SeitenJurnal Pendampingan Kesejahteraan JaninRita ChatrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W1Dokument11 SeitenDLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W1Emmanuel Ramirez0% (1)
- Endometriosis: Aetiology, Pathogenesis and TreatmentDokument16 SeitenEndometriosis: Aetiology, Pathogenesis and Treatmentyuyu tuptupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Mcas ReviewDokument142 SeitenGrade 8 Mcas Reviewapi-294483847Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alonge, Mark - The Hymn To Zeus From Palaikastro. Religion and Tradition in Post-Minoan Crete (Greece) (PHD Thesis Stanford, UMI 2006, 275pp)Dokument275 SeitenAlonge, Mark - The Hymn To Zeus From Palaikastro. Religion and Tradition in Post-Minoan Crete (Greece) (PHD Thesis Stanford, UMI 2006, 275pp)Marko MilosevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7040 02 Que 20100511Dokument28 Seiten7040 02 Que 20100511Mohammad Mohasin SarderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 5Dokument81 SeitenScience 5Michael Joseph Santos100% (2)
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDokument17 SeitenHow Do Organisms ReproduceBighnaraj ParichhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agrivita 2Dokument10 SeitenAgrivita 2Winda RachmadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-A202-Plant Development - Coursework AssignmentDokument10 Seiten04-A202-Plant Development - Coursework AssignmentFakrurazi NajmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Reproduction NotesDokument10 SeitenChapter 1 Reproduction NotesPoornimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vog QDokument62 SeitenVog QDeep PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeDokument4 SeitenMicroscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeLouie Jane EleccionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Selection Quiz (5.2Dokument2 SeitenNatural Selection Quiz (5.2laura pongutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fertilization to Childbirth ReactionDokument2 SeitenFertilization to Childbirth ReactionJulianne Kyla MercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCN LectureDokument8 SeitenMCN LectureEmily BernatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System With HighlightsDokument150 SeitenReproductive System With HighlightsReinand Joseff ServanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reptile ReproductionDokument5 SeitenReptile ReproductionDiyar Ahmad100% (1)
- The Genetic Foundations of DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenThe Genetic Foundations of Developmentmark bryan roblezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Feminization of ManDokument18 SeitenThe Feminization of Mananon-8733575% (8)
- Class Xii Biology Questions ChapterwiseDokument42 SeitenClass Xii Biology Questions Chapterwiseashok pradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioethicsDokument7 SeitenBioethicsClarissa Anne TabaosaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument4 SeitenPDFmbakpithi0% (1)
- Vaginal CytologyDokument4 SeitenVaginal Cytologyابراهيم عبدالله100% (1)
- Class 11 Chapter 3 BryophytesDokument6 SeitenClass 11 Chapter 3 BryophytesAshok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MARRIENILLA MERCADO Lab Report. Exercise 5. The Structure of A Flower and Seed DevelopmentDokument12 SeitenMARRIENILLA MERCADO Lab Report. Exercise 5. The Structure of A Flower and Seed DevelopmentMagisa JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 16.2: Self-And Cross-PollinationDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 16.2: Self-And Cross-PollinationShahed Bulbul PaponNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female Orgasm ReportDokument19 SeitenThe Female Orgasm ReportBob Cook100% (2)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 1-Reproduction in OrganismsDokument11 SeitenNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 1-Reproduction in OrganismsRajveer SinghNoch keine Bewertungen