Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Fluid Volume Deficit
Hochgeladen von
Betina De Jesus0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
153 Ansichten2 SeitenThe patient presented with difficulty breathing, coughing green sputum, and signs of dehydration including dark yellow urine, decreased sodium levels, and low blood pressure. Nursing diagnosed the patient with impaired gas exchange likely due to pneumonia and a fluid volume deficit. Interventions included assessing cough effectiveness, maintaining adequate hydration, encouraging deep breathing and mobility. The patient's respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and sodium levels normalized with treatment, indicating improved gas exchange and hydration status.
Originalbeschreibung:
NCP on FVD
Originaltitel
NCPs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe patient presented with difficulty breathing, coughing green sputum, and signs of dehydration including dark yellow urine, decreased sodium levels, and low blood pressure. Nursing diagnosed the patient with impaired gas exchange likely due to pneumonia and a fluid volume deficit. Interventions included assessing cough effectiveness, maintaining adequate hydration, encouraging deep breathing and mobility. The patient's respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and sodium levels normalized with treatment, indicating improved gas exchange and hydration status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
153 Ansichten2 SeitenNursing Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Fluid Volume Deficit
Hochgeladen von
Betina De JesusThe patient presented with difficulty breathing, coughing green sputum, and signs of dehydration including dark yellow urine, decreased sodium levels, and low blood pressure. Nursing diagnosed the patient with impaired gas exchange likely due to pneumonia and a fluid volume deficit. Interventions included assessing cough effectiveness, maintaining adequate hydration, encouraging deep breathing and mobility. The patient's respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and sodium levels normalized with treatment, indicating improved gas exchange and hydration status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
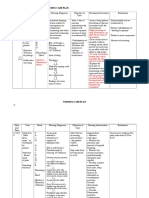
NURSING SCIENTIFIC NURSING
CUES/CLUES OBJECTIVES ANALYSIS EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS
• Coughing is the most
effective way to remove
• Assess cough
• Patient will effectiveness and
secretions.
maintain productivity
• Airway clearance is
• Objective:
Impaired gas optimal gas
hindered with inadequate
exchange as • Assess the patient’s
1. RR: 32 bpm exchange hydration and thickening
Impaired happens with evidenced hydration status.
of secretions. • Patient has
Gas an excess o by a normal decreased and
Subjective: • Elevate head of bed,
Exchange deficit in respiratory • promote chest expansion, normal RR of 20
change position
1. Complaint of related to aeration of lung segments, bpm.
oxygenation rate. frequently.
Difficulty of mobilization and
Breathing collection of and/or expectoration of • Patient verbalized
mucus in the carbon • Patient will • Teach and assist ease in breathing
2. Verbalized secretions.
dioxide verbalize patient with proper
feeling of airways deep-breathing
and better
“Hingal”
(Pneumonia) elimination at ease of • facilitates maximum expectoration of
3. Reported and the veolar- breathing expansion, most helpful sputum.
• Maintain adequate
greenish capillary after hydration by forcing
way to remove most
sputum upon secretions.
coughing membrane performing fluids to at least 3000
• aid in mobilization and
nursing mL/day unless
expectoration of
contraindicated
interventions secretions.
• Encourage ambulation
• Helps mobilize secretions
and prevent atelectasis
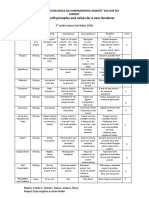
NURSING SCIENTIFIC NURSING
CUES/CLUES OBJECTIVES ANALYSIS EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS
• Patient is
• Objective:
state or normovolemic
- Dark Yellow condition where as evidenced • Oral fluid replacement is
urine
the fluid output indicated for mild fluid deficit
by systolic BP • Urge to increase oral • Patient has
- Turbid urine exceeds the fluid and is a cost-effective method
greater than or fluid intake or for replacement treatment. normalized BP
intake. It prescribed fluid Older patients have a
- Decreased Na and HR as well as
happens when equal to 90 decreased sense of thirst and
(120 meq) intake.
water mm HG (or may need ongoing reminders Sodium values.
- Decreased BP
• Maintain IV flow rate to drink.
and electrolytes
90/50 Fluid Volume patient’s • Provide measure to • To be able to properly monitor • Patient and
are lost as they
exist in normal baseline) and prevent excessive the amount of fluid going into
relatives can
- Tachycardia: Deficit electrolyte loss the patient’s system.
129 bpm body fluids. with a normal • Fluid losses from diarrhea and interventions to
Common • Emphasize the or vomiting should be prevent further
• Subjective: HR. relevance of
sources of fluid replaced or treated with
antidiarrheals and anti-emetics water loss to
- Report of watery loss are the maintaining proper
• Patient • increasing the patient’s prevent
stools gastrointestinal hydration and knowledge would help
explains nutrition. dehydration.
tract, polyuria, prevent and manage the
- 9 episodes of
vomiting and increased measures to problem.
perspiration prevent water
loss.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nursing Care PlansDokument7 SeitenNursing Care PlansJayson Sumampong100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDokument6 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationgabbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PTBDokument6 SeitenNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDokument2 SeitenCardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDanielle Patricia Valencia OtedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity intolerance, fear, infection risks in thalassemiaDokument1 SeiteActivity intolerance, fear, infection risks in thalassemiaHannah Clarisse Monge IgniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDokument2 SeitenAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Pre-operative AnxietyDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan for Pre-operative AnxietyVoid LessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Dokument6 SeitenIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDokument2 SeitenNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusDokument3 SeitenNURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusYsun Espino100% (1)
- Baiae NCPDokument1 SeiteBaiae NCPreignyfayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDokument5 SeitenAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Nursing CareplanDokument14 SeitenTB Nursing CareplanEstherThompson100% (1)
- Cu 4Dokument3 SeitenCu 4Paul SahagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPCamille VirayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientDokument2 SeitenDeficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientSeanmarie CabralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Letter BGHMCDokument1 SeiteApplication Letter BGHMCHerben T. BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDokument3 SeitenAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Evaluation: Subjective Cues: Short Term Goal: PreventiveDokument8 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Evaluation: Subjective Cues: Short Term Goal: PreventiveSharmaine Camille de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laryngeal Cancer Concept MapDokument1 SeiteLaryngeal Cancer Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student NurseDokument2 SeitenStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP DobDokument2 SeitenNCP DobPaulo GeneraloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCarolAnneRagpalaGaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistDokument12 SeitenWhat Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistLidiaAMonroyRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication ThalassemiaDokument3 SeitenMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDokument1 SeiteSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaJason A. AdoyoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Insomnia PDFDokument2 SeitenNCP For Insomnia PDFEca0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareDokument15 SeitenNursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Health Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERDokument6 SeitenHealth Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERCarla LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- NursesDokument36 SeitenNursesGilbert BagsicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJustine Mae A. LoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravido CardiacDokument19 SeitenGravido CardiacOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY COLLEGENoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - LeprosyDokument3 SeitenNCP - LeprosyKevin DareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialDokument2 SeitenHomework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialRianne BaetiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute PainDokument3 SeitenNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlanAlvin DagumbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Dokument10 SeitenProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute GastroenteritisDokument2 SeitenAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP BMDokument1 SeiteNCP BMSourabh MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing DiagnosisDokument3 SeitenNursing DiagnosislesternNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For COPDDokument3 SeitenNCP For COPDcy belNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDokument4 SeitenHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDokument2 Seiten"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- Date and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21Dokument2 SeitenDate and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21ANGEL AKIRA TORRESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesiologist Cover Letter SampleDokument1 SeiteAnesthesiologist Cover Letter SampleJr YansonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding URIs (Upper Respiratory InfectionsDokument40 SeitenUnderstanding URIs (Upper Respiratory InfectionsEarl JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsDokument22 SeitenNursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsG a i l R i c h w e l lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flail Chest (Tayug)Dokument25 SeitenFlail Chest (Tayug)Adrian MallarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for ChickenpoxDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for ChickenpoxAkeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypopituitarismDokument2 SeitenHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDokument3 SeitenHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PTBDokument2 SeitenNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan - BronchitisDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan - Bronchitisderic94% (36)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAmple CasaclangNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 3Dokument3 SeitenNCP 3James Francisco GarcesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 4 1st QDokument3 SeitenScience 4 1st QBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Summary Tables (Dragged)Dokument1 SeiteDrug Summary Tables (Dragged)Betina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rle-3 3Dokument1 SeiteRle-3 3Betina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Santo Tomas College of NursingDokument7 SeitenUniversity of Santo Tomas College of NursingBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 4 1st QDokument3 SeitenScience 4 1st QBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Notes: Lipids: Tests Test For Reagents Principles Positive ResultDokument1 SeiteLab Notes: Lipids: Tests Test For Reagents Principles Positive ResultBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 7 Lipids LabconDokument65 SeitenGroup 7 Lipids LabconBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishDokument6 SeitenEnglishBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemDokument2 SeitenChemBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article 7Dokument4 SeitenArticle 7Betina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipids LabconDokument17 SeitenLipids LabconBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipids Lab: A. Spotting EffectDokument2 SeitenLipids Lab: A. Spotting EffectBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Notes: Lipids: Tests Test For Reagents Principles Positive ResultDokument1 SeiteLab Notes: Lipids: Tests Test For Reagents Principles Positive ResultBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesDokument5 SeitenCarbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Empirical Method To Determine Inadequacy of Dietary WaterDokument2 SeitenAn Empirical Method To Determine Inadequacy of Dietary WaterBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Procedures2Dokument9 SeitenDiagnostic Procedures2Betina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- DE JESUS, Mary Betina 1NUR-3 Theme: Go, Grow & Glow Foods Title: Let's Eat Healthy! Target Age: 6-11 (School Age)Dokument2 SeitenDE JESUS, Mary Betina 1NUR-3 Theme: Go, Grow & Glow Foods Title: Let's Eat Healthy! Target Age: 6-11 (School Age)Betina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice: de Jesus, M.BDokument12 SeitenFundamentals of Nursing Practice: de Jesus, M.BBetina De Jesus0% (1)
- OLA HA LecDokument4 SeitenOLA HA LecBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych PDFDokument11 SeitenPsych PDFBetina De Jesus0% (1)
- PediatricsDokument9 SeitenPediatricsBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bula Defense M14 Operator's ManualDokument32 SeitenBula Defense M14 Operator's ManualmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simba s7d Long Hole Drill RigDokument2 SeitenSimba s7d Long Hole Drill RigJaime Asis LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Gen PsyDokument3 SeitenAssignment Gen PsyHelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Bags ReliefDokument27 SeitenEye Bags ReliefNatsu DragneelNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIST OF ENROLLED MEMBERS OF SAHIWAL CHAMBER OF COMMERCEDokument126 SeitenLIST OF ENROLLED MEMBERS OF SAHIWAL CHAMBER OF COMMERCEBASIT Ali KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Plan 1st GradeDokument3 SeitenAnnual Plan 1st GradeNataliaMarinucciNoch keine Bewertungen
- NABARD road inspection report formatDokument24 SeitenNABARD road inspection report formatSrinivas PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efaverenz p1Dokument4 SeitenEfaverenz p1Pragat KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalley Ltdn40k221twam Chassis msd6308 SM PDFDokument49 SeitenKalley Ltdn40k221twam Chassis msd6308 SM PDFjulio cesar calveteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Comparison of Homoeopathic MedicinesDokument22 SeitenThree Comparison of Homoeopathic MedicinesSayeed AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY210 Mechanism Ii and Thermal Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Applied Sciences Uitm Pahang (Jengka Campus)Dokument13 SeitenPHY210 Mechanism Ii and Thermal Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Applied Sciences Uitm Pahang (Jengka Campus)Arissa SyaminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bengali (Code No - 005) COURSE Structure Class - Ix (2020 - 21Dokument11 SeitenBengali (Code No - 005) COURSE Structure Class - Ix (2020 - 21Břîšťỹ ÃhmęđNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods to estimate stakeholder views of sustainabilityDokument7 SeitenMethods to estimate stakeholder views of sustainabilityAlireza FatemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pfr140 User ManualDokument4 SeitenPfr140 User ManualOanh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link Ratio MethodDokument18 SeitenLink Ratio MethodLuis ChioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Todo Matic PDFDokument12 SeitenTodo Matic PDFSharrife JNoch keine Bewertungen
- U2 All That You Can't Leave BehindDokument82 SeitenU2 All That You Can't Leave BehindFranck UrsiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weone ProfileDokument10 SeitenWeone ProfileOmair FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study IndieDokument6 SeitenCase Study IndieDaniel YohannesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 15 - Rams vs. VikingsDokument175 SeitenWeek 15 - Rams vs. VikingsJMOTTUTNNoch keine Bewertungen
- TJUSAMO 2013-2014 Modular ArithmeticDokument4 SeitenTJUSAMO 2013-2014 Modular ArithmeticChanthana ChongchareonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 5 Communications and Privacy: Unit 6 CommunicationDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 5 Communications and Privacy: Unit 6 Communicationwh45w45hw54Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uses and Soxhlet Extraction of Apigenin From Parsley Petroselinum CrispumDokument6 SeitenUses and Soxhlet Extraction of Apigenin From Parsley Petroselinum CrispumEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ielts Practice Tests: ListeningDokument19 SeitenIelts Practice Tests: ListeningKadek Santiari DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric 5th GradeDokument2 SeitenRubric 5th GradeAlbert SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 DeterminantsDokument3 SeitenChapter 4 Determinantssraj68Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure en 2014 Web Canyon Bikes How ToDokument36 SeitenBrochure en 2014 Web Canyon Bikes How ToRadivizija PortalNoch keine Bewertungen
- France Winckler Final Rev 1Dokument14 SeitenFrance Winckler Final Rev 1Luciano Junior100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet: 3 Quarter Week 1 Mathematics 2Dokument8 SeitenLearning Activity Sheet: 3 Quarter Week 1 Mathematics 2Dom MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNBONE_mPassbook_134611_6-4-2024_13-4-2024_0053XXXXXXXX00 (1) (1)Dokument3 SeitenPNBONE_mPassbook_134611_6-4-2024_13-4-2024_0053XXXXXXXX00 (1) (1)imtiyaz726492Noch keine Bewertungen