Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Timber Design Review
Hochgeladen von
Carlo Verano CatapiaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Timber Design Review
Hochgeladen von
Carlo Verano CatapiaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2) Design the wooden joists so as not to exceed the
TIMBER DESIGN
allowable shearing stress of 0.85 MPa.
a) 50 x 200 mm c) 50 x 300 mm
b) 50 x 250 mm d) 50 x 350 mm
CE REVIEW 3) Design the wooden joists so as not to exceed the
allowable deflection of 10 mm. Ew = 12135 MPa.
a) 50 x 200 mm c) 50 x 300 mm
b) 50 x 250 mm d) 50 x 350 mm
1. CE Board Nov. 4. Problem
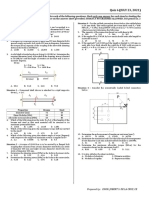
A rectangular wooden beam has a span of 6 m. and carries The beam shown on the figure is subjected to a uniform load
a total uniform load of 25 kN/m including its own weight. The of 5 kN/m.
beam is made up of 80% stress grade Apitong with allowable
stresses shown on table TM-6.
Allowable Stress for Apitong 80% Stress Grade:
Allowable bending - 16.5 MPa
Compression parallel to grain = 9.56 MPa
Compression perpendicular to grain
=2.20MPa
Shear parallel to grain = 1.73 MPa
Modulus of elasticity = 7310 MPa
Allowable deflection = L/240
1) Which of the following gives the smallest dimension of
beam that will not exceed the allowable bending stress? 1) Determine the placement "x" of the supports so that the
a) 220 x 440 mm c) 120 x 340 mm shear stress in the beam is as small as possible.
b) 320 x 540 mm d) 320 x 440 mm a) 1 m c) 3 m
b) 2 m d) 4 m
2) Which of the following gives the smallest dimension of
the beam that will not exceed the allowable shearing 2) Determine the minimum shear stress if h = 175 mm.
stress? a) 0.86 MPa c) 0.66 MPa
a) 100 x 200 mm c) 250 x 500 mm b) 0.96 MPa d) 0.76 MPa
b) 200 x 400 mm d) 300 x 600 mm
3) Determine the value of "h" for a maximum flexural stress
3) Which of the following gives the smallest dimension of of 7.5 MPa.
the beam that will not exceed the allowable deflection? a) 100 mm c) 300 mm
a) 100 x 200 mm c) 250 x 500 mm b) 200 mm d) 400 mm
b) 200 x 400 mm d) 300 x 600 mm
5. Problem
2. Problem
The timber beam has a rectangular cross section having a
width of 150 mm and a height of "h". Allowable bending
A floor is supported by 75 mm x 200 mm wooden joists stress is 10.5 MPa. and the allowable shearing stress is 0.35
spaced at 400 mm on centers with an effective span of 3 m. MPa. Modulus of elasticity of wood is 13800 MPa.
The total floor load transmitted to the joists is 5 kPa. Weight
of wood of 6.3 kN/m3. Ew = 12 x 103 MPa.
1) Which of the following gives the maximum bending
stress?
a) 2.71 MPa c) 4.71 MPa
b) 3.71 MPa d) 5.71 MPa
2) Which of the following gives the maximum shearing
stress?
a) 0.21 MPa c) 0.51 MPa
b) 0.41 MPa d) 0.31 MPa
3) Which of the following gives the maximum deflection of
the joist?
a) 2.18 mm c) 2.68 mm
b) 3.18 mm d) 3.68 mm 1) Compute the height "h" so that it simultaneously
reaches its allowable bending stress and allowable
3. Problem shearing stress.
a) 150 mm c) 250 mm
b) 200 mm d) 300 mm
Wooden joists are used to support a floor load of 6.95 kPa.
exclusive of its own weight. The joists will have an effective 2) Compute the maximum load P that the beam can
span of 4.25 m. and be placed at0.40 m. on centers. Weight support.
of wood is 7.5 kN/m3. a) 16 kN c) 15 kN
b) 13 kN d) 14 kN
1) Design the wooden joists so as not to exceed the
allowable bending stress of 10.35 MPa. 3) Compute the max. deflection of the beam, neglecting its
a) 50 x 200 mm c) 50 x 300 mm own weight.
b) 50 x 250 mm d) 50 x 350 mm a) 3.71 mm c) 5.71 mm
b) 4.71 mm d) 6.71 mm
3) Which of the following gives the uniform load it could
6. Problem support if deflection controls?
a) 3.32 kN/m c) 2.32 kN/m
b) 4.32 kN/m d) 5.32 kN/m
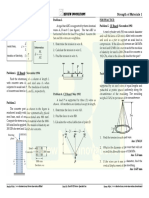
Four 50 mm x 200 mm section is to be framed to carry
maximum shear on a cantilever span of 4 m. Neglecting the
weight of the beam. Allowable shear stress is 0.70 MPa. 8. Problem
1) Compute the safe concentrated load that the beam
could carry at a distance of 1.5 m. from the fixed support A 50 mm x 200 mm Guijo floor joists carries a dead load
if the beam is arranged as shown. including its own weight of 2.5 kPa and a live load of 2 kPa.
The joist has a simple span of 3.6 m. Weight bf wood is 7.5
kN/m3.
Allowable stress:
Bending = 15.8 MPa
Shear = 0.90 MPa
Modulus of elasticity of wood = 13800 MPa
Allowable deflection = 1/300 of span.
Assume no impact allowance for live load.
a) 14.32 kN c) 11.67 kN
b) 15.32 kN d) 12.67 kN
2) Compute the safe concentrated load that the beam
could carry at distance of 1.5 m. from the fixed if the
beam is arranged as shown.
1) Which of the following gives the spacing of the joists if
bending controls?
a) 0.52 m c) 0.72 m
b) 0.62 m d) 0.82 m
a) 14.32 kN c) 11.67 kN 2) Which of the following gives the spacing of the joists if
b) 15.32 kN d) 12.67 kN shear controls?
a) 0.54 m c) 0.74 m
3) Compute the safe concentrated load that the beam b) 0.64 m d) 0.84 m
could carry at a distance of 1.5 m. from the fixed support
if it is arranged as shown. 3) Which of the following gives the spacing of the joists if
deflection controls?
a) 0.56 m c) 0.76 m
b) 0.66 m d) 0.86 m
9. Problem
A simply supported beam carrying a uniform load has a span
of 9 m. The beam has adequate lateral supports.
Allowable stress:
a) 18.667 kN c) 19.667 kN Bending = 10.21 MPa
b) 15.333 kN d) 16.333 kN Shear = 0.85 MPa
Modulus of elasticity of wood =13790 MPa
7. Problem
Allowable deflection = 1/360 of span
A masonry terrace of 75 mm concrete surface with 25 mm 1) Which of the following gives the depth of the beam so
cement tiles rests on a 75 mm x 200 mm lumber spaced at that when the allowable bending stress is reached the
300 mm on centers acting as simple beam with an effective deflection of the beam is 1/360 of span?
span of 3.6 m. Weight of wood is 7.5 kN/m3 and masonry to a) 200 mm c) 400 mm
be 24 kN/m3. Ew= 13800 MPa. The allowable stresses are b) 300 mm d) 500 mm
14 MPa for bending, 0.80 MPa for shear parallel to the grain 2) Which of the following gives the value of the safe
and deflection is 1/360 of span. uniform load it could carry if shearing stress governs for
a width of 250 mm?
1) Which of the following gives the uniform load it could a) 14.741 kN/m c) 16.741 kN/m
support if bending stress controls? b) 15.741 kN/m d) 17.741 kN/m
a) 3.49 kN/m c) 2.49 kN/m
b) 4.49 kN/m d) 5.49 kN/m 3) Which of the following gives the value of the safe
uniform load it could carry it bending stress governs for
2) Which of the following gives the uniform load it could the same width?
support if shear controls? a) 9.50 kN/m c) 11.50 kN/m
a) 3.61 kN/m c) 2.61 kN/m b) 10.50 kN/m d) 12.50 kN/m
b) 4.61 kN/m d) 5.61 kN/m
2) Compute the width of the beam so that it will not exceed
10. CE Board May the allowable shearing stress.
a) 147 mm c) 183 mm
b) 127 mm d) 163 mm
A timber beam having a simple span of 4 m. carries a total
load including its own weight of 3) Compute the shearing stress at point C 50 mm below
10 kN/m. lt has a width of 200 mm and a depth of 260 mm, the top of the beam.
used dressed dimension by reducing its dimensions by 10 a) 0.36 MPa c) 0.42 MPa
mm. The wooden section is made up of 80% grade Apitong. b) 0.56 MPa d) 0.62 MPa
Allowable bending stress, Fb = 16.5 MPa
13. Problem
Modulus of elasticity of wood, Ew = 7310 MPa
Allowable shearing stress, Fv = 1.75 MPa A wooden rectangular beam 200 mm x 350 mm has a simple
span of 6 m. Neglecting the weight of the beam.
1) Which of the following gives the max. flexural stress of
the beam?
a) 16.50 MPa c) 12.80 MPa
b) 17.50 MPa d) 13.80 MPa
2) Which of the following gives the max. shearing stress of
the beam?
a) 2.73 MPa c) 2.36 MPa
b) 1.73 MPa d) 1.36 MPa 1) Which of the following gives the value of the
concentrated load it could carry at its midspan if the
3) Which of the following gives the max. deflection of the allowable bending stress is 10.35 MPa?
beam? a) 29.17 kN c) 27.19 kN
a) 16.43 mm c) 15.66 mm b) 28.17 kN d) 26.19 kN
b) 18.43 mm d) 17.66 mm
2) Which of the following gives the value of the shear force
at the support if there is a notch at the end of the beam
11. Problem which is 100 mm deep if the allowable shearing stress is
1.10 MPa?
a) 29.17 kN c) 27.19 kN
A 100 mm x 300 mm rectangular beam caries a uniformly b) 28.17 kN d) 26.19 kN
distributed load of “W” kN/m over its entire span. The beam
is freely supported at its ends. lf the. max. allowable bendlng 3) Which of the following gives the value of the
stress is 8.27 MPa and simullaneously the max. allowable concentrated load at the midspan that it could support if
shearing stress is 0.70 MPa. there is a notch of 100 mm deep at the end support?
a) 42.38 kN c) 47.97 kN
1) Which of the following gives the value of max. vertical b) 52.38 kN d) 57.97 kN
shear?
a) 16 kN c) 15 kN
b) 13 kN d) 14 kN
14. Problem
2) Which of the following gives the value of the span of the
beam? A wooden beam having a span of 4 m. Is subjected to a
a) 6.45 m c) 4.54m uniform load of 10 kN/m. lt has a triangular cross section
b) 5.45 m d) 3.54 m having a base width of 140 mm and an altitude of 300 mm.
Neglecling the weight of the beam.
3) Which of the following gives the value of “W” in kN/m?
a) 6.91 c) 8.91
b) 7.91 d) 9.91
12. Problem
A laminated wooden beam supports a uniform distributed
loading of 12 kN/m. Allowable bending stress is 9 MPa and
allowable shear stress is 0.6 MPa. Neglecting the weight of
the beam and assuming the beam lo have a height to width
ratio of 1.5.
1) Which of the following gives the section modulus of the
beam?
a) 525000 mm3 c) 636000 mm3
b) 252000 mm3 d) 363000 mm3
2) Which of the following gives the flexural stress of the
beam?
a) 38.09 MPa c) 35.47 MPa
b) 39.09 MPa d) 36.47 MPa
3) Which of the following gives the max. shearing stress
developed on the beam?
a) 1.73 MPa c) 1.36 MPa
b) 1.43 MPa d) 1.66 MPa
1) Compute the width of the beam so that it will not exceed
the allowable bending stress.
a) 147 mm c) 183 mm
b) 127 mm d) 163 mm
15. Problem
A 150 mm x 350 mm wooden beam carries a concentrated
load of 30.36 kN at its midspan. It has a simple span of 8 m.
long. Allowable shear stress is 0.85 MPa.
1) Which of the following gives the depth of notches at the
support if notching is allowed using the NSCP
specifications?
a) 100 mm c) 300 mm
b) 200 mm d) 400 mm
2) Which of the following gives the allowable depth of
notches at the bottom and top faces of the beam at
quarter points?
a) 41 mm c) 61 mm
b) 51 mm d) 71 mm
3) Which of the following gives the flexural stress at the
quarter points after deducting for notching?
a) 17.74 MPa c) 19.74 MPa
b) 18.74 MPa d) 20.74 MPa
16. CE Board Nov.
A timber beam has a circular cross section having a
diameter of 250 mm. lt has a simple span of 4 m. NSCP
specs. states that in a circular beam the strength is equal to
the strength of square section having the same area.
Allowable stresses of wood are as follows:
Shearing stress parallel to the grain fv= 1.73 MPa
Bending stress fb = 16.5 MPa
Allowable deflection 1/240 of span
Modulus of elasticity of wood = 7.31 GPa
1) Which of the following gives the maximum uniform load
so that the allowable shear stress parallel to the grain is
not exceeded?
a) 31.56 kN/m c) 25.31 kN/m
b) 34.56 kN/m d) 28.31 kN/m
2) Which of the following gives the max. uniform load so
that the allowable bending stress is not exceeded?
a) 16.37 kN/m c) 11.95 kN/m
b) 19.37 kN/m d) 14.95 kN/m
3) Which of the following gives the max. uniform load so
that the allowable deflection is not exceeded?
a) 6.12 kN/m c) 4.34 kN/m
b) 9.12 kN/m d) 7.34 kN/m
17. Problem
An old Apitong post 200 mm x 300 mm x 4.25 m. long has
been previously designed with an allowable compressive
stress of 9.56 MPa. and a modulus of elasticity of 7310 MPa.
It is designed to substitute the old post with a Yakal post of
the same length as the old post. Allowable compressive
stress for Yakal is 15.8 MPa with a modulus of elasticity of
9780 MPa.
1) What is the capacity of Apitong?
a) 184400 N c) 203300 N
b) 194400 N d) 213300 N
2) What size of Yakal post is required to replace Apitong?
a) 150 x 150 mm c) 250 x 250 mm
b) 200 x 200 mm d) 300 x 300 mm
3) What is the percentage increase in the capacity of the
new post to the dd post?
a) 11.74% c) 33.74%
b) 22.74% d) 44.74%
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Module 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Dokument4 SeitenModule 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Glaiza MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design 3 April 2024Dokument3 SeitenSteel Design 3 April 2024Craeven AranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mech May 2021Dokument5 SeitenFluid Mech May 2021Naigell SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1Dokument2 SeitenReview Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1John andre MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module 45-RCD 5 - Part 1 & 2Dokument2 SeitenReview Module 45-RCD 5 - Part 1 & 2Arlyn ConsumeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stresses in Soil Mass Problem 1: Foundation Engineering 1Dokument3 SeitenStresses in Soil Mass Problem 1: Foundation Engineering 1Kristin ArgosinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEGA Review Module - RCD Shear (Part 2)Dokument1 SeiteMEGA Review Module - RCD Shear (Part 2)Study BuddiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCDokument14 SeitenRClexterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 6Dokument1 SeiteQuiz 6Nikki Marie G OclaritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nov 2021 CoachingDokument71 SeitenNov 2021 CoachingKenny CaluzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: 2 Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, ManilaDokument2 SeitenF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: 2 Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, ManilaBluezed14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Geo Online Preboard Questionnaire PDFDokument6 SeitenHydro Geo Online Preboard Questionnaire PDFCarl Justin AzucenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eccentric Welded ConnectionsDokument35 SeitenEccentric Welded ConnectionsDavid Reyes0% (1)
- Hydrogeo Preboard 3 ADokument6 SeitenHydrogeo Preboard 3 ALester SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psad - 2Dokument25 SeitenPsad - 2Mary Ann Toni N. RasonabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 42 - USD Beams RiDokument2 SeitenModule 42 - USD Beams RiClark SibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural AnalysisDokument14 SeitenStructural AnalysisPrincess Gupo Tañas100% (1)
- MechanicsDokument5 SeitenMechanicsElla ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos 2Dokument4 SeitenTos 2Mayya BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Flexural Members PDFDokument9 Seiten4 Flexural Members PDFCristan RetuermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADokument2 SeitenQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- Design 1qsy1718 QuestionsDokument9 SeitenDesign 1qsy1718 QuestionsRachel Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design 3 Nov 2021Dokument3 SeitenSteel Design 3 Nov 2021Lemuel TeopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.0 Learning Outcome: Principles of Reinforced Concrete/PrestressedDokument6 Seiten3.0 Learning Outcome: Principles of Reinforced Concrete/PrestressedAllysa Joy MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Dokument4 SeitenDiagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher Course Module - Structural Engineering: Hakuna Matata"Dokument1 SeiteRefresher Course Module - Structural Engineering: Hakuna Matata"Mohammad Hussein Masiu BacaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - IiDokument5 SeitenAssignment - IichritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design 6 April 2023 PDFDokument2 SeitenSteel Design 6 April 2023 PDFTristan CatapangNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument19 SeitenUntitledRojane FloraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Dokument9 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 5 ColoredDokument2 SeitenCE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 5 ColoredDale MalazzabNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Problem Solving (15 Pts Each) : Prepared By: Engr. Raquel A. AlmendaresDokument4 SeitenI. Problem Solving (15 Pts Each) : Prepared By: Engr. Raquel A. AlmendaresCarl LacanilaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCD Assignment 2Dokument3 SeitenRCD Assignment 2CE-Cret KuyaaDeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsDokument4 SeitenRefresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsJerome YangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Concrete With Coconut Husk and Dried Banana Leaffibers As Aggregate ReplacementintroductionrationaleDokument3 SeitenProperties of Concrete With Coconut Husk and Dried Banana Leaffibers As Aggregate Replacementintroductionrationalejohn philip s garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials 1 PDFDokument3 SeitenStrength of Materials 1 PDFMaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fliuids MechanicsDokument8 SeitenFliuids MechanicsCaro Kan LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Gtfiuctural Steel Dkign: Yletd Stress, Fy - Is That Unit Tensile Stress atDokument13 Seiten"Gtfiuctural Steel Dkign: Yletd Stress, Fy - Is That Unit Tensile Stress atMhiaBuenafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDokument13 SeitenStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 19Dokument1 SeiteCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 19Glenn Frey LayugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachDokument48 SeitenModule 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachVann AlfredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 - Allowable StressesDokument20 SeitenTopic 3 - Allowable StressesMohammad Taha PumbayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolveDokument2 SeitenSolveJea Clarie Mendioro Espinas67% (3)
- Reinforced ConcreteDokument5 SeitenReinforced ConcreteLYNSER CORONEL ABANZADO100% (1)
- Earthquake Engineering LectureDokument12 SeitenEarthquake Engineering LectureMeverlyn RoqueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design 4 May 2022Dokument3 SeitenSteel Design 4 May 2022tous les joursNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrasdaDokument3 SeitenBrasdaJayson Brylle MojaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsDokument3 SeitenMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- HydraulicsDokument8 SeitenHydraulicsKristin ArgosinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 115Dokument10 Seiten115Memo LyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Design of Compression MembersDokument21 SeitenAnalysis and Design of Compression MembersSilendrina Misha100% (1)
- Alejandro 3 MsteDokument2 SeitenAlejandro 3 MsteBack UpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Department: P R E - B O A R D E X A M I N A T I O NDokument8 SeitenCivil Engineering Department: P R E - B O A R D E X A M I N A T I O NBrian Unciano100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Dokument2 SeitenCE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Nov2023) PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION (PSAD) - CEBU (A-M) - QuestionsDokument63 Seiten(Nov2023) PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION (PSAD) - CEBU (A-M) - Questionsgt201901573Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stdl02e Final ExamDokument6 SeitenStdl02e Final ExamPaulo ValderamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Design ReviewDokument4 SeitenTimber Design ReviewaomineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Design Review PDFDokument4 SeitenTimber Design Review PDFJunar AmaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Design ReviewDokument4 SeitenTimber Design ReviewRoben Casano78% (9)
- Problem Set 2 V2Dokument3 SeitenProblem Set 2 V2RalphNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZDC Outstanding Works Photos 14 November 2019Dokument11 SeitenZDC Outstanding Works Photos 14 November 2019alfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Destructive Testing of ConcreteDokument1 SeiteNon Destructive Testing of ConcretealfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZDC Updated Outstanding Works (Archi. Rectification Works) Dated 22 October 2019Dokument45 SeitenZDC Updated Outstanding Works (Archi. Rectification Works) Dated 22 October 2019alfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attendance Sheet For (Resident Technical Officer)Dokument1 SeiteAttendance Sheet For (Resident Technical Officer)alfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfredo JR Arios Claro: This Is To Certify ThatDokument1 SeiteAlfredo JR Arios Claro: This Is To Certify ThatalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated ZDC Outstanding Works As of 5 October 2019Dokument36 SeitenUpdated ZDC Outstanding Works As of 5 October 2019alfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Checklist For Excavation, Lean Concrete and Backfiling AlfredoDokument1 Seite1 Checklist For Excavation, Lean Concrete and Backfiling AlfredoalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 December 2017Dokument32 Seiten4 December 2017alfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety in Deep ExcavationDokument1 SeiteSafety in Deep ExcavationalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV of Alfredo Jr. Arios Claro 7 June 2017rcyDokument20 SeitenCV of Alfredo Jr. Arios Claro 7 June 2017rcyalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Checklist For Excavation, Lean Concrete and BackfilingDokument1 Seite1 Checklist For Excavation, Lean Concrete and BackfilingalfieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site InstructionsDokument30 SeitenSite InstructionsalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Only If Additional Space Is Needed To List Additional Project/performance SitesDokument1 SeiteUse Only If Additional Space Is Needed To List Additional Project/performance SitesalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Cube Test Report: Cast Laboratories Pte LTDDokument1 SeiteConcrete Cube Test Report: Cast Laboratories Pte LTDalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Play Single Notes On The HarmonicaDokument19 SeitenHow To Play Single Notes On The HarmonicaxiaoboshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Where Riches Is Everlastingly - WarlockDokument1 SeiteWhere Riches Is Everlastingly - WarlockPaulo RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Infinitynest Starter GuideDokument9 SeitenComplete Infinitynest Starter GuideSeptian Citra KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC SplitTopRouboNotes Nov12Dokument28 SeitenBC SplitTopRouboNotes Nov12Noemi GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCCE July 2020 NewsletterDokument6 SeitenFCCE July 2020 NewsletterFirst Congregational Church of EvanstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team TextDokument6 SeitenTeam TextkensicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 TAHUN LAGI - PartsDokument6 Seiten50 TAHUN LAGI - PartsPak Gibio SiraitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Achievers A1 Diagnostic Test 111 AngeloDokument3 SeitenAchievers A1 Diagnostic Test 111 AngeloAngelo David Muñoz Semanate50% (2)
- Full Attention ChordsDokument2 SeitenFull Attention ChordsGreySugizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toomer, John Selden (Review)Dokument2 SeitenToomer, John Selden (Review)Ariel HessayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sponsorship Letter LeoDokument4 SeitenSponsorship Letter LeoLeopold BrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hegel Philosophy Application On Aeschylus AgamemnonDokument5 SeitenHegel Philosophy Application On Aeschylus AgamemnonMuhammad MohsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Escola Secundária Teixeira de Sousa English Worksheet Name: Number: ClassDokument2 SeitenEscola Secundária Teixeira de Sousa English Worksheet Name: Number: ClassKleber MonteiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris: Adjective ClauseDokument7 SeitenTugas Bahasa Inggris: Adjective Clauseanon_323638500Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6 Small GroupDokument2 SeitenLesson 6 Small GroupMark AllenNoch keine Bewertungen
- American History XDokument110 SeitenAmerican History XNick LaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beegees - Stayin Alive Bass PDFDokument2 SeitenBeegees - Stayin Alive Bass PDFEnrique Rosas100% (1)
- Dr. Quinn Medicine Woman Pilot ScriptDokument86 SeitenDr. Quinn Medicine Woman Pilot ScriptMohammad Muji Paliwala100% (4)
- A Heartbreaking Work of Staggering Genius LessonplanDokument229 SeitenA Heartbreaking Work of Staggering Genius LessonplanMahmoud El SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calinawan Re - Ed.NOT DONEDokument5 SeitenCalinawan Re - Ed.NOT DONERichard Jr CalinawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TravelCLICK Premium Consortia Directory PDFDokument31 SeitenTravelCLICK Premium Consortia Directory PDFquentinejamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet of DS-2DE5225IW-AE (C)Dokument6 SeitenDatasheet of DS-2DE5225IW-AE (C)nvnakumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selected Poems by Saigyo PDFDokument16 SeitenSelected Poems by Saigyo PDFVladimir NabokovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features/Principles of Indian EthosDokument16 SeitenFeatures/Principles of Indian EthosSIDDHANT TYAGI100% (1)
- Short Stories Buzz and Bobs Big Adventure WorksheetDokument2 SeitenShort Stories Buzz and Bobs Big Adventure WorksheetIsabel Gonzalez100% (1)
- Lissa PaulDokument28 SeitenLissa PaulApril Lei IrincoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harris Broadcasting Accessories 1982Dokument200 SeitenHarris Broadcasting Accessories 1982João Pedro AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language Unseen PoetryDokument2 SeitenLanguage Unseen PoetryWitchingDread10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bill Hybels 6x6 Leadership Strategy PDFDokument8 SeitenBill Hybels 6x6 Leadership Strategy PDFPabloRodríguezLucenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAGL 6-1 Watt PDFDokument12 SeitenBAGL 6-1 Watt PDFguillermoisedetNoch keine Bewertungen