Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Quiz 2
Hochgeladen von
senior high0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
336 Ansichten1 Seitepractice problem
Originaltitel
QUIZ 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenpractice problem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
336 Ansichten1 SeiteQuiz 2
Hochgeladen von
senior highpractice problem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
Foundation Engineering - Take Home Quiz 4.
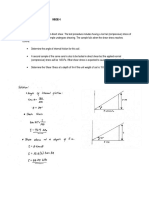
A triaxial shear test was performed on a well-drained sand
MIDTERM sample. The normal stress on the failure plane and the shear
stress on the failure plane, at failure were determined to be
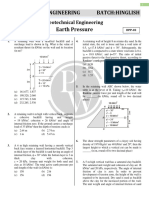
1. From the figure shown: Surcharge load is applied at the 6,300 psf and 4,200 psf, respectively.
ground surface qo = 40 kPa. a. Determine the angle of internal friction of the sand.
H1 = 3m, ɣ1 = 17 kN/m3, φ1 = 22° b. Determine the angle of the failure plane.
H2 = 4m, ɣ2 = 21 kN/m3, φ2 = 28° c. Determine the maximum principal stress.
5. A sample of moist sand was subjected to a series of triaxial
tests. The soil fails under the following stresses
Cell pressure Deviator Stress
Sample 1 14 kPa 20 kPa
Sample 2 25 kPa 31 kPa
Soil 1: What is the angle of internal friction of the soil in degrees?
H1
γ1, φ1
6. A consolidated undrained (CU) compression test was
conducted on a saturated clay soil by isotropically
consolidating the soil using a cell pressure of 150 kPa and then
incrementally applying loads on the plunger while keeping the
cell pressure constant. Failure was observed when the stress
Soil 2: exerted by the plunger (deviator stress) was 160 kPa and the
γ2, φ2 H2 pore water pressure recorded was 54 kPa.
a. Determine the undrained shear strength of the clay
b. Determine the undrained friction angle
c. Determine the drained friction angle
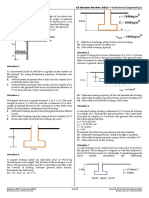
7. A footing 6 m square carries a total load, including its own
a. Determine the total lateral pressure at the base of the wall. weight, of 10,000 kN. The base of the footing is at depth of 3 m
b. Determine the total active force acting on the wall below the ground surface. The soil strata at the site consist of a
c. Determine the total active moment acting on the wall. layer of stiff saturated clay 27.5 m thick overlying dense sand.
The average bulk density of the clay is 1,920 kg/m3 and its
2. For the shown figure, plot the pressure diagram below and average shear strength determined from undrained triaxial test
find the resultant force F and its location under active is 130 kN/m2 and φ = 0°. Assume general shear failure. For φ =
condition. 0°, Nc = 5.7, Nq = 1.0 and Nγ = 0. Use Terzaghi’s ultimate bearing
capacity equations to:
a. Determine the gross foundation pressure in kPa
b. Determine the net foundation pressure
c. Calculate the factor of safety of the foundation against
complete shear failure under the undrained condition (both
gross and net). Side cohesion on the foundation may be
neglected.
8. A footing 1 m square carries a total load, including its own
weight of 59,130 kg. The base of the footing is at a depth of 1
m below the ground surface. The soil strata at the site consist
of a layer of stiff saturated clay 27.5 m thick overlying dense
sand. The average density of the clay is 1,846 kg/m3. Given is
Terzaghi’s ultimate bearing capacity for square footing:
a. Determine the gross foundation pressure
b. Determine the overburden pressure
3. From the figure shown, a vertical retaining wall with a c. Determine the ultimate bearing capacity of the soil
horizontal backfill. Note that the water table elevations in front d. Assuming local shear failure, determine the ultimate
of the wall and at the back of the wall are different. bearing capacity of the soil.
a. Determine the tension crack depth.
b. Determine the total thrust acting on the wall.
c. Determine the location of the total thrust from the base of
the wall.
Soil 1:
c = 10 kN/m3
γ = 18.5 kN/m3 4m
φ = 25°
Soil 2:
8m
c = 15 kN/m3
γ = 19.0 kN/m3
9m
φ = 30°
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Soil 1: γ, φ 3 3: K = 0.3 γ = 19.49 kN/mDokument1 SeiteSoil 1: γ, φ 3 3: K = 0.3 γ = 19.49 kN/msenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- MidtermDokument1 SeiteMidtermMau MauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation of SoilDokument8 SeitenConsolidation of SoilRay JillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotech 2 Questions 2022.10.10Dokument1 SeiteGeotech 2 Questions 2022.10.10reneotejrboardexamNoch keine Bewertungen
- .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sDokument2 Seiten.0106 Mm/s 0.075 Mm/s .106 Cm/s 0.750 Cm/s .106 Mm/s 0.750 Mm/s .0106 Mm/s 0.075 Cm/sReech Aerol AlmendralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set Foundation EngineeringDokument5 SeitenProblem Set Foundation EngineeringJohn Mathew BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Exam 04Dokument10 SeitenAssessment Exam 04TachooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil 6 Ap (Ril 2023Dokument2 SeitenSoil 6 Ap (Ril 2023Nica SudamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil 7 April 2023 1 of 2Dokument1 SeiteSoil 7 April 2023 1 of 2Nica SudamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Engineering Assessment ExamDokument7 SeitenGeotechnical Engineering Assessment ExamAndrea MagtutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Soil Mechanics Assignment SolutionsDokument2 SeitenAdvanced Soil Mechanics Assignment SolutionsrockyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Dokument2 SeitenCE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Lemuel TeopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Compressibility of SoilsDokument43 Seiten03 Compressibility of SoilsJoshua OrcalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Pressure CalculationsDokument35 SeitenEarth Pressure Calculationskeddy lamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral Earth PressureDokument3 SeitenLateral Earth PressureDupio German IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnic 2Dokument2 SeitenGeotechnic 2Faez El-NinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Lateral PressureDokument2 SeitenEarth Lateral PressureGlenn SeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotech - 2Dokument2 SeitenGeotech - 2Sanket AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 79. RM 47 - Geotechnical Engineering 7 (Conditions-Theory)Dokument2 Seiten79. RM 47 - Geotechnical Engineering 7 (Conditions-Theory)Abubakar SalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4-Effective Stress StudentDokument20 SeitenChapter 4-Effective Stress StudentKalsoma CarlsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotech Practice QuestionDokument2 SeitenGeotech Practice QuestionLucifer ShiversNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressDokument12 SeitenModule 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressShane IsorenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo - Session 4 Chapter 6-9Dokument7 SeitenGeo - Session 4 Chapter 6-9Heart VenturanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stresses & SettlementDokument2 SeitenStresses & SettlementJumari CaselesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Composition & Shear Stress AnalysisDokument3 SeitenSoil Composition & Shear Stress AnalysisXDXDXDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2-09Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 2-09Felix HabarugiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeoTech (Problems)Dokument2 SeitenGeoTech (Problems)Mariel VillalunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExaminationDokument1 SeiteFinal ExaminationJam Arambala AbelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo - 4Dokument2 SeitenGeo - 4SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT III Question BankDokument4 SeitenCAT III Question BankHanafiahHamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 99.earth Pressure - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03 & 04)Dokument3 Seiten99.earth Pressure - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03 & 04)wikita4906Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unconsolidated-Undrained, Unconfined-CompressionDokument9 SeitenUnconsolidated-Undrained, Unconfined-CompressionJemuel FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module 27 - Part 1 and Part 2Dokument3 SeitenReview Module 27 - Part 1 and Part 2Angelie RemediosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo - 3Dokument2 SeitenGeo - 3SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartDokument4 SeitenQuiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartBenjamin Benicarlo Juanillo IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 2)Dokument42 Seiten2 BAA3513 Lateral Earth Pressure (Part 2)احمد يوسفNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module: - Slope Stability and Terzaghi's Bearing CapacityDokument2 SeitenReview Module: - Slope Stability and Terzaghi's Bearing CapacityMa Ella Mae Logronio0% (1)
- For Problems 2016-05-27Dokument42 SeitenFor Problems 2016-05-27Christian D. OrbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 5Anonymous Vx9KTkM8n67% (3)
- 3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Dokument2 Seiten3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8JuDeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factor of Safety Against Sliding Refresher CourseDokument3 SeitenFactor of Safety Against Sliding Refresher CourseKim Ryan PomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1Dokument1 SeiteMath 1adonis bibatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial A7 & A8 Earth Pressure & Retaining WallsDokument3 SeitenTutorial A7 & A8 Earth Pressure & Retaining WallsSaiful Azhar Ahmad TajudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Module 28 - Rigid Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Dokument3 SeitenCE Module 28 - Rigid Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment For Mid 1Dokument9 SeitenAssignment For Mid 1Vũ Thị Hà TrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Mechanics IIDokument2 SeitenSoil Mechanics IIqwfqefwqefgefqeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Dokument4 Seiten620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Mona fabrigarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Sheet (1) Shear Strength (Fall2021)Dokument2 Seiten1-Sheet (1) Shear Strength (Fall2021)Mahmoud AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECV308. Soil Mechanics II Tutorial Questions: 10 KG/ CM 3 KG/ CMDokument2 SeitenECV308. Soil Mechanics II Tutorial Questions: 10 KG/ CM 3 KG/ CMEdwin KaranjqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolly S. Tambe Quiz 4 SolutionsDokument4 SeitenRolly S. Tambe Quiz 4 SolutionsFely TambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.E / B.Tech (Full Time) D E G R E E End S E M E S T E R Examinations, April / May 2014Dokument2 SeitenB.E / B.Tech (Full Time) D E G R E E End S E M E S T E R Examinations, April / May 2014AravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimating Skin Friction and End Bearing Capacity of PilesDokument6 SeitenEstimating Skin Friction and End Bearing Capacity of Pilesnishan_ravinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 95.earth Pressure - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02)Dokument3 Seiten95.earth Pressure - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02)wikita4906Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module 24 Geotechnical Engineering 5 Part 2Dokument1 SeiteReview Module 24 Geotechnical Engineering 5 Part 2Mark Daren Patrona RamonNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOUNDADokument22 SeitenFOUNDAShaina Mariz PanaliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- International School of Asia and the Pacific Technical Elective I ExamDokument1 SeiteInternational School of Asia and the Pacific Technical Elective I ExamSn CarbonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shallow Foundations: BCP and Settlement AnalysisDokument2 SeitenShallow Foundations: BCP and Settlement AnalysisAnonymous Vx9KTkM8nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow NetsDokument29 SeitenFlow Netsmark galangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Dokument21 SeitenCE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Irmak ÜnalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table MLZDokument1 SeitePeriodic Table MLZsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work and Kinetic Energy LessonDokument5 SeitenWork and Kinetic Energy Lessonsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Testing: An Overview of Tests, Purposes, and EthicsDokument27 SeitenPsychological Testing: An Overview of Tests, Purposes, and Ethicssenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of Organic Compounds: Review of Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Ifas)Dokument13 SeitenPhysical Properties of Organic Compounds: Review of Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Ifas)Darielle JovenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Journal Lesson 1-12 - LisondraDokument4 SeitenStudy Journal Lesson 1-12 - Lisondrasenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChiralityDokument17 SeitenChiralitysenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Journal Lesson 23-32 - LisondraDokument3 SeitenStudy Journal Lesson 23-32 - Lisondrasenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Journal Lesson 1-12 - LisondraDokument4 SeitenStudy Journal Lesson 1-12 - Lisondrasenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Journal Lesson 23-32 - LisondraDokument3 SeitenStudy Journal Lesson 23-32 - Lisondrasenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gantt Charts, Took Several Different Forms, Depending On TheirDokument5 SeitenGantt Charts, Took Several Different Forms, Depending On Theirsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 PDFDokument4 SeitenLesson 1 PDFsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1Dokument1 SeiteTest 1senior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- I MC S M F: Timber Advantages and Disadvantages of Wood Bending Stress in BeamsDokument4 SeitenI MC S M F: Timber Advantages and Disadvantages of Wood Bending Stress in Beamssenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum Deflection. Recall Your Lessons in Determining The Deflection of Determinate Beams From Structural Theory Subject) (Dokument2 SeitenMaximum Deflection. Recall Your Lessons in Determining The Deflection of Determinate Beams From Structural Theory Subject) (senior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- BENEDICT - Anthropology and The AbnormalDokument4 SeitenBENEDICT - Anthropology and The Abnormalanon_137579236Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aristotle's Nicomachean Ethics: Happiness as the Supreme Human GoodDokument4 SeitenAristotle's Nicomachean Ethics: Happiness as the Supreme Human Goodsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proper handling and toxicity of butanol, glacial acetic acid, glycine, lysine, tyrosine and leucine solutionsDokument3 SeitenProper handling and toxicity of butanol, glacial acetic acid, glycine, lysine, tyrosine and leucine solutionssenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research EnvironmentDokument2 SeitenResearch Environmentsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literary Devices Elements TechniquesDokument38 SeitenLiterary Devices Elements Techniquessenior high100% (2)
- Running Head: DATA ANALYSIS 1Dokument4 SeitenRunning Head: DATA ANALYSIS 1senior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Summary of The Theology of The BodyDokument2 SeitenA Summary of The Theology of The Bodysenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mga IeeditDokument1 SeiteMga Ieeditsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- DatusDokument3 SeitenDatussenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocumentDokument1 SeiteDocumentsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Reflection On Genesis Chapters One To ThreeDokument1 SeiteA Reflection On Genesis Chapters One To Threesenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hundred Foot JourneyDokument2 SeitenThe Hundred Foot Journeysenior high0% (2)
- This Is A DocumentDokument1 SeiteThis Is A Documentsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument5 SeitenAsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Quarter ExamDokument3 SeitenFirst Quarter ExamJunard AsentistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mayne 1990 UnlockedDokument308 SeitenMayne 1990 UnlockedJorge Ordóñez100% (2)
- Grade 6 DLL Science 6 q3 Week 1Dokument5 SeitenGrade 6 DLL Science 6 q3 Week 1MICHELE PEREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Road Construction Structure WorksDokument86 SeitenRoad Construction Structure Worksadnriod100% (1)
- Riprap Project ProposalDokument2 SeitenRiprap Project ProposalSHEILA MAE PERTIMOS50% (6)
- Grade 11 Earth Science Pretest PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenGrade 11 Earth Science Pretest Philippinesbenes salamancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocean Floor TopographyDokument3 SeitenOcean Floor TopographyZannatul NayemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - Different Types of Plate BoundariesDokument19 SeitenLesson 2 - Different Types of Plate Boundariesken arellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Suitability for Crops and Fruits in Sudan's River Nile TerracesDokument5 SeitenLand Suitability for Crops and Fruits in Sudan's River Nile TerracesKani ManikandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pallavi Model School Subject: Social Science Class: VII Geography - Ls-1 Our Environment Read Text Book Write New Words and Define Terms: D: Explain The Following TermsDokument2 SeitenPallavi Model School Subject: Social Science Class: VII Geography - Ls-1 Our Environment Read Text Book Write New Words and Define Terms: D: Explain The Following TermsSakshi JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science Module-RasgoDokument27 SeitenEarth and Life Science Module-RasgoApril Jane Elandag RasgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studi Kerentanan Wilayah Dan Ketahanan Masyarakat Pesisir Kecamatan Gedangan Kabupaten Malang Terhadap Bencana TsunamiDokument8 SeitenStudi Kerentanan Wilayah Dan Ketahanan Masyarakat Pesisir Kecamatan Gedangan Kabupaten Malang Terhadap Bencana TsunamiPT HAE DONG JAYA ABADINoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 6 - Modules - Q4 - Sir AljonDokument9 SeitenScience 6 - Modules - Q4 - Sir AljonNojla SenoirbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth: An Introduction To Physical Geology, 9e (Tarbuck/Lutgens)Dokument32 SeitenEarth: An Introduction To Physical Geology, 9e (Tarbuck/Lutgens)ryan patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- WN N DR G W W I C CC e (M) : (Kedalaman) (Jenis Tanah) (Warna) Gravel Sand Silt ClayDokument1 SeiteWN N DR G W W I C CC e (M) : (Kedalaman) (Jenis Tanah) (Warna) Gravel Sand Silt ClayChyntia RaharsiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Metamorphic ClassificationDokument22 Seiten2 Metamorphic ClassificationVinay Pratap Singh ShekhawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes Grade 9 Third QuarterDokument50 SeitenVolcanoes Grade 9 Third QuarterChelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrecciaDokument21 SeitenBrecciaLleixer Eiram AlagedNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEOENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONSDokument34 SeitenGEOENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONSNero PangpangdeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 10: Modified ProctorDokument20 SeitenLab 10: Modified Proctorkim suarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Stress and Seafloor SpreadingDokument16 SeitenRock Stress and Seafloor SpreadingFefeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processes Features of Convergent BoundaryDokument31 SeitenProcesses Features of Convergent BoundaryfloridohannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science Module 15Dokument10 SeitenEarth and Life Science Module 15cherry cheolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compaction Test Results: Berat Isi Basah (Wet Density)Dokument13 SeitenCompaction Test Results: Berat Isi Basah (Wet Density)AnsmunandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marine SeismicDokument86 SeitenMarine SeismicMuhammad BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uliana M. & Biddle K. (1988) .Dokument19 SeitenUliana M. & Biddle K. (1988) .fo saldiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Soil FormationDokument16 Seiten3 Soil FormationTimothy SimirenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kajian Penerapan Soil NailingDokument5 SeitenKajian Penerapan Soil Nailinghandry solimudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 364 419 PDFDokument56 Seiten364 419 PDFVince Bagsit PolicarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science CT 3Dokument1 SeiteScience CT 3floridohannahNoch keine Bewertungen