Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ketamine
Hochgeladen von
yanti anggrenie100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
1K Ansichten2 Seitenketamin
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenketamin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
1K Ansichten2 SeitenKetamine
Hochgeladen von
yanti anggrenieketamin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
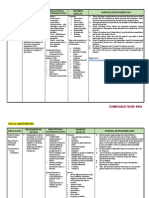
Name /bks_53161_deglins_md_disk/ketamine 02/14/2014 03:50PM Plate # 0-Composite pg 1 # 1
1 rhage; Hyperthyroidism; History of psychiatric problems;qintraocular pressure; Se-
vere eye trauma.
PDF Page #1
ketamine (ket-a-meen) Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Ketalar CNS: emergence reactions,qintracranial pressure. EENT: diplopia,qintraocular
Classification pressure, nystagmus. Resp: laryngospasm, respiratory depression and apnea (rapid
Therapeutic: general anesthetics IV administration of large doses). CV: hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmias,
Pregnancy Category UK bradycardia, hypotension. GI: excessive salivation, nausea, vomiting. GU: cystitis.
Derm: erythema, rash. Local: pain at injection site. MS:qskeletal muscle tone.
Indications Interactions
Anesthesia for short-term diagnostic and surgical procedures. As induction before Drug-Drug: Use with barbiturates, hydroxyzine and opioid analgesics may
the use of other anesthetics. As a supplement to other anesthetics. Unlabeled Use: result in prolonged recovery time. Use with halothane may result inpBP, cardiac
Provides sedation and analgesia. output, and heart rate. Use with tubocurarine or nondepolarizing neuromus-
cular blocking agents may result in prolonged respiratory depression. Concurrent
Action use with thyroid hormoneqrisk of tachycardia and hypertension. Concurrent ad-
Blocks afferent impulses of pain perception. Suppresses spinal cord activity. Affects
ministration with diazepam maypincidence of emergence reaction. Concurrent ad-
CNS transmitter systems. Therapeutic Effects: Anesthesia with profound analge-
ministration with atropine mayqincidence of unpleasant dreams.
sia, minimal respiratory depression, and minimal skeletal muscle relaxation.
Pharmacokinetics Route/Dosage
Absorption: Rapidly absorbed after IM administration. General Anesthesia
Distribution: Rapidly distributed. Enters the CNS; crosses the placenta. IV (Adults): Induction— 1– 2 mg/kg (range 1– 4.5 mg/kg)– 2 mg produces 5–
Metabolism and Excretion: Mostly metabolized by the liver. Some conversion 10 min of surgical anesthesia or 1– 2 mg/kg as a single injection or infused at 0.5 mg/
to another active compound. min. May be used with concurrent diazepam. Maintenance— Increments of 1⁄2 to
Half-life: 2.5 hr. the full induction dose may be repeated as needed. If given with concurrent diaze-
TIME/ACTION PROFILE (anesthesia) pam, an infusion of 0.1– 0.5 mg/min may be used, augmented by 2– 5 mg doses of
ROUTE ONSET PEAK DURATION
diazepam.
IV (Children): 0.5– 2 mg/kg, use smaller doses (0.5– 1 mg/kg)for minor proce-
IV 30 sec unknown 5–10 min dures.
IM 3–4 min unknown 12–25 min IM (Adults): 3– 8 mg/kg (10 mg/kg produces 12– 25 min of surgical anesthesia).
IM (Children): 3– 7 mg/kg.
Contraindications/Precautions PO (Children): 6– 10 mg/kg for 1 dose (mix in cola or other beverage) 30 min
Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity; Psychiatric disturbances; Hypertension;q prior to procedure.
intracranial pressure; OB, Lactation: Pregnancy or lactation.
Use Cautiously in: Cardiovascular disease; Procedures involving larynx, pharynx, Sedation/Analgesia (Unlabeled)
or bronchial tree (muscle relaxants required); Gastroesophageal reflux; Hepatic dys- IV (Adults): 200– 750 mcg (0.2– 0.75 mg)/kg over 2– 3 min initially, followed by
function; History of alcohol abuse; Cerebral trauma; Intracerebral mass or hemor- 5– 20 mcg (0.005– 0.02 mg)/kg/min as an infusion.
⫽ Canadian drug name. ⫽ Genetic Implication. CAPITALS indicate life-threatening, underlines indicate most frequent. Strikethrough ⫽ Discontinued.
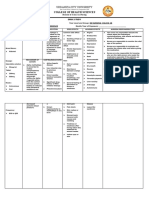
Name /bks_53161_deglins_md_disk/ketamine 02/14/2014 03:50PM Plate # 0-Composite pg 2 # 2
2 sequence induction technique is indicated. More rapid administration may cause
respiratory depression, apnea, and hypertension. Do not exceed 0.5 mg/kg/min.
IV (Children): 5– 20 mcg/kg/min. ● Continuous Infusion: Diluent: Dilute 10 mL of 50 mg/mL concentration or 5 PDF Page #2
IM (Adults): 2– 4 mg/kg initially, then 5– 20 mcg (0.005– 0.02 mg)/kg/min as an mL of 100 mg/mL concentration with 500 mL of 0.9% NaCl or D5W and mix well.
IV infusion. Concentration: 1 mg/mL. Dilution with 250 mL may be used if fluid restriction
is needed, for a maximum concentration of 2 mg/mL. Rate: Administer at a rate
NURSING IMPLICATIONS of 0.5 mg/kg/min for induction. Maintenance infusion may be administered at a
Assessment rate of 1– 2 mg/min or 0.1– 0.5 mg/min given concurrently with diazepam. Dose
● Assess level of consciousness frequently throughout therapy. Ketamine produces a must be titrated according to individual patient requirements. Tonic-clonic move-
dissociative state. The patient does not appear to be asleep and experiences a feel- ments during anesthesia do not indicate the need for more ketamine.
ing of dissociation from the environment. ● Y-Site Compatibility: albumin, amikacin, amiodarone, atropine, caffeine cit-
● Monitor BP, ECG, and respiratory status frequently throughout therapy. May cause rate, calcium gluconate, cefazolin, cefepime, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, cefurox-
hypertension and tachycardia. May cause increased CSF pressure and increased ime, chlorpromazine, clindamycin, clonidine, digoxin, diphenhydramine, dobu-
intraocular pressure. tamine, dopamine, epinephrine, gentamicin, haloperidol, hydrocortisone,
● Toxicity and Overdose: Respiratory depression or apnea may be treated with magnesium sulfate, meperidine, metoclopramide, metronidazole, midazolam,
mechanical ventilation or analeptics. milrinone, morphine, multivitamins, naloxone, oxytocin, pancuronium, penicillin
Potential Nursing Diagnoses G, piperacillin/tazobactam, potassium chloride, promethazine, propofol, raniti-
Risk for injury (Side Effects) dine, sufentanil, tobramycin, vancomicin.
Disturbed sensory perception (Adverse Reactions) ● Y-Site Incompatibility: acyclovir, ampicillin, furosemide, heparin, insulin,
meropenem, phenytoin, potassium phosphates, sodium bicarbonate, trimetho-
Implementation prim/sulfamethoxazole.
● Do not confuse Ketalar (ketamine) with ketorolac.
● Administer on an empty stomach to prevent vomiting and aspiration. Patient/Family Teaching
● May be administered concurrently with a drying agent (atropine, scopolamine); ● Psychomotor impairment may last for 24 hr after anesthesia. Caution patient to
ketamine increases salivary and tracheobronchial mucous gland secretions. Atro- avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is
pine may also increase the incidence of unpleasant dreams. known.
● Patients may experience a state of confusion (emergence delirium) during recov- ● Advise patient to avoid alcohol or other CNS depressants for 24 hr after anesthesia.
ery from ketamine. Administering a benzodiazepine and minimizing verbal, tac-
tile, and visual stimulation may prevent emergence delirium. Severe emergence
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
● Sense of dissociation and general anesthesia without muscle relaxation.
delirium may be treated with short- or ultra-short-acting barbiturates.
● PO: Use 100 mg/mL IV solution and mix appropriate dose in 0.2– 0.3 mL/kg of Why was this drug prescribed for your patient?
cola or other beverage.
IV Administration
● Direct IV: Diluent: Dilute 100 mg/mL concentration with equal parts of sterile
water for injection, 0.9% NaCl, or D5W. Concentration: Maximum concentra-
tion for slow IV push 50 mg/mL. Rate: Administer over 60 sec unless a rapid-
䉷 2015 F.A. Davis Company
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Name of Drugs Indications Contraindications ADVERSE Reactions To Watch Out For Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsDokument2 SeitenName of Drugs Indications Contraindications ADVERSE Reactions To Watch Out For Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsAlexis SilvestreNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabetalolDokument3 SeitenLabetalolTri Purma Sari50% (2)
- A Random-Walk-Down-Wall-Street-Malkiel-En-2834 PDFDokument5 SeitenA Random-Walk-Down-Wall-Street-Malkiel-En-2834 PDFTim100% (1)
- 8 Propofol Drug StudyDokument4 Seiten8 Propofol Drug Studyshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- KetamineDokument1 SeiteKetamineLorraine80% (5)
- Susan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Dokument297 SeitenSusan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Marelin Hernández SaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparative Look at Jamaican Creole and Guyanese CreoleDokument18 SeitenA Comparative Look at Jamaican Creole and Guyanese CreoleShivana Allen100% (3)
- APFC Accountancy Basic Study Material For APFCEPFO ExamDokument3 SeitenAPFC Accountancy Basic Study Material For APFCEPFO ExamIliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- BupivacaineDokument6 SeitenBupivacaineAngelica Dalit MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Card PropofolDokument1 SeiteDrug Card PropofolBenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyDimple calloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fentanyl Dosage and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument3 SeitenFentanyl Dosage and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDavid Villanueva67% (3)
- DocetaxelDokument4 SeitenDocetaxelfnurdiansah002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyAnne Lorraine RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Cautiously in: History of suicide attempts or substance abuseDokument2 SeitenUse Cautiously in: History of suicide attempts or substance abuseidullrufaidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diazepam Drug Study: Effects, Uses, InteractionsDokument4 SeitenDiazepam Drug Study: Effects, Uses, InteractionsCheezy BreadNoch keine Bewertungen
- इंटरनेट मानक का उपयोगDokument16 Seitenइंटरनेट मानक का उपयोगUdit Kumar SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study RLE PDFDokument15 SeitenDrug Study RLE PDFCzarina Isabela Tuazon100% (1)
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Dokument2 SeitenNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MidazolamDokument2 SeitenMidazolamDesireemae Riosa-Candaroma100% (6)
- Ketorolac and NalbuphineDokument4 SeitenKetorolac and NalbuphineMaureen Campos-PineraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LorazepamDokument3 SeitenLorazepamgovind_soni_15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Epinephrine Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenEpinephrine Drug StudyAbigail De Leon80% (5)
- Yoga Practice Guide: DR - Abhishek VermaDokument26 SeitenYoga Practice Guide: DR - Abhishek VermaAmarendra Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - MidazolamDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORDokument7 SeitenORMay EvelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midazolam Drug Study SaclotDokument1 SeiteMidazolam Drug Study SaclotMaybelle Cababat Saclot100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Dokument2 SeitenDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Responsibilities for Propofol AdministrationDokument2 SeitenNursing Responsibilities for Propofol AdministrationJoevence Gazo Cuaresma100% (2)
- Fentanyl Citrate Medication Indication Side Effects NursingDokument2 SeitenFentanyl Citrate Medication Indication Side Effects Nursing5S CASTILLEJO Danica M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Karnataka Email Id DataDokument5.173 SeitenKarnataka Email Id DataSumalatha Venkataswamy100% (6)
- DRUG STUDY: MORPHINE SULFATE AND ITS USES, MECHANISM OF ACTION, EFFECTS, AND INTERACTIONSDokument8 SeitenDRUG STUDY: MORPHINE SULFATE AND ITS USES, MECHANISM OF ACTION, EFFECTS, AND INTERACTIONSShara Lailanie A. Azis100% (1)
- Drug Study - MidazolamDokument8 SeitenDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan Presentation ON Air Conditioner: Presented By-V.Sowmith REG NO-2121BM010112Dokument16 SeitenBusiness Plan Presentation ON Air Conditioner: Presented By-V.Sowmith REG NO-2121BM010112Kavya Madanu100% (1)
- 9 PropofolDokument2 Seiten9 PropofolAbdelhafiz Susmiran100% (3)
- OfloxacinDokument2 SeitenOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug Studyunkown userNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUPIVACAINEDokument1 SeiteBUPIVACAINEVoid Less0% (2)
- Dextrose Injection Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument2 SeitenDextrose Injection Nursing ResponsibilitiesSalwa ZeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PropofolDokument3 SeitenPropofolamelwd100% (1)
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificDokument1 SeiteVii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificnuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug Studyw dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symphonological Bioethical Theory: Gladys L. Husted and James H. HustedDokument13 SeitenSymphonological Bioethical Theory: Gladys L. Husted and James H. HustedYuvi Rociandel Luardo100% (1)
- DexmedetomidineDokument2 SeitenDexmedetomidineapt48 ukwmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- KETAMINEDokument2 SeitenKETAMINERPh Krishna Chandra JagritNoch keine Bewertungen
- PropofolDokument2 SeitenPropofolFarkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDAZOLAM DRUG STUDYDokument5 SeitenMIDAZOLAM DRUG STUDYShara Lailanie A. AzisNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDokument3 SeitenDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDokument2 SeitenGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ONDANSETRONDokument1 SeiteONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDokument3 SeitenDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atracurium BesylateDokument4 SeitenAtracurium BesylateStill DollNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atropine Drug ProfileDokument2 SeitenAtropine Drug ProfileShahpmdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Tabulation orDokument23 SeitenDrug Tabulation orChin Villanueva UlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDokument1 SeiteDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZonisamideDokument2 SeitenZonisamideRo-anne AkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeostigmineDokument4 SeitenNeostigmineDonna Lyn B. DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - VancomycinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - VancomycinKhatlen BagaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- DORMICUMDokument1 SeiteDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDokument1 SeiteMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMarina Wasem NetzlaffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fentanyl SublimazeDokument2 SeitenFentanyl SublimazeENoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyJan Lianne BernalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDokument3 SeitenDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esmolol adverse reactions and nursing implicationsDokument3 SeitenEsmolol adverse reactions and nursing implicationsTri Purma SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- AirwaydrugsDokument5 SeitenAirwaydrugshevere6273Noch keine Bewertungen
- AtropineDokument3 SeitenAtropinegovind_soni_15Noch keine Bewertungen
- EpinephrineDokument4 SeitenEpinephrinegovind_soni_15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Life of a VoyageurDokument8 SeitenLife of a VoyageurBruce GuthrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Electronic MaterialsDokument10 SeitenJournal of Electronic MaterialsSanjib BaglariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questionnaire For New Omani QAQC Staff - DLQ DeptDokument7 SeitenPractice Questionnaire For New Omani QAQC Staff - DLQ DeptSuliman Al RuheiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspartame Literature ReviewDokument10 SeitenAspartame Literature Reviewapi-272556824Noch keine Bewertungen
- Public Policy For Nigerian EnviromentDokument11 SeitenPublic Policy For Nigerian EnviromentAbishai Auta GaiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Man of Sorrows Wednesday of Holy Week Divine IntimacyDokument5 SeitenThe Man of Sorrows Wednesday of Holy Week Divine IntimacyTerri ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eric Bennett - Workshops of Empire - Stegner, Engle, and American Creative Writing During The Cold War (2015, University of Iowa Press) - Libgen - LiDokument231 SeitenEric Bennett - Workshops of Empire - Stegner, Engle, and American Creative Writing During The Cold War (2015, University of Iowa Press) - Libgen - LiÖzge FındıkNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIN 1050 - Final ExamDokument6 SeitenFIN 1050 - Final ExamKathi100% (1)
- VT JCXDokument35 SeitenVT JCXAkshay WingriderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6-Modul - PTI412 - IoT-1-2020Dokument17 Seiten6-Modul - PTI412 - IoT-1-202020200801015 Joko SulistyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krittika Takiar PDFDokument2 SeitenKrittika Takiar PDFSudhakar TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Member OrientationDokument41 SeitenNew Member OrientationM.NASIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meesho FDokument75 SeitenMeesho FAyan khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionDokument2 SeitenEng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionNiña RasonableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Suisse AI ResearchDokument38 SeitenCredit Suisse AI ResearchGianca DevinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FACS113 MineralswebDokument51 SeitenFACS113 MineralswebMohammad Amjad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of Indiana, County of Marion, SS: Probable Cause AffidavitDokument1 SeiteState of Indiana, County of Marion, SS: Probable Cause AffidavitIndiana Public Media NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDIA'S DEFENCE FORCESDokument3 SeitenINDIA'S DEFENCE FORCESJanardhan ChakliNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 2 2008Dokument7 SeitenRTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 2 2008iwan93Noch keine Bewertungen
- All EscortsDokument8 SeitenAll Escortsvicky19937Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A Cover Letter For A Training ProgramDokument4 SeitenHow To Write A Cover Letter For A Training Programgyv0vipinem3100% (2)