Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 1
Hochgeladen von
Abby Kimball0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
24 Ansichten1 SeiteApproaching the challenge of quantitatively analyzing multiplexed
immunohistochemistry data.
Originaltitel
Kimball et al 2019, Figure 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenApproaching the challenge of quantitatively analyzing multiplexed
immunohistochemistry data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
24 Ansichten1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 1
Hochgeladen von
Abby KimballApproaching the challenge of quantitatively analyzing multiplexed
immunohistochemistry data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
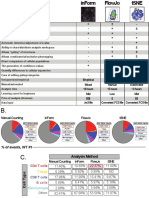
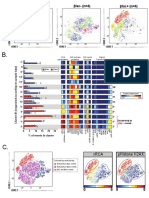
A.
Flow or Mass Cytometry Multiplexed IHC
(Vectra, Codex, IMC)
Basic principle Analysis of dissociated tissue Analysis of intact tissue as
as a single-cell suspension cross-sections on a slide
Field of analysis Entire dissociated tissue Tissue cross-section(s)
Cell identification Single-cell suspension. Cells in close physical proximity.
Unit of analysis is individual cell. Cell identification requires cell
segmentation.
Cell loss Significant, due to tissue No cell loss
processing
Spatial context Destroyed Preserved
Tissue architecture Destroyed Preserved
Rate of event collection Rapid Slow
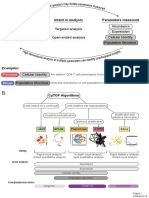
B.
Data Preprocessing
1. Experimental Design, 2. Region Selection 3. Spectral Unmixing 4. Cell Segmentation
Staining & Imaging & Visualization
•Region selection •Segment cells (inForm®)
•Experimental question in Phenochart™ •Spectrally unmix (inForm®)
•Panel design & optimization •Region scan (≥20x) •Assign pseudocolors
•Whole slide scan (4x) •Verify staining
Continue to:
•phenotype in inForm®
•convert .txt file to .fcs
and phenotype using
other methods
5. Cell Phenotyping
Cell phenotyping options:
x,y coordinates
A) Manual inspection B) inForm® C) FlowJo® D) tSNE E) PhenoGraph
Confidence %
Input: inForm® spectrally Input: inForm® defined Input: inForm® defined cell segmentation
unmixed composite images cell segmentation .txt file export, converted to .fcs file
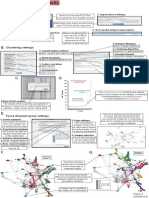
6. mIHC Specific Analysis
Manual Inspection Analysis using FlowJo Analysis in phenoptrReports
•Cell morphology •Structural association •Nearest neighbors
•Cell behavior •Protein expression •Cellular interactions
•Tissue architecture
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 5Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 5Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 6Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 6Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 8Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 8Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 4Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 4Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Tobin Et Al 2019, Figure 1Dokument1 SeiteTobin Et Al 2019, Figure 1Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 7Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 7Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 4Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 4Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Tobin Et Al 2019, Figure 2Dokument1 SeiteTobin Et Al 2019, Figure 2Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 2Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 2Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Oko Et Al 2019, Figure 8Dokument1 SeiteOko Et Al 2019, Figure 8Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Tobin Et Al, 2019 Figure 3Dokument1 SeiteTobin Et Al, 2019 Figure 3Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 1Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 1Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 3Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 3Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Neuwelt Et Al, Figure 2Dokument1 SeiteNeuwelt Et Al, Figure 2Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Graph Features:: Events Sampled Per File: 9,141 Minimum Cluster Size: 5% Group Assignment: CorrectDokument1 SeiteGraph Features:: Events Sampled Per File: 9,141 Minimum Cluster Size: 5% Group Assignment: CorrectAbby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 10Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 10Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Kimball Et Al 2019, Figure 1Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2019, Figure 1Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 3Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 3Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 8Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 8Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 9Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 9Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 4Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 4Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 5Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 5Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 2Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 2Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimball Et Al 2018, Figure 7Dokument1 SeiteKimball Et Al 2018, Figure 7Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Bullock Et Al 2018, Supplemental Figure 5Dokument1 SeiteBullock Et Al 2018, Supplemental Figure 5Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bullock Et Al 2018, Figure 6Dokument1 SeiteBullock Et Al 2018, Figure 6Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Berger Et Al 2019, Figure 2Dokument1 SeiteBerger Et Al 2019, Figure 2Abby KimballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances: Development Therapeutic Monoclonal AntibodiesDokument11 SeitenAdvances: Development Therapeutic Monoclonal AntibodiesVinod YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Mentoring (Mod 6)Dokument26 SeitenMentoring (Mod 6)Mayrigen DominguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics, Lecture 2, Purines and Pyrimidines (Lecture Notes)Dokument16 SeitenGenetics, Lecture 2, Purines and Pyrimidines (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trinity Continuum - Æon - Æon Æxpansion (2019) PDFDokument111 SeitenTrinity Continuum - Æon - Æon Æxpansion (2019) PDFMichel M. Silva Pedó88% (8)
- B.SC - BiochemistryDokument39 SeitenB.SC - BiochemistryJaseena AlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erns & YoungDokument37 SeitenErns & YoungRadhika BhattadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA and MSC - GeneralDokument6 SeitenMA and MSC - Generalクマー ヴィーンNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRADokument1 SeiteSRADee ZeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Courses (Neuroscience and Pharmacology) (PCOL)Dokument2 SeitenPharmacology Courses (Neuroscience and Pharmacology) (PCOL)Alec AnonNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) : Hafiz.M.Zeeshan - Raza Research Associate - HEC - NRPUDokument22 SeitenEuropean Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) : Hafiz.M.Zeeshan - Raza Research Associate - HEC - NRPUIshan SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1: "Cool But Fearful" Cell MembraneDokument23 SeitenGeneral Biology 1: "Cool But Fearful" Cell MembraneMikhael Oira100% (1)
- DNA Profiling ReportDokument9 SeitenDNA Profiling Reportbroleo100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Theory, Part B - Final-InADokument72 SeitenTheory, Part B - Final-InAHanifah Ainun AryanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synaptic TransmissionDokument35 SeitenSynaptic TransmissiondehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Reading 2Dokument43 SeitenPaper Reading 2anyou.5487.md07Noch keine Bewertungen
- PESTLE Analysis of Pharma SectorDokument5 SeitenPESTLE Analysis of Pharma Sectorshambhavi jhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Messengers Camp CGMPDokument42 SeitenSecond Messengers Camp CGMPMirza Shaharyar BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Insight Into The Role of Exosomes in VitiligoDokument18 SeitenNew Insight Into The Role of Exosomes in VitiligoAndrea AguirrePerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms of Cell Death NotesDokument30 SeitenMechanisms of Cell Death NotesPatel AnkurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recording Forms g1 g4 g7 ImmunizationDokument4 SeitenRecording Forms g1 g4 g7 ImmunizationGirlie Harical GangawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division SEDokument6 SeitenCell Division SERicky DunlapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of COVID VaccinesDokument1 SeiteTypes of COVID VaccinesEmre ÇELİKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein SequenceDokument36 SeitenProtein SequenceHarshitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascorbate and Glutathione: Keeping Active Oxygen Under ControlDokument31 SeitenAscorbate and Glutathione: Keeping Active Oxygen Under ControlPhilip Blair OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Introduction To Molecular Medicine PDFDokument11 Seiten11 Introduction To Molecular Medicine PDFErlinda NavalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise MetabolismDokument1 SeiteExercise MetabolismLew MingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsDokument2 SeitenMaklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsYusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Original Pdfbiology Exploring The Diversity of Life 4th 1 3 by Peter Russell PDFDokument41 SeitenOriginal Pdfbiology Exploring The Diversity of Life 4th 1 3 by Peter Russell PDFbonnie.eaton513100% (36)
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSEDokument3 SeitenSummary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSEAiko KameishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Dokument5 SeitenBio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Megadirectioner 21Noch keine Bewertungen