Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Problem 3.37 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Kauê BrittoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Problem 3.37 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Kauê BrittoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Problem 3.
37 [Difficulty: 4]
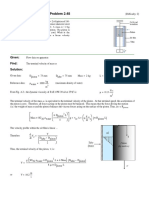
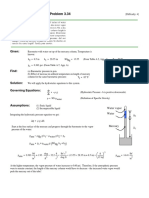
Given: Sealed tank is partially filled with water. Water drains slowly from the
tank until the system attains equilibrium. U-tube manometer is connected
to the tank as shown. (Meriam blue in manometer)
L = 3⋅ m D1 = 2.5⋅ m D2 = 0.7⋅ m d = 0.2⋅ m SGoil = 1.75 (From Table A.2, App. A)
Find: The manometer deflection, l, under equilibrium conditions
Solution: We will apply the hydrostatics equations to this system.
Governing Equations: dp
= ρ⋅ g (Hydrostatic Pressure - h is positive downwards)
dh
p ⋅ V = M⋅ R⋅ T (Ideal gas equation of state)
ρ = SG⋅ ρwater (Definition of Specific Gravity)
Assumptions: (1) Static liquid
(2) Incompressible liquid patm
(3) Air in tank behaves ideally p0
Integrating the hydrostatic pressure equation we get:
L
Δp = ρ⋅ g⋅ Δh D1 d
H
l
To determine the surface pressure po D2 c
under equilibrium conditions
we assume that the air expands at constant temperature: d
pa⋅ Va
=
M⋅ R⋅ Ta
Thus, po =
Va
⋅ pa =
(
L − D1 ⋅ A
⋅p
)
po⋅ Vo M⋅ R⋅ To Vo ( L − H) ⋅ A a
Simplifying: po =
L − D1( ⋅p
) Now under equilibrium conditions: po + ρwater⋅ g⋅ H = pa Combining these expressions:
( L − H) a
( L − D 1) ⋅ p
( )
2
( L − H) a + ρwater⋅ g⋅ H = pa Upon rearranging: ρwater⋅ g⋅ H − pa + ρwater⋅ g⋅ L ⋅ H + D1⋅ pa = 0
Now we apply the quadratic formula to solve for H:
kg m 3 Pa
a = ρwater⋅ g a = 999⋅ × 9.81⋅ a = 9.8 × 10 ⋅
3 2 m
m s
⎛ × 9.81⋅ × 3⋅ m⎟⎞
( )
5 N kg m 5
b = − pa + ρwater⋅ g⋅ L b = −⎜ 1.013 × 10 ⋅ + 999⋅ b = −1.307 × 10 Pa
2 3 2
⎝ m m s ⎠
5 N 5
c = D1⋅ pa c = 2.5⋅ m × 1.013 × 10 ⋅ c = 2.532 × 10 ⋅ Pa⋅ m
2
m
2 (
− −1.307 × 10 ⋅ Pa +
5 ) (−1.307 × 105⋅ Pa)2 − 4 × 9.8 × 103⋅ Pa × 2.532 × 105⋅ Pa⋅ m
−b + b − 4⋅ a⋅ c m
Hupper = Hupper =
2⋅ a 3 Pa
2 × 9.8 × 10 ⋅
m
Hupper = 10.985 m
2 (
− −1.307 × 10 ⋅ Pa −
5 ) (−1.307 × 105⋅ Pa)2 − 4 × 9.8 × 103⋅ Pa × 2.532 × 105⋅ Pa⋅ m
−b − b − 4⋅ a⋅ c m
Hlower = Hlower =
2⋅ a 3 Pa
2 × 9.8 × 10 ⋅
m
Hlower = 2.352 m
Since H can not be greater than 3 m (otherwise the tank would overflow!), we must select the lower value for H: H = 2.352 m
( 3⋅ m − 2.5⋅ m) 5 4
Solving for the pressure inside the tank: po = × 1.013 × 10 ⋅ Pa po = 7.816 × 10 Pa
( 3⋅ m − 2.352⋅ m)
po + ρwater⋅ g⋅ ⎛⎜ H − D2 + d − ⎟ + ρoil⋅ g⋅ l = pa
l⎞
Applying the hydrostatic pressure equation to the manometer:
⎝ 2⎠
⎛ pa − po ⎞ 1
Solving for the manometer deflection: l=⎜ − H + D2 − d⎟ ⋅
⎝ ρwater⋅ g ⎠ SGoil − 1
2
⎡ 3 2 ⎤
l = ⎢⎛⎜ 1.013 × 10 ⋅ − 7.816 × 10 ⋅ ⎞⎟ ×
kg⋅ m
− 2.352⋅ m + 0.7⋅ m − 0.2⋅ m⎥ ⋅
5 N 4 N 1 m 1 s 1
⋅ × ⋅ ×
⎢ 2 2 999 kg 9.81 m 2 ⎥ 1 l = 0.407 m
⎣⎝ m m ⎠ N⋅ s ⎦ 1.75 −
2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cap. 03Dokument165 SeitenCap. 03lucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.35 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.35 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Solutions (Global Edition) : Sketch The Band DiagramDokument8 SeitenChapter 10 Solutions (Global Edition) : Sketch The Band Diagram성민김Noch keine Bewertungen
- Potter Mechanics of Fluids Chap 2 SolManDokument15 SeitenPotter Mechanics of Fluids Chap 2 SolManJen MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW1 Solution PDFDokument6 SeitenHW1 Solution PDFZuhair AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.62 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.62 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.31 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.31 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.26 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.26 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 6.54Dokument1 SeiteProblem 6.54Matheus SantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Fluids 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualDokument35 SeitenMechanics of Fluids 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manualleroyweavervpgnrf100% (18)
- Problem 3.58 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.58 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Section A - Mathcad SolutionsDokument55 SeitenChapter 3 - Section A - Mathcad Solutionsjames.HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fox and Mcdonalds Introduction To Fluid Mechanics 8th Edition Pritchard Solutions Manual 2Dokument2 SeitenFox and Mcdonalds Introduction To Fluid Mechanics 8th Edition Pritchard Solutions Manual 2dextrermachete4amgqgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7Dokument14 SeitenSolutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7SUNIL KUMAR JANGRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Section A - Mathcad Solutions: Proprietary MaterialDokument8 SeitenChapter 1 - Section A - Mathcad Solutions: Proprietary Materialammar05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.43 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.43 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualDokument35 SeitenMechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manualleroyweavervpgnrf100% (18)
- Dwnload Full Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual PDFDokument35 SeitenDwnload Full Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual PDFtatting.itacistpjkl100% (10)
- Cap 03 Mecanica Dos Fluidos Fox Mcdonald 8a Edicao SolutionDokument166 SeitenCap 03 Mecanica Dos Fluidos Fox Mcdonald 8a Edicao SolutionAlice LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.17Dokument1 SeiteFox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.17Patricia RodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucion Ejercicio 8.163 (Mecanica de Fluidos)Dokument2 SeitenSolucion Ejercicio 8.163 (Mecanica de Fluidos)Jairo RondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEL FormelsamlungDokument2 SeitenMEL FormelsamlungLuka VartušekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.55: Given: Find: Assumptions: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.55: Given: Find: Assumptions: SolutionKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robert 4Dokument436 SeitenRobert 4로헬Noch keine Bewertungen
- PEA's: B.E. Model Entrance ExamDokument10 SeitenPEA's: B.E. Model Entrance ExamajenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.29 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.29 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.44 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.44 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualDokument25 SeitenMechanics of Fluids Si Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions ManualJodiAguilareibd100% (49)
- Problem 1.20 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.20 PDFGabriel CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.5: Given: Find: SolutionDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.5: Given: Find: SolutionMatheus SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Solution: C F L DDokument27 SeitenData Solution: C F L DJMVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrostatic PressureDokument5 SeitenHydrostatic PressureEj BeatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02Dokument22 SeitenChapter 02HERNAN EDUARDO CHAVEZ SANDOVALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Solution: C F L D KDokument27 SeitenData Solution: C F L D KTech ManagerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correction TD 2 Fluids MechanicsDokument3 SeitenCorrection TD 2 Fluids Mechanicsno NameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.16Dokument1 SeiteFox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.16Patricia RodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.34 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.34 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chương 6: 6.1. The Eye Can Be Treated, To A First Approximation, As A Thin - x0002 - Walled ElasticDokument39 SeitenChương 6: 6.1. The Eye Can Be Treated, To A First Approximation, As A Thin - x0002 - Walled ElasticTran TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Largest Area of Space Is at The Center Where There Are 23 TubesDokument2 SeitenLargest Area of Space Is at The Center Where There Are 23 TubesRenzel ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad - Cracked Rect Section Deflection Analysis of Continuous BeamDokument6 SeitenMathcad - Cracked Rect Section Deflection Analysis of Continuous BeamSteven Raynaldo HNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1034purl Fluid-Mechanics TYSDokument13 Seiten1034purl Fluid-Mechanics TYSVivek RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.49 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 2.49 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad - ViscosidadDokument1 SeiteMathcad - ViscosidadCARMEN HENAONoch keine Bewertungen
- Fox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.12Dokument2 SeitenFox Fluid Mechanics 8th Solved Problem 3.12Patricia RodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fick's Law Sample ProblemsDokument7 SeitenFick's Law Sample ProblemsAj SedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.73: Given: Find: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.73: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 4.158Dokument2 SeitenProblem 4.158문jmtNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Dimensions 2. B. Unit Weight and LoadsDokument4 SeitenA. Dimensions 2. B. Unit Weight and LoadsMike GocotanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolated Footing DesignDokument15 SeitenIsolated Footing DesignAzzirrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap. 08Dokument286 SeitenCap. 08Ent Qa NepalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 206 Tutorial 7 SolutionsDokument14 SeitenCH 206 Tutorial 7 SolutionspushkalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015Dokument10 Seiten2015ZaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fox and Mcdonalds Introduction To Fluid Mechanics 8th Edition Pritchard Solutions Manual 2Dokument3 SeitenFox and Mcdonalds Introduction To Fluid Mechanics 8th Edition Pritchard Solutions Manual 2finificcodille6d3h100% (22)
- Solution: Page 9 of 21Dokument13 SeitenSolution: Page 9 of 21Khan Mohd TanfeesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucionario Fox Problem 2.78Dokument1 SeiteSolucionario Fox Problem 2.78Alessandro PintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2 TensorsDokument4 SeitenP2 TensorsSebastian hanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT6 013S09 Eqn Quiz1 PDFDokument3 SeitenMIT6 013S09 Eqn Quiz1 PDFJohan ArcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beta Fun.Dokument12 SeitenBeta Fun.prithviraj gavhaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 1 B 1 C 0 2 4 6 X y y y Y: Streamline PlotDokument1 SeiteA 1 B 1 C 0 2 4 6 X y y y Y: Streamline PlotKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.49: Given: Find: AssumptionsDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.49: Given: Find: AssumptionsKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.36 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.36 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.16 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 2.16 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.30 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.30 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.28 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 2.28 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.27: Given: Find: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.27: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.32 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.32 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.25 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.25 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.80: Open-Ended Problem StatementDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.80: Open-Ended Problem StatementKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.27 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.27 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.11 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 2.11 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.44 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.44 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.22 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 2.22 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.48: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.28 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.28 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.27: Given: Find: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.27: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.49 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.49 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.49 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 2.49 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.42 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.42 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.43 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.43 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.57 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.57 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.44 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 3.44 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.59 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.59 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.22 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.22 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 3.31 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 3.31 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.77 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 2.77 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1.19 PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem 1.19 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 2.68 PDFDokument2 SeitenProblem 2.68 PDFKauê BrittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BVP NotesDokument104 SeitenBVP NotesGEORGE FRIDERIC HANDELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Kinetic Theory of GasesDokument16 SeitenPhy Kinetic Theory of GasesSachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial - Transport Eqn, EosDokument15 SeitenTutorial - Transport Eqn, Eossiti azilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9Dokument21 SeitenLecture 9song perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Einstein-Hilbert ActionDokument5 SeitenEinstein-Hilbert Actionrr1819Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Soal Radiasi Dan KonveksiDokument5 SeitenContoh Soal Radiasi Dan Konveksi038 - ahmad sidikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 5Dokument7 SeitenSet 5Gil Diane AlcontinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYC10001 Physics 1 Advanced: Where We AreDokument15 SeitenPHYC10001 Physics 1 Advanced: Where We AreChung Chee YuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo MCQDokument23 SeitenThermo MCQAnmol ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principal Strains and InvariantsDokument8 SeitenPrincipal Strains and InvariantsLong Đinh HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions SolutionsDokument12 SeitenSec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions Solutionsjiajing shenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 7Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 7Virendra SheoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 8 Applications of Vector CalculusDokument12 SeitenTopic 8 Applications of Vector CalculusAhtisham ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Transfer CoefficientDokument24 SeitenMass Transfer Coefficientxaishuang9791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Mode PDFDokument38 SeitenNormal Mode PDFBiswajit BhowmickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer 03 One Dimensional Steady ConductionDokument41 SeitenHeat Transfer 03 One Dimensional Steady ConductionAhmad Alifian LirajabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE 311 Problem Set With Answer KeyDokument5 SeitenChE 311 Problem Set With Answer KeyGian BanaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH142 General Physics II Class A: Ch. 33: RelativityDokument29 SeitenPH142 General Physics II Class A: Ch. 33: Relativity우현성Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Tips For Tuning of PID Loops: by Steve MackayDokument21 Seiten10 Tips For Tuning of PID Loops: by Steve Mackayali_gudarzi2249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3 - Volumetric Properties of FluidDokument38 SeitenChap 3 - Volumetric Properties of FluidHonestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alilean, Special & General Relativity: Física Del Cosmos: Lecture IDokument24 SeitenAlilean, Special & General Relativity: Física Del Cosmos: Lecture IGuillermo Martínez RamónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4: One-Dimensional, Steady State Heat Conduction With Heat GenerationDokument19 SeitenLesson 4: One-Dimensional, Steady State Heat Conduction With Heat Generationmehaksinghgill098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isye 6416: Computational Statistics Spring 2023: Prof. Yao XieDokument44 SeitenIsye 6416: Computational Statistics Spring 2023: Prof. Yao XieVikash MovvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Soal Energi Kinetik GasDokument13 SeitenLatihan Soal Energi Kinetik GasDevita Mira Lestari100% (2)
- Quantum Roundabout ProgrammeDokument28 SeitenQuantum Roundabout Programmeapi-196256157Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matrices and Determinant NotesDokument17 SeitenMatrices and Determinant NotesKeshav GGSUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Description: Physics Semester I: Course Instructor: Dr. Rajneesh AtreDokument12 SeitenCourse Description: Physics Semester I: Course Instructor: Dr. Rajneesh AtreAnurag SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Numbers I by Aakash Jee NotesDokument83 SeitenComplex Numbers I by Aakash Jee NotesOnly StudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Robotics - Model PapersDokument3 SeitenIndustrial Robotics - Model PapersraminenieNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceVon EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyVon EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesVon EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2193)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayVon EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (125)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldVon EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (64)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidVon EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1396)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowVon EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (49)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldVon EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (60)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldVon EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessVon EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterVon EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (410)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Von EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (157)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingVon EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessVon EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (57)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeVon EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceVon EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseVon EverandThe Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itVon EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (13)
- Transform Your Life And Save The World: Through The Dreamed Of Arrival Of The Rehabilitating Biological Explanation Of The Human ConditionVon EverandTransform Your Life And Save The World: Through The Dreamed Of Arrival Of The Rehabilitating Biological Explanation Of The Human ConditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeVon EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNoch keine Bewertungen