Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
2018 Physics (1) (Sample Past Paper) PDF
Hochgeladen von
AkuOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2018 Physics (1) (Sample Past Paper) PDF
Hochgeladen von
AkuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
USEFUL INFORMATION:
Acceleration due to gravity, 𝑔𝑔 ≈ 9.80 m s −2
Avogadro’s number, 𝑁𝑁𝐴𝐴 ≈ 6.022 × 1023 particles⁄mol
Universal gas constant, 𝑅𝑅 ≈ 8.314 J K −1 mol−1
Gravitational constant, 𝐺𝐺 ≈ 6.673 × 10−11 N m2 kg −2
Coulomb constant, 𝑘𝑘 ≈ 8.99 × 109 N m2 C−2
Magnitude of charge of electron, 𝑒𝑒 ≈ 1.602 × 10−19 C
Mass of electron, 𝑚𝑚𝑒𝑒 ≈ 9.109 × 10−31 kg
Mass of proton, 𝑚𝑚𝑝𝑝 ≈ 1.673 × 10−27 kg
Mass of neutron, 𝑚𝑚𝑛𝑛 ≈ 1.675 × 10−27 kg
E
Speed of light, 𝑐𝑐 ≈ 2.998 × 108 m s −1
PL
Planck’s constant, ℎ ≈ 6.626 × 10−34 J s
Atomic mass unit, 𝑢𝑢 ≈ 1.661 × 10−27 kg
M
SA
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 2
1. A displacement vector with a magnitude of 20 m could have perpendicular
components with magnitudes of
A 20 m and 20 m
B 10 m and 10 m
C 12 m and 16 m
D 12 m and 80 m
E 16 m and 8m
2. What is the center of gravity of an object?
A the geometrical center of the object
B the point about which the total torque is zero
C the point at which the weight of the object may be considered to act
D the point through which gravity acts
E the intersection of the vertical symmetrical line and the horizontal
symmetrical line
E
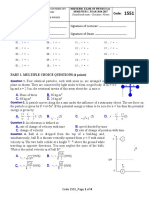
3. The following graph shows how the horizontal displacement of a car moving
on a flat ground changes with time for part of its journey.
PL
An improvised accelerometer, used to measure the acceleration of the car,
is made by sandwiching a rubber ring between the two glass plates and
S
introducing some coloured water insider the ring. The accelerometer is
subsequently fastened at the door of the car. Diagram D corresponds to
point X on the graph.
Which diagram shows the angle of water surface in the accelerometer at
point Y?
A B C D
E None of the above
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 3
4. An object starts from rest and falls freely for 40 m near the surface of a
planet. If the time of fall is 4 s, what is the magnitude of the acceleration
due to gravity on the planet?
A 0 m/s2
B 5.0 m/s2
C 10 m/s2
D 20 m/s2
E 40 m/s2
5. A motorist travelling at 10 ms-1 can bring his car to rest in a braking distance
of 10 m. In what distance could he bring the car to rest from a speed of 30
ms-1 using the same braking force?
A 17 m
B 30 m
C 52 m
D 90 m
E
E 98 m
PL
6. Newton’s third law concerns the forces of interaction between two bodies.
Which of the following statements relating to the third law is not correct?
A The two forces must be of the same type.
B
M
The two forces must act on different bodies.
C The two forces are always opposite in direction.
D The two forces are equal and opposite so the bodies are in
equilibrium.
SA
E None of the above.
7. In a Formula One race, Sebastian Vettel driving the Ferrari race car has to
make a pit-stop to re-fuel the petrol tank. After the re-fueling, he starts
from rest with a constant acceleration of 11.0 ms-2 and takes 3.5 s to enter
the main speedway from the pit area. At the instance Sebastian enters the
main speedway, another race car on the speedway, driven by Hamilton,
traveling at a constant velocity of 69.4 ms-1 passes Sebastian’s car.
What is the total time required for Sebastian’s car to catch up with Hamilton
from the time he completes the re-fueling? Assume that Sebastian
maintains a constant acceleration throughout this time.
A 5.62 s
B 9.12 s
C 12.6 s
D 16.1 s
E 18.2 s
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 4
8. Two satellites in space collide inelastically. What happens to the kinetic
energy and momentum?
kinetic energy momentum
A conserved conserved
B conserved reduced
C reduced conserved
D reduced reduced
E reduced increased
9. A cyclist is riding at a steady speed on a level road.
According to Newton’s third law of motion, what is equal and opposite to
the backward push of the back wheel on the road?
A the force exerted by the cyclist on the pedals
B the forward push of the road on the back wheel
C the tension in the cycle chain
E
D the total air resistance and friction force
E the force provided by the break pads on the wheels.
PL
10. What is meant by the weight of an object?
A the gravitational field acting on the object
B the gravitational force acting on the object
M
C the mass of the object multiplied by gravity
D the object’s mass multiplied by its acceleration
E the object’s mass multiplied by its velocity
SA
11. A fighter-bomber flies towards a target at a speed of 750 kmh-1. At a height
of 500 m above the ground, it releases a 150-kg bomb while diving at an
angle of 20° below the horizontal.
How far ahead of the target horizontally must the bomb be released?
A 173 m B 1013 m C 3013 m D 3813 m E 4813 m
12. A projectile will attain its largest height if it is fired at an angle of
A 0°
B 30°
C 45°
D 60°
E 90°
from the horizontal.
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 5
13. A roller coaster of mass m moves in a vertical circle of radius r. The roller
coaster will be up-ide-down when it is at the highest point of the circle.
At what minimum speed v must the roller coaster be travelling at the
bottom of the circle so that the ride will be safe?
A rg
B 2rg
E
C 3rg
D 4rg
PL
E 5rg
M
14. A ball of mass 200 g is projected up a smooth inclined plane of length
0.50 m, at an angle 30° above the horizontal, with an initial speed of
2.5 ms-1. The ball subsequently leaves the other end of the plane and
A
proceeds with a projectile motion.
Assuming that the air resistance is negligible, what is the minimum of the
kinetic energy for the whole flight?
A 0J
B 0.10 J
C 0.13 J
D 0.47 J
E 0.62 J
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 6
15. A model car is released from rest at a height h on a frictionless track.
The car goes around the loop of diameter D without dropping from the track.
What is the minimum possible value of the initial height h required for the
car to remain on the track while going around the loop?
E
5D
A
4
3D
PL
B
2
C 2D
5D
D
2
M
5D
E
3
SA
16. A lead pellet is shot vertically upwards into a clay block that is stationary at
the moment of impact but is able to rise freely after the impact.
The pellet hits the block with an initial velocity of 200 ms-1. It embeds itself
in the block and does not emerge.
How high above its initial position will the block
rise?
A 5.1 m
B 5.6 m
C 10 m
D 14 m
E 22 m
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 7
17. A car mass of 1.2 × 103 kg travels along a horizontal road at a speed of
10 ms-1. It then accelerate at 0.20 ms-2. At the time it begins to accelerate,
the total resistive force acting on the car is 160 N.
What total output is developed by the car as it begins the acceleration?
A 0.80 kW
B 1.6 kW
C 2.4 kW
D 4.0 kW
E 5.6 kW
18. A snooker ball of mass m travels at a speed v towards the side of a snooker
table. The ball strikes the side of the table at an angle of 30° as shown. The
time of contact between the ball and the side is ∆t . What is the expression
for the average force acting on the ball?
E
M
Plan View
SA
mv
A
∆t
mv × cos 30 o
B
∆t
2mv × cos 30 o
C
∆t
2mv × csc 30 o
D
∆t
2mv × sin 30 o
E
∆t
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 8
19. The figure below shows forces acting on a piece of square cardboard of
negligible mass on a horizontal plane. The cardboard has a length of 5.0 cm
on each side.
E
Which of the following statements is possibly true?
A The cardboard is not in equilibrium.
PL
B The cardboard is in rotational equilibrium.
C The cardboard is not in translational equilibrium.
D The cardboard will rotate in an anticlockwise direction.
E The cardboard will undergo linear acceleration.
M
20. Assuming heat capacity of a 10 g of water to be 42 J⁄K, heat required to
raise its temperature from 25 °C to 35 °C would be
SA
A 42 J
B 420 J
C 4200 J
D 42000 J
E None of above
21. When the pressure of an ideal gas is increased at constant volume, the
average kinetic energy of the gas molecules
A may either increase or decrease, depending on whether or not the
process is carried out adiabatically.
B may or may not change, but insufficient information is given to make
such a determination.
C does not change.
D increases.
E decreases.
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 9
22. One junction X of a thermocouple is placed in melting ice at 273 K and the
other junction Y in steam at 373 K. The e.m.f. measured is 2.0 mV.
Junction Y is then transferred to a bath at a temperature of 398 K.
Assuming that the variation of e.m.f. with temperature difference is linear,
the e.m.f., in mV, recorded will now be
746
A
273
796
B
273
796
C
373
25
D
50
125
E
50
E
PL
23. A brass bar and a steel bar, each 0.800 m long, are at a temperature of
20oC . Each bar is placed at that temperature between rigid walls 0.800 m
apart. The cross-sectional areas for the brass and steel bars are 0.005 m 2
M
and 0.003 m 2 , respectively. The coefficient of linear expansion and Young
modulus of the two materials are given in the table below.
SA
Coefficient of Linear Young modulus
Expansion
Brass 2.0 × 10 −5 K −1 0.90 × 1011 Pa
Steel 1.2 × 10 −5 K −1 2.0 × 1011 Pa
The temperature is raised until the combined force exerted by the two bars
is 1.8 MN. The temperature at which this occurs, in oC , is closest to
A 140
B 130
C 120
D 110
E 100
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 10
24. A heat-conducting rod, 1.10 m long, is made of an aluminium section,
0.20 m long, and a copper section, 0.90 m long. Both sections have a
cross-sectional area of 0.0004 m 2 . The aluminium end and the copper end
are maintained at temperatures of 10oC and 250o C , respectively. The
thermal conductivities of aluminium and copper are 205 W m −1K −1 and
385 W m −1K −1 , respectively. The temperature of the aluminium-copper
o
junction in the rod, in C , is closest to
A 54
B 59
C 66
D 73
E 81
25. The speed of light in a material is 0.50c. What is the critical angle of a light
ray at the interface between the material and a vacuum?
E
A 21°
B 24°
PL
C 27°
D 30°
E 34°
M
26. An electromagnetic wave, passing from medium X to medium Y, undergoes
a 30% increase in wave speed. If the angle of incidence at the interface of
SA
o
X and Y is 45 , what is the angle of refraction in medium Y?
A 33o
B 35o
C 45o
D 59o
E 67 o
27. Three flat layers of transparent material are stacked upon one another. The
top layer has index of refraction n1, the middle n2 and the bottom one n3. If
n1 > n2 > n3, and a ray of light in air strikes the top layer, at which surface
given can total internal reflection occur first?
A the top surface
B the surface between materials with indices n1 and n2
C the surface between materials with indices n2 and n3
D the bottom surface
E Total internal reflection cannot occur at any of these surfaces.
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 11
28. A convex lens has a focal length f. An object is placed between infinity and
2f from the lens along a line perpendicular to the center of the lens. The
image is located at what distance from the lens?
A farther than 2f
B 2f
C f
D between f and 2f
E between the lens and f
29. Parallel water waves of wave length 20 m strike a straight sea wall. The
wavefronts make an angle 30˚ with the wall. What is the difference in
phases between the waves at two points 10 m apart along the wall?
A 30˚
B 45˚
C 90˚
E
D 180˚
E None of the above.
PL
30. Two narrow slits, 0.30 mm apart, are illuminated by a beam of light of
wavelength 700 nm. An interference pattern is observed on a screen
normal to the beam and 3.0 m from the slits. The distance in mm between
M
adjacent dark lines on the screen is
A 1.0
SA
B 3.0
C 5.0
D 7.0
E 9.0
5
31. Light of wavelength 420 nm is incident on a diffraction grating of 3.8 × 10
lines per metre. Which one of the following is the highest diffraction order
which can be observed?
A 2
B 3
C 4
D 5
E 6
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 12
32. The least distance between two points of a progressive transverse wave
which have a phase difference of 2π 3 rad is 0.050 m. If the frequency of
the wave is 500 Hz, what is the speed of the wave?
A 24 m/s
B 25 m/s
C 75 m/s
D 150 m/s
E 300 m/s
33. Two conducting spheres A and B, of radii rA and rB , carry charges + QA and
+ QB respectively. The centres of the spheres are a distance d apart with d
slightly greater than rA + rB . Which of the following statements about the
electrostatic forces F between the spheres is true?
QAQB
E
A F<
4πε0 d 2
QQ
B F = A B2
PL
4πε0 d
QQ
C F > A B2
4πε0 d
QAQB
D F =
M
4πε0 (d + rA + rB ) 2
QAQB
E F <
4πε0 (d + rA + rB ) 2
SA
34. The electrostatic potential at a distance of 150 mm from an isolated point
charge, in vacuum, is 6.0 × 10 4 V . The electric field, in V/m, at the same
point is
A 1.6 × 106
B 2.7 × 106
C 4.0 × 102
D 4.0 × 105
E 9.0 × 10 4
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 13
35. Four point charges are arranged at the corners of a square of length 3 m as
shown.
−Q +Q
+ 3Q − 3Q
The electric field at the centre of the square is
2Q
A to the East
9πε0
2Q
B to the West
9πε0
E
2Q
C to the East
9πε0
PL
2Q
D to the West
9πε0
E 0
M
36. An electron is emitted from an electron gun with a speed of 3.0 × 10 6 m s . It
moves towards a metal grid which is positioned at 10.0 cm away from the
gun. The grid is maintained at a potential of − 20 V with respect to the
SA
electron gun. What is the speed of the electron as it reaches the grid?
A 1.4 × 106 m s
B 2.3 × 106 m s
C 3.0 × 106 m s
D 3.5 × 106 m s
E 4.0 × 106 m s
37. A 4.0 µF capacitor has a potential difference of 5.0 V applied across its plates.
If the potential difference across its plates is increased to 8.0 V, how much
additional energy does the capacitor store?
A 36 µJ
B 50 µJ
C 78 µJ
D 130 µJ
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 14
E 160 µJ
38. Wire of resistivity ρ and cross-sectional area A is formed into a square of
side b, as shown below.
X b
b b
Y b
The resistance between two vertices of the square, X and Y, is
3 ρb
A
4 A
ρb
B 4
A
ρb
E
C
A
A
D
PL
4
ρb
4 A
E
3 ρb
M
39. The battery is disconnected from a series RC circuit after the capacitor is
fully charged and is replaced by an open switch. When the switch is closed,
A the capacitor does not allow current to pass.
SA
B the current stops in the resistor.
C the potential difference across the resistor is always greater than the
potential difference across the capacitor.
D the potential difference across the resistor is always less than the
potential difference across the capacitor.
E the potential difference across the resistor is always equal to the
potential difference across the capacitor.
40. In defining the ampere it is said that the force per metre between two thin,
infinitely long parallel straight wires in vacuum one metre apart, is
2 × 10 −7 N m when the current in each wire is 1 A. The force per metre, in
N/m, when the wires each carry currents of 3 A and are 2 m apart is
A 1.8 × 10 −6
B 2.0 × 10 −7
C 2.3 × 10 −7
D 4.5 × 10 −7
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 15
E 9 × 10 −7
41. A neutral sub-atomic particle is at rest in a uniform magnetic field of
magnitude B. It splits into two particles each of mass m, one of which has
a positive charge + Q . The particles then move with velocities
perpendicular to the magnetic field. After what time will the particles collide?
5mπ
A
2QB
2mπ
B
QB
3mπ
C
2QB
mπ
D
QB
mπ
E
2QB
E
PL
42. A flat search coil containing 100 turns each of area 2.0 × 10 −2 m 2 is
connected to a galvanometer. The total resistance of the circuit is 50 Ω .
The coil is placed such that its plane is normal to a magnetic field of
magnitude 0.25 T. What is the quantity of charge induced when the coil is
turned over through an angle of 90o ?
M
A 0C
B 2.0 × 10 −4 C
SA
C 0.010 C
D 0.020 C
E 0.040 C
43. A circular loop of wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 1.2 T that is
normal to the plane of the loop. The loop shrinks from a radius of 0.20 m
to a radius of 0.10 m in 0.050 s, at a rate which generates a steady electro-
motive force (emf). The induced emf is
A 0V
B 0.75 V
C 1.1 V
D 2.3 V
E 3.0 V
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 16
44. A solenoid with a large number of turns of wire is connected in series with
an ammeter and a battery.
An iron rod is passed through the solenoid at constant speed. Which graph
shows the variation with time t of the reading I of the ammeter?
E
A B
P
M
SA
C D
E None of the above.
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 17
45. The graph shows a rectangular waveform with a peak current of 2 A.
Current/A
Time
–2
To give the same root-mean-square current as the waveform shown, a
sinusoidal current of the same frequency will have a peak value of
A 2 A
B 2 2 A
C 3 2 A
D 2A
E 4A
E
PL
46. A sinusoidal current of peak value I 0 passes through a resistor R with a
diode connected in series with it. The average rate of heat dissipated in R
is
M
A I 02 R
B 0.25 I 02 R
C 0.35 I 02 R
SA
D 0.50 I 02 R
E 0.71I 02 R
47. In a nuclear reaction, energy equivalent to 10−10 kg of matter is released.
The energy released is approximately
A 4.5 × 10-5 J
B 9.0 × 10-5 J
C 3.0 × 10-5 J
D 4.5 × 106 J
E 9.0 × 106 J
UEE 2018 – PHY / 02 18
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Final Roud QBDokument3 SeitenFinal Roud QBxerxes uclm100% (1)
- PHYS1534 Exam 2018 MainDokument16 SeitenPHYS1534 Exam 2018 MainGiftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray OpticsDokument38 SeitenRay OpticsLavanya Sathya100% (1)
- 102 Physics Answers-EK EditionDokument15 Seiten102 Physics Answers-EK Editionadom09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Unit PDFDokument102 SeitenWave Unit PDFPrensess BerfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics I Quiz # 2 - 01/07/2022Dokument9 SeitenPhysics I Quiz # 2 - 01/07/2022Nathaly SosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Sample Physics 71Dokument11 SeitenFinal Exam Sample Physics 71Jay VeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grades 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level IV Teacher Learning Area Science Date and Time Quarter 3Dokument7 SeitenGrades 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level IV Teacher Learning Area Science Date and Time Quarter 3Johnace_87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mil HDBK 728 - 6 PDFDokument90 SeitenMil HDBK 728 - 6 PDFretrospect100050% (2)
- OAPT - Grade 11 Physics Contest - 2012 OAPT Grade 11 Physics ContestDokument7 SeitenOAPT - Grade 11 Physics Contest - 2012 OAPT Grade 11 Physics ContestMircea PanteaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genphysics 2ND Sem FidpDokument14 SeitenGenphysics 2ND Sem FidpCris Simon100% (3)
- AQA AS Physics A Chapter 13 Textbook AnswersDokument3 SeitenAQA AS Physics A Chapter 13 Textbook AnswerscathylisterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDokument14 SeitenRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDokument17 SeitenRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donald C. OShea Elements of Modern Optical DesiBookFiDokument408 SeitenDonald C. OShea Elements of Modern Optical DesiBookFiRicardo Pimentel100% (2)
- GTE Lenkurt BookDokument172 SeitenGTE Lenkurt Bookdpsguard-buy8922Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics72.1 Laboratory ManualDokument79 SeitenPhysics72.1 Laboratory ManualJay JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apr 2022 P1 MSDokument18 SeitenApr 2022 P1 MSOlamide AkinyosoyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A B CD A B CD A B CD 1oooo 6 Oooo11Oooo 2oooo 7 Oooo12Oooo 3oooo 8 Oooo13Oooo 4oooo 9 Oooo14Oooo 5Oooo10Oooo15OoooDokument5 SeitenA B CD A B CD A B CD 1oooo 6 Oooo11Oooo 2oooo 7 Oooo12Oooo 3oooo 8 Oooo13Oooo 4oooo 9 Oooo14Oooo 5Oooo10Oooo15Oooominh nguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: KinematicsDokument38 SeitenMultiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: Kinematics张书Noch keine Bewertungen
- University Entrance Examination: PhysicsDokument20 SeitenUniversity Entrance Examination: PhysicsHuy Ngọc DươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Grade 11 Unit 4 WorksheetDokument14 SeitenPhysics Grade 11 Unit 4 Worksheetsample nameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam A1Dokument3 SeitenMidterm Exam A1Bá Phong LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 PhysicsDokument20 Seiten2017 PhysicsPutri Rizki FitrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 6: Circular Motion: Self-Review QuestionsDokument5 SeitenTutorial 6: Circular Motion: Self-Review QuestionsAgus LeonardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term2 Test1 CH 5 and 6Dokument10 SeitenTerm2 Test1 CH 5 and 6Darren ChristoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Paper 1 Ans 2018 GDokument23 SeitenPhy Paper 1 Ans 2018 GSUNIL0% (1)
- 03 - Circular Motion - ExerciseDokument7 Seiten03 - Circular Motion - Exercisekenchan0810.kcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Olympiad: Entia Non Multiplicanda Sunt Praeter NecessitatemDokument10 SeitenPhysics Olympiad: Entia Non Multiplicanda Sunt Praeter Necessitatemsanjeev1000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ProblemsDokument3 SeitenPhysics ProblemsKenneth BailadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Dokument2 SeitenStudent's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Nam Anh Nguyễn HữuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Physics SA2 Singapore Chinese GirlsDokument52 Seiten2019 Sec 4 Pure Physics SA2 Singapore Chinese GirlsFrancis Ho HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestDokument14 Seiten(UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestMon Belle AmourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askiitians: Class: Xi Subject: Physics Topic: Motion in A Plane No. of Questions: 30Dokument7 SeitenAskiitians: Class: Xi Subject: Physics Topic: Motion in A Plane No. of Questions: 30Akshit GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Sajc h2 Prelim Paper 1Dokument26 Seiten2010 Sajc h2 Prelim Paper 1Aaron Kang JunyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test PhysicsDokument2 SeitenTest PhysicsShams ShamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addis Ababa Physics Model Examination For Grade 12 Ginbot .: General DirectionDokument8 SeitenAddis Ababa Physics Model Examination For Grade 12 Ginbot .: General DirectionKhalid A.100% (2)
- Ce2a 105 f08Dokument5 SeitenCe2a 105 f08Mona Mohamed SafwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics C 1998 With AnswersDokument16 SeitenAP Physics C 1998 With AnswersjhbmleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce2a 105 f08Dokument5 SeitenCe2a 105 f08jessieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grav and Energy Practice AP: Multiple ChoiceDokument11 SeitenGrav and Energy Practice AP: Multiple ChoiceJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics PDFDokument7 SeitenKinematics PDFBetseha MerawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics P-22 IgcseDokument20 SeitenPhysics P-22 IgcseareebNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS 960/1: Lower 6 Time: 1 HoursDokument10 SeitenPHYSICS 960/1: Lower 6 Time: 1 HoursLee Jia XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Physics Test 2 NDokument1 SeiteGrade 12 Physics Test 2 NAmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Olympic Physics USA 1997Dokument9 SeitenOlympic Physics USA 1997Nguyễn Đức HiệpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Uee Physics (1) (Sample Past Paper)Dokument21 Seiten2019 Uee Physics (1) (Sample Past Paper)Diệp Nguyễn Bảo NgọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Dokument15 SeitenPhysics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Emmyr FaiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Motion and Gravitation 2Dokument16 SeitenCircular Motion and Gravitation 2martinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy G11 - PQ2Dokument5 SeitenPhy G11 - PQ2RonaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Dokument14 Seiten(Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Haigou WaaaahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Physics Model YekaDokument9 Seiten2010 Physics Model YekaTizita EmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ 2Dokument5 SeitenMCQ 2gaya8404Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 SJPO-2013-GenDokument19 Seiten4 SJPO-2013-Genronghui009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phy102 Practise Problems For Exam2Dokument4 SeitenPhy102 Practise Problems For Exam2Renz Dane TametaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SwerdwsDokument4 SeitenSwerdwsTú ĐoànNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam 2016 2017 01Dokument4 SeitenMidterm Exam 2016 2017 01Bá Phong LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionDokument9 SeitenChapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionJunLi CaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physice IX First Term 2020 Paper I A (Answer Key)Dokument12 SeitenPhysice IX First Term 2020 Paper I A (Answer Key)Haseeb MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument5 SeitenPhysics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsNader HijaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Projectile Is Fired Horizontally From A Launching DeviceDokument10 SeitenA Projectile Is Fired Horizontally From A Launching DeviceharshanauocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Test Paper 2023 FinalDokument21 SeitenPhy Test Paper 2023 Finalshallom udehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock 1 QP (PQ, Kine, Dyna)Dokument28 SeitenMock 1 QP (PQ, Kine, Dyna)Tahmedul Hasan TanvirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Grade 10Dokument5 SeitenPhysics Grade 10hannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy G12 P1 2019 MarchDokument17 SeitenPhy G12 P1 2019 MarchSUNILNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics SPDokument4 Seiten11 Physics SPvikas vyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetDokument9 SeitenAP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetEAGLEFORCE06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 71 1 Long Sample ExamDokument4 SeitenPhysics 71 1 Long Sample ExamManna Pinto100% (1)
- Chapter 6Dokument70 SeitenChapter 6mrsm fizik100% (1)
- Compilation of Science Activities (Maricel Nanolan)Dokument4 SeitenCompilation of Science Activities (Maricel Nanolan)arlie joy alvarez100% (1)
- IGCSE 2004-2008 PhysicsDokument373 SeitenIGCSE 2004-2008 PhysicsashokNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01-01-2024 - Jr-Co-Super-Chaina - Star-Ii (New) - Jee Main Model - CTM-6 - QP FinalDokument12 Seiten01-01-2024 - Jr-Co-Super-Chaina - Star-Ii (New) - Jee Main Model - CTM-6 - QP FinalnakkinasrinikeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prism ExperimentDokument31 SeitenPrism ExperimentFred100% (1)
- Refraction Phet Lab: ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenRefraction Phet Lab: ObjectivesTạ Ngọc DiệpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam I - OPT201Dokument11 SeitenExam I - OPT201rittaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NotesDokument52 SeitenNotesSwati SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- OweiDokument1 SeiteOweiitskillerdake daekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument15 SeitenChapter 2kingstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- II Pu Physics VivaDokument2 SeitenII Pu Physics VivashrishantkambarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icjephpu 20Dokument10 SeitenIcjephpu 20jadenrichard8357Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prism PDFDokument14 SeitenPrism PDFHarold MangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sol 0593Dokument12 SeitenSol 059327nstaffordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDokument27 SeitenHuman Eye and Colourful WorldSreejith SurendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muhammad Haris-MEE173017Dokument103 SeitenMuhammad Haris-MEE173017Muhammad Sohail AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Fall Optics (I) Homework #2, Due 10/26: 0 R I R 0 I 0 - 1Dokument1 Seite2023 Fall Optics (I) Homework #2, Due 10/26: 0 R I R 0 I 0 - 1藍博懷Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 - Student HandoutDokument19 SeitenLecture 1 - Student HandoutJeric LumantasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glass PrismDokument3 SeitenGlass PrismPulkit BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light EditedDokument41 SeitenLight Editedmarc daniel ortizNoch keine Bewertungen