Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pharmacologic Study Mi
Hochgeladen von
Izhra Margate0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
45 Ansichten22 SeitenThis document summarizes information about the drugs tramadol and clindamycin, including their general and specific actions, indications, contraindications, side effects, adverse effects, and nursing responsibilities. Tramadol is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic indicated for moderate to severe pain. Common side effects include dizziness, nausea, constipation, and headache. Clindamycin is an antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis and is used to treat various infections. Potential side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Nursing responsibilities for both drugs involve monitoring for side effects, drug interactions, and ensuring patient safety.
Originalbeschreibung:
h
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document summarizes information about the drugs tramadol and clindamycin, including their general and specific actions, indications, contraindications, side effects, adverse effects, and nursing responsibilities. Tramadol is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic indicated for moderate to severe pain. Common side effects include dizziness, nausea, constipation, and headache. Clindamycin is an antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis and is used to treat various infections. Potential side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Nursing responsibilities for both drugs involve monitoring for side effects, drug interactions, and ensuring patient safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
45 Ansichten22 SeitenPharmacologic Study Mi
Hochgeladen von
Izhra MargateThis document summarizes information about the drugs tramadol and clindamycin, including their general and specific actions, indications, contraindications, side effects, adverse effects, and nursing responsibilities. Tramadol is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic indicated for moderate to severe pain. Common side effects include dizziness, nausea, constipation, and headache. Clindamycin is an antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis and is used to treat various infections. Potential side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Nursing responsibilities for both drugs involve monitoring for side effects, drug interactions, and ensuring patient safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 22
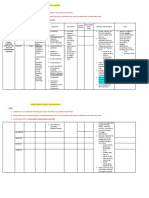
PHARMACOLOGIC STUDY
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Tramadol Centrally Binds to mu- Indicated for Acute alcohol Dizziness Seizures Assess onset, type,
50mg per 8 acting opioid receptors, the intoxication Vertigo reported in location, duration of
hours synthetic inhibits reuptake management Concurrent use of Nausea patients pain.
opioid of norepinephrine, of moderate centrally acting Constipation receiving Assess drug history, esp.
analgesic serotonin, to analgesics, hypnotics, Headache tramadol within carbamazepine,
inhibiting moderately s opioids, psychotropic Drowsiness recommended analgesics, CNS
ascending and evere pain in drugs, hypersensitivity Vomiting dosage range. depressants, MAOIs.
descending pain adults. to opioids. Pruritus May have Review past medical
pathways. CNS prolonged history, esp. epilepsy,
Stimulation duration of seizures.
Asthenia action, Assess renal function,
Diaphoresis cumulative LFT.
Dyspepsia effect in Monitor pulse, BP,
Dry mouth patients with renal/hepatic function.
Diarrhea hepatic/renal Assist with ambulation
Malaise impairment, if dizziness, vertigo
Vasodilation serotonin occurs. Dry crackers,
Anorexia syndrome cola may relieve nausea.
Flatulence (agitation, Palpate bladder for
Rash hallucinations, urinary retention.
Blurred vision tachycardia, Monitor daily pattern of
Urinary hyperreflexia) bowel activity, stool
Retention consistency.
Menopausal Sips of water may
symptoms relieve dry mouth.
Assess for clinical
improvement, record
onset of relief of pain.
Avoid alcohol, OTC
medications
Report severe
constipation, difficulty
breathing, excessive
sedation, seizures.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Clindamycin Antibiotic Inhibits protein Treatment of Hypersensitivity Abdominal CNS: dizziness, Assess for infection
600 mg per 8 synthesis of Pneumocystic Regional enteritis or pain headache, (vital signs; appearance
hours bacterial cell wall carinii ulcerative colitis Nausea vertigo of wound, sputum, urine
by binding to pneumonia, Previous Vomiting CV: PSEUDO- and stool; WBC) at
bacterial ribosomal CNS pseudomembranous Diarrhea MEMBRANO beginning of and during
receptor sites. toxoplasmosis colitis Pruritus US COLITIS, therapy
Topically, , and Severe liver impairment Phlebitis diarrhea, bitter Obtain specimens for
decreases fatty babesiosis. Diarrhea taste (IV only). culture and sensitivity
acid concentration Known alcohol Derm: rash. prior to initiating
on skin. intolerance (topical therapy. First dose may
Bacteriostatic or solution, suspension) be given before
bactericidal. receiving results.
Monitor bowel
elimination. Diarrhea,
abdominal cramping,
fever and bloody stools
should be reported to
health care professional
promptly as a sign of
pseudomembranous
colitis. This may begin
up to several weeks
following the cessation
of therapy.
Assess patient for
hypersensitivity (skin
rash, urticaria)
Monitor CBC; may
cause transient in
leukocytes, eosinophils,
and platelets.
May cause alkaline
phosphatase, bilirubin,
CPK, AST, and ALT
concentrations.
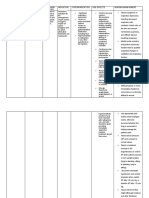
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECT RESPONSIBILITIES
Digoxin Antiarrhythmi Increases the force Heart failure Hypersensitivity Dizziness CNS: fatigue, Monitor apical pulse for
125mcg 1 tab cs, inotropics of myocardial Atrial Uncontrolled Headache headache, 1 full min before
OD contraction. fibrillation ventricular Diarrhea weakness. administering. Withhold
Prolongs Atrial flutter arrhythmias; AV block Rash EENT: blurred dose and notify health
refractory period (slows (in absence of Visual vision, yellow care professional if
of the AV node. ventricular pacemaker) disturbances or green vision. pulse rate is <60 bpm in
Decreases rate) Idiopathic hypertrophic . CV: an adult. Also notify
conduction Paroxysmal subaortic stenosis Arrhythmias, health care professional
through the SA atrial Constrictive bradycardia, promptly of any
and AV nodes. tachycardia. pericarditis ECG changes, significant changes in
Known alcohol AV block, SA rate, rhythm, or quality
intolerance block. of pulse.
GI: anorexia, Monitor BP periodically
nausea, in patients IV digoxin.
vomiting, Monitor ECG
diarrhea. throughout IV
Hemat: administration and 6 hr
thrombocytopen after each dose. Notify
ia health care professional
Metab: if bradycardia or new
electrolyte arrhythmias occur.
imbalances with Monitor intake and
acute digoxin output ratios and daily
toxicity. weights. Assess for
peripheral edema, and
auscultate lungs for
rales/crackles
throughout therapy.
Before administering
initial loading dose,
determine whether
patient has taken any
digitalis preparations in
the preceding 2-3 wk.
Teach patient to take
pulse and to contact
HCP before taking med.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Prednisone Adrenal Inhibits Acute or Acute superficial Insomnia Long-term Obtain baselines for
20 mg 1 tab corticosteroid accumulation of chronic herpes simples keratitis Heartburn therapy: height, weight, BP,
OD inflammatory cells adrenal Systemic fungal Nervousness muscle wasting serum glucose,
at inflammation insufficiency infections Abdominal (esp. in arms, electrolytes.
sites, Congenital Varicella distention legs) Check results of initial
phagocytosis, adrenal Administration of live Diaphoresis Osteoporosis tests (TB skin test,
lysosomal enzyme hyperplasia or attenuated virus Acne Spontaneous EKG). Never give live
release/synthesis, Adrenal vaccines Mood swings fractures virus vaccine.
release of insufficiency Increased Amenorrhea Monitor BP, serum
mediators of secondary to Cautions: appetite Cataracts electrolytes, glucose,
inflammation. pituitary Hyperthyroidism Facial Glaucoma results of bone mineral
Prevents/suppreses insufficiency Cirrhosis flushing Peptic ulcer density test, height,
cell-mediated Delayed HF weight, in children. Be
Arthritis Ocular herpes simplex
immune reactions. wound Abrupt alert to infection; assess
Rheumatic Respiratory
Decreases/prevents carditis healing withdrawal oral cavity daily for
tuberculosis
tissue response to Increased following long- signs of candida
inflammatory
Prevention of Untreated systemic susceptibility infection.
postherpetic term therapy:
infections
process. to infection Anorexia, Report fever, sore
neuralgia, Renal/hepatic Diarrhea nausea, fever, throat, muscle aches,
relief of impairment
acute pain in Constipation headache, sudden weight, swelling,
pts with Headache rebound loss of appetite, or
herpes Edema inflammation, fatigue.
zoster, Change in fatigue, Avoid alcohol, minimize
autoimmune skin color weakness, use of caffeine
hepatitis. Frequent lethargy, Maintain fastidious oral
urination dizziness, hygiene.
Tachycardia orthostatic Do not abruptly
Allergic hypotension. discontinue without
reaction (rash, Sudden physician’s approval.
urticarial) discontinuance Avoid exposure to
Psychological may be fatal. chickenpox, measles.
changes
Hallucinations
Depression
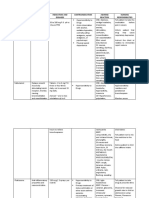
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Atorvastatin Anti- Inhibits HMG- Primary Active hepatic disease Headache Potential for Obtain baseline
20mg 20 mg hyperlipidemi CoA reductase, the prevention of Breastfeeding Myalgia cataracts, cholesterol,
1tab OD HS a enzyme that cardiovascul Pregnancy Rash photosensitivity triglycerides, LFT.
catalyzes the early ar disease in Unexplained elevated Pruritus ,myalgia, Question for possibility
step in cholesterol high-risks LFT results Allergy rhabdomyolysis of pregnancy before
synthesis. pts. . initiating therapy.
Reduces risk Cautions: Obtain dietary history.
of stroke and Anticoagulant therapy Monitor for headache.
heart attack History of hepatic Assess for rash, pruritus,
in pts with disease malaise.
type 2 Monitor cholesterol,
Substantial alcohol
diabetes with triglyceride lab values
consumption
or without for therapeutic response.
evidence of Monitor hepatic
heart disease. function tests, CPK.
Reduces risk Follow special diet
of stroke in Periodic lab tests are
patients with essential part of therapy
or without Do not take other
evidence of medications without
heart disease consulting physician.
with multiple Do not chew, crush,
risk factors dissolve or divide
other than tablets.
diabetes. Report dark urine,
Adjunct to muscle fatigue, bone
diet therapy pain.
in manage- Avoid excessive alcohol
ment of intake, large quantities
hyperlipidem of grapefruit products.
ias,
homo/hetero
zygous
familial
hypercholest
erolemia
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Lactulose Hyperosmotic Inhibits diffusion Prevention, Pts requiring a low- Abdominal Severe diarrhea Encourage adequate
70mg OD HS laxative, of NH3 into blood treatment of galactose diet. cramping indicates fluid intake.
ammonia by converting NH3 portal- Flatulence overdose Assess bowel sounds for
detoxicant. to NH4+; enhances systemic Cautions: Increased Long-term use peristalsis.
diffusion of NH4+; encephalopat Diabetes mellitus, thirst may result in Monitor daily pattern of
produces osmotic hy (including hepatic impairment, Abdominal laxative bowel activity, stool
effect in colon. hepatic pre- dehydration. discomfort dependence consistency; record time
coma, coma) Nausea Chronic of evacuation.
Treatment of Vomiting constipation Assess for abdominal
constipation. Loss of normal disturbances.
bowel function Monitor serum
electrolytes in pts with
prolonged, frequent,
excessive use of
medication.
Evacuation occurs in 24-
48 hrs of initial dose.
Institute measures to
promote defecation:
increase fluid intake,
exercise, high-fiber diet.
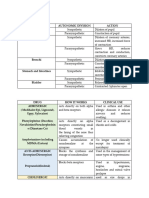
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Enalapril Antihypertens Suppresses renin- Treatment of History of angioedema Headache Excessive Obtain BP immediately
5 mg 1 tab ive, angiotensin- hypertension from previous Dizziness hypotension before each dose.
OD vasodilator aldosterone system alone or in treatment with ACE Orthostatic may occur in Assist with ambulation
(prevents combination inhibitors. hypotension pts with HF if dizziness occurs.
conversion of with other Idiophatic/hereditary Fatigue Severe salt or Monitor CBC, serum
angiotensin I to antihypertens angioedema. Diarrhea volume BUN, potassium,
angiotensin II, a ives. Concomitant use of Cough depletion creatinine, BP.
potent Adjunctive aliskerin in pts with Syncope Angioedema Monitor daily pattern of
vasoconstrictor; therapy for diabetes. Angina (facial, lip bowel activity, stool
may inhibit symptomatic Abdominal swelling), consistency.
angiotensin II at HF. Cautions: pain hyperkalemia To reduce hypotensive
local vascular, Treatment of Renal impairment Vomiting occur rarely effect, go from lying to
renal sites). left Hypertrophic Nausea Agranulocytosis standing slowly.
Decreases plasma ventricular cardiomyopathy Rash Neutropenia Several weeks may be
angiotensin II, dysfunction. with outflow tract Asthenia Collagen needed for full
increases plasma Treatment of obstruction vascular therapeutic effect of BP
renin activity, hypertension diseases reduction.
decreases in adults and Nephrotic Skipping doses or
aldosterone children syndrome voluntarily
secretion. older than 1 discontinuing drug may
mo. produce severe, rebound
hypotension.
Limit alcohol intake
Report vomiting,
diarrhea, diaphoresis,
persistent cough,
difficulty breathing;
swelling of face, lips,
tongue.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Isosorbide Antianginal Stimulates Prevention of Hypersensitivity to Headache Blurred vision Record onset, type
mononitrate intracellular cyclic angina nitrates, concurrent use Transient Severe (sharp, dull, squeezing),
30 mg OD guanosine pectoris. of sildenafil, tadalafil, flushing of orthostatic radiation, location,
monophosphate. verdenafil. face/neck, hypotension intensity, duration of
Relaxes vascular dizziness, manifested by anginal pain;
smooth muscle of Cautions: weakness, syncope, precipitating factors
atrial, venous Inferior wall MI, orthostatic pulselessness, (exertion, emotional
vasculature. head trauma, hypotension, cold/clammy stress).
Decreases preload, increased ICP, nausea, skin, and If headache occurs
afterload, cardiac orthostatic vomiting, diaphoresis has during management
oxygen demand. hypotension, blood restlessness. been reported. therapy, administer
volume depletion GI upset, Tolerance may medication with meals.
from diuretic blurred vision, occur with Assist with ambulation
therapy, systolic BP dry mouth. repeated, if light headedness,
less than 90 mmHg, Burning, prolonged dizziness occurs.
hypertrophic tingling at therapy, but Assess for facial/neck
cardiomyopathy. oral point of may not occur flushing.
dissolution. with extended- Monitor number of
release form. anginal episodes,
Minor tolerance orthostatic BP.
with Do not chew, crush,
intermittent use dissolve or divide
of sublingual sublingual, extended-
tablets. release-sustained-release
High dose tends forms.
to produce Take sublingual tablets
severe while sitting down.
headache. Go from lying to
standing slowly.
Dissolve sublingual
tablet under tongue; do
not swallow.
Avoid alcohol
Report signs/symptoms
of hypotension, angina.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Verapamil Calcium Inhibits calcium Treatment of Atrial fibrillation/flutter Constipation Rapid Check BP for
500 mg 1 tab channel ion entry cross hypertension, in presence of Dizziness ventricular rate hypotension, pulse for
OD blocker; cardiac, vascular angina accessory bypass tract Light- in atrial bradycardia immediately
Antihypertens smooth-muscle pectoris, Severe left ventricular headedness flutter/fibrillatio before giving
ive, cell membranes, supraventricu dysfunction Asthenia n, marked medication.
Antianginal, dilating coronary lar Cardiogenic shock Nausea hypotension, Assess pulse for quality,
antiarrhythmi arteries, peripheral tachyarrhyth Second- or third-degree Peripheral extreme rate, rhythm.
c, arteries, arterioles. mias (SVT), heart block edema bradycardia, Monitor BP. Monitor
hypertrophic Decreases heart atrial Hypotension Hypotension HF, asystole, EKG for cardiac
cardiomyopat rate, myocardial fibrillation/fl Sick sinus syndrome Bradycardia second- or changes, particularly
hy therapy contractility; slow utter (rate Dermatitis third-degree AV prolongation of PR
adjunct. SA, AV control) Cautions: Rash block occur interval. Notify
conduction. rarely. physician of any
Renal/hepatic
Decreases total significant EKG interval
impairment
peripheral vascular changes.
Concomitant use of
resistance by Assist with ambulation
beta blockers
vasodilation. if dizziness occurs.
and/or digoxin
Assess for peripheral
Myasthenia Gravis edema.
Hypertrophic Monitor daily pattern of
cardiomyopathy bowel activity, stool
consistency.
Do not abruptly
discontinue medication.
Compliance with
therapy regimen is
essential to control
anginal pain.
Avoid tasks that require
alertness, motor skills
until response to drug is
established.
Limit caffeine.
Report continued,
persistent angina pain
and irregular heartbeats,
SOB, swelling.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Colchicine Antigout Decreases Prevention, Concomitant use of a Nausea Long-term Obtain baseline
1 tab OD leukocyte motility, treatment of P-glycoprotein (e.g., Vomiting therapy: bone laboratory studies.
phagocytosis, acute gouty cyclosporine) or strong Abdominal marrow Assess involved joints
lactic acid arthritis. CYP3A4 inhibitor in discomfort depression for pain, mobility, and
production. Used to presence renal/hepatic Anorexia Burning feeling edema.
Decreases urate reduce impairment Hypersensitivi in skin/throat Assess abdominal pain,
crystal deposits, frequency of ty reaction, Severe diarrhea fever, chills, erythema,
reduces recurrence of Cautions: including Abdominal pain swollen skin lesions.
inflammatory familial Hepatic impairment, angioedema. Fever Discontinue medication
process. Mediterranea elderly, debilitated, Seizures immediately if GI
n fever renal impairment. Delirium symptoms occur.
Renal Encourage high fluid
impairment intake (3L/day).
Hair loss Monitor I&O, BC,
Leukocytosis hepatic/renal function
Stomatitis tests.
Monitor serum uric acid.
Assess for therapeutic
response: relief of pain,
stiffness, swelling;
increased joint mobility;
reduced joint
tenderness; improved
grip strength.
Report skin rash, sore
throat, fever unusual
bruising/bleeding,
weakness, fatigue,
numbness.
Stop medication as soon
as gout pain is relieved
or at first sign of nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea.
Avoid grapefruit
products.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Aspirin Anti- Inhibits cyclo- Treatment of Hypersensitivity to GI distress GI bleeding Assess type, location,
80 mg OD inflammatory, oxygenase enzyme mild to salicylates, NSAIDs. Abdominal and/or gastric duration of pain,
antipyretic, via acetylation. moderate Asthma distention mucosal lesions inflammation.
anticoagulant Inhibits formation pain, fever. Rhinitis Cramping Dehydration Inspect appearance of
of prostaglandin Reduces Nasal polyp Heartburn Reye’s affected joints for
derivative inflammation Inherited or acquired Mild nausea syndrome immobility, deformities,
thromboxane A. related to bleeding disorders Allergic Vomiting skin condition.
Reduces rheumatoid Avoid use in reaction Tinnitus Do not chew, crush,
inflammatory arthritis, pregnancy, esp. third Bronchospas Headache dissolve or divide
response, intensity juvenile trimester. m Dizziness tablets.
of pain; decreases arthritis, Pruritus Flushing Avoid alcohol
fever; inhibits osteoarthritis, Cautions: Urticaria Hyperventilatio Report tinnitus or
platelet rheumatic n persistent abdominal GI
Platelet/bleeding
aggregation. fever. Diaphoresis pain, bleeding
disorder
Used as Thirst Behavioral changes,
Severe hepatic/renal
platelet Hyperthermia persistent vomiting may
impairment
aggregation Restlessness be early signs of Reye’s
Dehydration Seizures syndrome; contact
inhibitor in
Erosive gastritis Abnormal physician.
the
Peptic ulcer disease breathing
prevention of
transient pattern
ischemic Respiratory
attacks, failure
cerebral Coma
thromboemb
olism, MI or
reinfarction.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Omeprazole Proton pump Inhibits hydrogen- Short-term Hypersensitivity to Headache Pancreatitis Evaluate for therapeutic
40 mg 1 tab inhibitor potassium treatment (4- other proton pump Diarrhea Hepatotoxicity response (relief of GI
OD adenosine 8 wks) of inhibitors. Abdominal Interstitial symptoms).
triphosphatase erosive pain nephritis occur Questions if GI
(H+/K+ ATP esophagitis Cautions: Nausea rarely. discomfort, nausea,
pump), and Symptomatic May increase risk of Dizziness diarrhea occurs.
enzyme on the GERD fractures, Asthenia (loss Report headache, onset
surface of gastric poorly gastrointestinal of strength, of black, tarry stools,
parietal cells. responsive to infections energy) diarrhea, and abdominal
Increases gastric other Hepatic impairment, Vomiting pain.
pH, reduces gastric treatment esp. of Asian Constipation Avoid alcohol intake.
acid production. Long-term descent. Upper Swallow capsules
treatment of respiratory whole; do not chew,
pathologic tract infection crush, dissolve, or
hypersecretor Back pain divide.
y conditions, Rash Take before eating.
treatment of Cough
active
duodenal
ulcer or
active benign
gastric ulcer.
Maintenance
healing of
erosive
esophagitis.
Treatment of
frequent
uncomplicate
d heartburn
occurring 2
or more
days/wk
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Spironolacton Potassium- Interferes with Management Acute renal Hyperkalemia Severe Weight pt; initiate strict
e 25 g per tab sparing sodium of edema insufficiency Dehydration hyperkalemia I&O.
BID diuretic, reabsorption by associated Anuria Hyponatremia may produce Evaluate hydration
antihypertensi competitively with Hyperkalemia Lethargy arrhythmias, status by assessing
ve, inhibiting action of excessive Addison’s disease Nausea bradycardia, mucous membranes,
antihypokale aldosterone in aldosterone Concomitant use of Vomiting EKG changes skin turgor.
mic. distal tubule, excretion or eplerenone Anorexia May proceed to Obtain baseline serum
promoting sodium with HF; Abdominal cardiac electrolytes,
and water hypertension; Cautions: cramps standstill, renal/hepatic function,
excretion, cirrhosis of Dehydration Diarrhea ventricular and urinalysis.
increasing liver with Headache fibrillation Assess for edema; note
Hyponatremia
potassium edema or Ataxia Cirrhosis pts at location, extent.
Renal/hepatic
retention. Produces ascites, Drowsiness risk for hepatic Check baseline vital
impairment
diuresis, lowers hypokalemia, Confusion decompensation signs, note pulse
BP. Concurrent use of Fever if dehydration, rate/regularity.
nephrotic
supplemental
syndrome, Gynecomastia hyponatremia Monitor BP.
potassium, elderly.
severe HF; Impotence, occurs. Monitor serum
primary decreased Pts with electrolytes values, esp.
hyperaldoster libido. primary for increased potassium,
onism. aldosteronism BUN, creatinine.
may experience Monitor for signs of
rapid weight hyperkalemia.
loss, severe Obtain daily weight.
fatigue during Note changes in edema,
high-dose skin turgor.
therapy. Avoid foods high in
potassium, such as
whole grains, legumes,
meat, bananas, apricots,
orange juice, potatoes
and raisins.
Avoid tasks that require
alertness, motor skills
until response to drug is
established (may cause
drowsiness).
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Potassium Potassium Necessary for Treatment, Severe renal Nausea Hyperkalemia Assess for hypokalemia.
chloride tab replenisher multiple cellular prevention of impairment Vomiting manifested as PO should be given with
TID metabolic hypokalemia Adrenal insufficiency Diarrhea paresthesia, food or after meals with
processes. Primary when Hyperkalemia Flatulence feeling of full glass of water, fruit
action is necessary to Abdominal heaviness in juice (minimizes GI
intracellular. avoid Cautions: discomfort lower irritation)
Required for nerve chloride or Cardiac disease, with extremities, Monitor serum
impulse acid/base acid-base disorders distention cold skin, potassium.
conduction, imbalance. Potassium-altering Rash grayish pallor, Be alert to decreased
contraction of disorders hypotension, urinary output
cardiac, skeletal, confusion, Monitor daily pattern of
smooth muscle; irritability, bowel activity, stool
maintains normal flaccid consistency.
renal function, paralysis, Assess I&O diligently
acid-base balance. cardiac during diuresis.
arrhythmias. Report paresthesia,
feeling of heaviness of
lower extremities, tarry
or bloody stools,
weakness, unusual
fatigue.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Carvedilol Antihypertens Possess Treatment of Bronchial asthma or Fatigue Bradycardia Assess BP, apical pulse
6.25 mg 1 tab ive nonselective beta- mild to related bronchospastic Dizziness Hypotension immediately before drug
BID blocking and severe HF, conditions, cardiogenic Diarrhea Bronchospasm is administered.
alpha-adrenergic left shock, decompensated Bradycardia Cardiac Monitor BP for
blocking activity. ventricular HF requiring Rhinitis insufficiency hypotension,
Cause dysfunction intravenous inotropic Back pain Cardiogenic respirations for dyspnea.
vasodilation. following therapy, severe hepatic Orthostatic shock Assess pulse for quality,
Reduces cardiac MI, impairment, second- or hypotension Cardiac arrest regularity, rate; monitor
output, exercise- hypertension. third-degree AV block, Drowsiness Abrupt for bradycardia.
induced Treatment of severe bradycardia, or UTI withdrawal may Monitor EKG for
tachycardia, reflex angina sick sinus syndrome. Viral result in cardiac arrhythmias.
orthostatic pectoris, infection diaphoresis, Assist with ambulation
tachycardia; idiopathic Cautions: palpitations, if dizziness occurs.
reduces peripheral cardiomyopa Concurrent use of headache, and Assess for evidence of
vascular thy. digoxin, diltiazem, tremors. HF: Dyspnea, night
resistance. or verapamil; May precipitate cough, peripheral
diabetes, HF, MI in pts edema, distented neck
myasthenia gravis, with cardiac veins.
psychiatric disease, disease; thyroid Monitor I&O.
mild to moderate storm in pts Monitor renal/hepatic
hepatic impairment. with function tests.
Withdraw gradually thyrotoxicosis; Avoid tasks that require
to avoid acute peripheral alertness, motor skills
tachycardia, vascular until response to drug is
hypertension, disease. established.
and/or ischemia. Hypoglycemia Report excessive
may occur in fatigue, prolonged
pts with dizziness.
previously Do not use nasal
controlled decongestants, OTC
diabetes. cold preparations
(stimulants) without
physician’s approval.
Restrict salt, alcohol
intake.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Clopidogrel Antiplatelet Inhibits binding of Unstable Active bleeding (e.g., Dizziness Agranulocytosis Obtain baseline
75 mg OD enzyme adenosine angina/non- peptic ulcer, Skin disorders Aplastic chemistries
phosphate (ADP) ST-segment intracranial Upper anemia/ Platelet count
to its platelet elevation MI. hemorrhage) respiratory pancytopenia PFA level
receptor and ST-segment tract infection Thrombotic Perform platelet counts
subsequent ADP- elevation, Cautions: Chest pain thrombocytopen before drug therapy,
mediated acute MI. Severe hepatic/renal Flu-like ia purpura Abrupt discontinuation
activation of a Recent MI, impairment symptoms (TTP) occur of drug therapy
glycoprotein stroke, or Pts at risk of Headache rarely produces elevated
complex. Inhibits established increased bleeding Arthralgia Hepatitis platelet count within 5
platelet peripheral Concurrent use of Fatigue Hypersensitivit days.
aggregation. arterial anticoagulants Edema y reaction Monitor platelet count
disease. Avoid concurrent Hypertension Anaphylactoid for evidence of
use of CYP2C19 Abdominal reaction have thrombocytopenia.
inhibitors. pain been reported. Assess Hgb, Hct, WBC;
Dyspepsia serum ALT, AST,
Diarrhea bilirubin, BUN,
Nausea creatinine;
Epistaxis signs/symptoms for
Dyspnea hepatic insufficiency
Rhinitis during therapy.
It may take longer to
stop bleeding during
drug therapy.
Report any unusual
bleeding.
Inform physicians,
dentists if clopidogrel is
being taken, esp. before
surgery is scheduled or
before taking any new
drug.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Diclofenac gel Analgesic, Inhibits Treatment of Asthmatic pts nausea, Rash Evaluate therapeutic
on affected anti- prostaglandin acute pain Hypersensitivity to stomach pain, Abdominal pain response by assessing
site every inflammatory. synthesis, intensity due to minor aspirin, diclofenac, upset Diarrhea pain, joint stiffness, joint
morning of pain stimulus strains, other NSAIDs stomach, Dark urine swelling and mobility.
reaching sensory sprains, CABG surgery ulcers, or Assess any worsening of
nerve endings. contusions. itching, asthma in appropriate
Produces Cautions: dryness, patients.
analgesic, anti- HF redness, Regular full dosage has
inflammatory Hypertension scaling, both lasting analgesic
effects. Renal/hepatic numbness and and anti-inflammatory
impairment tingling, effects, making it useful
cysts, for continuous pain
Hepatic porphyria
pimples, or associated with
History of GI
other inflammation.
disease
skin irritation Nurses should refer to
where the manufacturer’s
medicine was summary of product
applied characteristics and to
appropriate local
guidelines.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Paracetamol Antipyretics, Inhibits the Treatment of Previous Low fever Allergic reactio Assess patient’s fever or
500 mg 1 tab nonopioid synthesis of mild pain hypersensitivity Nausea n, which can pain: typeof pain, location,
per 6H analgesics prostaglandins that Fever Products containing cause a rash and intensity, duration,
Stomach pain temperature, and
may severe as alcohol, aspartame, swelling.
mediators of pain Loss of flushing, low diaphoresis.
saccharin, sugar, or Assess allergic reactions:
and fever, appetite blood pressure
tartrazine should be rash, urticaria; if these
primarily in the avoided in patients who Dark urine and a fast occur, drug may have to
CNS. Has no have hypersensitivity Clay-colored heartbeat be discontinued.
significant anti- intolerance to these stools. Teach patient to recognize
inflammatory compounds Jaundice (yell signs of chronic overdose:
properties or GI Severe hepatic owing of the bleeding, bruising,
toxicity. impairments/active skin or eyes). malaise, fever, sore throat.
liver disease Tell patient to notify
prescriber for pain/ fever
lasting for more than 3
days.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Erythromycin Antibiotic, Penetrates Treatment of Hepatic impairment Nausea Antibiotic- Monitor daily pattern of
antiacne. bacterial cell susceptible Concomitant Vomiting associated bowel activity, stool
membranes, infections administration with Diarrhea colitis consistency.
reversibly binds to Treatment of ergot derivatives Rash Super infections Assess skin for rash.
bacterial acne vulgaris Urticaria Reversible Assess for
ribosomes, Treatment of Cautions: cholestatic hepatotoxicity
inhibiting protein minor Elderly hepatitis may Be alert for
synthesis. bacterial skin Myasthenia gravis occur superinfection: fever;
infections Uncorrected High dosage in vomiting, diarrhea,
hypokalemia pts with renal anal/genital pruritus,
impairment may oral mucosal changes
lead to Check for phlebitis
reversible Monitor for high-dose
hearing loss hearing loss.
Ventricular
arrhythmias
Prolonged QT
interval occur
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Nicardipine Antianginal, Inhibits calcium Treatment of Advanced aortic Headache Overdose Concurrent therapy with
antihypertensi ion movement chronic stenosis Facial produces sublingual nitroglycerin
ve across cell stable flushing confusion may be used for relief of
membranes; anginas, Cautions: Peripheral Slurred speech angina pain.
depressing hypertension. Cardiac/renal/hepat edema Drowsiness Record onset, type,
contraction of HF ic dysfunction Light- Marked radiation, location,
cardiac, vascular Control HF headedness hypotension intensity, duration, of
smooth muscle. blood Hypertrophic Dizziness Bradycardia angina pain,
pressure in cardiomyopathy Asthenia precipitating factors.
acute Aortic stenosis Palpitations Monitor BP during and
ischemic Coronary artery Angina following IV infusion.
stroke disease Tachycardia Assess for peripheral
Nausea edema,
Portal hypertension
Abdominal Assess skin for facial
cramps flushing, dermatitis,
Dyspepsia rash.
Dry mouth Question for asthenia,
Rash headache.
Monitor LFT results.
Assess EKG, pulse for
tachycardia.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Isosorbide Antianginal Stimulates Prevention Hypersensitivity to Headache Blurred vision Record onset, type
dinitrate 30 intracellular cyclic and treatment nitrates, concurrent use Transient Severe (sharp, dull, squeezing),
mg OD guanosine angina. of sildenafil, tadalafil, flushing of orthostatic radiation, location,
monophosphate. verdenafil. face/neck, hypotension intensity, duration of
Relaxes vascular dizziness, manifested by anginal pain;
smooth muscle of Cautions: weakness, syncope, precipitating factors
atrial, venous Inferior wall MI, orthostatic pulselessness, (exertion, emotional
vasculature. head trauma, hypotension, cold/clammy stress).
Decreases preload, increased ICP, nausea, skin, and If headache occurs
afterload, cardiac orthostatic vomiting, diaphoresis has during management
oxygen demand. hypotension, blood restlessness. been reported. therapy, administer
volume depletion GI upset, Tolerance may medication with meals.
from diuretic blurred vision, occur with Assist with ambulation
therapy, systolic BP dry mouth. repeated, if light headedness,
less than 90 mmHg, Burning, prolonged dizziness occurs.
hypertrophic tingling at therapy, but Assess for facial/neck
cardiomyopathy. oral point of may not occur flushing.
dissolution. with extended- Monitor number of
release form. anginal episodes,
Minor tolerance orthostatic BP.
with Do not chew, crush,
intermittent use dissolve or divide
of sublingual sublingual, extended-
tablets. release-sustained-release
High dose tends forms.
to produce Take sublingual tablets
severe while sitting down.
headache. Go from lying to
standing slowly.
Dissolve sublingual
tablet under tongue; do
not swallow.
Avoid alcohol
Report signs/symptoms
of hypotension, angina.
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG ACTION ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Enoxaparin Anticoagulant Potentiates action Prevention of Active bleeding Injection site May lead to Obtain baseline CBC.
of antithrombin postop DVT Concurret hea\parin hematoma bleeding Note platelet count
III, inactivates surgery therapy Nausea complications Assess potential risk of
coagulation factor Acute ST- Hypersensitivity to Peripheral ranging from bleeding,
Xa. Produces segment heparin edema local Assess for any signs of
anticoagulantion. elevation Pork products ecchymoses to bleeding
Does not Treatment of Thrombocytopenia major Do not take any OTC
significantly acute associated with positive hemorrhage medication without
influence PT, coronary in vitro test for May cause consulting physician
aPTT. syndrome antiplatelet antibodies. heparin-induced Report unusual bleeding
Not for IM use. thrombocytopen or bruising.
ia
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Finding Love After Heartbreak EbookDokument201 SeitenFinding Love After Heartbreak EbookNancy Sarakikya100% (3)
- CITICOLINE, Drugs in MedicalDokument10 SeitenCITICOLINE, Drugs in MedicalInosanto May AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex 9. DSWD-RLA-F009 Work and Financial PlanDokument2 SeitenAnnex 9. DSWD-RLA-F009 Work and Financial PlanAli NamlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - Army TM 9 6115 729 24 Air Force To 35c2 3 519 2 Marine PDFDokument1.013 SeitenDokumen - Tips - Army TM 9 6115 729 24 Air Force To 35c2 3 519 2 Marine PDFABDUL QADIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument2 SeitenUntitledPRINCESS KOBAYASHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument2 SeitenName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Matthew SuperioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adu Drug Study Edited 1Dokument3 SeitenAdu Drug Study Edited 1Lerry Claire LimosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGstudyDokument2 SeitenDRUGstudyMahledJoy EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarlac State University College of Science Nursing DepartmentDokument5 SeitenTarlac State University College of Science Nursing DepartmentKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenBenztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyHamimah Bint AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse EffectDokument3 SeitenDrug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse EffectyssatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tramadol Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenTramadol Drug StudyPrincess Faniega SugatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study RLEDokument2 SeitenDrug Study RLEminezki44Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - Tramadol, Hyoscine-N-Butylbromide, Co-Trimoxazole, Potassium CitrateDokument4 SeitenDrug Study - Tramadol, Hyoscine-N-Butylbromide, Co-Trimoxazole, Potassium CitratemissmakaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study (Ify Okwuosa)Dokument4 SeitenDrug Study (Ify Okwuosa)ifyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AripiprazoleDokument2 SeitenAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AripiprazoleDokument2 SeitenAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selectively: Inhibitors Inhibit Serotonin Reuptake and Elicit An Antidepressan T ResponseDokument2 SeitenSelectively: Inhibitors Inhibit Serotonin Reuptake and Elicit An Antidepressan T ResponseDanii LuvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsDokument15 SeitenSubiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsNicole ObispoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Post PartumDokument3 SeitenDrugs Post PartumanreilegardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Name Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Drug Interaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument4 SeitenDrug Name Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Drug Interaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesJamaica Area Abella SenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDokument10 SeitenDrug Therapeutic RecordstrawberryNoch keine Bewertungen
- New!!Dokument10 SeitenNew!!Jeff Angelo ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crisostomo Micaela Nubain DSDokument3 SeitenCrisostomo Micaela Nubain DSMicaela CrisostomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugstudy - OsteoarthritisDokument3 SeitenDrugstudy - OsteoarthritisLizli Loredo100% (1)
- DoxofyllineDokument2 SeitenDoxofylline3C LAGRANA, Rea Lyn F.Noch keine Bewertungen
- HALOPERIDOLDokument1 SeiteHALOPERIDOLAlyxen Pelingen75% (4)
- Tramadol Drug Study PDFDokument3 SeitenTramadol Drug Study PDFMa. Eloisa YrogirogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Care For Mca LabDokument1 SeiteDrug Study Care For Mca LabAlessandro MadrigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indication and DosagesDokument2 SeitenIndication and DosagesloveskissesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Make A Drug Study On The Medications Given To JaneDokument2 SeitenMake A Drug Study On The Medications Given To JaneYoko Mae YanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Mcp1Dokument2 SeitenDrugs Mcp1Ahrjey DUey PanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrilDokument2 SeitenGENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrildanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing AlertDokument3 SeitenDrug Study: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing AlertkingpinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - Ibuprofenanon-326479Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyRuby Mae AguavivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteDrug StudyMarichu BajadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyzenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiazepamDokument3 SeitenDiazepamGwyn RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ClozapineleponexDokument1 SeiteClozapineleponexAaron Paul RomualdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluphenazine Drug Study - DoxDokument3 SeitenFluphenazine Drug Study - Doxan naNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effector OrganDokument2 SeitenEffector OrganCamille De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Format EheheDokument17 SeitenDrug Study Format EhehejesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demerol DrugDokument2 SeitenDemerol DrugMsOrange100% (1)
- Drugs Can Affects The CnsDokument9 SeitenDrugs Can Affects The CnsDayan CabrigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 2 Narcotics & NMJDokument7 SeitenActivity 2 Narcotics & NMJKristineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument17 SeitenDrug StudyTherese ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDokument9 SeitenName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsJaysellePuguonTabije100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY - SALBUTAMOL (Revised)Dokument2 SeitenDRUG STUDY - SALBUTAMOL (Revised)Jelaveil De VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Case AnalysisDokument7 SeitenDrug Study Case AnalysisNine SaguiboNoch keine Bewertungen
- IX. Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenIX. Drug StudyRizza ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: College of NursingDokument3 SeitenDrug Study: College of NursingA.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: College of NursingDokument3 SeitenDrug Study: College of NursingA.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 4Dokument9 SeitenDrug Study 4bobo gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyAlmiah MaruhomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Task - Week 7Dokument34 SeitenCourse Task - Week 7JoelynMacalintalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonilla Drug Study 2 20Dokument9 SeitenBonilla Drug Study 2 20YLA KATRINA BONILLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug Studyunkown userNoch keine Bewertungen
- LortabDokument2 SeitenLortabKatie McPeek100% (1)
- DS GadDokument2 SeitenDS Gadbianca musicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quetiapine Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenQuetiapine Drug StudyEula Angelica Oco100% (1)
- ClonidineDokument1 SeiteClonidineYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formulating Theoretical/Concep Tual FrameworksDokument33 SeitenFormulating Theoretical/Concep Tual FrameworksIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Method ResearchDokument19 SeitenMixed Method ResearchIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Research: Prepared By: Mark Angelo Cristino, RN, ManDokument12 SeitenEthical Research: Prepared By: Mark Angelo Cristino, RN, ManIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhancing Rigor in Quantitative ResearchDokument21 SeitenEnhancing Rigor in Quantitative ResearchIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bemonc: Basic Emergency Obstetric and Newborn CareDokument32 SeitenBemonc: Basic Emergency Obstetric and Newborn CareIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women and Childre N's RightsDokument10 SeitenWomen and Childre N's RightsIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- REDCOPDokument4 SeitenREDCOPIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Baby FNCPDokument7 SeitenWell Baby FNCPIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHINGLESDokument27 SeitenSHINGLESIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Voluntary Blood Services ProgramDokument9 SeitenNational Voluntary Blood Services ProgramIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- FilariasisDokument23 SeitenFilariasisIzhra MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- POLIOMYELITISDokument26 SeitenPOLIOMYELITISIzhra Margate100% (1)
- StrongyloidiasisDokument24 SeitenStrongyloidiasisIzhra Margate0% (1)
- GMDSS Exam Schedule For Year 2022Dokument7 SeitenGMDSS Exam Schedule For Year 2022Mani ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terhadap Pelibatan Intelijen Negara Dalam Penanganan Covid-19 Di IndonesiaDokument18 SeitenTerhadap Pelibatan Intelijen Negara Dalam Penanganan Covid-19 Di IndonesiaheriandikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Un MLT 86 PDFDokument273 SeitenUn MLT 86 PDFNicolás SaccoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALT GPT (IFCC) Single Vial: BiolaboDokument2 SeitenALT GPT (IFCC) Single Vial: Biolabowindy ajengNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Usmle Cs2Dokument27 Seiten"Usmle Cs2Drbee10Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of Critical ThinkingDokument2 SeitenThe Art of Critical ThinkingAmeer Youseff MarotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 14001: Identifying and Evaluating Environmental Aspects: N131206 VERSION OF 14 J U LY 2014Dokument34 SeitenISO 14001: Identifying and Evaluating Environmental Aspects: N131206 VERSION OF 14 J U LY 2014jaskaran singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ihssan Tahir RNDokument5 SeitenIhssan Tahir RNapi-574405992Noch keine Bewertungen
- MicroDokument65 SeitenMicroHafiz UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancel Keys - Atherosclerosis: A Problem in Newer Public HealthDokument22 SeitenAncel Keys - Atherosclerosis: A Problem in Newer Public Healthacolpo100% (1)
- Human Body - A Visual Encyclopedia - Brown, Morgan, Walker, Woodward (DK Publishing 2012 9780756693077 Eng) PDFDokument258 SeitenHuman Body - A Visual Encyclopedia - Brown, Morgan, Walker, Woodward (DK Publishing 2012 9780756693077 Eng) PDFchbenengeli94% (17)
- PJ Nicholoff Steroid ProtocolDokument6 SeitenPJ Nicholoff Steroid ProtocolYanna RizkiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maggi FinalDokument10 SeitenMaggi FinalDeepak Singh NegiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlanAlvin DagumbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiparkinson DrugsDokument19 SeitenAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Nursing AbbreviationsDokument8 SeitenCommon Nursing AbbreviationsHana-Lou Taquiqui100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal and HepatobiliaryDokument54 SeitenGastrointestinal and Hepatobiliaryjeshema100% (2)
- Strength BiasDokument11 SeitenStrength BiasnmosilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tito IRBRPDokument13 SeitenTito IRBRPTito TiehiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Day Trial Pack Manual USENDokument13 Seiten3 Day Trial Pack Manual USENCristiano AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correcting Mold MisinformationDokument8 SeitenCorrecting Mold MisinformationhazmatlinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- BarbituratesDokument5 SeitenBarbituratesGlenn Mark Frejas RinionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaitlin Bateman CV 2015Dokument2 SeitenKaitlin Bateman CV 2015api-222304611Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spleen PercussionDokument13 SeitenSpleen PercussionRatusweethella Intan Yudagrahania PuspitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coat DiseaseDokument24 SeitenCoat DiseaseRaissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International JournalDokument5 SeitenInternational JournalPutri Nur HandayaniNoch keine Bewertungen