Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Els Lc11 Lc12
Hochgeladen von
Ana Maria Gerson Tongco0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
33 Ansichten1 Seiteweathering of rocks
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenweathering of rocks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
33 Ansichten1 SeiteEls Lc11 Lc12
Hochgeladen von
Ana Maria Gerson Tongcoweathering of rocks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
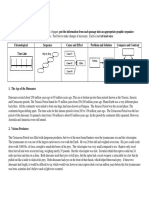
Learning Competency 11: Describe how rocks undergo weathering Streams- flowing water will lift and carry
l lift and carry small sediments such as silt and
Learning Competency 12: Explain how the products of weathering are sand
carried away by erosion and deposited elsewhere Stream Erosion and Deposition
Where water moves more swiftly there will be more erosion.
Continental Drift Theory - proposed by Alfred Wegener Where the water slows down, sediments will be deposited.
- the Earth was once a giant landmass called Pangaea Ocean Dynamics - tidal action and waves carry away weathered materials
Weathering- the process of breaking down rocks into smaller pieces called Types of Erosion
sediments 2. Wind erosion - happens when light materials, such as small rocks and
Types of Weathering pebbles, are carried by wind to different places
1. Mechanical weathering - a process wherein rocks are broken down Wind Transport of Sediments
into smaller pieces without changing its chemical composition due Wind will carry fine, dry sediments over long distances.
to different temperatures and water Wind Transport of Dust
- Example: rocks in the highway develop cracks and small fractures Transport by Gravity
because of too much exposure to heat When sediments are weathered they may be transported downward by
gravity. The general term for this is mass wasting. When sediments are
2. Chemical weathering - a process wherein rock materials are changed weathered they may be transported downward by gravity as a slump.
into other substances that have different physical and chemical Loose sediments transported by gravity are called scree.
compositions 3. Glacial erosion- happens when the ice moves downhill and plucks out
- some agents of chemical weathering include water, strong acids, chunks of rocks and causes scraping between the ice and the rock
and oxygen - plucking and scraping can lead to the development of other landforms if,
- water hydrates and breaks the minerals in the rocks through the for example, the glaciers hit a mountain and erode it
process of hydrolysis Glaciers
- oxygen combines with metals to produce oxides while acids from Glacial ice drags rocky material that scours the surface it flows over . The
vents and volcanoes increase the speed of weathering process glacier deposits debris as it melts.
- Example: when rainwater hydrolyzed the feldspar minerals to Glaciers are large ice fields that slowly flow downhill over time.
form clay minerals 4. Soil erosion
3. Biological weathering- a process when living things, such as insects and - happens when the top soil is removed and leaves the soil infertile
roots of the trees, contribute to the disintegration of rock materials - this is caused by wind or flood in an area
- Example: mosses and fungi that grow on rocks produce weak Deposition
acids that can destroy or dissolve the rocks - the laying down of sediments to its depositional environment or final
Erosion- the transportation of weathered rocks Destination
- agents like running water or rivers, wind, gravity, groundwater, wave - the depositional environment can be continental, coastal, or marine
currents, and glaciers contribute to erosion • continental includes streams, swamps, caves, and deserts
Types of Erosion • coastal includes lagoons, estuaries, and deltas
1. Water erosion - a type of erosion where the water carries the • marine includes slopes and bottom of the ocean or abyssal zone
sediments to different parts of the bodies of water such as rivers Deposition Formation- transported sediments are deposited in layers and
generate strata like those found in the Grand Canyon
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nature Is a Sculptor: Weathering and ErosionVon EverandNature Is a Sculptor: Weathering and ErosionNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEATHERINGDokument3 SeitenWEATHERINGMarilou Chalanao EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureVon EverandKid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic Processes: WeatheringDokument56 SeitenExogenic Processes: WeatheringVicki Punzalan100% (1)
- Weathering Erosion StemscopediaDokument6 SeitenWeathering Erosion Stemscopediaapi-506851645Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Quiz 6 ReviewerDokument2 SeitenEarth and Life Quiz 6 Revieweririshpajarillaga13Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3 Earth's ProcessesDokument4 Seiten1.3 Earth's ProcessesRufo FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument3 SeitenChapter 6Xiao ZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth ScienceDokument4 SeitenEarth ScienceTae BearNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic ProcessDokument4 SeitenExogenic Processkhayceemeade2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic ProcessesDokument40 SeitenExogenic ProcessesKristineMaeFernandezCarmeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic Process EalsDokument4 SeitenExogenic Process EalsSamantha EspinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Module 2Dokument11 SeitenGeology Module 2Marilou Chalanao EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewerDokument16 SeitenReviewerMark OximasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kim GulapaDokument2 SeitenKim GulapaFrederick FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic Process - Process Which Occur On Earth's Surface Due To The Influence of Exogenic ForcesDokument7 SeitenExogenic Process - Process Which Occur On Earth's Surface Due To The Influence of Exogenic ForcesAngelbec TabaconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: Exogenic ProcessesDokument8 SeitenChapter 5: Exogenic ProcessesSevy MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Natural ProcessDokument45 SeitenEarth Natural ProcessJosh FuriscalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5. Endogenic and Exogenic ProcessesDokument27 SeitenLesson 5. Endogenic and Exogenic ProcessesMa Melissa DelavinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic Process ReviewerDokument1 SeiteExogenic Process ReviewerSharlize Veyen RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2.2 Exogenic ProcessesDokument31 SeitenChapter 2.2 Exogenic ProcessesLeonessa CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic Processes: Earth Materials and ProcessesDokument41 SeitenExogenic Processes: Earth Materials and Processesanon_26027812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic Process HandoutsDokument6 SeitenExogenic Process HandoutsMG GadonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth ProcessesDokument25 SeitenEarth ProcessesMary Ann FactorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geographical Processes Earth ScienceDokument4 SeitenGeographical Processes Earth ScienceoctavianojanineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weathering and Erosion PPT (ABMHUMMS)Dokument89 SeitenWeathering and Erosion PPT (ABMHUMMS)myrrdane100% (3)
- Earth Science ReviewerDokument11 SeitenEarth Science ReviewerGemzsar BacualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Els Week 6Dokument3 SeitenEls Week 6Jessica BorromeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6, Weathering, Erosion, and DepositionDokument6 SeitenUnit 6, Weathering, Erosion, and DepositionYohana ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Geomorphic ProcessDokument10 SeitenThe Geomorphic Processrosana f.rodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science: WeatheringDokument85 SeitenEarth Science: WeatheringElijah Raphael YasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weathering Describes The Breaking Down Or: I. General Geology WeatheringDokument3 SeitenWeathering Describes The Breaking Down Or: I. General Geology WeatheringJanina Frances RuideraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1. Weathering: Chapter 5: Surface and Earth ProcessesDokument15 Seiten5.1. Weathering: Chapter 5: Surface and Earth ProcessesdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic ProcessDokument5 SeitenExogenic ProcessKim AllyzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Test 21stDokument4 SeitenPre Test 21stHanna cayogyogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weathering and ErosionDokument39 SeitenWeathering and ErosionVerniel Jason JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology ReportDokument76 SeitenGeology ReportPrime Rose CutaonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic and Endogenic Processes NotesDokument10 SeitenExogenic and Endogenic Processes NotesMargaret SesaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dtw.9.wheathering and DenudationDokument5 SeitenDtw.9.wheathering and DenudationniroopswaradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orca Share Media1693631053377 7103603501707130609Dokument18 SeitenOrca Share Media1693631053377 7103603501707130609Joshua T. CederiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endogenous and Exogenous P Rocesses: Mr. L.A - Fronda, LPTDokument26 SeitenEndogenous and Exogenous P Rocesses: Mr. L.A - Fronda, LPTMeann OberioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1: Exogenic ProcessesDokument5 SeitenLesson 1: Exogenic ProcessesSelene HmpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Module 3 ReviewerDokument5 SeitenGeology Module 3 ReviewerElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELS Geological ProcessDokument139 SeitenELS Geological ProcessHannah AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Earth's ProcessesDokument10 SeitenExternal Earth's Processesshannon.tuan02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gte 1Dokument20 SeitenGte 1Samta TayadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic Processes 2ND GRADINGDokument4 SeitenExogenic Processes 2ND GRADINGkarylle.garrafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenic ProcessesDokument17 SeitenExogenic ProcessesAngelica SeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WeatheringDokument40 SeitenWeatheringtjeremyalleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth ScienceDokument3 SeitenEarth Scienceallan celedonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Forces Shaping The EarthDokument11 SeitenExternal Forces Shaping The EarthJesse RamroopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Midterm ReviewerDokument5 SeitenScience Midterm ReviewerAuberyn ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science Week 5Dokument47 SeitenEarth Science Week 5Brenan BaltazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Geology 2Dokument16 SeitenGeneral Geology 2Jayse SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Geology 2Dokument16 SeitenGeneral Geology 2Jayse SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Chapter FourDokument42 SeitenGeology Chapter FourYoni RebumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science: WeatheringDokument4 SeitenEarth Science: WeatheringLucky GeminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weathering Erosion and TransportationDokument22 SeitenWeathering Erosion and TransportationchetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Week 2 Origin of SoilDokument12 Seiten2 Week 2 Origin of SoilBrylle JamenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Mechanicsclass 1Dokument2 SeitenSoil Mechanicsclass 1SUNILKHUNTIA1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Development Worksheets WK 1 - 1Dokument7 SeitenPersonal Development Worksheets WK 1 - 1Ana Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk13 - Solve The Following - ActivityDokument18 Seitenwk13 - Solve The Following - ActivityAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk13 - Gravitational ForceDokument18 Seitenwk13 - Gravitational ForceAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk16 - Photon Theory - Galileo RoemerDokument28 Seitenwk16 - Photon Theory - Galileo RoemerAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk15 LIGHTDokument54 Seitenwk15 LIGHTAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 13 - CellsDokument30 SeitenWeek 13 - CellsAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk13 - Gravitational ForceDokument18 Seitenwk13 - Gravitational ForceAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW - wk14 - Project Proposl - BDokument5 SeitenRW - wk14 - Project Proposl - BAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk12 - Motion - Chapter TestDokument41 Seitenwk12 - Motion - Chapter TestAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk12 - Motion - Chapter TestDokument41 Seitenwk12 - Motion - Chapter TestAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk11 - MotionSpeedVelocity and AccelerationDokument40 Seitenwk11 - MotionSpeedVelocity and AccelerationAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW - wk14 - Position Paper - CDokument5 SeitenRW - wk14 - Position Paper - CAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- wk11 - MotionSpeedVelocity and AccelerationDokument40 Seitenwk11 - MotionSpeedVelocity and AccelerationAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW - wk14 - Project Proposl - BDokument5 SeitenRW - wk14 - Project Proposl - BAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW wk12 BDokument16 SeitenRW wk12 BAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Text Structure 2Dokument2 SeitenIdentifying Text Structure 2api-328694348Noch keine Bewertungen
- RW - wk11 Writing ActivityDokument3 SeitenRW - wk11 Writing ActivityAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Text Structure 2Dokument2 SeitenIdentifying Text Structure 2api-328694348Noch keine Bewertungen
- RW wk12 BDokument16 SeitenRW wk12 BAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW wk12 BDokument16 SeitenRW wk12 BAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW wk10 BDokument12 SeitenRW wk10 BAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Structure 3Dokument4 SeitenText Structure 3api-328694348Noch keine Bewertungen
- RW Quiz wk1 To wk5Dokument18 SeitenRW Quiz wk1 To wk5Ana Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Text StructureDokument2 SeitenIdentifying Text StructureTíff ẶŋŷNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK 13 Intro To LifeDokument51 SeitenWK 13 Intro To LifeAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Structures Activity Sheets From e ReadingDokument1 SeiteText Structures Activity Sheets From e ReadingAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW wk5Dokument38 SeitenRW wk5Ana Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ReadingDokument24 SeitenCritical ReadingAdrian SanicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW wk9 ExplicitandimplicitDokument36 SeitenRW wk9 ExplicitandimplicitAna Maria Gerson TongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engpropertiesofwell Writtentext 180224135654 PDFDokument53 SeitenEngpropertiesofwell Writtentext 180224135654 PDFjulie portacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPSC Decoding SyllabusDokument32 SeitenUPSC Decoding Syllabuslipu das100% (3)
- FullDokument395 SeitenFullIkee NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Layers of Rocks (Stratified Rocks) Are FormedDokument23 SeitenHow Layers of Rocks (Stratified Rocks) Are FormededricNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Rock Cycle & Igneous Rocks (B)Dokument13 Seiten4 - Rock Cycle & Igneous Rocks (B)Saad AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igneous RockDokument2 SeitenIgneous RockVenice EdañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Looking For Yemen's Hidden TreasureDokument18 SeitenLooking For Yemen's Hidden Treasurehasanriaz361100% (2)
- Rock PDFDokument288 SeitenRock PDFRahul BarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sdea Mock Test 045Dokument6 SeitenSdea Mock Test 045Pritam MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Earth Science: Name - Class - DateDokument69 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Earth Science: Name - Class - DateIsaiah DouglasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vol 1 3drillingDokument12 SeitenVol 1 3drillingVamshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Western ArtDokument52 SeitenWestern ArtObed CapunongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Science Eog Study GuideDokument11 Seiten8th Science Eog Study Guideapi-353567032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lectura RocasDokument20 SeitenLectura RocasAndres NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three: Bearing Capacity of Soils (Shallow Foundations)Dokument15 SeitenChapter Three: Bearing Capacity of Soils (Shallow Foundations)Wubetie MengistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Oil and GasDokument35 SeitenFundamentals of Oil and GasPhilippe HittiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engg - GeologyDokument49 SeitenEngg - GeologyKyaw Zin HeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce2131 Geology For Civil Engineers PDFDokument129 SeitenCe2131 Geology For Civil Engineers PDFnicole b75% (4)
- Models For Volcanic-Hosted Epithermal Precious Metal Deposits A ReviewDokument11 SeitenModels For Volcanic-Hosted Epithermal Precious Metal Deposits A ReviewOrlando B Santa CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Candelaria Punta Del Cobre IOCG Deposits PDFDokument27 Seiten08 Candelaria Punta Del Cobre IOCG Deposits PDFDiego Morales DíazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Geochemical Methods in Geothermal ExplorationDokument12 SeitenApplication of Geochemical Methods in Geothermal ExplorationJuan JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Bsce 2 Non StemDokument24 SeitenGeology Bsce 2 Non Stemhax turdleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Classiifcation System Part 1Dokument52 SeitenRock Classiifcation System Part 1CRYSTAL AMOR DELIGERONoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarrying ExplainedDokument3 SeitenQuarrying ExplainedTanmay ShrimaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling TechnologyDokument267 SeitenDrilling TechnologyAndreas BastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Mining PDFDokument6 SeitenChapter 6 Mining PDFhamza zalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 002-KLH-GMP Geology and Sedimentary RocksDokument66 Seiten002-KLH-GMP Geology and Sedimentary RocksFibri BalunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Communication Uses Various Strategies in Order To Avoid Communication BreakdownDokument16 SeitenOral Communication Uses Various Strategies in Order To Avoid Communication BreakdownRuth MuldongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letest Final Year Project Special For PrintingDokument127 SeitenLetest Final Year Project Special For Printinggolicha jarsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile PDFDokument436 SeitenPile PDFAnonymous v1blzDsEWANoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 - Rocks and Weathering - The Rock CycleDokument10 SeitenYear 8 - Rocks and Weathering - The Rock CycleBioScMentor-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessVon EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (33)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionVon EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (811)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesVon EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (21)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersVon EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldVon EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterVon EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsVon EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (65)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutVon EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (142)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeVon EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (19)
- The Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Von EverandThe Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsVon EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (13)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsVon EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (223)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogVon EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeVon EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)