Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Keywords-Battery Thermal Management System, Li Ion Battery Cooling, Passive Battery Air Cooling
Hochgeladen von
yogesh shindeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Keywords-Battery Thermal Management System, Li Ion Battery Cooling, Passive Battery Air Cooling
Hochgeladen von
yogesh shindeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ABSTRACT
The depletion of non-renewable energy resources is compelling us to search and innovate for
the more reliable options. The reduction in the use of petroleum in the automobiles can
significantly affect the use of non-renewable energy resources. In the long run, Electric vehicles
are the best alternatives to the conventional IC engine automobiles. In electric vehicles, lithium-
ion batteries are most commonly used as an energy source due to their high energy density,
high capacity, and low self-discharge rate. During discharging, excessive heat generation inside
the battery will lead to thermal runaway. To operate efficiently, these batteries should be
maintained within the desired temperature range of 20oC to 40oC. Among the various cooling
methods, in this study air cooling is adopted. The battery pack is discharged at various constant
C ratings. The effect of air flow rate on the battery surface temperature is studied with
experimentation. Heat transfer coefficient is calculated by considering the average surface
temperature of the battery as the wall surface temperature. The CFD analysis is done by
considering steady state condition and boundary conditions are taken with experimental
observations. Experimental results are compared with CFD results with appropriate
approximations.
Keywords- Battery thermal management system, Li ion battery cooling, passive battery air
cooling.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Off-grid & On-grid Design Solar Systems from Scratch: Bonus: Guide to Project Design in Autodesk© Autocad©.Von EverandBasic Off-grid & On-grid Design Solar Systems from Scratch: Bonus: Guide to Project Design in Autodesk© Autocad©.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Thermal Management of Lithiumion Batteries For Electric VehiclesDokument12 SeitenThermal Management of Lithiumion Batteries For Electric Vehiclestoldo sanalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0360544221027353 Main@@Dokument16 Seiten1 s2.0 S0360544221027353 Main@@tahreem hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Themal Management of Li-Ion Battery (Report 1)Dokument9 SeitenThemal Management of Li-Ion Battery (Report 1)NIKHIL ATUL NARALENoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Reports: Y. Lyu, A.R.M. Siddique, S.H. Majid, M. Biglarbegian, S.A. Gadsden, S. MahmudDokument6 SeitenEnergy Reports: Y. Lyu, A.R.M. Siddique, S.H. Majid, M. Biglarbegian, S.A. Gadsden, S. MahmudVishal ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Recuperative Cooling of Li-Ion Batteries in Electric VehiclesDokument5 SeitenA Review On Recuperative Cooling of Li-Ion Batteries in Electric VehiclesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing and CFD Analysis of Two-Wheeler Electric Vehicle BatteryDokument16 SeitenDesigning and CFD Analysis of Two-Wheeler Electric Vehicle BatterySikander Ahmed JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies 16 02196Dokument23 SeitenEnergies 16 02196antony johnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Optimization of Lithium-Ion Battery For Improving Thermal Performance Based On A Liquid Cooling SystemDokument9 SeitenStructural Optimization of Lithium-Ion Battery For Improving Thermal Performance Based On A Liquid Cooling SystemSrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symmetry 14 02126 v3Dokument19 SeitenSymmetry 14 02126 v3Jicheng PiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S037877531730959X MainDokument13 Seiten1 s2.0 S037877531730959X MainGabriel AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Power Sources: Kailong Liu, Kang Li, Cheng ZhangDokument14 SeitenJournal of Power Sources: Kailong Liu, Kang Li, Cheng Zhangyasvanthkumar sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Review On Thermal ManagementDokument11 SeitenDetailed Review On Thermal Managementvinay shimpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiator Heat DissipationDokument13 SeitenRadiator Heat DissipationValentina Mejia GallonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Science and Technology, An International JournalDokument13 SeitenEngineering Science and Technology, An International JournalSazib MollikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Energy Storage: SciencedirectDokument23 SeitenJournal of Energy Storage: Sciencedirecttahreem hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- FluidsDokument21 SeitenFluidsSikander Ahmed JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batteries: Thermal Analysis of Cold Plate With Di Configurations For Thermal Management of A Lithium-Ion BatteryDokument11 SeitenBatteries: Thermal Analysis of Cold Plate With Di Configurations For Thermal Management of A Lithium-Ion BatteryHarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies: Battery Thermal Management Systems: Current Status and Design Approach of Cooling TechnologiesDokument32 SeitenEnergies: Battery Thermal Management Systems: Current Status and Design Approach of Cooling TechnologiesAnjali prajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Pre-Proofs: Applied Thermal EngineeringDokument32 SeitenJournal Pre-Proofs: Applied Thermal EngineeringPavan Kumar NarendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Energy Storage: SciencedirectDokument25 SeitenJournal of Energy Storage: Sciencedirecttahreem hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1359431118343965 Main - &&&Dokument12 Seiten1 s2.0 S1359431118343965 Main - &&&tahreem hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Thermal ManagementDokument20 SeitenBattery Thermal ManagementvadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batteries 08 00179Dokument20 SeitenBatteries 08 00179moonstarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exhaust Gas Heat Recovery Power GenerationDokument52 SeitenExhaust Gas Heat Recovery Power GenerationabhinavkarthickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies in Thermal EngineeringDokument11 SeitenCase Studies in Thermal EngineeringRahmat Iman MainilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Temp Prediction Model Under Diff Cooling ModesDokument11 SeitenInternal Temp Prediction Model Under Diff Cooling ModesOsama SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Cooling in A Battery Pack (Ansys)Dokument18 SeitenAnalysis of Cooling in A Battery Pack (Ansys)tamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- (1553779X - International Journal of Emerging Electric Power Systems) Development of Thermal Model For Estimation of Core Temperature of BatteriesDokument11 Seiten(1553779X - International Journal of Emerging Electric Power Systems) Development of Thermal Model For Estimation of Core Temperature of BatteriesShiv KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management System Using Thermoelectric Module and Microcontroller.Dokument13 SeitenLithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management System Using Thermoelectric Module and Microcontroller.Aniket DusaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONVERGE FOR BATTERIES - DESIGNING SAFER BATTERIES THROUGH SIMULATION - CONVERGE CFD SoftwareDokument5 SeitenCONVERGE FOR BATTERIES - DESIGNING SAFER BATTERIES THROUGH SIMULATION - CONVERGE CFD SoftwaretamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies: Analysis of Cooling Effectiveness and Temperature Uniformity in A Battery Pack For Cylindrical BatteriesDokument17 SeitenEnergies: Analysis of Cooling Effectiveness and Temperature Uniformity in A Battery Pack For Cylindrical BatteriesThuận Vũ ĐìnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Thermal Engineering: Chuanjin Lan, Jian Xu, Yu Qiao, Yanbao MaDokument9 SeitenApplied Thermal Engineering: Chuanjin Lan, Jian Xu, Yu Qiao, Yanbao MaRafael MacedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Investigation On A Thermoelectric Cooler ForDokument11 SeitenExperimental Investigation On A Thermoelectric Cooler ForJoshua Roberto GrutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symmetry 15 01322Dokument30 SeitenSymmetry 15 01322imagine dragonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of The Effects of Preheating On Discharge Characteri - 2024 - Journal of EDokument10 SeitenStudy of The Effects of Preheating On Discharge Characteri - 2024 - Journal of Emosab.backkupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalkan 2021Dokument13 SeitenKalkan 2021mayankGITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies 11 02856Dokument27 SeitenEnergies 11 02856himmafirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesma 0704, IJEASTDokument11 SeitenTesma 0704, IJEASTFatehsingh parabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction of Industrial Battery ChargerDokument33 SeitenConstruction of Industrial Battery ChargerPETERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Paper On CFD Analysis of Electrical Vehicle Battery PackDokument4 SeitenReview Paper On CFD Analysis of Electrical Vehicle Battery PackSikander Ahmed JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Novel Design Approach For Small Scale Low Enthalpy Binary GeothermalDokument10 SeitenA Novel Design Approach For Small Scale Low Enthalpy Binary GeothermalDidit Setyo PamujiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind-to-Wheel Energy Assessment: Patrick Mazza and Roel HammerschlagDokument8 SeitenWind-to-Wheel Energy Assessment: Patrick Mazza and Roel HammerschlagkramtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergiesDokument14 SeitenEnergiesRichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies 09 00320Dokument14 SeitenEnergies 09 00320jorlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models - Bfc.li Battery Thermal 2d AxiDokument16 SeitenModels - Bfc.li Battery Thermal 2d AxijehadyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Methods ComparisonDokument9 SeitenCooling Methods Comparisonvinay shimpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EffectOfThermo PhysicalpropertDokument17 SeitenEffectOfThermo Physicalproperthache eseeseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Energies-14-04187Dokument19 Seiten2 Energies-14-04187shubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Thermal Model and Simulation For A Cylindrical Li-Ion BatteryDokument8 SeitenFinite Element Thermal Model and Simulation For A Cylindrical Li-Ion BatteryEashan PendseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Thermal Management in EVs and HEVsDokument10 SeitenBattery Thermal Management in EVs and HEVsSant NientNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Design of Air Flow Configuration For Cooling Lithium Ion Battery in Hybrid Electric VehiclesDokument7 SeitenA Design of Air Flow Configuration For Cooling Lithium Ion Battery in Hybrid Electric VehiclesdftghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research On Control Strategy of Rapid Preheating For Pow 2024 Applied ThermaDokument11 SeitenResearch On Control Strategy of Rapid Preheating For Pow 2024 Applied Thermamosab.backkupNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0196890421003216 MainDokument13 Seiten1 s2.0 S0196890421003216 Mainzhaocr2018Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling and Simulation of Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Leena. O, Dr. Jyoti.P.KoujalagiDokument10 SeitenModelling and Simulation of Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Leena. O, Dr. Jyoti.P.KoujalagiinventionjournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0196890419311823 MainDokument13 Seiten1 s2.0 S0196890419311823 Mainzhaocr2018Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0017931017350391 MainDokument14 Seiten1 s2.0 S0017931017350391 MainAnıl TAŞKINNoch keine Bewertungen
- BatteryDokument18 SeitenBatterysafal shaNoch keine Bewertungen
- REDEC 2020 (Saqli)Dokument7 SeitenREDEC 2020 (Saqli)Antonio BatataNoch keine Bewertungen
- DE102005052974B4 - Double Walled Pipe - Google Patents PDFDokument9 SeitenDE102005052974B4 - Double Walled Pipe - Google Patents PDFyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name - Roll No-Answer C: A. 10.36 KW B. 11.3 KW C. 7.068 KW D. 9.12 KWDokument2 SeitenName - Roll No-Answer C: A. 10.36 KW B. 11.3 KW C. 7.068 KW D. 9.12 KWyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIS Oil Separator Standard CommnetsDokument1 SeiteBIS Oil Separator Standard Commnetsyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set C) : SR No. AnsDokument6 SeitenRdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set C) : SR No. Ansyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set B) : SR NoDokument7 SeitenRdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set B) : SR Noyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set B) : SR NoDokument7 SeitenRdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set B) : SR Noyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set B) : SR NoDokument7 SeitenRdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set B) : SR Noyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient Indian ScienceDokument23 SeitenAncient Indian Scienceyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set A) : SR No. AnsDokument7 SeitenRdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set A) : SR No. Ansyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set C) : SR No. AnsDokument6 SeitenRdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set C) : SR No. Ansyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set A) : SR No. AnsDokument7 SeitenRdiation and Heat Exchanger Mcqs (Set A) : SR No. Ansyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
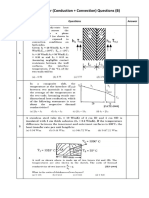
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set DDokument4 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Dyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set ADokument3 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Ayogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set CDokument3 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Cyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set ADokument3 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Ayogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set DDokument4 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Dyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set ADokument3 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Ayogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set DDokument4 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Dyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set BDokument3 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set Byogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
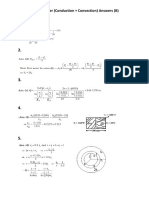
- Conduction and Convection 15 Questions Set B AnswersDokument4 SeitenConduction and Convection 15 Questions Set B Answersyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction MCQsDokument4 SeitenConduction MCQsyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction MCQsDokument4 SeitenConduction MCQsyogesh shindeNoch keine Bewertungen