Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
5A Chemical Bonds - Answer
Hochgeladen von
Wong Wai Lun100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
311 Ansichten3 SeitenOriginaltitel
5A Chemical Bonds- Answer
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
311 Ansichten3 Seiten5A Chemical Bonds - Answer
Hochgeladen von
Wong Wai LunCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
MARKING SCHEME - CHEMICAL BONDS
ACTIVITY ANSWERS
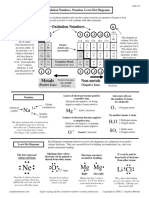
1 No.1 Inert, monoatomic, stable, duplet, arrangement
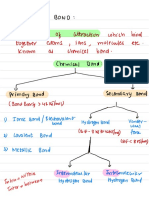
2 Chemical bonds
3 (i) ionic (ii) covalent , sharing
2 1 (i) donates, positive (ii) non-metal, negative
2(a)
(b) 2-
3 1 • Electron arrangement of sodium atom is 2.1
• A sodium atom donates one electron to achieve the stable electron
arrangement which is 2.8.
• Sodium ion, Na+ , is formed
• Electron arrangement of chlorine atom is 2.8.7
• Electron from sodium atom is transferred to a chlorine atom
• A chlorine atom receives/gains electron from sodium atom to achieve
the stable electron arrangement which is 2.8.8
• Chloride ion, Cl- is formed
• The sodium ion, Na + and chloride ion, Cl − formed are attracted to
one another to form an ionic compound sodium chloride, NaCl .
• The strong electrostatic forces between the opposite-charged ions is
called ionic bond.
2 Refer to page 86 - F4 Chemistry text book for guidance
3(a) • Electron arrangement of magnesium atom is 2.8.2
• A magnesium atom donates two electrons to achieve the stable
electron arrangement which is, 2.8.
• Magnesium ion, Mg2+ is formed
• Electron arrangement of chlorine atom is 2.8.7
• Electrons from magnesium atom is transferred to two chlorine atoms
• A chlorine atom receives/ gains electron from magnesium atom to
achieve the stable electron arrangement which is 2.8.8.
• Chloride ion, Cl- is formed
• The magnesium ion,Mg2+ and two chloride ions, Cl − formed are
attracted to one another to form an ionic compound magnesium
chloride, MgCl2
• The strong electrostatic forces between the opposite-charged ions is
called ionic bond
(b) Refer to page 86 - F4 Chemistry text book
4 1 Non-metal, share, stable
2 (i) single bond ,(ii) double bond, (iii) triple bond
3 A pair, two pairs, three pairs
4 one,1, one, stable, two, contribute, sharing, a single bond, nucleus
5 Refer to page 87 -88 F4 Chemistry text book for guidance
5 1 Six, 2.6, two, octet, two ,two, double
2 Refer to page 88 - F4 Chemistry textbook for guidance
3 Five, 2.5, three, octet, two, three, triple
4 Refer to page 89 - F4 Chemistry textbook for guidance
6 1 Refer to page 86 as guidelines - F4 Chemistry textbook
2 Refer to page 87 - 88 - as guidelines F4 Chemistry textbook
3 Ionic bond Characteristic Covalent bond
Valence electrons Electrons involved Valence electrons
Metals atom and non- metal Elements Non-metals atom and non
atoms metal atoms
Electron transfer to achieve Bond formation Electron sharing to achieve
stable electron arrangement stable electron arrangement
Positive ions (cation) and Particles Molecules
negative ions (anion)
7 1 Ionic compound Properties Covalent compound
solid Physical states at room Solid, liquid or gas
temperature
high Melting point Low
high Boiling points low
Conduct in aqueous Electrical Conductivity Do not conduct electricity
solution or molten state
Soluble Solubility in water insoluble
insoluble Solubility in organic solvent soluble
2,3,4 Refer to page 90 - 91 - F4 Chemistry textbook for giudance
5 Alcohol, acetone, ether, hexane,
Uses of covalent compound – cosmetics, medical, industries
8 (a) 2.8.2
(b) (i) Ionic bond
(ii) Atom A releases 2 electrons to atom B
(iii) to achieve octet electron arrangement / to form ion A2+.
(iii) Each ion drawn correctly
(Iv) high melting point or boiling point/soluble in water / conducts electricity in
aqueous solution or molten state
(c)(i) CB2
(ii) 12 + 2(32) / 12 + 64 = 76
9 (a) Ionic compound
• Electron arrangement of an atom of element G is 2.8.1
• Atom G donates one electron to achieve the stable electron
arrangement which is 2.8
• G ion, G+ is formed
• Electron arrangement of atom W is 2.8.7
• Electron from atom G is transferred to an atom of W
• Atom W receives one electron from atom G to achieve the stable
electron arrangement which is 2.8.8
• W ion, W- is formed
• The G ion, G+ and W ion W- , formed are attracted to one another to
form an ionic compound, GW
• The strong electrostatic forces between the opposite-charged ions is
called ionic bond.
Covalent bond
• Atom E has four valence electrons, with an electron arrangement of 2.4
• It needs four more electrons to achieve the stable electron arrangement
• One atom of E contributes 4 electrons for sharing
• Atom W has seven valence electrons, with an electron arrangement of
2.8.7
• It needs one more electron to achieve the stable electron arrangement
• One atom of E share a pair of electrons with four atoms of W
• Covalent compound of EW4 is formed
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Chapter 5: Chemical Bonds: A Formation of Compounds Learning OutcomesDokument9 SeitenChapter 5: Chemical Bonds: A Formation of Compounds Learning OutcomesWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- 4 Periodic Table of ElementsDokument17 Seiten4 Periodic Table of ElementsWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDokument20 SeitenElectrolysis of Aqueous SolutionshanifzainolNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Level Chemistry Notes PDFDokument16 SeitenA Level Chemistry Notes PDFRAMAN KUMAR100% (1)
- Chapter 8: SaltsDokument23 SeitenChapter 8: SaltsWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining Empirical Formula of Copper(II) OxideDokument24 SeitenDetermining Empirical Formula of Copper(II) OxideAidil Firdaus100% (3)
- Permutation and CombinationDokument4 SeitenPermutation and CombinationNarendrn KanaesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Device PDFDokument38 SeitenElectronics Device PDFFariz Azhar AbdillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKTaiwan港澳台0819Dokument7 SeitenHKTaiwan港澳台0819Wong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- VariablesDokument2 SeitenVariablesWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- f5 c6 Permutations and Combinations AnswerDokument1 Seitef5 c6 Permutations and Combinations AnswerWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument15 SeitenChapter 2Wong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- LicenseDokument2 SeitenLicenseWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5a MT TovDokument1 Seite5a MT TovWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5a MT TovDokument1 Seite5a MT TovWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- VariablesDokument2 SeitenVariablesWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Takwim Semester I Sesi 2014-2015 - DwibahasaDokument1 SeiteTakwim Semester I Sesi 2014-2015 - DwibahasaWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- F5 C4 VectorsDokument9 SeitenF5 C4 VectorsWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physic Formulae F4Dokument1 SeitePhysic Formulae F4Wong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitational AccelerationDokument1 SeiteGravitational AccelerationWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inclined PlaneDokument1 SeiteInclined PlaneWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorsDokument19 SeitenVectorsWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryDokument4 SeitenPeka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryWong Wai Lun75% (8)
- Template Index NumberDokument1 SeiteTemplate Index NumberWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A Manufactured Substances in Industry - AnswerDokument6 Seiten9A Manufactured Substances in Industry - AnswerWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Manufactured Substances in IndustryDokument17 Seiten9 Manufactured Substances in IndustryWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8A Salts - AnswerDokument14 Seiten8A Salts - AnswerWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6A Electrochemistry - AnswerDokument6 Seiten6A Electrochemistry - AnswerWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- 7A Acids and Bases - AnswerDokument2 Seiten7A Acids and Bases - AnswerWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerDokument11 Seiten3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Acids and BasesDokument18 Seiten7 Acids and BasesWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4A Periodic Table of Elements - AnswerDokument7 Seiten4A Periodic Table of Elements - AnswerWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Trends - Chemistry LibreTextsDokument1 SeitePeriodic Trends - Chemistry LibreTextsHendySuwandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2: The Chemical Level of Organization: Topic: Basic Chemistry & Biochemistry Learning TargetsDokument15 SeitenModule 2: The Chemical Level of Organization: Topic: Basic Chemistry & Biochemistry Learning Targetsalmira garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science The Periodic TableDokument26 SeitenPhysical Science The Periodic TableTanaka ChirawuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table MCQsDokument21 SeitenPeriodic Table MCQsΙήήΘςέήτ βόγNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test Q2 Si 9 10 ItemsDokument3 SeitenSummative Test Q2 Si 9 10 ItemsorculloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming of Compounds - Part2Dokument2 SeitenNaming of Compounds - Part2Linh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry3 96) PDokument43 SeitenChemistry3 96) PShlok ParekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLASS IX, Selina, The Periodic TableDokument10 SeitenCLASS IX, Selina, The Periodic TableHirakjyoti SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 7Th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument32 SeitenChemistry 7Th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjuliette.brewer310100% (13)
- Chemical BondingDokument2 SeitenChemical Bondingsatya176Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Basic Questions ObjectiveDokument82 SeitenElectronics Basic Questions ObjectiveKrishan Gupta100% (3)
- Science7 Q1 M2C v1Dokument24 SeitenScience7 Q1 M2C v1Diane Bano0% (1)
- Chemistry Class 9 Chapter 4 McqsDokument15 SeitenChemistry Class 9 Chapter 4 McqsΙήήΘςέήτ βόγNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 BTHDokument19 SeitenChapter 2 BTHPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Science Chapter NotesDokument192 SeitenClass 10 Science Chapter NotesTarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 02Dokument158 SeitenLab Manual 02Stephen VivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- slaters ruleDokument2 Seitenslaters rulelubaajamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding Summary NotesDokument17 SeitenBonding Summary NotesaleenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17-Physics of Solids Important Questions With AnswersDokument30 SeitenChapter 17-Physics of Solids Important Questions With AnswersManoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 WorksheetsDokument4 SeitenCH 10 Worksheetsadaglio001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bond: The Force that Binds Atoms TogetherDokument15 SeitenChemical Bond: The Force that Binds Atoms TogetherShreyas PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation BondingDokument12 SeitenSimulation BondingCristina Nicomedes Aguinaldo0% (2)
- Bab 2 IbadDokument27 SeitenBab 2 IbadHeri SapoeteraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem101 Lecture Notes AllDokument15 SeitenChem101 Lecture Notes AllChima ArukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes PDFDokument19 SeitenChemistry Notes PDFAman RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHMBKLTDokument23 SeitenCHMBKLTелизабетаNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Periodic Table (Compatibility Mode)Dokument18 SeitenLecture 4 Periodic Table (Compatibility Mode)Ahmed MinhazNoch keine Bewertungen