Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Air Pollution and Its Control Home Assignment-3 Year: 2018-19 Odd Semester
Hochgeladen von
Mukul ChandraOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Air Pollution and Its Control Home Assignment-3 Year: 2018-19 Odd Semester
Hochgeladen von
Mukul ChandraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CE666A
Air Pollution and Its Control
Home Assignment-3
Year: 2018-19 Odd Semester
1. A power plant is burning 2000 tons of coal per day with an ash content of 45% and sulphur
content of 1 percent; assume all sulphur is burnt as SO 2. 85% of ash shows up as fly ash in the
chimney. The following chimney details are given: diameter 2m, exit velocity 15 m/sec,
temperature 120 degoC and stack pressure is 1 atm. Estimate the emission rates of particulate
in Kg/day, mg/m3 (25 deg C, 1 atm) and for SO 2 in terms of Kg/day, mg/m3 (25 degoC 1 atm)
and ppm.
2. Small quantities of NO2 can be formed in combustion exhaust gases by third-order reaction:
2NO+O2→2NO2 (rate constant = k). Assume plug flow conditions and the concentration of
NO at the beginning of the exhaust system be 2000 ppm and initial O 2 concentration be 100
ppm, compute the concentration of NO2 formed for a residence time of 2 sec if the temperature
of the exhaust gases is constant at 800oC.
The reaction rate constant is given by k=1.066 x 10-2 T-2 exp(530/T) ppm-2 min-1
3. Uncontrolled emissions from a 100,000 tpy (tons per year) aluminium plant are 20 kg Ft
(total fluoride i.e. particulate and gaseous) for every ton of aluminium produced. The industry
wishes to install both primary and secondary emission controlled systems to attain an emission
discharge of 1 kg Ft/ t of Al. Additional information:
Gaseous fluoride = 0.4 Ft
Removal efficiency of secondary controlled system(for gaseous and particulate F)= 50%
Removal efficiency of primary controlled system (for gaseous and particulate F) = 98%
The collection efficiency for gaseous and particulate fluoride at hoods varies. If the collection
efficiency for gaseous F is 91%, what should be minimum design collection efficiency for
particulate fluoride (at hood) so that industry meets the emission discharge of 1kg Ft /t of Al?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceVon EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- CE-105 12 Air Pollution - Numerical Problems 1Dokument8 SeitenCE-105 12 Air Pollution - Numerical Problems 1Ayush0% (1)
- Assign 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteAssign 2 PDFRizwan ullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCN2252 Environmental and Energy Engineering T02 Energy Resources and Climate ChangeDokument2 SeitenCCN2252 Environmental and Energy Engineering T02 Energy Resources and Climate ChangefelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ammonia Nitrite Nitrate Forms: 5% and 2% 95% Ash 50% Ash and inDokument1 SeiteAmmonia Nitrite Nitrate Forms: 5% and 2% 95% Ash 50% Ash and inIamellahollic KathportsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Thermal Power Plant in IndiaDokument23 SeitenManagement of Thermal Power Plant in Indiasurajsingh50% (2)
- Management of Thermal Power Plants in India: Paper Presented at BAQ 2006 at Yogykarta, IndonesiaDokument19 SeitenManagement of Thermal Power Plants in India: Paper Presented at BAQ 2006 at Yogykarta, Indonesiaapi-26797747Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emission QuantificationDokument1 SeiteEmission QuantificationEmgr. Muhammad FahdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 3HARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Problems On Unit and Mass BalanceDokument8 SeitenNumerical Problems On Unit and Mass BalanceMeharSinghGrewalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Calculation Py Qs by Dev SirDokument97 SeitenProcess Calculation Py Qs by Dev SirVIKAS SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 2 - Basic Calculations - SolutionsDokument3 SeitenProblem Set 2 - Basic Calculations - SolutionsAshish KotwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taller 1Dokument2 SeitenTaller 1juan camilo montenegro cañonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - 4 - Air Pollution - Part I - 20 - 27 Dec 2021Dokument87 SeitenLecture 3 - 4 - Air Pollution - Part I - 20 - 27 Dec 2021Sachin YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Polution and Air Pollution Control in Cement IndustryDokument26 SeitenAir Polution and Air Pollution Control in Cement IndustryPRAFULKUMAR PARMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 18 - Examples On ElectrolysisDokument12 SeitenLect 18 - Examples On ElectrolysisSalem GarrabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture #3 - Understanding Air PollutionDokument63 SeitenLecture #3 - Understanding Air PollutionDeep RedriffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regular Paper 2 - Set A: Section - Ii: Short Descriptive QuestionsDokument23 SeitenRegular Paper 2 - Set A: Section - Ii: Short Descriptive QuestionsYogaAnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air PolutionDokument39 SeitenAir PolutionLaura DucaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poluarea AeruluiDokument40 SeitenPoluarea AeruluiclaudiutpNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Dokument6 SeitenENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Manel SashikalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid MistDokument13 SeitenAcid MistAnastasia YuandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pollutant Emissions From A Steam Boiler: Amount of Emission of PollutantsDokument3 SeitenPollutant Emissions From A Steam Boiler: Amount of Emission of PollutantsAlexa NicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wuhuan - MR Pi JinlinDokument34 SeitenWuhuan - MR Pi JinlinAmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTRL FDokument192 SeitenCTRL FRani GarginalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAO - Industrial Charcoal ProductionDokument33 SeitenFAO - Industrial Charcoal ProductionFabiano de Souza0% (1)
- Thermo 5th Chap02P079Dokument30 SeitenThermo 5th Chap02P079HZ. TYMOFEINoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Conentration and Unit Problems - T1Dokument9 SeitenECE Conentration and Unit Problems - T1DanialNoch keine Bewertungen
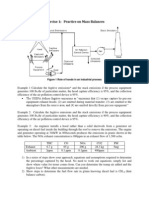
- Exercise 1: Practice On Mass Balances: Figure 1 Role of Hoods in An Industrial ProcessDokument2 SeitenExercise 1: Practice On Mass Balances: Figure 1 Role of Hoods in An Industrial Process24deschainNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Environmental Quality Standards For Industrial Gaseous Emission (Mg/Nm3, Unless Otherwise Defined)Dokument3 SeitenNational Environmental Quality Standards For Industrial Gaseous Emission (Mg/Nm3, Unless Otherwise Defined)tariqshah99Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPCDokument39 SeitenCPCNaresh NaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1-2 QuestionsDokument2 SeitenLecture 1-2 QuestionsYas MonazahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambient Air Quality Mining Clusters in Western Kachchh Region, Gujarat, IndiaDokument5 SeitenAmbient Air Quality Mining Clusters in Western Kachchh Region, Gujarat, IndiaShofa R HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- CementCO2coststudyIEAGHG 2006Dokument6 SeitenCementCO2coststudyIEAGHG 2006Marco HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGR4426 Assignment1 2023Dokument4 SeitenENGR4426 Assignment1 2023France DiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMBE Assignment No. 4Dokument1 SeiteCOMBE Assignment No. 4AwesomeArchie 0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air Pollution Control Technology Fact SheetDokument5 SeitenAir Pollution Control Technology Fact SheetSiddharth RajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10CH14 TUFAIL MUSTAFA KHOSAEnvironmental Impact of Power PlantDokument6 Seiten10CH14 TUFAIL MUSTAFA KHOSAEnvironmental Impact of Power PlantTufail MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission Estimates Using EFDokument22 SeitenEmission Estimates Using EFPrincess Jean L. GalabinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline Waste Incinerator 2001Dokument5 SeitenGuideline Waste Incinerator 2001chongchoifattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Soal 1 2020Dokument1 SeiteLatihan Soal 1 2020aldo islamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 3passionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMTB TEST 2 2014 - MemoDokument12 SeitenCMTB TEST 2 2014 - MemoThabo ThaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ragone Solution Manual From Nanyang UniversityDokument67 SeitenRagone Solution Manual From Nanyang UniversityRijalCok71% (14)
- Waste To EnergyDokument31 SeitenWaste To EnergyMichaelCoffeeBNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016-Me-169-Pp CepDokument22 Seiten2016-Me-169-Pp CepafaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDokument16 SeitenEnvironmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsThambidurai KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air EmissionDokument11 SeitenAir EmissionBenson Harison MajabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW#6 - 2021 Solutions - Combustion and Air PollutionDokument4 SeitenHW#6 - 2021 Solutions - Combustion and Air PollutionCendur AbithanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EllinghamDokument19 SeitenEllinghamJuan Ignacio GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13techrepo Publicver e 121128Dokument22 Seiten13techrepo Publicver e 121128ctkah_hamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tasarım Soruları PDFDokument2 SeitenTasarım Soruları PDFAkbey ApaydınNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Incinerare Deseuri MadridDokument4 Seiten1 - Incinerare Deseuri MadridmonalinamaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of CO2 Gas Requirement For Coal Bin InterisationDokument2 SeitenCalculation of CO2 Gas Requirement For Coal Bin Interisationvvijaybhan100% (1)
- UntitledDokument8 SeitenUntitledMothish SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extractive Metallurgy 3: Processing Operations and RoutesVon EverandExtractive Metallurgy 3: Processing Operations and RoutesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementVon EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Institute of Energy's Second International Conference on COMBUSTION & EMISSIONS CONTROL: Proceedings of The Institute of Energy Conference Held in London, UK, on 4-5 December 1995Von EverandThe Institute of Energy's Second International Conference on COMBUSTION & EMISSIONS CONTROL: Proceedings of The Institute of Energy Conference Held in London, UK, on 4-5 December 1995Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- ME-341A - Heat and Mass TransferDokument34 SeitenME-341A - Heat and Mass TransferMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpicyclicGear ExperimentDokument2 SeitenEpicyclicGear ExperimentMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- c00s00 PDFDokument10 Seitenc00s00 PDFMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispersion Handout PDFDokument72 SeitenDispersion Handout PDFArcangelo Di TanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco101a Tutorial Problem Set 06 Summer Term 2018 (16079)Dokument4 SeitenEco101a Tutorial Problem Set 06 Summer Term 2018 (16079)Mukul Chandra0% (1)
- ME352A - Lab 1: Make The Following Mechanisms Using The Kit ProvidedDokument2 SeitenME352A - Lab 1: Make The Following Mechanisms Using The Kit ProvidedMukul Chandra100% (1)
- Mitacs Globalink Reference Letter Instructions June2016 PDFDokument1 SeiteMitacs Globalink Reference Letter Instructions June2016 PDFpreeteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Senate Scholarships and Prizes Committee Application Form For Free-Basic-Mess (FBM) ScholarshipDokument2 SeitenIndian Institute of Technology Kanpur Senate Scholarships and Prizes Committee Application Form For Free-Basic-Mess (FBM) ScholarshipMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lake CityDokument1 SeiteThe Lake CityMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 Template PDFDokument1 SeiteAssignment 3 Template PDFMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMMDokument2 SeitenCMMMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMMDokument2 SeitenCMMMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are You Good at Group DiscussionDokument6 SeitenAre You Good at Group DiscussionNikhil PaliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machining PDFDokument25 SeitenMachining PDFMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Analysis of Inboard Braking SystemDokument4 SeitenDesign & Analysis of Inboard Braking SystemMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAJA Parameters - Season-II - Sheet1Dokument3 SeitenBAJA Parameters - Season-II - Sheet1Mukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Analysis of Inboard Braking SystemDokument4 SeitenDesign & Analysis of Inboard Braking SystemMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment-3 Study of Critical Heat Flux (Boiling Heat Transfer)Dokument7 SeitenExperiment-3 Study of Critical Heat Flux (Boiling Heat Transfer)Mukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of CentroidsDokument6 SeitenList of CentroidsMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Analysis & Optimization of Hub Used in FSAE CarsDokument10 SeitenDesign Analysis & Optimization of Hub Used in FSAE CarsMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lake CityDokument1 SeiteThe Lake CityMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MV - Unit Iv - Lect 5Dokument5 SeitenMV - Unit Iv - Lect 5Mukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsDokument4 SeitenME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsMukul Chandra0% (1)
- Assignment 3 Template PDFDokument1 SeiteAssignment 3 Template PDFMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Pen: by Mukul Chandra, Roll Number 160421Dokument1 SeiteA Pen: by Mukul Chandra, Roll Number 160421Mukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Report For ESI 2019 (Combustion & Electric) : Thermal AnalysisDokument1 SeiteDesign Report For ESI 2019 (Combustion & Electric) : Thermal AnalysisMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are You Good at Group DiscussionDokument6 SeitenAre You Good at Group DiscussionNikhil PaliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machining PDFDokument25 SeitenMachining PDFMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychrometric Chart: Theory and ApplicationDokument42 SeitenPsychrometric Chart: Theory and ApplicationMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen