Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
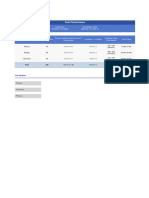
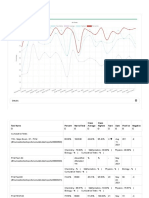
Section Total Questions Correct/ Partial Correct/ Incorrect/ Unattempted +ve Marks / - Ve Marks Obtained / Max (Percentage) Time Taken
Hochgeladen von
pratyaya alamOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Section Total Questions Correct/ Partial Correct/ Incorrect/ Unattempted +ve Marks / - Ve Marks Obtained / Max (Percentage) Time Taken
Hochgeladen von
pratyaya alamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Test Performance
Student Name Form Number
Pratyaya Alam 18663763
Test Name Completion Date
Minor Test-1 2018-10-21 09:51:45
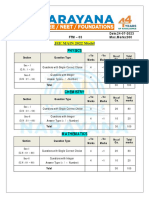
Obtained /
Total Correct/ Partial Correct/ +ve Marks / -ve
Section Max Time Taken
Questions Incorrect/ Unattempted Marks
[Percentage]
60 / 180
Physics 45 21 / 0 / 24 / 0 84.00 / -24 49 Min 53 Sec
[33.33%]
80 / 180
Chemistry 45 25 / 0 / 20 / 0 100.00 / -20 70 Min 30 Sec
[44.44%]
215 / 360
Biology 90 61 / 0 / 29 / 0 244.00 / -29 42 Min 47 Sec
[59.72%]
355 / 720 163 Min 10
Total 180 107 / 0 / 73 / 0 428.00 / -73
[49.31%] Sec / 180 Min
Test Syllabus
Biology DIVERSITY IN LIVING WORLD : What is living? ; Biodiversity; Need for classification; Three domains of life; Taxonomy &
Systematics; Concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature; Tools for study of Taxonomy –
Museums, Zoos, Herbaria, Botanical gardens. Five kingdom classification; salient features and classification of Monera;
Protista and Fungi into major groups; Lichens; Viruses and Viroids. Prokaryotic Cell (Bacteria). Salient features and
classification of plants into major groups-Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms (three to five
salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category); Angiosperms- classification up to class,
characteristic features and examples).
Chemistry SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY : General Introduction : Importance and scope of chemistry. Laws of chemical
combination, Dalton's atomic theory: concept of elements, atoms and molecules. Atomic and molecular masses. Mole
concept and molar mass; percentage composition and empirical and molecular formula; chemical reactions, stoichiometry
and calculations based on stoichiometry.
Physics Basic Mathematics used in Physics - ALGEBRA : Quadratic Equation (Roots of quadratic equation, Solution by Factorization
and by Shridharacharya Formula, Properties of roots (real, equal, imaginary etc), Application of Quadratic equation in
physics), Binomial Theorem and binomial approximation, Logarithm and Exponents (Laws of logarithms and exponents
with applications /examples), Series (Arithmetic Progression and its general term and Sum, Sum of first n Natural numbers,
Geometrical Progression and its general term and Sum, Sum of infinite GP), Componendo & Dividendo rule.
TRIGONOMETRY : Angle & its measurement (Sexagesimal and Circular system), Trigonometricratios, Trigonometric
identities, Four Quadrants & ASTC rule, T-ratios for general angles, Addition/subtraction Formulae, Small angle
Approximation, Ranges of T-functions. CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY : Define Origin, Axis or Axes, Co-ordinates of a point in
a plane or space (2D or 3D), Distance Formula, Slope of a line and its interpretation, Graphs of commonly used functions
(Straight line, Parabola, Circle, Ellipse, Hyperbola including rectangular hyperbola, Sinusoidal functions (sine and cosine
functions), Exponential functions. CALCULUS: Differential calculus (Average rate of change and Instantaneous rate of
change, Differentiation of commonly used functions, Rules of differentiation including Product and Quotient rules,
Application of derivatives: Increasing and Decreasing nature, Maxima and Minima with geometrical/graphical explanation),
Integral calculus (Integration is the reverse process of differentiation, Indefinite and Definite Integration, Integration of
commonly used functions, Rules of Integration, Application of Integral calculus: Area under a curve and Average value of a
continuous function in an interval) VECTORS : Definition of scalar and vector quantities, Graphical representation of vectors,
Notation of Vectors, Angle between two vectors, Types of Vectors (Unit vector, Null vector, Equal vectors and equality of
vectors, opposite and Negative of a vector, Parallel and anti-parallel vectors, Co-planar vectors, axial vectors), Position and
displacement vectors, Addition/subtraction of two vectors (Triangle law, Parallelogram law), Addition of many vectors
(Polygon law), Unit vectors and their significance (Representation of vector in terms of unit vector in plane and in space),
Resolution of a Vector into components i.e. Cartesian Components in two and three dimensions and Direction Cosines,
Multiplication or Division of a Vector by a Scalar (i.e. Real number), Scalar (Dot) product of two Vectors and component of a
vector in the direction of another vector, Vector (Cross) product of two Vectors with its geometrical interpretation and Right
hand rule for direction. UNIT, DIMENSIONS AND MEASUREMENTS : Classification of Physical Quantities according to their
dependency i.e. Fundamental (or Base) and Derived quantities, Need for measurement (Units of measurement), Systems of
units (FPS, CGS, MKS, SI system of units and Supplementary units, fundamental and derived units, Some idea about
Practical and Improper units), Standards of Length, mass and time measurements, Dimensions of physical quantities,
Dimensional Formulae of important physical quantities, Dimensional analysis and its applications & its limitations, SI
prefixes and general guidelines for using Symbols of SI units, Errors in measurement (Systematic, Random and Least count
Errors), Accuracy and precision of measuring instruments ; Absolute Error, Relative Error, Percentage Error and
Combination of Errors, Significant figures and its rules for Arithmetic operations (i.e. addition, subtraction, multiplication and
division), Rounding off the uncertain digits.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NEET UG Nurture Unit Test 5 Performance ReportDokument1 SeiteNEET UG Nurture Unit Test 5 Performance ReportRahulPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian - Ahmad787@gmail - Com 5144 Analysis ReportDokument1 SeiteIndian - Ahmad787@gmail - Com 5144 Analysis ReportAHMADNoch keine Bewertungen
- MURLIDHAR DESHMUKH@ESSAR COM-5616-analysis - Report PDFDokument2 SeitenMURLIDHAR DESHMUKH@ESSAR COM-5616-analysis - Report PDFMurlidhar DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurture Online Test Series For AipmtDokument5 SeitenNurture Online Test Series For AipmtvjaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurture Online Test Series For Neet Ug 2019 PDFDokument5 SeitenNurture Online Test Series For Neet Ug 2019 PDFANIL SRIVASTAVANoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurture Online Test Series For Neet Ug 2019Dokument5 SeitenNurture Online Test Series For Neet Ug 2019GAURI MALHOTRANoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET UG Major Major Test 13 Performance ReportDokument1 SeiteNEET UG Major Major Test 13 Performance ReportSantosh TummewarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Performance: Student Name Form Number Test NameDokument1 SeiteTest Performance: Student Name Form Number Test Nameaarav parikh 2868Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pp:neet-Ug 2020Dokument1 SeitePp:neet-Ug 2020Reflex OP GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Performance: Student Name Form Number Test NameDokument1 SeiteTest Performance: Student Name Form Number Test NameMayank GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Performance: Student Name Form Number Test NameDokument1 SeiteTest Performance: Student Name Form Number Test NameSayak SenGuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Iit Ir FTM-03 24.07.2023 QPDokument14 SeitenXi Iit Ir FTM-03 24.07.2023 QPiitb.akkharcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMiDDaT Lab HPLC Report Form 1Dokument3 SeitenAMiDDaT Lab HPLC Report Form 1Kent Harry CumpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam & Syllabus Notice: Test NameDokument2 SeitenExam & Syllabus Notice: Test Nameshridhi.chNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Test 5 JEE MAIN Result AnalysisDokument1 SeitePhase Test 5 JEE MAIN Result AnalysisShivendra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechatronics - 13seriesDokument22 SeitenMechatronics - 13seriesIsmail HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neet Ug Test Series Leader SyllabusDokument12 SeitenNeet Ug Test Series Leader Syllabusss3227618Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Medical Nurture SyllabusDokument7 SeitenPre Medical Nurture SyllabusPREM277272Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Sept - 2 2020Dokument1 Seite3 Sept - 2 2020Mayank GhatpandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Mathematics PDFDokument4 SeitenBasic Mathematics PDFvims1248993100% (1)
- Exam & Syllabus Notice: Test NameDokument2 SeitenExam & Syllabus Notice: Test Nameshridhi.chNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Advanced Leader CBT SyllabusDokument5 SeitenJee Advanced Leader CBT SyllabusBhavya BodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Term Wise Syllabus 2021 22Dokument5 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Term Wise Syllabus 2021 22Lakshay JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Term Wise Syllabus 2021 22Dokument5 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Term Wise Syllabus 2021 22afaz arhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIATS First Step JEE (Main & Advanced) Sesson 2023-24 Phase 1 & Phase 2Dokument1 SeiteAIATS First Step JEE (Main & Advanced) Sesson 2023-24 Phase 1 & Phase 2Apurva PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- (F) (2) SR AIIMS S60 & MPL NEET - 2023 - Final Phase Revision Schedule - 1-1Dokument2 Seiten(F) (2) SR AIIMS S60 & MPL NEET - 2023 - Final Phase Revision Schedule - 1-1tejaspeaks2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic MathematicsDokument4 SeitenBasic MathematicsManav HnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry-B.sc. PCM SyllabusDokument67 SeitenChemistry-B.sc. PCM SyllabusMohd Abu ZaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bms College of Engineering, BengaluruDokument2 SeitenBms College of Engineering, BengaluruShiva Kumar RamachandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 Tos ScienceDokument1 SeiteG8 Tos ScienceJessah Chris Eve ValleNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPS T.S. XI Class ScheduleDokument3 SeitenRPS T.S. XI Class ScheduleMohit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jl. Pertamina Kampus II Gambesi Kel. Gambesi, TernateDokument4 SeitenJl. Pertamina Kampus II Gambesi Kel. Gambesi, TernateErin MaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC ChemistryDokument56 SeitenMSC ChemistryChhagan Lal Sahu JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPCET 2021: Syllabus of Examination For Admission To MCA (Integrated)Dokument5 SeitenUPCET 2021: Syllabus of Examination For Admission To MCA (Integrated)rohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of SpecificationDokument7 SeitenTable of SpecificationMedy JacoboNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 101 - Sem 1 - Matrices and Differential Calculus - NEP Based - Autonomy - Proposed - SyllabusDokument6 SeitenBS 101 - Sem 1 - Matrices and Differential Calculus - NEP Based - Autonomy - Proposed - Syllabuslovelyboy.yashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii Maths 22-23Dokument196 SeitenXii Maths 22-23Aashay Parate100% (1)
- Jee Main Leader CBT SyllabusDokument2 SeitenJee Main Leader CBT SyllabusFOOTBALL 10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024 - Test PlannerDokument2 SeitenArjuna JEE 2.0 2024 - Test Plannerranjot singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Test For Medical StudentDokument12 SeitenA Test For Medical StudentMayank GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Test PlannerDokument6 SeitenFinal Test PlannerYash RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC MathematicsDokument14 SeitenBSC MathematicsPrashant SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos IcuDokument1 SeiteTos IcuMary Cris RombaoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover Page Lab Report Clb21303Dokument1 SeiteCover Page Lab Report Clb21303hnszulaikhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Tests Whole Year: DetailsDokument7 SeitenAll Tests Whole Year: DetailsP.S. Mithul SouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Iit Ic Ir CFTM-03 30.10.23 QPDokument18 SeitenXi Iit Ic Ir CFTM-03 30.10.23 QPiitb.akkharcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-04 - 6 - 11 - 2023 - QPDokument18 SeitenXi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-04 - 6 - 11 - 2023 - QPiitb.akkharcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3131 APIGet Individual Result by FRM Roll Page Size 1&id 887943&from Roll 044232120245Dokument1 Seite3131 APIGet Individual Result by FRM Roll Page Size 1&id 887943&from Roll 044232120245Sai kumar BairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demo - LP - Findstringcodezak Wipro: Shyam Apr 13, 2001 7844335454 Male India 10000 SatnaDokument3 SeitenDemo - LP - Findstringcodezak Wipro: Shyam Apr 13, 2001 7844335454 Male India 10000 SatnaSambhu LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECTS-Bogen MechatronicsDokument2 SeitenECTS-Bogen MechatronicsUmair SarwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHO of Calculus and Statistical AnalysisDokument7 SeitenCHO of Calculus and Statistical AnalysisMukul RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 - KA Deeksha Test - Schedule For CET-11 - V 6.0 (June Batch)Dokument1 Seite08 - KA Deeksha Test - Schedule For CET-11 - V 6.0 (June Batch)Samarth KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- JMET - Strategize and Practice: MBA 2007 SeriesDokument7 SeitenJMET - Strategize and Practice: MBA 2007 SeriesAnirban BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test JEE (Adv.) P, F, D, RDokument1 SeitePractice Test JEE (Adv.) P, F, D, RHarsh PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLASS: 11th Class (CRP) : PHASE PLANNER-2022-24Dokument1 SeiteCLASS: 11th Class (CRP) : PHASE PLANNER-2022-24Rayan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test 01 - Test Schedule and Syllabus (02 - 07 - 2023) - Prayas JEE 2.0 2024Dokument2 SeitenPractice Test 01 - Test Schedule and Syllabus (02 - 07 - 2023) - Prayas JEE 2.0 2024arpit sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aiats Topic Wise Schedule Class 9 10Dokument1 SeiteAiats Topic Wise Schedule Class 9 10Shreya AttriNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOS (Anna Mae S. Nazareno BSED-MATH 3) 1Dokument1 SeiteTOS (Anna Mae S. Nazareno BSED-MATH 3) 1elsiegumoc0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Level Sets and Extrema of Random Processes and FieldsVon EverandLevel Sets and Extrema of Random Processes and FieldsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collision Detection: Understanding Visual Intersections in Computer VisionVon EverandCollision Detection: Understanding Visual Intersections in Computer VisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocr Additional Maths Formula - Not Given in The Examination!Dokument2 SeitenOcr Additional Maths Formula - Not Given in The Examination!Pritpal Singh100% (1)
- (Quadratic Equations 2Dokument5 Seiten(Quadratic Equations 2Rohit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics (Mid Term) Time:1Hr 30mins Class:X Mm:40 General InstructionsDokument6 SeitenMathematics (Mid Term) Time:1Hr 30mins Class:X Mm:40 General InstructionsFERA Future electronics and research administrationNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1A StandardsDokument1 SeiteA1A StandardsStephanie ClareyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assertion and Reason Mathematics Class X Supplement Uncurves 1Dokument72 SeitenAssertion and Reason Mathematics Class X Supplement Uncurves 1Divyansh SawriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SA Material S2 SA2 2122Dokument2 SeitenSA Material S2 SA2 2122lixx nmiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC SirDokument5 SeitenMC SirmirsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algone62022 ExamDokument24 SeitenAlgone62022 Exammitboyusa17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Inequalities - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Solving Inequalities by FactorisingDokument16 SeitenQuadratic Inequalities - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Solving Inequalities by Factorisingerin zietsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument45 SeitenUntitledsarthak patilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardan Polynomials and ...Dokument7 SeitenCardan Polynomials and ...Pedro A. Marrone G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFDokument5 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFLavan NimsNoch keine Bewertungen
- G12 Scheme of WorkDokument5 SeitenG12 Scheme of WorkmyeboockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic EquationsDokument131 SeitenQuadratic Equationssujaritha sureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - Unit 8 - Quadratic Functions and Equations - 20220306062819Dokument4 SeitenUnit - Unit 8 - Quadratic Functions and Equations - 20220306062819Micah GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 10X Itb AqDokument179 SeitenModul 10X Itb AqEmmyr FaiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- VCE Maths Methods CAS Units 1 2 Text BookDokument600 SeitenVCE Maths Methods CAS Units 1 2 Text Bookzhenyu100% (1)
- Elementary Geometry For College Students 6Th Edition Full ChapterDokument41 SeitenElementary Geometry For College Students 6Th Edition Full Chapterrhonda.taylor352100% (25)
- Solution Manual For Applied Numerical Methods With Matlab For Engineers and Science Chapra 3rd EditionDokument15 SeitenSolution Manual For Applied Numerical Methods With Matlab For Engineers and Science Chapra 3rd EditionDouglasWhiteheadxkwi100% (41)
- 9709 s10 - ms31Dokument118 Seiten9709 s10 - ms31ShoummaShamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSSSF: PJBHSH ""Dokument68 SeitenSSSSF: PJBHSH ""Hopeson Kang'omaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EJADDokument21 SeitenEJADKiNah XpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matf 4Dokument14 SeitenMatf 4api-158285296Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Revision SM015 LatestDokument27 SeitenQuick Revision SM015 LatestninaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra I - GA Milestones Formulas PDFDokument1 SeiteAlgebra I - GA Milestones Formulas PDFAlexander Roman SichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Made EasyDokument76 SeitenMaths Made Easybfactory 01Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Quarter SLEM 9Dokument159 Seiten2nd Quarter SLEM 9Samantha Eunice Osuya EspiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNPACKING DIAGRAM and CURRICULUM MAPDokument6 SeitenUNPACKING DIAGRAM and CURRICULUM MAPRojelyn ConturnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Work Book 1 - 210501 - 131004Dokument38 SeitenMathematics Work Book 1 - 210501 - 131004Lucy DickinsonNoch keine Bewertungen