Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
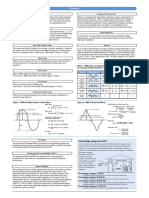
Base The Curve Area Under Lue Average Va MAX Value Average: Wave) (Sine 2
Hochgeladen von
angela ortegaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Base The Curve Area Under Lue Average Va MAX Value Average: Wave) (Sine 2
Hochgeladen von
angela ortegaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CIRCUITS
Cycle - complete change in value and direction of an alternating quantity.
1 cycle = 360 electrical degrees
f - cycles/sec or Hertz by Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
T - time to complete one cycle
1
T
Instantaneous value - the value of f alternating quantity at any instant
Maximum value - the maximum value attained during positive or negative half
cycle
Average value - average of all instantaneous values of half-cycle
Area Under The Curve
Average Va lue
2
Average Value MAXBase(sine wave)
Root Mean Square (RMS) or
Effective value
2
Area Under the Curve
(sine wave) RMS value 1
RMS value Base
MAX
RMS value2
Form Factor 1.11(sine wave)
MAX value
Peak Factor Ave 1.414(sine wave)
Phase Difference or RMS value
Phase Angle - the angular displacement between alternating quantities
In Phase - if the two alternating quantities attain their maximum and minimum values at the
same time
Out of Phase - does not attain their maximum and minimum values at the same time
RMS AVE
SINUSOIDAL WAVE MAX 2
MAX
HALF WAVE MAX2 MAX
TRIANGULAR MAX
2
MAX
SEMI-CIRCULAR 2 3 2
MAX MAX
TRAPEZOIDAL 3 0.
47 MAX
MAX
SQUARE MAX 5 MAX
D’ARSONVAL - REQUIRES AVE VALUE
WAVELENGTH() - length of one complete cycle
V1c
- velocity of TmV
3 x108 m
sec (radio
c ff
sec waves)
propagation==344 (sound waves)
f = frequency (Hertz)
ALTERNATION - equal to one-half of a cycle
SUM OF TWO ALTERNATING WAVES
In phase out-of-phase by 90
out-of-phase by an angle θ
I T I1 I TITI 2 I1I
2 2 I
2
1 2I
1 I22 cos
2 180 θ
FIGURE OF MERIT - reciprocal of power factor
=secθ 1
FM
cosθ
POWER FACTOR CAN BE
OBTAIN:
1. ANGLE OF APPARENT POWER
2. ANGLE OF IMPEDANCE
3. PHASE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN VOLTAGE AND CURRENT
4. POWER TRIANGLE
5. IMPEDANCE TRIANGLE OR ADMITTANCE
PERCENTAGE HARMONIC CONTENT
En
%HC x100%
ROOT MEAN SQUARE E1
(RMS) OF NON-SINUSOIDAL
WAVE
IE EDCRMS
RMS I
RMS
2
2 1 I RMS
E RMS
1
2
2
E2RMS2 ......
IRMS
2
3
2
2 2I M I M I M I M I M IM
HARMONICS I DC
I AVEI AVE 1 1 2 2 3 3
π π1 1 2 2 3 3
At fundamental
at 3rd harmonics
L2ππf
XL X 3L1ωL
At fundamental at 3rd harmonics
X1C
XXC3c
C
3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Functional Waveforms For Electronics: Learning ObjectivesDokument9 SeitenFunctional Waveforms For Electronics: Learning ObjectivesVincent GregorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beee 2Dokument26 SeitenBeee 2SARTHAK SHROFF (RA2111030010023)Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE8552 Unit-5Dokument48 SeitenEE8552 Unit-5balafetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDokument4 SeitenElectrical Engineering Formulasarthur guil-anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis: Alternating Current (Ac) Dr. CKVDokument4 SeitenSynopsis: Alternating Current (Ac) Dr. CKVvishwanath c kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2A (AC Fundamentals)Dokument102 SeitenModule 2A (AC Fundamentals)vipin10thj.27828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alternating-Current Circuits: Physics 2212Dokument10 SeitenAlternating-Current Circuits: Physics 2212deskaug1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alternating Current (Ac) Circuits Part 1 - Single Phase (1) SystemDokument22 SeitenAlternating Current (Ac) Circuits Part 1 - Single Phase (1) SystemDrofer ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDokument4 SeitenElectrical Engineering FormulasMehdi Aydın DuramazNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC CircuitsDokument10 SeitenAC CircuitsMarlon BlasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - AC-AC Converters (Compatibility Mode)Dokument32 Seiten5 - AC-AC Converters (Compatibility Mode)OmkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Line Ee SubjectsDokument2 SeitenPower Line Ee SubjectsCristele Mae GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical AC SirDokument93 SeitenElectrical AC SirVedant SheshkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Multimeter SeriesDokument12 SeitenDigital Multimeter SeriesRamdane AkediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Width Modulation TechniquesDokument38 SeitenPulse Width Modulation TechniquesEla ResearchNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 098 Alternating Current Circuits EditDokument53 Seiten11 098 Alternating Current Circuits EditDanish Fitri RoslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.7 RMS and Average Values Garland Patton Jr. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Missouri University of Science & TechnologyDokument5 SeitenExperiment No.7 RMS and Average Values Garland Patton Jr. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Missouri University of Science & TechnologyGee Patt'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurements Lecture - 6 7 Rev1 2023Dokument38 SeitenMeasurements Lecture - 6 7 Rev1 2023domisia.palmusia9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergyDokument19 SeitenPhysics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergySucharita KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purdue PHYS 241 Final Exam Crib Sheet - Optics and AC CircuitsDokument1 SeitePurdue PHYS 241 Final Exam Crib Sheet - Optics and AC CircuitsDaniel MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Electrical EnggDokument79 SeitenModule 3 Electrical EnggAnand ANoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - IntroductionDokument28 Seiten1 - Introductionmohamed ghoneemNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 411-Lecture 05Dokument7 SeitenME 411-Lecture 05Harun SarıçamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude ModulationDokument31 SeitenAmplitude ModulationShubham KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES Unit-2Dokument55 SeitenES Unit-2Mazin VoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary: Integral Action Time Frequency CharacteristicDokument1 SeiteGlossary: Integral Action Time Frequency CharacteristicRakesh SandarativjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRX旋转变压器Dokument2 SeitenBRX旋转变压器严浩斌Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Lecture#13Dokument25 SeitenChapter 5 - Lecture#13AHMAD ASRI ABD SAMATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Meter in Ac MeasurementsDokument69 SeitenBasic Meter in Ac MeasurementsWatashiNoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steady State Sinusoidal AnalysisDokument16 SeitenSteady State Sinusoidal AnalysisPramit PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding RF Experiment 2Dokument6 SeitenUnderstanding RF Experiment 2Harold Fabian Bonilla RestrepoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument8 SeitenPower Electronicskibrom atsbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Jee Em+Gm Ac, EmwDokument91 Seiten12th Jee Em+Gm Ac, EmwEeea EearNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 - Alternating Current CircuitsDokument152 SeitenUnit 3 - Alternating Current CircuitsRodney Takundanashe MandizvidzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC CIRCUITS ReviewerDokument7 SeitenAC CIRCUITS ReviewerKyle Joshua BunhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- New My PPT 124Dokument19 SeitenNew My PPT 124chhuny100% (4)
- Amplitude ModulationDokument92 SeitenAmplitude ModulationjjaazzmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula of Vrms and VDCDokument1 SeiteFormula of Vrms and VDCBeta TesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternating CurrentDokument13 SeitenAlternating Currentmakivad893Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Institute of Technology: Electrical and Electronics Engineering DepartmentDokument6 SeitenCambridge Institute of Technology: Electrical and Electronics Engineering DepartmentKarthik PariharNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 AM Lecture-OnlineDokument10 Seiten09 AM Lecture-OnlineAsdffghhklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - I: Basic Performance Equations of D.C. MotorsDokument21 SeitenUnit - I: Basic Performance Equations of D.C. MotorsNoah AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication EngineeringDokument24 SeitenCommunication EngineeringThanusriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - Induction Motor (Steady State)Dokument27 SeitenChapter 6 - Induction Motor (Steady State)arifulNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEE Module 3Dokument17 SeitenBEE Module 3John craxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7Dokument4 SeitenLecture 7api-3702538Noch keine Bewertungen
- RS 485 Oscilloscope Screenshots - 100179Dokument15 SeitenRS 485 Oscilloscope Screenshots - 100179Dante LupuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Dynamics L7Dokument6 SeitenStructural Dynamics L7kahdha313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude ModulationDokument89 SeitenAmplitude Modulationelyk herreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00-Basic VibrationDokument91 Seiten00-Basic VibrationMohamed Al-OdatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ir Spectroscopy LatestDokument103 SeitenIr Spectroscopy Latest5fdt78kgscNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Wave Rectifier: Instruction CircuitDokument1 SeiteFull Wave Rectifier: Instruction CircuitAtharv LokhandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2Dokument66 SeitenChap 2Nur MuzzammirNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Circuis: Dr. Ashwini Kumar Nayak Asst. Professor School of Electrical Sciences NistDokument28 SeitenAC Circuis: Dr. Ashwini Kumar Nayak Asst. Professor School of Electrical Sciences NistssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swastik Agarwal Aec Exp 4Dokument11 SeitenSwastik Agarwal Aec Exp 4Swastik AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 33 ch7Dokument8 Seiten33 ch7Srinivas H v100% (1)
- Paper To ISSE 2007Dokument4 SeitenPaper To ISSE 2007tunghtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- R7 - Reference - Part 3Dokument44 SeitenR7 - Reference - Part 3danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Introduction To Ac Voltage, RMS, Average, Form Factor, Peak FactorDokument16 SeitenModule 2 Introduction To Ac Voltage, RMS, Average, Form Factor, Peak FactorHisham MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- In NT AMF 1.2 Reference GuideDokument81 SeitenIn NT AMF 1.2 Reference GuideAnonymous uEt1sNhU7lNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 15 H2 AC Notes TeacherDokument16 Seiten14 15 H2 AC Notes TeacherAgus LeonardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D0924 - 1 (En)Dokument7 SeitenAstm D0924 - 1 (En)Maria Isa SequeirosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masibus DA-DV-DW-DVA-DH-DPF - R6F - 1217 - AC Line TransducerDokument4 SeitenMasibus DA-DV-DW-DVA-DH-DPF - R6F - 1217 - AC Line TransducerSrinivas K VamanamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors: Research On The Single-Value Indicators For Centrifugal Pump Based On Vibration SignalsDokument18 SeitenSensors: Research On The Single-Value Indicators For Centrifugal Pump Based On Vibration SignalsAka ShriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscillator Design Guide For STM8 and STM32 MCUs PDFDokument54 SeitenOscillator Design Guide For STM8 and STM32 MCUs PDFDenis IvanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medium Voltage FusesDokument92 SeitenMedium Voltage FusesEliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ags 55 2Dokument194 SeitenAgs 55 2MD1000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Converter 120ac 4-20ma YokogawaDokument5 SeitenConverter 120ac 4-20ma YokogawaJlavieraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boston VFD CourseDokument61 SeitenBoston VFD CourseDEADMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Aspects of Impact Analysis of A Planned New 25 KV AC Railway Lines Systel On The Existing 3Kv DC Railway System in A Traction Supply Transition ZoneDokument5 SeitenSome Aspects of Impact Analysis of A Planned New 25 KV AC Railway Lines Systel On The Existing 3Kv DC Railway System in A Traction Supply Transition ZoneAnass BakNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Link Capacitor Current Good Paper PDFDokument9 SeitenDC Link Capacitor Current Good Paper PDFMukesh CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) or Mean Absolute Error (MAE) - Arguments Against Avoiding RMSE in The Literature (University Research Court)Dokument4 SeitenRoot Mean Square Error (RMSE) or Mean Absolute Error (MAE) - Arguments Against Avoiding RMSE in The Literature (University Research Court)logaritma19095Noch keine Bewertungen
- Urf1005 Urf1020Dokument2 SeitenUrf1005 Urf1020javirojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 20816 8 2018Dokument13 SeitenIso 20816 8 2018aravind.reliabilityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis Level - 1 FinalDokument265 SeitenVibration Analysis Level - 1 FinalSaadKianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal UAS-softDokument7 SeitenSoal UAS-softRahman Wahyu NurmajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Averaging Types What's The Difference - Siemens PLM Community - 364121Dokument7 SeitenAveraging Types What's The Difference - Siemens PLM Community - 364121Vili KamenovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InteliLite 9 1 3 0 Global GuideDokument422 SeitenInteliLite 9 1 3 0 Global GuideshashirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-20 Ma LPS Series Transducer Selection Guide: Wilcoxon Sensing TechnologiesDokument15 Seiten4-20 Ma LPS Series Transducer Selection Guide: Wilcoxon Sensing TechnologiesSeaman NoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelilite4 Amf8 Global GuideDokument573 SeitenIntelilite4 Amf8 Global GuideJaime Igor100% (1)
- Battjes & Janssen (2008) - Random Wave Breaking ModelsDokument13 SeitenBattjes & Janssen (2008) - Random Wave Breaking ModelsRodrigo Campos-CabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Motor Speed Controller With Triac and Microcontroller PDFDokument35 SeitenAC Motor Speed Controller With Triac and Microcontroller PDFarmarcelo100% (1)
- Power Probe Comparison Chart Breakdown: Product Power Probe 3 Power Probe 3S Power Probe 4Dokument1 SeitePower Probe Comparison Chart Breakdown: Product Power Probe 3 Power Probe 3S Power Probe 4Toño Luis Cervantes RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01-Beginning Vibration AnalysisDokument153 Seiten01-Beginning Vibration AnalysisAnonymous ffje1rpa100% (1)
- Real-Time Time-Domain Pitch Tracking Using WaveletsDokument12 SeitenReal-Time Time-Domain Pitch Tracking Using WaveletsyoudiezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FuseAutoChangeOver RDSO SPN 209 2012 VER 2Dokument17 SeitenFuseAutoChangeOver RDSO SPN 209 2012 VER 2Pooja SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC Short Circuit Ratings For The Circuit Breakers - Electric Power & Transmission & Distribution - Eng-TipsDokument6 SeitenIEC Short Circuit Ratings For The Circuit Breakers - Electric Power & Transmission & Distribution - Eng-TipssesabcdNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE STD 291-1991Dokument61 SeitenIEEE STD 291-1991sishio11100% (1)