Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
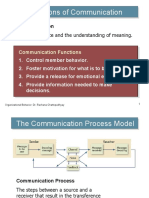
Communication: Communications Process
Hochgeladen von
Rafael OcampoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Communication: Communications Process
Hochgeladen von
Rafael OcampoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
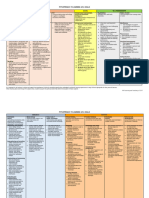
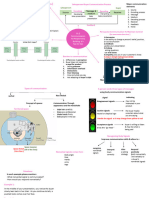
A process of creating and Importance of
sharing ideas, information, COMMUNICATION Communication
views, facts, feelings, etc.
among the people to reach
1. The Basis of
Dr. Albert Mehrabian’s Types of Coordination
a common understanding 7-38-55% Rule Communication 2. Fluent Working
Elements of Personal 3. The Basis of Decision
Communication Formal Communication Making
Communications
7% spoken words 4. Increases Managerial
Process
38% voice, tone Classification Efficiency
55% body language 5. Increases Cooperation
Sender Vertical and Organizational
Peter Drucker on Communication
communication Place
Message Horizontal
6. Boosts Morale of the
“The most important thing in Employees
Communication
communication is hearing
Encoding what isn’t said.” Measures to improve
Feedback
communication
Paul Rankin’s Types of communication
Media Noise effectiveness
Research networks
1. Communication of
70% of our waking time is
Receiver spent in communicating
clarification of the idea.
2. Communication should
9% writing be according to the needs
Decoding 16% reading of the receiver.
30% speaking 3. Consulting others before
45% listening communication.
Barriers to 4. Awareness about the
Communication Geier and Downey
Informal Communication language, tone and body
on listening
postures and gestures.
Attitudinal Listening Profile 5. Convey information
1. Semantic Barriers Types of Grapevine useful to the receiver.
2. Psychological Barriers Listening Styles network 6. Ensure proper feedback.
3. Organizational Barriers Leisure 7. Follow up
4. Personal Barriers Inclusive communications.
Stylistic 8. Be a good listener.
Technical
Communication Empathic
Created by: Group 2
Mentored by: Prof. Geuel F. Auste Nonconforming
MBA-Organization and Management This mental model is professionally used for academic discussion and consulting only.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- BrochureDokument3 SeitenBrochureAeron Jasper OquendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommunicationDokument35 SeitenCommunicationHARSH CHAUDHARINoch keine Bewertungen
- COMMUNICATION SKILLS FOR PROFESSIONALs BookDokument86 SeitenCOMMUNICATION SKILLS FOR PROFESSIONALs Bookshipra shakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perception and Communication in Businesss Organization: COMMUNICATION Is A Technique Involving TheDokument3 SeitenPerception and Communication in Businesss Organization: COMMUNICATION Is A Technique Involving TheEethan ENoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 - Communications - Information TechnologyDokument4 Seiten07 - Communications - Information TechnologyLee Ann Peñano CabanlitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purcom ReviewerDokument2 SeitenPurcom Reviewergimboongaling489Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advocacy BrochureDokument3 SeitenAdvocacy BrochureAeron Jasper OquendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Economics 2ND TermDokument12 SeitenModule 1 Economics 2ND TermClarisse De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pub Speak Tut 1Dokument8 SeitenPub Speak Tut 1Lhekkah SivarajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommunicationDokument26 SeitenCommunicationKelly Kavita100% (1)
- CommunicationDokument21 SeitenCommunicationIsha ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 (GNED05)Dokument3 SeitenLesson 1 (GNED05)Ralph ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Communication Lecture Notes Unit I PDFDokument5 SeitenBusiness Communication Lecture Notes Unit I PDFabhay kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral CommunicationDokument12 SeitenOral CommunicationTin CabosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Interpesonal CommunicationDokument30 Seiten2.1 Interpesonal Communicationsudirman612Noch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic CommunicationDokument6 SeitenTherapeutic CommunicationElleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negotiation Techniques Part 3Dokument17 SeitenNegotiation Techniques Part 3OzzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Sharing FinalDokument23 SeitenCommunication Sharing FinalYến TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Comms - Reviewer For Oral Test 1Dokument7 SeitenOral Comms - Reviewer For Oral Test 1Ken Juliana Fe IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Communication and Organizational Behavior: Section 6: Communication in An OrganizationDokument40 SeitenBusiness Communication and Organizational Behavior: Section 6: Communication in An OrganizationHoàng Hạnh Trang SV FTUNoch keine Bewertungen
- PComm Lesson 1 Ethics and PrinciplesDokument10 SeitenPComm Lesson 1 Ethics and PrinciplesShanley ConcordiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Mapping SHS ORAL COM 11 - For Merge MS WORDDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Mapping SHS ORAL COM 11 - For Merge MS WORDanon_148926655Noch keine Bewertungen
- HUMAN BEHAVIOR IN ORGANIZATIONDokument12 SeitenHUMAN BEHAVIOR IN ORGANIZATIONCrystal ValeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial CommunicationDokument6 SeitenManagerial CommunicationSubrahmanyam AchantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 Soft SkillsDokument76 SeitenModule 4 Soft SkillsDemo RayneraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyp Approach To Learning Skills Al Jabr Islamic SchoolDokument2 SeitenPyp Approach To Learning Skills Al Jabr Islamic SchoolZahra SalsabilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module FinalDokument84 SeitenModule Finalasif nadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication: MDM B002 Organization and Management By: Denver L. CornelDokument27 SeitenCommunication: MDM B002 Organization and Management By: Denver L. CornelDenver L Cornel100% (1)
- Rev 1 (GNED05)Dokument3 SeitenRev 1 (GNED05)Ralph ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Comm Nature of CommunicationDokument2 SeitenOral Comm Nature of CommunicationLaila Marie BuccatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop On Interpersonal Skills - TentativeDokument13 SeitenWorkshop On Interpersonal Skills - TentativeAbhinav ChopraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devoir de Communication GRPE 7Dokument11 SeitenDevoir de Communication GRPE 7N'ZI KOUASSI JEAN JACQUESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purposive CommDokument3 SeitenPurposive CommCherith May DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purposive CommunicationDokument6 SeitenPurposive CommunicationThea MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Contemporary Management Canadian 5th Edition Jones Solutions ManualDokument27 SeitenEssentials of Contemporary Management Canadian 5th Edition Jones Solutions Manualderrickgrantpnykbwjzfx100% (23)
- Commonication SkillsDokument57 SeitenCommonication SkillsrumsfeldzindogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purposive Communication STUDY GUIDEDokument4 SeitenPurposive Communication STUDY GUIDEjean ApostolNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELT 5 Mitrix Research BSEDDokument34 SeitenELT 5 Mitrix Research BSEDPrince josua RivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCM 04 Assessment Task 2Dokument5 SeitenMCM 04 Assessment Task 2Eula Cary MagpantayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comm Skills OutlineDokument5 SeitenComm Skills Outlinemichellegichuhi94Noch keine Bewertungen
- OralDokument9 SeitenOralJhoanne CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CustomerRelation Reviewer3 04Dokument11 SeitenCustomerRelation Reviewer3 04Julius MuicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disciplines of CommunicationDokument14 SeitenDisciplines of CommunicationMary Angeline L. BatacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Map For SHS ORAL COM - For MergeDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Map For SHS ORAL COM - For MergeCarole Janne Endoy100% (2)
- Bussinus Communication AhmadDokument43 SeitenBussinus Communication AhmadIbrar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENE05 - Module 1Dokument13 SeitenGENE05 - Module 1FERNANDEZ BEANoch keine Bewertungen
- Ge-Com Midterms TransDokument13 SeitenGe-Com Midterms TranszapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Communication and Presentation SkillsDokument44 SeitenBusiness Communication and Presentation SkillsAbinash JasrotiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module - 1 - Lesson - 1 STSDokument9 SeitenModule - 1 - Lesson - 1 STSAm AsdfghjklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purposive CommunicationDokument4 SeitenPurposive CommunicationMiguel Jude Espanto Bautista Jr.100% (1)
- Poblacion 3, Gerona, Tarlac Senior High School DepartmentDokument6 SeitenPoblacion 3, Gerona, Tarlac Senior High School DepartmentMarvin Dagdag MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Training ProgramDokument25 SeitenCommunication Training Programchetan bhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 246 - Organizational Behaviour-Pearson Education Limited (2020)Dokument5 Seiten246 - Organizational Behaviour-Pearson Education Limited (2020)mozam haqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process, Principlesðics CommunicationDokument15 SeitenProcess, Principlesðics CommunicationAyanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Map ch.5Dokument3 SeitenMind Map ch.5minaayyman27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sampe Core CompetencyDokument1 SeiteSampe Core CompetencyAbet SionoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng 3a - Note1Dokument3 SeitenEng 3a - Note1chezyl cadinongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of TopicsDokument2 SeitenSummary of TopicsSaila mae SurioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral CommunicationDokument24 SeitenOral CommunicationMackee SubongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADJUSTING ENTRIES Mumu NotesDokument2 SeitenADJUSTING ENTRIES Mumu NotesRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilagan - First AidDokument1 SeiteIlagan - First AidRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SJ and SL NotesDokument2 SeitenSJ and SL NotesRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Grading: Body Shapes and Action: Phiilppine Cultural College Manila Campus Scope and Sequence S.Y.:2018-2019Dokument10 SeitenFirst Grading: Body Shapes and Action: Phiilppine Cultural College Manila Campus Scope and Sequence S.Y.:2018-2019Rafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Budgeting Process in More Detail (Problem On Last Page)Dokument5 SeitenThe Budgeting Process in More Detail (Problem On Last Page)Rafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Management Self Study ExercisesDokument15 SeitenInventory Management Self Study ExercisesG VVLNRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample PPT On FS AnalysisDokument29 SeitenSample PPT On FS AnalysisRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template OSHprogramDokument7 SeitenTemplate OSHprogramRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample PPT On FS AnalysisDokument29 SeitenSample PPT On FS AnalysisRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Introduction To AccountingDokument22 SeitenLesson 1 Introduction To AccountingRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template OSHprogramDokument10 SeitenTemplate OSHprogramRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trade Discount - Supplementary ProblemsDokument2 SeitenTrade Discount - Supplementary ProblemsRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Discount - Supplementary ProblemsDokument2 SeitenCash Discount - Supplementary ProblemsRafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam On JE & AEDokument1 SeiteExam On JE & AERafael OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TC2-Cross Reference Table For Standards On Rotating MachineryDokument4 SeitenTC2-Cross Reference Table For Standards On Rotating MachineryNguyenBaCuocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.5Dokument32 SeitenChapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.5PREEVITHANoch keine Bewertungen
- AL3452 Operating Systems Lecture Notes 1Dokument278 SeitenAL3452 Operating Systems Lecture Notes 1rishashri004Noch keine Bewertungen
- AutoCAD MEP Sistemas Electricos PDFDokument104 SeitenAutoCAD MEP Sistemas Electricos PDFtabman59Noch keine Bewertungen
- OptiSystem 7.0 Release NotesDokument3 SeitenOptiSystem 7.0 Release NotesRonald SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significant Ships 1994Dokument96 SeitenSignificant Ships 1994Joe Tahir100% (2)
- Technical Overview On AHUDokument12 SeitenTechnical Overview On AHUJahidul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A DSL For Collaborative Business ProcessDokument6 SeitenA DSL For Collaborative Business ProcesskenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 - Overview of C#Dokument31 SeitenModule 2 - Overview of C#api-19796528Noch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Six Exam of C++Dokument10 SeitenSenior Six Exam of C++Christian AMANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Washer Tech Data SheetDokument16 SeitenWasher Tech Data SheetDavid LovatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revolutionize Today'S Workspace: Multifunction, Color, Wireless Laser PrinterDokument8 SeitenRevolutionize Today'S Workspace: Multifunction, Color, Wireless Laser PrinterNBS MarketingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants of Success For Online CommunitiesDokument11 SeitenDeterminants of Success For Online CommunitiesCleopatra ComanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate: of ConformityDokument3 SeitenCertificate: of ConformityGerson SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Removal of Default Vbe 8 - BBB GraphicsDokument4 SeitenRemoval of Default Vbe 8 - BBB Graphicsmario nogueraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTS Installation GuidelineDokument74 SeitenBTS Installation Guidelinekhalis@hotmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Wireless Power Transfer System For RailwDokument9 SeitenDesign of Wireless Power Transfer System For Railw19TK5AO265 V.NavaneethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- So NetDokument110 SeitenSo NetRaj_Jai03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solong: and Thanks For All The Fish!Dokument10 SeitenSolong: and Thanks For All The Fish!Allan GoublaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual: CX501 CX501B CX501ADokument31 SeitenService Manual: CX501 CX501B CX501AAriNetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling System Electrolysis: Ron Davis Racing Products IncDokument2 SeitenCooling System Electrolysis: Ron Davis Racing Products IncLazarus GutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VU - Software Testing March 21Dokument17 SeitenVU - Software Testing March 21Srikanth MarepalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shilpi Agarwal ResumeDokument3 SeitenShilpi Agarwal ResumeShilpi AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vi Editor Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteVi Editor Cheat SheetChris HarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SC 37 Operating Instructions 0928Dokument148 SeitenSC 37 Operating Instructions 0928Pranav PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Waste Recyclers in GurgaonDokument2 SeitenE Waste Recyclers in Gurgaonewaste gurgaonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project EEE PDFDokument7 SeitenMini Project EEE PDFAmit Kr SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- (02.i.pm2 Template.v3) .Business Case. (ProjectName) - (DD MM Yyyy) - (VX.X)Dokument14 Seiten(02.i.pm2 Template.v3) .Business Case. (ProjectName) - (DD MM Yyyy) - (VX.X)programando facilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study: Reverse Engineering FacemojiDokument16 SeitenCase Study: Reverse Engineering Facemojizappergod100% (1)
- Module 2Dokument13 SeitenModule 2PHEBE CIASNoch keine Bewertungen