Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BPSY 50 Ch1 Introduction To Psychology
Hochgeladen von
Katherine Sapo0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
36 Ansichten2 Seitenit is all about the basic introduction to psychology
Originaltitel
BPSY 50 Ch1 Introduction to Psychology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenit is all about the basic introduction to psychology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
36 Ansichten2 SeitenBPSY 50 Ch1 Introduction To Psychology
Hochgeladen von
Katherine Sapoit is all about the basic introduction to psychology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
BPSY 50: Introduction to Psychology secretions of the ductless glands biologically
Prepared by: Gideon Luke P. Ty, RPm affect behavior.
2. Behavioral Perspective
Goals of Psychology Behavior refers to all acts and activities of the
1. Describe organism. According to John B. Watson who first
2. Explain proposed behaviorism, strict objectivity should
3. Understand be practiced when determining the cause of
4. Predict behavior. External events can be modified and
5. Control/Change also controlled to give rise to behavior that may
be desirable or undesirable. With so much belief
Significant Persons in the History of Psychology and in his perspective of behavior, Watson challenged
their contributions skeptics to give him a dozen infants and boasted
1. Aristotle – wrote budy and mind relationship in that he will train the infants to be whatever he
his book De Anima would want them to be (doctors, lawyers,
2. John Locke – ideas are acquired through politicians etc).
experience and interaction with the environment 3. Cognitive Perspective
3. Rene Descartes – innate ideas already exist at Cognition, particularly involves mental processes
birth or the internal workings of the individual such as
4. Wilhelm Wundt – established the first thinking, remembering, learning, perceiving,
psychological experimental laboratory at Liepzig, imagining, analyzing and the like. These
Germany processes cannot be directly observed or
5. G. Stanley Hall – established the first measured and has been proposed to overcome the
psychological lab in the US shortcomings of the behavioral perspective.
6. Raymond Cattell – designed the 16PF 4. Psychodynamic Perspective
Questionnaire Sigmund Freud seemed to have become so
7. Sir Francis Galton – studied individual engrossed in studying his patients’ behavior to
differences; introduced intelligence test have established the workings of an unconscious
8. E.B. Titchener – introduced structuralism; mind. According to his theory, undesirable
introspection experiences of the individual are forced out of
9. William James – introduced functionalism awareness into the unconscious mind. These
10. Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Kohler, Kurt “undesirables”, however, become manifested in
Koffka – introduced Gestalt Psychology our dreams, slips of speech, mannerisms, and
11. Sigmund Freud – used hypnosis to treat patients may not turn out to be the cause of emotional
suffering from hysteria problems.
12. John Watson – introduced Behaviorism 5. Humanistic Perspective
13. B.F. Skinner – introduce operant conditioning Also known as the Phenomenological Perspective
14. Edward Thorndike – introduced connectionism (the “third force” in Psychology) and was
15. Sinforoso Padilla – the first major in Psychology developed by Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers,
from the undergraduate to the doctorate level both were American psychologists. This
16. Angel de Blas – established the Experimental approach to behavior is subjective and considers
Psychology laboratory in UST the person’s concept of himself and his
17. Estefania Aldaba-Lim – first Filipino to receive experience as basis for his behavior.
a PhD in Clinical Psychology from the University Phenomenology further elevates the status of man
of Michigan from the animals.
18. Alfredo Lagmay – chairman of UPDP for 22 6. Sociocultural Perspective
years This is one of the two recent additions to
19. Jaime Bulatao, S.J. – established the the perspectives in psychology and offers a new
Department of Psychology at Ateneo de Manila angle to explaining behavior. The sociocultural
University perspective is a combination of Social
Psychology, which focuses primarily on the study
Perspectives/Approaches in Psychology of group dynamics, social roles, behavior as
1. Neurobiological Perspective affected by norms and interpersonal
The nervous system and the endocrine system are relationships. The other is that of Cultural
two body systems that have much impact on Psychology which focuses on lifestyle as a
behavior. The electrochemical activities in the product of cultural norms, values, and
brain and the neural pathway and the chemical expectations.
7. Evolutionary Perspective 12. Cultural Psychology - Studies the ways in which
This is the other new addition to the list of an thindividual’s culture, subculture, and ethnic
perspectives in psychology. The focus is on the group membership influence behavior.
biological basis of mental characteristics that all 13. Social Psychology - Investigates human social
living organisms share. Here, the mind is seen as behavior as it is affected by attitudes, conformity,
a set of information processing machines attraction, aggression, group dynamics, etc.
designed to function in the same way as Darwin’s
Natural Selection. Methods used in Psychological Research
1. Naturalistic Observation
Specializations in Psychology 2. Survey – Questionnaire
1. Clinical Psychology - Concentrates on the 3. Case Study
alleviation of the client’s condition by conducting 4. Archival Research
clinical investigation, assessment, and 5. Experimental Method
psychotherapy. 6. Correlation Method
2. Developmental Psychology - Studies and
conducts research on human development from Notes:
conception to adulthood, works with children
with special needs, consulting with their parents
and schools.
3. Educational Psychology - Investigates the
teaching-learning situation, develops appropriate
measurements, and evaluates educational
programs/curricula
4. Engineering Psychology - Conducts research on
human factors that will affect the design of
machineries, computers, airplanes, automobiles,
architectures, space shuttles for industry, business
and the military.
5. Sports Psychology - It involves the study of
how psychological factors affect performance
and how participation in sport and exercise
affect psychological and physical factors
6. Forensic Psychology - Studies the etiology of
crime, profiles criminal behavior, and acts as
consultant for rehabilitation programs and
prisons.
7. Industrial-Organizational Psychology - Do
selection, training, and evaluation of employees
on-the-job; improves human relations and work
environment organizations.
8. Consumer Psychology - Conducts research on
the characteristics of consumers and the proposed
techniques in advertising, marketing, packaging
goods based on the results
9. Counselling Psychology - Does one-on-one
counselling and psychotherapy and conducts
researches on the etiology of emotional
disturbances
10. Paranormal Psychology - Studies documents
and events which may be classified as
supernatural and provide possible explanations
for such.
11. Health Psychology - Studies the relationship
between the mind and the body and how behavior
affects health; applies psychological principles in
promoting health and preventing illness.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Humanbehaviorpart 1Dokument10 SeitenHumanbehaviorpart 1Faith CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- QE ReviewerDokument12 SeitenQE ReviewerMicaela Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to PsychologyDokument7 SeitenIntroduction to PsychologyMichelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTROPSY Reviewer (Book-Based Only) Chapters 1-2Dokument12 SeitenINTROPSY Reviewer (Book-Based Only) Chapters 1-2RAYNE BERNADETTE BALINASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Au PRN General Psychology Handouts Psychology Course Audit 1 2023 2024Dokument7 SeitenAu PRN General Psychology Handouts Psychology Course Audit 1 2023 2024Edrian SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Psychology Chapter 1 OverviewDokument32 SeitenGeneral Psychology Chapter 1 Overviewroyal mimingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide: History & Approaches: Vikram Akam AP Psychology Per. 2 09/30/2011Dokument3 SeitenStudy Guide: History & Approaches: Vikram Akam AP Psychology Per. 2 09/30/2011Vik6370Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Psychology Prelims 2Dokument8 SeitenIntroduction To Psychology Prelims 2Kamille Hannah JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTROPSY Reviewer (Book and Lecture Notes) Chapters 1 and 2Dokument11 SeitenINTROPSY Reviewer (Book and Lecture Notes) Chapters 1 and 2jonaxx enthusiastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alina Rafique's Psychology Assignment on Major ConceptsDokument17 SeitenAlina Rafique's Psychology Assignment on Major ConceptsAlina MahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Cherryl Calades - Copy (Autosaved)Dokument184 SeitenPsychology Cherryl Calades - Copy (Autosaved)carlo john balleta100% (1)
- Intro To PsychologyDokument5 SeitenIntro To PsychologyBailey EtormaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology - Scientific Study of Behavior and MentalDokument2 SeitenPsychology - Scientific Study of Behavior and MentalErwin CabangalNoch keine Bewertungen
- General PsychologyDokument5 SeitenGeneral PsychologyFeisty BelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PsychologyDokument31 SeitenIntroduction To PsychologyAshish Kaswan100% (1)
- Unit 1 and 2Dokument13 SeitenUnit 1 and 2Rachelle EspañolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PsychologyDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To PsychologyAbdulqadir AbdallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Psych Chapter One NotesDokument5 SeitenIntro To Psych Chapter One NotesPaul IkonenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University PSYC01 1st Term NotesDokument9 SeitenAteneo de Zamboanga University PSYC01 1st Term NoteshaohanskendrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Intro To PsychologyDokument9 SeitenModule 1 Intro To PsychologyGinelQuenna De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity #1Dokument5 SeitenActivity #1Anne Caryl Cabral AfableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication 3 13990 494Dokument34 SeitenPublication 3 13990 494tejuc12082005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PsychologyDokument40 SeitenIntroduction To PsychologyRuzaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS Psychology Notes: By-: Asad Chaudhary CSS Online Coaching, LahoreDokument131 SeitenCSS Psychology Notes: By-: Asad Chaudhary CSS Online Coaching, LahoreCh Hassan TajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition and Goals of PsychologyDokument8 SeitenDefinition and Goals of PsychologyDhom Ortiz CandelariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology NotesDokument3 SeitenPsychology NotesJona D'johnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Unit 1 2 3 4Dokument38 SeitenPsychology Unit 1 2 3 4yuwak chhantelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PsychologyDokument5 SeitenPsychologyAfrasiab HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenStax Psychology2e LN01Dokument5 SeitenOpenStax Psychology2e LN01Shehib GulaimidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PsychologyDokument34 SeitenIntroduction To PsychologyRazi BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psyc 1133 Notes: Video: Week 1 IntroductionDokument9 SeitenPsyc 1133 Notes: Video: Week 1 IntroductionTyler MangumNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Psyc-All in One-2013Dokument237 SeitenGeneral Psyc-All in One-2013Galoo LagesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRUCTURALISM. Wundt Is Best Known For Turning The Study Of: Section 1 IntroDokument6 SeitenSTRUCTURALISM. Wundt Is Best Known For Turning The Study Of: Section 1 Introjohn FlanneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.introduction To PsychologyDokument5 Seiten1.introduction To PsychologyShahinur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Psychology 023526Dokument582 SeitenGeneral Psychology 023526Solomon MesfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Introduction and Research MethodsDokument4 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction and Research MethodsMarco RagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoritical FoundationDokument45 SeitenTheoritical FoundationDipti PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ciccarelli 6e CH01 PPT ForuploadDokument76 SeitenCiccarelli 6e CH01 PPT ForuploadLynn YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is PsychologyDokument4 SeitenWhat Is PsychologyKhim Wanden AvanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology2 PDFDokument7 SeitenPsychology2 PDFRahat Fardin RiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSYCHOLOGYDokument8 SeitenPSYCHOLOGYAbubakkars SiddiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Science of PsychologyDokument5 SeitenThe Science of PsychologyWallen LagradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Origins of PsychologyDokument12 SeitenOrigins of PsychologyShane GerolagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Psychology: Psychology Is The Study of Human BehaviourDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To Psychology: Psychology Is The Study of Human BehaviourZhel CarolinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PsychologyDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To PsychologyLornie SagarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint Presentation: General PsychologyDokument423 SeitenPowerpoint Presentation: General PsychologyAdesh Nidhi TiwaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Week - Intro To PsychologyDokument32 Seiten1st Week - Intro To PsychologyDaniyal QuddusiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Psych Reviewer Na Di Ko Na AlamDokument14 SeitenIntro To Psych Reviewer Na Di Ko Na Alamshayreyes0401Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Nature of Psychology: Psychology As A ScienceDokument4 SeitenThe Nature of Psychology: Psychology As A ScienceHope AlternadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tree Map - How Psychology Started & DevelopedDokument5 SeitenTree Map - How Psychology Started & DevelopedAliz328Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual 1introductionDokument24 SeitenManual 1introductionL YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Psychology Lec. Notes FinalDokument134 SeitenBasic Psychology Lec. Notes FinalPhilip Mutua100% (1)
- Lecture 2Dokument27 SeitenLecture 2Raja Awais LiaqautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bba 4th Sem Psychology @MBK PDFDokument138 SeitenBba 4th Sem Psychology @MBK PDFAastha Sharma75% (4)
- Psychology Chapter 1Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Chapter 1kar fangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen. Pschology ModuleDokument61 SeitenGen. Pschology ModuleGRACE VERIDIANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology As A ScienceDokument13 SeitenPsychology As A SciencedimitriyzizkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psyc 101 Assignment 1Dokument22 SeitenPsyc 101 Assignment 1lola988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes of Ch-1 Psychology (Paid Batch)Dokument13 SeitenNotes of Ch-1 Psychology (Paid Batch)AishleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unlocking the Mind: Exploring the Depths of Human PsychologyVon EverandUnlocking the Mind: Exploring the Depths of Human PsychologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- College AdministrationDokument13 SeitenCollege AdministrationGirmaye HaileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pinnacle Sdit68l1 l42cs12css2c h12c h22c Ps1 p1 Batches 1Dokument9 SeitenPinnacle Sdit68l1 l42cs12css2c h12c h22c Ps1 p1 Batches 1Snehal RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Research Title: Pictionary: A Tool in Introducing Filipino Sign Language To Out of School Youth Who Is DeafDokument3 SeitenAction Research Title: Pictionary: A Tool in Introducing Filipino Sign Language To Out of School Youth Who Is Deafkishia peronceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Interpersonal Relationship: An Individual Cannot Work or Play Alone Neither Can He Spend His Life AloneDokument2 SeitenImportance of Interpersonal Relationship: An Individual Cannot Work or Play Alone Neither Can He Spend His Life AlonenavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Paper: Instructions: Draw A Line Through Either A, B, or C To Answer Each Question. B BDokument8 SeitenListening Paper: Instructions: Draw A Line Through Either A, B, or C To Answer Each Question. B BLila LilakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015/16 MOCK EXAM MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 1: Question-Answer BookDokument34 Seiten2015/16 MOCK EXAM MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part Paper 1: Question-Answer BookCheuk Nam LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Admit Card 2019-20 Odd-SemDokument2 SeitenAdmit Card 2019-20 Odd-SemVIKASH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Podar Education Presentation 2020Dokument14 SeitenPodar Education Presentation 2020MohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sally-Mangan SADokument30 SeitenSally-Mangan SAAlex NichollsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Examination Routine A 2021 NewDokument2 SeitenMock Examination Routine A 2021 Newmufrad muhtasibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges Encountered by Students, Parents, and Teachers in The Implementation of Modular Distance Learning at Baras National High SchoolDokument7 SeitenChallenges Encountered by Students, Parents, and Teachers in The Implementation of Modular Distance Learning at Baras National High SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Calendar Semester 1 2019 - 2020 SessionDokument2 SeitenAcademic Calendar Semester 1 2019 - 2020 Sessionchee pin wongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Education Allowance FormDokument2 SeitenEducation Allowance FormGaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Language Test B: GrammarDokument2 SeitenUnit 2: Language Test B: GrammarBelen GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 - Unit Test 1Dokument1 Seite15 - Unit Test 1gildae219100% (1)
- Orthodontist Career PosterDokument1 SeiteOrthodontist Career Posterapi-347444805Noch keine Bewertungen
- Validity and Reliability of The BOD POD S / T Tracking SystemDokument5 SeitenValidity and Reliability of The BOD POD S / T Tracking SystemCallum BromleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vicente - Chapter 3Dokument4 SeitenVicente - Chapter 3VethinaVirayNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPA Visual Arts CGDokument30 SeitenSPA Visual Arts CGMary Cris63% (8)
- VTU-Viva - Time Table August - 2020 - B-Arch - Thesis and PT PDFDokument1 SeiteVTU-Viva - Time Table August - 2020 - B-Arch - Thesis and PT PDFCulinary InterestsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume - Takamura, AimeeDokument1 SeiteResume - Takamura, AimeeAimeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Both Texts Discuss The Topic of Technological Changes That Museums Have Undergone Over The Last DecadeDokument2 SeitenBoth Texts Discuss The Topic of Technological Changes That Museums Have Undergone Over The Last DecadefonderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zamboanga National High School West: Lesson 1: Use Sewing Machines CDokument1 SeiteZamboanga National High School West: Lesson 1: Use Sewing Machines CJenniferCarabotMacasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Critical Review Form Qualitative StudiesDokument12 SeitenGuidelines For Critical Review Form Qualitative StudiesTopo SusiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohini Jain v. State of KarnatakaDokument12 SeitenMohini Jain v. State of KarnatakaNagendraKumar NeelNoch keine Bewertungen
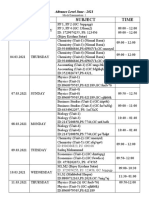
- Re - Examination 2020: Second Term Examinations - 2020Dokument16 SeitenRe - Examination 2020: Second Term Examinations - 2020hitarth shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thapar ScholarshipDokument12 SeitenThapar ScholarshipDHRUVAL SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science and Orthodoxy: A Historical PerspectiveDokument4 SeitenScience and Orthodoxy: A Historical PerspectiveVeselin SvorcanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top IELTS Coaching Centers in AhmedabadDokument12 SeitenTop IELTS Coaching Centers in AhmedabadDimpleMahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sidneys ResumeDokument3 SeitenSidneys Resumeapi-355088892Noch keine Bewertungen