Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Auditor's Responsibilities Relating to Fraud
Hochgeladen von
JaJ08Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Auditor's Responsibilities Relating to Fraud
Hochgeladen von
JaJ08Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ISA 240 Financing
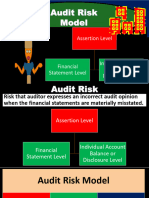
The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud
in an Audit of Financial Statements
(Beginning on or after December 15, 2009)
Application of ISA 315 (Revised) and ISA 330 in relation to RMM due to fraud
Misstatements in FS can arise from either fraud or error. Fraud vs error? Intentional or unintentional.
TWO TYPES MISSTATEMENTS RELEVANT TO AUDITOR: reasonable assurance na free fr. MM
1. Misstatements Resulting from fraudulent Reporting Auditor doesn’t make legal determinations
2. Misstatements from misappropriation of assets of whether fraud has actually occurred.
OBJECTIVES OF THE AUDITOR
a. To identify and assess the RMM of FS due to fraud
b. To obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding MM due to fraud, through designing and
implementing appropriate responses; and
c. To respond appropriately to fraud or suspected fraud identified during the audit.
Fraud risk factors – events or conditions that indicate an incentive or pressure to commit fraud or
opportunity to commit fraud
REQUIREMENTS
Professional Skepticism
Discussion among the engagement Team – matters to be communicated to team members not
involved in the discussion
Risk Assessment Procedures and Related Activities
o Management and Others within the Entity
Auditor shall make inquiries regarding management’s
a. assessment of RMM in FS
b. process for identifying and responding to the risks of fraud
c. communication to those charged with governance – processes for identifying and
responding to the risks of fraud
d. communication to employees – views on business practices and ethical behavior
Inquiries to determine whether they [mgt, others within the entity, IA function (for entities
who have)] have knowledge of any actual, suspected or alleged fraud affecting the entity.
o Those Charged with Governance (unless involved in managing the entity)
Understanding of how they exercise oversight of processes for identifying risks of fraud
Inquiries to determine whether they have knowledge…
o Unusual or Unexpected Relationships Identified o Other Information
Evaluate whether it may indicate RMM Consider if it indicates RMM
o Evaluation of Fraud Risk Factors
Fraud risk factors may not necessarily indicate existence of fraud but have often been
present in circumstances where frauds have occurred = may indicate RMM due to fraud
Identification and Assessment of the RMM Due to Fraud
o ISA 315 (Revised): Identify and assess RMM due to fraud at FS level and at assertion level for
classes of transactions, account balances and disclosures.
o Fraud in revenue recognition o RMM due to fraud = significant risks
Responses to the Assessed RMM Due to Fraud
o Overall Responses
Inquiries to determine whether they have knowledge…
o Audit Procedures Responsive to Assessed RMM Due to fraud at the Assertion level
Inquiries to determine whether they have knowledge…
o Audit Procedures Responsive to Risks Related to Management Override of Controls
Inquiries to determine whether they have knowledge…
Evaluation of Audit Evidence
o Evaluation of Fraud Risk Factors
Auditor Unable to Continue Engagement
o Evaluation of Fraud Risk Factors
Written Representations
o Evaluation of Fraud Risk Factors
Communications to Management and with Those Charged with Governance
o Evaluation of Fraud Risk Factors
Communications to Regulatory and Enforcement Authorities
o Evaluation of Fraud Risk Factors
Documentation
o Evaluation of Fraud Risk Factors
Internal Control
TOC
Sales
Purchases
Inventories
Fixed Assets
Cash Receipts
Cash Disbursements
Payroll
Investing
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Fraud Audit: Responding to the Risk of Fraud in Core Business SystemsVon EverandThe Fraud Audit: Responding to the Risk of Fraud in Core Business SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT.0105 - Fraud Error and Non ComplianceDokument9 SeitenAT.0105 - Fraud Error and Non ComplianceMaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction to Anti-Bribery Management Systems (BS 10500): Doing right thingsVon EverandAn Introduction to Anti-Bribery Management Systems (BS 10500): Doing right thingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRAUDDokument3 SeitenFRAUDprincess manlangitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk-Based Audit Approach RoadmapDokument141 SeitenRisk-Based Audit Approach RoadmapDanielle May CequiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- At.106.1 Fraud Error and Non Compliance My StudentsDokument9 SeitenAt.106.1 Fraud Error and Non Compliance My StudentsLimuel NievoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isa 240Dokument67 SeitenIsa 240Darren LowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 11. Plan The Audit - Risk Assessment - Inherent Risk (Kuliah 12)Dokument43 SeitenPertemuan 11. Plan The Audit - Risk Assessment - Inherent Risk (Kuliah 12)aulia fadilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- HO2-B - Risk-Based Audit of Financial Statements Part 2 (Risk Assessment)Dokument10 SeitenHO2-B - Risk-Based Audit of Financial Statements Part 2 (Risk Assessment)Jaynalyn MonasterialNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT - Fraud, Error, NoncomplianceDokument9 SeitenAT - Fraud, Error, NoncomplianceRey Joyce Abuel100% (1)
- Fraud Is Something That Is Done With Intent.: For Classroom Discussion Purposes OnlyDokument12 SeitenFraud Is Something That Is Done With Intent.: For Classroom Discussion Purposes OnlyKim EllaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Error Fraud and Non Compliance LAR in An Audit of Financial PDFDokument12 SeitenError Fraud and Non Compliance LAR in An Audit of Financial PDFAureen TabamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isa 240 Auditor Responsibility Relating To FraudDokument6 SeitenIsa 240 Auditor Responsibility Relating To Fraudnurmaisarahnurazim1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fraud in Audit-RevisedDokument6 SeitenFraud in Audit-Revisedbehroz khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detecting Financial Statement Fraud and Profiling FraudstersDokument12 SeitenDetecting Financial Statement Fraud and Profiling FraudstersAureen TabamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA 240 Audit ProjectDokument20 SeitenISA 240 Audit ProjectKarina Indus KahwagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing and Responding to Risks of Fraud in a Financial Statement AuditDokument173 SeitenAssessing and Responding to Risks of Fraud in a Financial Statement AuditTony amador gonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA 240 Audit of Financial Statements for Fraud RisksDokument4 SeitenISA 240 Audit of Financial Statements for Fraud RisksAnonymous XlHWbwyeq5100% (1)
- A UDI T: Chapter 10: Assessing and Re Sponding To Fraud RisksDokument48 SeitenA UDI T: Chapter 10: Assessing and Re Sponding To Fraud RisksMạnh hưng LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fraud Risk Document With AppendixDokument17 SeitenFraud Risk Document With AppendixNathalie PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditor's responsibility to detect fraud in financial auditsDokument10 SeitenAuditor's responsibility to detect fraud in financial auditsAra Jane T. Pinili100% (1)
- 14considering The Risk of Frauds, ErrorsDokument8 Seiten14considering The Risk of Frauds, ErrorsIrish SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 3 NotesDokument20 SeitenExam 3 NotesVince Cinco ParconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th Edition Alvin A Arens Randal J Elder Mark S Beasley Chris e HoganDokument31 SeitenSolution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th Edition Alvin A Arens Randal J Elder Mark S Beasley Chris e HoganMeredithFleminggztay100% (79)
- P - Fraud Risk InquiriesDokument4 SeitenP - Fraud Risk InquiriesHis HerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fraud Error Non-Compliance and Legal Liability Final1 PDFDokument7 SeitenFraud Error Non-Compliance and Legal Liability Final1 PDFJa NilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Note Audit From The Book. Learning Object 1 Define The Various Types of Fraud That Affect OrganizationDokument12 SeitenChapter 2 Note Audit From The Book. Learning Object 1 Define The Various Types of Fraud That Affect OrganizationkimkimNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUDIT KAMAL GARGDokument54 SeitenAUDIT KAMAL GARGBijay AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Ethics, Fraud and Internal Control</TITLEDokument91 SeitenChapter 3 Ethics, Fraud and Internal Control</TITLEJoelyn MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ca PDFDokument3 SeitenCa PDFHindutav aryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSA 315 and FraudDokument4 SeitenPSA 315 and FraudAngelo Gian CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Fraud Management TechniquesDokument40 SeitenEffective Fraud Management TechniquesAfan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sa 240Dokument2 SeitenSa 240Azru KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rodriguez Zyra-Denelle 09 JournalDokument9 SeitenRodriguez Zyra-Denelle 09 JournalDaena NicodemusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Assesing The Risk of Material Misstatement: Nama: Anissa Dinar Paraswansa NIM:12030122410010Dokument6 SeitenChapter 9 Assesing The Risk of Material Misstatement: Nama: Anissa Dinar Paraswansa NIM:12030122410010Anissa DinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AF W12 - Fraud Risk Assessment - ENGDokument17 SeitenAF W12 - Fraud Risk Assessment - ENGjokitugasbro.idNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing fraud and errorsDokument6 SeitenAuditing fraud and errorskris salacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th by ArensDokument32 SeitenSolution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th by ArensMeredithFleminggztay100% (80)
- 4 5850471109056532138Dokument39 Seiten4 5850471109056532138Yehualashet MulugetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective and General Principles Governing An Audit of Financial StatementsDokument137 SeitenObjective and General Principles Governing An Audit of Financial StatementsPia Verna Irish ToraynoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Professional Services, Inc.: Discussion QuestionsDokument6 SeitenExcel Professional Services, Inc.: Discussion QuestionskæsiiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Auditors' ResponsibilityDokument51 SeitenChapter 3 - Auditors' ResponsibilityddddddaaaaeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT.2814 - Considering Risks of Fraud Error and NOCLAR PDFDokument6 SeitenAT.2814 - Considering Risks of Fraud Error and NOCLAR PDFMaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 NotesDokument7 SeitenChapter 7 NotesSavy DhillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- At.3215 - Considering The Risk of Frauds Errors and NOCLARDokument10 SeitenAt.3215 - Considering The Risk of Frauds Errors and NOCLARDenny June CraususNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives and Scope of Financial Statement AuditDokument54 SeitenObjectives and Scope of Financial Statement AuditKogilavani a/p ApadoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA 240: The Auditor's Responsibilities Related To Fraud in An Audit of Financial StatementsDokument25 SeitenISA 240: The Auditor's Responsibilities Related To Fraud in An Audit of Financial StatementsIndriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing Theory 2Dokument13 SeitenAuditing Theory 2Ceejay FrillarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is FraudDokument8 SeitenWhat Is FraudVeneranda AtriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SA240 Sandeep ShahDokument40 SeitenSA240 Sandeep ShahKING OF TIK TOKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fraud RiskDokument56 SeitenFraud RiskJoman CorderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAFP Backgroud PDFDokument165 SeitenFAFP Backgroud PDFRahul KhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditor's Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in a Financial Statement AuditDokument25 SeitenAuditor's Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in a Financial Statement AuditNicole TondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Forensic Accounting PPTsDokument30 Seiten01 Forensic Accounting PPTsISHAAN VARSHNEYNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 - AudTheoDokument6 SeitenCHAPTER 3 - AudTheoVicente, Liza Mae C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Internal Controls, Fraud Motives and Experience in Assessing Likelihood of Fraud RiskDokument7 SeitenEffects of Internal Controls, Fraud Motives and Experience in Assessing Likelihood of Fraud RiskLeo CerenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 43) FraudDokument4 Seiten43) FraudkasimranjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditors ResponisbilityDokument5 SeitenAuditors ResponisbilityGigi LuceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- AA - Chapter 2Dokument5 SeitenAA - Chapter 2Jacqueline Kanesha JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 - Internal Control - NotesDokument14 SeitenUnit 3 - Internal Control - NotesNabhan JafferNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Great Challenges of the 21st CenturyDokument3 Seiten17 Great Challenges of the 21st CenturyArnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Accounting Issues (Draft)Dokument3 SeitenB. Accounting Issues (Draft)JaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fraud - Internal Auditing PDFDokument4 SeitenFraud - Internal Auditing PDFJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- DemianDokument16 SeitenDemianAngeline Qianhua0% (1)
- Strategy, Organization Design and EffectivenessDokument16 SeitenStrategy, Organization Design and EffectivenessJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR)Dokument8 SeitenModified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR)JaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fraud - Internal Auditing PDFDokument4 SeitenFraud - Internal Auditing PDFJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Subtotal SDokument18 SeitenSubtotal SJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data ValidationDokument5 SeitenData ValidationJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial analysis spreadsheetDokument6 SeitenFinancial analysis spreadsheetJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- SparklinesDokument3 SeitenSparklinesJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sorting ExcelDokument109 SeitenSorting ExcelJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- CORPORATION LAW PRINCIPLESDokument20 SeitenCORPORATION LAW PRINCIPLESStephanie Valentine100% (10)
- X y Formulatext 1 5 2 10 3 15 Column A Isformula? Column B Isformula?Dokument6 SeitenX y Formulatext 1 5 2 10 3 15 Column A Isformula? Column B Isformula?JaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Subtotals in Excel Ver2Dokument5 SeitenSubtotals in Excel Ver2JaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Subtotal SDokument18 SeitenSubtotal SJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exceljet Excel Shortcuts 150827Dokument22 SeitenExceljet Excel Shortcuts 150827Erika HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SparklinesDokument3 SeitenSparklinesJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- CIA Exam SampleDokument20 SeitenCIA Exam SampleJaJ0880% (5)
- For A Given Price, How Many Glasses of Lemonade Does A Lemonade Store Need To Sell Per Year To Break Even?Dokument10 SeitenFor A Given Price, How Many Glasses of Lemonade Does A Lemonade Store Need To Sell Per Year To Break Even?JaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jose Rizal and Emilio Jacinto: Two Heroes of the Philippine RevolutionDokument7 SeitenJose Rizal and Emilio Jacinto: Two Heroes of the Philippine RevolutionJaJ08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Russian Revolution History Grade 9 NotesDokument6 SeitenRussian Revolution History Grade 9 NotesYesha ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Research Agenda For Creative Tourism: OnlineDokument1 SeiteA Research Agenda For Creative Tourism: OnlineFelipe Luis GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musical Plays: in The PhilippinesDokument17 SeitenMusical Plays: in The Philippinesgabby ilaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pure TheoryDokument3 SeitenPure TheoryAshima MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payment of Bonus Form A B C and DDokument13 SeitenPayment of Bonus Form A B C and DAmarjeet singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICAO EDTO Course - Basic Concepts ModuleDokument63 SeitenICAO EDTO Course - Basic Concepts ModuleLbrito01100% (1)
- Agreement For Consulting Services Template SampleDokument6 SeitenAgreement For Consulting Services Template SampleLegal ZebraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russell's View On World Government in His Essay The Future of MankindDokument3 SeitenRussell's View On World Government in His Essay The Future of MankindRafaqat Ali100% (1)
- Courtroom Etiquette and ProcedureDokument3 SeitenCourtroom Etiquette and ProcedureVineethSundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hamilton EssayDokument4 SeitenHamilton Essayapi-463125709Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sunway Berhad (F) Part 2 (Page 97-189)Dokument93 SeitenSunway Berhad (F) Part 2 (Page 97-189)qeylazatiey93_598514100% (1)
- ePass for Essential Travel Between Andhra Pradesh and OdishaDokument1 SeiteePass for Essential Travel Between Andhra Pradesh and OdishaganeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hue University Faculty Labor ContractDokument3 SeitenHue University Faculty Labor ContractĐặng Như ThànhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Appian PlatformDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To The Appian PlatformbolillapalidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consent of Action by Directors in Lieu of Organizational MeetingsDokument22 SeitenConsent of Action by Directors in Lieu of Organizational MeetingsDiego AntoliniNoch keine Bewertungen
- English The Salem Witchcraft Trials ReportDokument4 SeitenEnglish The Salem Witchcraft Trials ReportThomas TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Member ListDokument487 SeitenLife Member Listpuiritii airNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esmf 04052017 PDFDokument265 SeitenEsmf 04052017 PDFRaju ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acts and Statutory Instruments: The Volume of UK Legislation 1850 To 2019Dokument24 SeitenActs and Statutory Instruments: The Volume of UK Legislation 1850 To 2019Adam GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Trends in The Popular Sector Traditional Medicine in Sri LankaDokument10 SeitenCurrent Trends in The Popular Sector Traditional Medicine in Sri Lankammarikar27Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Meaning of Life Without Parole - Rough Draft 1Dokument4 SeitenThe Meaning of Life Without Parole - Rough Draft 1api-504422093Noch keine Bewertungen
- PSEA Self Assessment Form - 2024 02 02 102327 - YjloDokument2 SeitenPSEA Self Assessment Form - 2024 02 02 102327 - Yjlokenedy nuwaherezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CardingDokument9 SeitenCardingSheena JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Map All in One PBA-2021-08-20 12-38-51Dokument1 SeiteMind Map All in One PBA-2021-08-20 12-38-51MikosamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment Decision RulesDokument113 SeitenInvestment Decision RulesHuy PanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 City Sheriff of Iligan City v. Fortunado (CANE)Dokument2 Seiten5 City Sheriff of Iligan City v. Fortunado (CANE)Jerry CaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Verses Proving Jesus Is GodDokument5 SeitenBible Verses Proving Jesus Is GodBest OfAntonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- History, and Culture of DenmarkDokument14 SeitenHistory, and Culture of DenmarkRina ApriliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business and Transfer Taxation Chapter 11 Discussion Questions AnswerDokument3 SeitenBusiness and Transfer Taxation Chapter 11 Discussion Questions AnswerKarla Faye LagangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gopal Bhar Golpo BengaliDokument2 SeitenGopal Bhar Golpo BengaliDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionVon EverandBusiness Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Be the Unicorn: 12 Data-Driven Habits that Separate the Best Leaders from the RestVon EverandBe the Unicorn: 12 Data-Driven Habits that Separate the Best Leaders from the RestBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (17)
- When to Jump: If the Job You Have Isn't the Life You WantVon EverandWhen to Jump: If the Job You Have Isn't the Life You WantBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (16)
- Speak With No Fear: Go from a nervous, nauseated, and sweaty speaker to an excited, energized, and passionate presenterVon EverandSpeak With No Fear: Go from a nervous, nauseated, and sweaty speaker to an excited, energized, and passionate presenterBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (78)
- Job Interview: Outfits, Questions and Answers You Should Know aboutVon EverandJob Interview: Outfits, Questions and Answers You Should Know aboutBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Freight Dispatcher Training: How to Build and Run a Successful Truck Dispatching Business Without Owning a Single TruckVon EverandFreight Dispatcher Training: How to Build and Run a Successful Truck Dispatching Business Without Owning a Single TruckBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- HOW SUCCESSFUL PEOPLE THINK: CHANGE YOUR LIFEVon EverandHOW SUCCESSFUL PEOPLE THINK: CHANGE YOUR LIFEBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- How to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpVon EverandHow to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Designing Your Life - Summarized for Busy People: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeVon EverandDesigning Your Life - Summarized for Busy People: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Your Talent Stack: How to Develop Your Skills and Talents, Stand Out, and Thrive in Your CareerVon EverandYour Talent Stack: How to Develop Your Skills and Talents, Stand Out, and Thrive in Your CareerBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)
- A Joosr Guide to... What Color is Your Parachute? 2016 by Richard Bolles: A Practical Manual for Job-Hunters and Career-ChangersVon EverandA Joosr Guide to... What Color is Your Parachute? 2016 by Richard Bolles: A Practical Manual for Job-Hunters and Career-ChangersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Find What You Love: 5 Tips to Uncover Your Passion Quickly and EasilyVon EverandFind What You Love: 5 Tips to Uncover Your Passion Quickly and EasilyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Jungian 16 Types Personality Test: Find Your 4 Letter Archetype to Guide Your Work, Relationships, & SuccessVon EverandJungian 16 Types Personality Test: Find Your 4 Letter Archetype to Guide Your Work, Relationships, & SuccessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (12)
- The Future-Proof Career: Strategies for thriving at every stageVon EverandThe Future-Proof Career: Strategies for thriving at every stageNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Monk and the Riddle: The Art of Creating a Life While Making a LivingVon EverandThe Monk and the Riddle: The Art of Creating a Life While Making a LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- The PMP Project Management Professional Certification Exam Study Guide PMBOK Seventh 7th Edition: The Complete Exam Prep With Practice Tests and Insider Tips & Tricks | Achieve a 98% Pass Rate on Your First AttemptVon EverandThe PMP Project Management Professional Certification Exam Study Guide PMBOK Seventh 7th Edition: The Complete Exam Prep With Practice Tests and Insider Tips & Tricks | Achieve a 98% Pass Rate on Your First AttemptNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideVon Everand(ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideBewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (2)
- 7 Rules of Power: Surprising - But True - Advice on How to Get Things Done and Advance Your CareerVon Everand7 Rules of Power: Surprising - But True - Advice on How to Get Things Done and Advance Your CareerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (26)
- Get That Job! The Quick and Complete Guide to a Winning InterviewVon EverandGet That Job! The Quick and Complete Guide to a Winning InterviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (15)
- Summary of Deep Work: by Cal Newport | Includes AnalysisVon EverandSummary of Deep Work: by Cal Newport | Includes AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Summary of Henriette Anne Klauser's Write It Down Make It HappenVon EverandSummary of Henriette Anne Klauser's Write It Down Make It HappenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taking the Work Out of Networking: An Introvert's Guide to Making Connections That CountVon EverandTaking the Work Out of Networking: An Introvert's Guide to Making Connections That CountBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (71)
- Virtual Assistant: Jobs, Companies, Services, Training, and SalaryVon EverandVirtual Assistant: Jobs, Companies, Services, Training, and SalaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 2-Hour Job Search: Using Technology to Get the Right Job Faster, 2nd EditionVon EverandThe 2-Hour Job Search: Using Technology to Get the Right Job Faster, 2nd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- How to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpVon EverandHow to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (231)
- Quitter: Closing the Gap Between Your Day Job and Your Dream JobVon EverandQuitter: Closing the Gap Between Your Day Job and Your Dream JobBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (31)
- The Job Interview Phrase Book: The Things to Say to Get You the Job You WantVon EverandThe Job Interview Phrase Book: The Things to Say to Get You the Job You WantBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)