Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Gerund or Infinitive 2 5478
Hochgeladen von
Claudia Claudia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
523 Ansichten1 Seiteexercises
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenexercises
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
523 Ansichten1 SeiteGerund or Infinitive 2 5478
Hochgeladen von
Claudia Claudiaexercises
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
2 - GERUND OR INFINITIVE
1st. option - RULE OF THUMB
Gerunds are often used when actions are real, concrete or completed:
I stopped smoking.
(The smoking was real and happened until I stopped.)
Infinitives are often used when actions are unreal, abstract, or future:
I stopped to smoke.
(I was doing something else, and I stopped; the smoking had not happened yet.)
FILL THE GAPS WITH EITHER AN INFINITIVE OR A GERUND ACCORDING TO THE RULE ABOVE:
1. Why don’t you stop (work) ______________ and take a rest?
2. The annoyed man threatened (call) __________________ the police.
3. When we told him the plan, he agreed (join) ________________ our team.
4. We can’t afford (buy) _____________ a new car.
5. Do you enjoy (make) _____________ other people angry?
6. This kind of sport involves (train) ____________ daily.
7. If you have finished (have) __________ your lunch, clear the table, please.
8. I had never anticipated (pay) ____________ so much for the redecoration.
9. Everybody dislikes (do) ___________ exams.
10. I was a bit lazy this time, but I promise (study) ____________ harder next time.
11. He managed (fix) _____________ the TV set himself.
12. If you want a quiet holiday, you should avoid (go) ____________ the coast in summer.
13. Do you intend (get) _____________ fit?
14. I admit (cheat) ____________ in the exam.
15. I missed (have) _____________ dinner with my old school mates.
2nd option - STUDY LISTS OF VERBS
VERBS FOLLOWED BY -ING
admit enjoy mind understand
anticipate escape miss
avoid excuse pardon It’s no good
consider finish postpone It’s no use
delay forgive practise It isn’t worth
deny involve risk
detest keep stop can’t stand / resist
dislike mention suggest can’t help
VERBS FOLLOWED BY TO- INFINITIVE
agree fail manage
appear hesitate prepare swear
arrange hope promise tend
care intend refuse threaten
decide learn seem afford
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- P You Must Answer This QuestionDokument6 SeitenP You Must Answer This QuestionzinminkyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placement Touchstone 1Dokument8 SeitenPlacement Touchstone 1LasBarrancasCiberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple Versus Present Continuous Board GameDokument6 SeitenPresent Simple Versus Present Continuous Board GameCrystal HuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making SuggestionsDokument1 SeiteMaking SuggestionsFmga GaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Course A2+ Test. Unit 9Dokument3 SeitenOn Course A2+ Test. Unit 9Taamaa Col LarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect Grammar Drills Warmers Coolers - 117983Dokument1 SeitePresent Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect Grammar Drills Warmers Coolers - 117983toma100% (1)
- Conditional-Sentences All TypesDokument2 SeitenConditional-Sentences All TypesClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditional-Sentences All TypesDokument2 SeitenConditional-Sentences All TypesClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverbs of Frecuency - ExercicesDokument2 SeitenAdverbs of Frecuency - ExercicesAne GaitónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple - All FormsDokument1 SeitePast Simple - All FormsrenataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Countable Uncountable NounsDokument23 SeitenCountable Uncountable NounsEmmanuel PaulinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverbs of DegreeDokument5 SeitenAdverbs of DegreeLuis Francisco Herrera GarayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal and Informal LettersDokument22 SeitenFormal and Informal LettersGABRIELLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Will Vs Be Going To QuizDokument1 SeiteWill Vs Be Going To QuizScarleth Caroline Bula PaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- I - Choose The Correct Option To Complete The Sentences.: Grammar NotesDokument3 SeitenI - Choose The Correct Option To Complete The Sentences.: Grammar Notessonia martinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExercisesDokument10 SeitenExercisesClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- There Is There Are PDFDokument2 SeitenThere Is There Are PDFMarileissy AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple Present Continuous Past Simple Comparative Superlative Must Mustn't Should Shouldn't Can Can't One or OnesDokument3 SeitenPresent Simple Present Continuous Past Simple Comparative Superlative Must Mustn't Should Shouldn't Can Can't One or Onesslavica_volkanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test EnglezaDokument8 SeitenTest EnglezaGuvernanta Ideala100% (1)
- All TensesDokument5 SeitenAll Tensesclaudiasimona90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question TagsDokument2 SeitenQuestion TagsAnonymous YC7SBiH7Wp57% (7)
- Simple Past and Past ContinuousDokument3 SeitenSimple Past and Past ContinuousDuddy EffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are You Going To... / X Follow-Up Question AnswerDokument2 SeitenAre You Going To... / X Follow-Up Question AnswerWilliam Mauricio RODRIGUEZ CLAVIJO100% (1)
- Perfect-English-Grammar ConditionalsDokument1 SeitePerfect-English-Grammar ConditionalsXheni RelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Victorias Milling v. CA G.R. No. 117356Dokument1 SeiteVictorias Milling v. CA G.R. No. 117356Pring SumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write Sentences From The Words in The Given Tense!: Tenses T 18Dokument2 SeitenWrite Sentences From The Words in The Given Tense!: Tenses T 18Lilli0% (1)
- Numbers Worksheet Homework PDFDokument3 SeitenNumbers Worksheet Homework PDFJohanna Corrales100% (1)
- Worksheet Simple - Past Tense 01Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet Simple - Past Tense 01Camilo Antonio Venegas Vicencio0% (1)
- B1 Too and Enough AD012Dokument2 SeitenB1 Too and Enough AD012Ayesha100% (1)
- BoardgameDokument1 SeiteBoardgameTBI WritingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zero Conditional If + Present Simple, PresentDokument2 SeitenZero Conditional If + Present Simple, PresentJoher TraslavinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Difference Between DO and MAKEDokument4 SeitenBasic Difference Between DO and MAKELenaps100% (1)
- Present - Perfect - or - Past - Simple X 3 PDFDokument7 SeitenPresent - Perfect - or - Past - Simple X 3 PDFClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Succeed in Cambridge B1 Preliminary SpeakingDokument42 SeitenSucceed in Cambridge B1 Preliminary SpeakingClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'Will & Going To' - English Quiz & Worksheet PDFDokument2 Seiten'Will & Going To' - English Quiz & Worksheet PDFjorge figueroa NarvaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Perfect Vs Past Simple Fun Activities Games Grammar Drills 48650Dokument2 SeitenPresent Perfect Vs Past Simple Fun Activities Games Grammar Drills 48650Andrei VasilicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Am Proud To Be MalaysianDokument3 SeitenI Am Proud To Be MalaysianXiao Dre86% (14)
- Have To, Don't Have ToDokument6 SeitenHave To, Don't Have ToTHO HỒNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple Past Perfect: ExamplesDokument2 SeitenPast Simple Past Perfect: ExamplesNur HafezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comic RubricDokument1 SeiteComic Rubricapi-354845873Noch keine Bewertungen
- ESL Brains Being Unproductive Uses of Gerund TV 7949Dokument4 SeitenESL Brains Being Unproductive Uses of Gerund TV 7949Вікторія K100% (1)
- Test VIII Module 1 ADokument2 SeitenTest VIII Module 1 ASamantha Pace100% (1)
- LearnEnglish British CouncilComparing and Contrasting - Modifying ComparativesDokument4 SeitenLearnEnglish British CouncilComparing and Contrasting - Modifying ComparativesÆónLunikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple Vs Cont PDFDokument1 SeitePast Simple Vs Cont PDFТатьяна МирнаяNoch keine Bewertungen
- What's The Difference? 'Will' and 'Be Going To'Dokument2 SeitenWhat's The Difference? 'Will' and 'Be Going To'TuyenLeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full and LessDokument2 SeitenFull and LessMariCarmenDoblasFloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Perfect WorksheetDokument1 SeitePresent Perfect WorksheetJane100% (1)
- Easter Egg HuntDokument1 SeiteEaster Egg HuntAngela P.0% (1)
- Wish Exercise 1Dokument2 SeitenWish Exercise 1Sevgi Ebru İnceelNoch keine Bewertungen
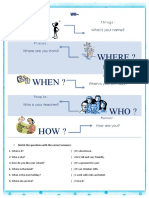
- WH Words and Questions Crosswords Fun Activities Games Grammar Guides One 32320Dokument3 SeitenWH Words and Questions Crosswords Fun Activities Games Grammar Guides One 32320NataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISE II Conversation. Society and Living StandardsDokument3 SeitenISE II Conversation. Society and Living StandardsHelena AlcónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cluster Word Web 2Dokument1 SeiteCluster Word Web 2api-430754451100% (1)
- Intermediate 2 Final Exam ReviewDokument9 SeitenIntermediate 2 Final Exam ReviewalejandrogvrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Make, Do, Have & TakeDokument6 SeitenMake, Do, Have & TakeBoke PachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dates in English ON + Dates and DaysDokument4 SeitenDates in English ON + Dates and DaysNiessel Esteban Vaca AstaizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humour Vocabulary LessonDokument2 SeitenHumour Vocabulary Lessonyouness100% (1)
- By Before (+time) : RememberDokument8 SeitenBy Before (+time) : RememberfranosullivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Much Many A Lot of PDFDokument2 SeitenMuch Many A Lot of PDFlunesmalditoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indefinite PronounsDokument8 SeitenIndefinite Pronounssonia martinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- City Vs Countrylife Test 7th Grade Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests 53720Dokument3 SeitenCity Vs Countrylife Test 7th Grade Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests 53720BEATRIZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 1 Grammar Extension 1 4Dokument1 SeiteLevel 1 Grammar Extension 1 4hector hernanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Will and Going To - ActivityDokument3 SeitenWill and Going To - ActivityGabriela FlórezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Perfect Time ExpressionsDokument1 SeitePresent Perfect Time ExpressionsDENILSON NOYOLA MARCIAL CERVANTESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roadmap A2 WB Unit 1Dokument6 SeitenRoadmap A2 WB Unit 1Sara Duda100% (1)
- A Family Affair A Family Affair: GrammarDokument4 SeitenA Family Affair A Family Affair: GrammarKaung Si Thu100% (1)
- Check Your Grammar: Gap Fill - This, That, These and ThoseDokument2 SeitenCheck Your Grammar: Gap Fill - This, That, These and ThoseOlga TrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giving Directions - Exercises 0Dokument3 SeitenGiving Directions - Exercises 0mitarmdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can T Stand Don't Mind Enjoy: I To Heavy Metal. I My Laptop. I L Around The Country. They Jane WeDokument3 SeitenCan T Stand Don't Mind Enjoy: I To Heavy Metal. I My Laptop. I L Around The Country. They Jane WeRobinson SuárezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerund-Or-Infinitive - TASK 1 - Juan YateDokument2 SeitenGerund-Or-Infinitive - TASK 1 - Juan YateDaniel HolguínNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerund and Infinitive 1st BTODokument2 SeitenGerund and Infinitive 1st BTOLuna Gaona VazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1 If It's Possible, Make A Sentence With Would + Infinitive'. If It's Not Possible, Use Used To + Infinitive'Dokument1 SeiteExercise 1 If It's Possible, Make A Sentence With Would + Infinitive'. If It's Not Possible, Use Used To + Infinitive'Claudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read The Following Text and Answer The Questions:: Exam Card 1Dokument40 SeitenRead The Following Text and Answer The Questions:: Exam Card 1Monica Petruta ArotariteiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TestDokument1 SeiteTestClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Admitere Clasa aIXa Liceu BilingvDokument4 SeitenTest Admitere Clasa aIXa Liceu BilingvClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Based On Upstream Unit 1Dokument4 SeitenHomework Based On Upstream Unit 1Claudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Based On UpstreamDokument4 SeitenHomework Based On UpstreamClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Unit 1&2Dokument3 SeitenHomework Unit 1&2Claudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument7 SeitenTensesClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teste OfiteriDokument10 SeitenTeste OfiteriClaudia BoianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From Cambridge Preliminary English Test 5 BookDokument8 SeitenPages From Cambridge Preliminary English Test 5 BookClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present PerfectDokument8 SeitenPresent PerfectClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Grammar Drills 103604Dokument1 SeiteRevision Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Grammar Drills 103604Claudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All TensesDokument3 SeitenAll TensesClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From Flyersx2Dokument14 SeitenPages From Flyersx2Claudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Present Simple Tense.: + N V, Vs - N V ? N VDokument1 SeiteUse Present Simple Tense.: + N V, Vs - N V ? N VClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- School TripDokument3 SeitenSchool TripClaudia ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cunning Hare and The Witless LionDokument5 SeitenThe Cunning Hare and The Witless LionvangakishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beyond Ethnicity - Hindu and Muslim in South Asia - Shail MayaramDokument20 SeitenBeyond Ethnicity - Hindu and Muslim in South Asia - Shail MayaramAkansha RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supreme CourtDokument6 SeitenSupreme CourtSean ArcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 7: Language Test: GrammarDokument2 SeitenUNIT 7: Language Test: GrammarPatricia PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Class Drill Badge Criteria 2014Dokument2 Seiten3rd Class Drill Badge Criteria 2014api-2539652580% (1)
- CasestudyDokument2 SeitenCasestudyAjmal AhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giovanni Battista Lemoyne - Biographical Memoirs of Don Bosco. 1 (1965)Dokument414 SeitenGiovanni Battista Lemoyne - Biographical Memoirs of Don Bosco. 1 (1965)petar colakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cuestionario InglesDokument10 SeitenCuestionario InglesAndres Esteban AreasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anthony Lee Cunningham v. Warren T. Diesslin, Warden, Buena Vista Correctional Facility, Colorado Department of Corrections, 92 F.3d 1054, 10th Cir. (1996)Dokument13 SeitenAnthony Lee Cunningham v. Warren T. Diesslin, Warden, Buena Vista Correctional Facility, Colorado Department of Corrections, 92 F.3d 1054, 10th Cir. (1996)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Collection On GST Portal 2019 2020Dokument16 SeitenTax Collection On GST Portal 2019 2020Disha MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Truth About Mohammed MorsiDokument9 SeitenThe Truth About Mohammed MorsiGMBWatchNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDIA Poltical Map PDFDokument1 SeiteINDIA Poltical Map PDFSamarth PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsDokument2 SeitenCertified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsSunStar Philippine NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDokument3 SeitenTSHESASHTHINY A/P MANICKA RAO MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States v. Brenton Holmes, 3rd Cir. (2010)Dokument3 SeitenUnited States v. Brenton Holmes, 3rd Cir. (2010)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- People v. DaganiDokument13 SeitenPeople v. DaganiLance LagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kids Camp Invitation Letter With Consent FormDokument3 SeitenKids Camp Invitation Letter With Consent FormChynna Mei A. BongalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iii. Prescription A. Types of Prescription 1. AcquisitiveDokument5 SeitenIii. Prescription A. Types of Prescription 1. Acquisitivemailah awingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Profile:: Dr. C.V. Ananda BoseDokument7 SeitenProfessional Profile:: Dr. C.V. Ananda BoseGokul KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equal Employment Opportunity EeoDokument20 SeitenEqual Employment Opportunity Eeoapi-664413574Noch keine Bewertungen
- Child Protection Policy - SNHSDokument6 SeitenChild Protection Policy - SNHSAnnalie Delera CeladiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pak NavyDokument23 SeitenPak NavyZeeshan AmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Northwest Orient Airlines, Inc. v. CADokument14 SeitenNorthwest Orient Airlines, Inc. v. CAHannah MedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Lawyers in BramptonDokument5 SeitenBusiness Lawyers in BramptonVirender SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEA State On NYS Juvenile Detention CentersDokument3 SeitenCSEA State On NYS Juvenile Detention CenterserikvsorensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bouncing Checks NotesDokument3 SeitenBouncing Checks NotesRyDNoch keine Bewertungen