Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Brain: Structure, Parts, and Functions
Hochgeladen von
Jemimah Tostos GonzaloOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Brain: Structure, Parts, and Functions
Hochgeladen von
Jemimah Tostos GonzaloCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Prepared by: Noel Adriano
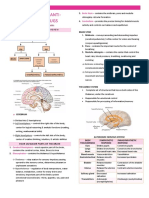
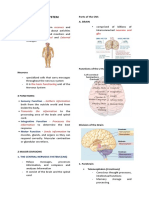
BRAIN
- Processes sensory info OTHER PARTS
- Regulates blood ressure and breathing
- Releases hormones 1. CEREBRAL CORTEX
- Attention, percetion, thought, memory,
language
4 LOBES OF BRAIN 2. HIPPOCAMPUS
- Memory (long-term)
3. HYPOTHALAMUS
- hunger, thirst, sleep, and sexual response.
It also regulates body temperature, blood
pressure, emotions, and secretion of
hormones.
4. PITUITARY GLAND
- “master gland”
- Promotes bone and muscle growth
- Responds to stress
5. PINEAL GLAND
- Regulates body’s internal clock
6. THALAMUS
3 MAIN PARTS OF THE BRAIN - Consciousness, sleep, memory
1. CEREBRUM: is the largest part of the brain 7. HYPOTHALAMUS
and is composed of right and left - Maintains homeostasis
hemispheres. It performs higher functions
like interpreting touch, vision and hearing,
as well as speech, reasoning, emotions, NERVOUS SYSTEM
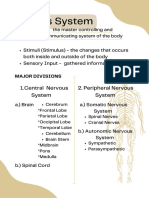
learning, and fine control of movement.
- Consists of brain, sinal cord, sensory
2. CEREBELLUM: is located under the
organs, and nerves that connect these
cerebrum. Its function is to coordinate
organs to the rest of the body.
muscle movements, maintain posture, and
- Responsible forcontrol of the body and
balance.
communication among its parts.
3. BRAINSTEM: acts as a relay center
connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to 2 TYPES OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
the spinal cord. It performs many automatic
1. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
functions such as breathing, heart rate,
- Consists of brain and spinal cord
body temperature, wake and sleep cycles,
- Mission control center of body that analyzes
digestion, sneezing, coughing, vomiting,
things and decides what to do
and swallowing.
- Sends signal to Periheral Nervous System
Prepared by: Noel Adriano
2. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEUROTRANSMITTERS
- Located all over the rest of the body
- Stimulates the appropriate muscle or gland - Known as chemical messengers
- Has motor division - Transmits impulses
- Detects stimuli and sends signals to CNS - Sends info through neurons by crossing a
*Stimuli – indicate if body is in danger and synapse
it will only pass through spinal cord and - Can be excitatory, inhibitory, and
reflexes will occur modulatory
8 MAIN KINDS OR TYPES
2 MAIN PARTS OR TYPES
ACETYLCHOLINE Sleep cycle
1. SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM NOREPINEPHRINE Alertness
- Voluntary control of body movements via EPINEPHRINE Fight or flight response
skeletal muscles DOPAMINE Growth hormone
GABA Reduces neuronal
excitability
2. AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
GLUTAMATE Regulates CNS
- Involuntary control system and control SEROTONIN Body temperature
visceral functions HISTAMINE Wakefulness
HOW DO NEURONS TRANSMIT
MESSAGES? ENDOCRINE SYTEM
1. Receives stimuli in dendrites - Made up of glands that produce and secrete
2. Signals travels through axon then to the hormones, chemical substances produced
axon terminal in the body that regulate the activity of cells
3. Travels through synapse (junction bet. 2 or organs
neurons)
4. Arrive in dendrite of another neuron GLANDS
2 TYPES OF SYNAPSES
1. ELECTRICAL SYNAPSE
- Transmits electrical impulse w/o changing it
- Fast process
- Used in PNS to accomplish autonomic
actions
2. CHEMICAL SYNAPSES
- Can amplify or modify electrical impulse w/c
allows more complex messages to be
transmitted
- Slower process
- Used in CNS and certain parts of PNS
When a signal travels through axon, special
molecules called neurotransmitters are
released
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Biological Perspective on Mental DisordersDokument17 SeitenBiological Perspective on Mental DisordersAngela Abigail AbingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain and Psychotropic Drugs ReviewDokument5 SeitenBrain and Psychotropic Drugs ReviewMichaela BernadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm #1 Neuro Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDokument15 SeitenMidterm #1 Neuro Anatomy and Physiology ReviewMonica JubaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Science Quarter 3 ReviewerDokument7 SeitenGrade 10 Science Quarter 3 Reviewerselfie princessNoch keine Bewertungen
- HANDOUTSDokument3 SeitenHANDOUTSElaiza Eline LaguaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Lec FDokument11 SeitenAnaphy Lec FclarecielaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidDokument1 SeiteNervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidVincent Franciz T. FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cha Pter Two Biology and Psychology Nervous SystemDokument8 SeitenCha Pter Two Biology and Psychology Nervous SystemMary Princess ArasulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorDokument37 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorIsh Gallito100% (1)
- Nervous, Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Test GuideDokument2 SeitenNervous, Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Test GuideSean CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of the Nervous System in 40 CharactersDokument5 SeitenFunctions of the Nervous System in 40 CharactersXandra BasnilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument1 SeiteNervous Systemcarla lizondraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Midterm Week 2 Notes (Nervous System)Dokument20 SeitenAnaphy Midterm Week 2 Notes (Nervous System)Zosia SageNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biological PerspectiveDokument4 SeitenThe Biological Perspectiveleanne antazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of The Nerivious SystemDokument1 SeiteParts of The Nerivious SystemVirny Uno AceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci Q3 ReviewerDokument2 SeitenSci Q3 ReviewerYsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE - ResearchDokument9 SeitenSCIENCE - Researchmarealyn.hermida.camachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSDokument37 SeitenNSVanessa Joy SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Coordination in Animals - NotesDokument6 SeitenControl and Coordination in Animals - NotesKarishmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyDokument19 SeitenScience Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 Biologylesterjohns150Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1. Body Control and ResponseDokument51 Seiten1. Body Control and ResponseAngelyn AbuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychobiological Concepts: - Relationship of Neuroanatomy and - Relationship of Psychiatric Illnesses ToDokument56 SeitenPsychobiological Concepts: - Relationship of Neuroanatomy and - Relationship of Psychiatric Illnesses ToRhaine EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Nervous 1. System 2. Peripheral Nervous SystemDokument8 SeitenCentral Nervous 1. System 2. Peripheral Nervous SystemashianaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 33-2Dokument20 SeitenChapter 33-2nancie8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument6 SeitenNervous SystemAndrea RicamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology (Nervous System)Dokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology (Nervous System)Fei Jai100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDokument35 SeitenNervous SystemChloeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nervous System ExplainedDokument57 SeitenThe Nervous System ExplainedGeelin Crizza AlbisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical SurgicalDokument119 SeitenMedical SurgicalNursyNurseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Nervous System: Spinal Cord BrainDokument4 SeitenCentral Nervous System: Spinal Cord BrainRaizah GozosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurological Disorder: NeuronDokument8 SeitenNeurological Disorder: NeuronMaica Lectana100% (2)
- NCM 106 (PHARMA) - Lec 19 To 28Dokument18 SeitenNCM 106 (PHARMA) - Lec 19 To 28Aine Jermaine GatchalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy 3RD EXAM NOTESDokument2 SeitenAnaphy 3RD EXAM NOTESJoel CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ADokument5 SeitenNeurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ALexie KepnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Nervous SystemDokument5 SeitenBiology Nervous SystemFatima PueblaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Anatomy and FunctionsDokument4 SeitenNervous System Anatomy and FunctionsIrish Buaya Gementiza100% (1)
- CHP 3 PSYCHDokument8 SeitenCHP 3 PSYCHEmma Mahoney100% (1)
- Endocrine System and Nervous SystemDokument27 SeitenEndocrine System and Nervous SystemKyla MarcellanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System HandoutsDokument5 SeitenNervous System HandoutsmarioangelosurioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2. Models of Abnormal BehaviorDokument7 SeitenWeek 2. Models of Abnormal BehaviorPaul JacalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems: Neurones (Or Neurons)Dokument14 Seiten8.1 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems: Neurones (Or Neurons)KasspapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and Functions of the Nervous SystemDokument27 SeitenParts and Functions of the Nervous SystemChamain MarreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical-Surgical Nursing The Neurologic Concepts: Jimmellee Ellen P. Olilang, RNDokument225 SeitenMedical-Surgical Nursing The Neurologic Concepts: Jimmellee Ellen P. Olilang, RNKatrina Sarah Mae MabasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Kel 4Dokument10 SeitenNervous System Kel 4Talitha FatihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and NeurotransmittersDokument3 SeitenOrganization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1,2,3Dokument8 SeitenChapter 1,2,3세핌Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System 2023Dokument31 SeitenNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY 10: Brain Stem and Sacral Regions of the Central Nervous SystemDokument9 SeitenBIOLOGY 10: Brain Stem and Sacral Regions of the Central Nervous System12 Dy NicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System CNS 1481841Dokument5 SeitenNervous System CNS 1481841Jglacier godNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Nervous SystemDokument15 SeitenChapter 8: Nervous SystemAndrea BoocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Human Body Nervous System - PPT Grade12 Ch29 Lesson 2Dokument24 Seiten2 Human Body Nervous System - PPT Grade12 Ch29 Lesson 2kheloudmamdouhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro 0411-1323Dokument21 SeitenNeuro 0411-1323Lea Jane ArmeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sleep Physiology 1st YrDokument45 SeitenSleep Physiology 1st YrJeffrey RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDokument17 SeitenBiological Basis of BehaviorAasma IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science-Reviewer-3rd-Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyDokument19 SeitenScience-Reviewer-3rd-Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyIce Cold94% (86)
- Neuro Ana and PhysioDokument2 SeitenNeuro Ana and PhysioJacqueline de AsisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Assessment: FinalsDokument25 SeitenHealth Assessment: FinalsPauline AñesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.Von EverandPolyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.Bewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideVon EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Von EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Malvar F2Dokument1 SeiteMalvar F2Jemimah Tostos GonzaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Miguel Malvar MagazineDokument3 Seiten2 Miguel Malvar MagazineJemimah Tostos Gonzalo100% (1)
- 2 Miguel Malvar MagazineDokument3 Seiten2 Miguel Malvar MagazineJemimah Tostos Gonzalo100% (1)
- Simbahan Pandot: Relation of The Worship of The Tagalogs, Their Gods and Their Burials and SuperstitionsDokument2 SeitenSimbahan Pandot: Relation of The Worship of The Tagalogs, Their Gods and Their Burials and SuperstitionsJemimah Tostos GonzaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP About Multimodal and Its ElementsDokument7 SeitenLP About Multimodal and Its ElementsAdelaide RefugioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stakeholders in Planning ProcessDokument9 SeitenStakeholders in Planning ProcessMd mostafizur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1.physiology and PsychophysicsDokument29 Seiten7.1.physiology and Psychophysicsuitsig.photoclubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialogue Script Between The A Bcba and ClientDokument3 SeitenDialogue Script Between The A Bcba and Clientcrystal mcintoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manikchand Oxyrich WaterDokument30 SeitenManikchand Oxyrich Watergbulani11Noch keine Bewertungen
- TS25 - 2017 (23112017)Dokument31 SeitenTS25 - 2017 (23112017)CASEY MG YUMAN100% (1)
- Alfred Marshall & Neocassical EconomicsDokument12 SeitenAlfred Marshall & Neocassical EconomicsIrsyad KhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child Health Problems, Under 5 Clinic, Delivery of MCH ServicesDokument23 SeitenChild Health Problems, Under 5 Clinic, Delivery of MCH ServicesNidhi KaushalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 N015 28867Dokument15 Seiten05 N015 28867Archana SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflecting On The Lessons You Taught or Observed: 4. Plan Action 1. DescribeDokument2 SeitenReflecting On The Lessons You Taught or Observed: 4. Plan Action 1. DescribeIsam MrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sjaakies Succes Via TwitterDokument218 SeitenSjaakies Succes Via TwitterAlphonse ScafNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Lär de Sig Något På Språkresan?" en Explorativ Intervjustudie Med Indikationer På Vad en Språkresa Kan Ge.Dokument62 Seiten"Lär de Sig Något På Språkresan?" en Explorativ Intervjustudie Med Indikationer På Vad en Språkresa Kan Ge.Ernst-Heinrich SchiebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embracing and Overcoming Fear by Zion Margaret LubogoDokument15 SeitenEmbracing and Overcoming Fear by Zion Margaret LubogolubogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflective Practice: The Foundation of Purposeful LearningDokument14 SeitenReflective Practice: The Foundation of Purposeful LearningHatem FaroukNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERM EXAM (Professional Development and Apllied Ethics Answer Key)Dokument2 SeitenMIDTERM EXAM (Professional Development and Apllied Ethics Answer Key)Daniel BeloncioNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of Extraordinary Confid - DR Aziz Gazipura PsyDDokument1.034 SeitenThe Art of Extraordinary Confid - DR Aziz Gazipura PsyDSourav Mishra100% (10)
- Chapter 2Dokument20 SeitenChapter 2Tahia Anjum100% (1)
- Lesson 8 I. Objectives: DMRDokument8 SeitenLesson 8 I. Objectives: DMRSharmaine LappayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis OBDokument10 SeitenCase Analysis OBRuchita Munish33% (3)
- Interoception 101: Interoc Eption Explanation, Interoc Eption Tracking Sheet and Interoception ActivitiesDokument41 SeitenInteroception 101: Interoc Eption Explanation, Interoc Eption Tracking Sheet and Interoception ActivitiesJennifer Jones100% (1)
- Burnout Syndrome: Causes, Risk Factors and ManagementDokument26 SeitenBurnout Syndrome: Causes, Risk Factors and ManagementJisha JanardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem-Based Learning What and How Do Students Le PDFDokument33 SeitenProblem-Based Learning What and How Do Students Le PDFViolettaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activityideabank FinalDokument72 SeitenActivityideabank FinalJoy Tu TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boston Qualitative Scoring System for Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Effective for Detecting Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson's DiseaseDokument9 SeitenBoston Qualitative Scoring System for Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Effective for Detecting Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson's DiseaseJuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antoinette Fox 1Dokument63 SeitenAntoinette Fox 1CAILNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAPP Lesson 1 Academic TextDokument17 SeitenEAPP Lesson 1 Academic TextJennifer DumandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Digital ThesisDokument194 SeitenAustralian Digital ThesisGinger KalaivaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Report in Eed Eng 2Dokument4 SeitenWritten Report in Eed Eng 2paula macatangayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 6. Developmental Reading Topic 6. Comprehension - Theories and StrategiesDokument11 SeitenMODULE 6. Developmental Reading Topic 6. Comprehension - Theories and StrategiesBeverly Panganiban CadacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creative Writing: By: Kesia Mae Leonora AB PsychologyDokument7 SeitenCreative Writing: By: Kesia Mae Leonora AB PsychologyKesia Mae LeonoraNoch keine Bewertungen