Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Common Emitter Amplifier Working Principle and Its Applications PDF
Hochgeladen von
sidarth158Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Common Emitter Amplifier Working Principle and Its Applications PDF
Hochgeladen von
sidarth158Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
fb tw yt
HOME ELECTRICAL › ELECTRONICS › COMMUNICATION › ROBOTICS PROJECTS › GENERAL ›
Expert Outreach Communication Giveaways IC › Infographics Projects › Tools › White Papers
Common Emitter Ampli.er (CE) Circuit
Working and Applications
ELECTRONICS 4 COMMENTS
The Amplifier is an electronic circuit that is used to increase the strength of a weak input signal in terms of
voltage, current, or power. The process of increasing the strength of a weak signal is known as Amplification. One
most important constraint during the amplification is that only the magnitude of the signal should increase and
there should be no changes in original signal shape. The transistor (BJT, FET) is a major component in an
amplifier system. When a transistor is used as an amplifier, the first step is to choose an appropriate SEARCH
configuration, in which device is to be used. Then, the transistor should be biased to get the desired Q-point. The
signal is applied to the amplifier input and output gain is achieved. In this article, we will discuss common
emitter amplifier analysis.
Common Emitter Amplifier Configuration SPONSORED SEARCHES
applications of ce amplifier
In Common Emitter Amplifier Configuration, the Emitter of a BJT is common to both the input and output signal
as shown below. The arrangement is the same for a PNP transistor, but bias will be opposite w.r.t NPN transistor. common emitter amplifier applications
ce amplifier frequency response
npn transistor
Manganin Shunt Resistor
circuit diagram design
High Precision Low TCR Value
Customized Manganin Shunt, Temperature Coe?cient 20ppm,
Tolerance 1-5% RECENT POSTS
Pressure Transducer Working and Its
ctcores.com OPEN Applications
IoT Protocols and Its Architectures
Phase Shift Keying (PSK) : Types and Its
Applications
ATmega16 – Next Generation Micro
Controller
Antenna Gain – Directivity, Efficiency and
Its Conversion
Ripple Carry Adder : Working, Types and
Its Applications
Active and Passive Transducer and Their
Differences
NPN and PNP CE Configuration Amplifier
Pulse Sensor : Working Principle and Its
Applications
Operation of Common Emitter Amplifier
Triggering of Thyristors or SCR
When a signal is applied across the emitter-base junction, the forward bias across this junction increases during Triggering
the upper half cycle. This leads to increase the flow of electrons from the emitter to a collector through the base,
Labview Projects for Engineering
hence increases the collector current. The increasing collector current makes more voltage drops across the Students
collector load resistor RC.
The negative half cycle decreases the forward bias voltage across the emitter-base junction. The decreasing
collector-base voltage decreases the collector current in the whole collector resistor Rc. Thus, the amplified load
resistor appears across the collector resistor. The common emitter amplifier circuit is shown below figure (a).
CE Amplifier
From the voltage waveforms for the CE circuit shown in Fig. (b) It is seen that there is an 180-degree phase shi!
between the input and output waveforms.
SPONSORED SEARCHES
NPN Transistor
Electrical Resistance MOST READ POSTS
Half Adder and Full Adder with Truth
Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit Elements and their Functions Table
Biasing Circuit/ Voltage Divider MOSFET Basics, Working Principle and
Applications
The resistances R1, R2 and RE used to form the voltage biasing and stabilisation circuit. The biasing circuit needs
Latest Electronics Project Ideas
to establish a proper operating Q-point otherwise, a part of the negative half cycle of the signal may be cut-o" in
the output. How Does a PID Controller Work? -
Structure & Tuning Methods
Input Capacitor (C1) New 100+ Top Electrical Projects Ideas
The capacitor C1 is used to couple the signal to the base terminal of the BJT. If it is not there, the signal source
resistance, Rs will come across R2 and hence, it will change the bias. C1 allows only the AC signal to flow but
isolates the signal source from R2
Emitter Bypass Capacitor (CE)
An Emitter bypass capacitor CE is used parallel with RE to provide a low reactance path to the amplified AC
signal. If it is not used, then the amplified AC signal following through RE will cause a voltage drop across it,
thereby dropping the output voltage.
Coupling Capacitor (C2)
The coupling capacitor C2 couples one stage of amplification to the next stage. This technique used to isolate the
DC bias settings of the two coupled circuits.
CE amplifier circuit currents
Base current iB = IB +ib where,
IB = DC base current when no signal is applied.
ib = AC base when AC signal is applied and iB = total base current.
Collector current iC = IC+ic where,
iC = total collector current.
IC = zero signal collector current.
ic = AC collector current when AC signal is applied.
Emitter Current iE = IE + ie where,
IE = Zero signal emitter current.
Ie = AC emitter current when AC signal is applied.
iE = total emitter current.
Kikusui PCR-WE series, 6kVA to
36kVA Compact high power AC…
Ad IEC standard test ready. max 144kVA
Ad
with easy control and programmable with…
Kikusui Electronics Corp.
Learn more
CE Amplifier Frequency Response
The voltage gain of a CE amplifier varies with signal frequency. It is because reactances of the capacitors in the
circuit changes with signal frequency and hence a"ects the output voltage. The curve drawn between voltage
gain and the signal frequency of an amplifier is known as frequency response. Below figure shows the frequency
response of a typical CE amplifier.
Frequency Response of Common Emitter Amplifier
From the above graph, we observe that the voltage gain drops o" at low (< FL) and high (> FH) frequencies,
whereas it is constant over the mid-frequency range (FL to FH).
At low frequencies (< FL) The reactance of coupling capacitor C2 is relatively high and hence very small part of
the signal will pass from amplifier stage to the load.
Moreover, CE cannot shunt the RE e"ectively because of its large reactance at low frequencies. These two factors
cause a drops o" of voltage gain at low frequencies.
At high frequencies (> FH) The reactance of coupling capacitor C2 is very small and it behaves as a short circuit.
This increases the loading e"ect of the amplifier stage and serves to reduce the voltage gain.
Moreover, at high frequencies, the capacitive reactance of base-emitters junction is low which increases the base
current. This frequency reduces the current amplification factor β. Due to these two reasons, the voltage gain
drops o" at high frequency.
At mid frequencies (FL to FH) The voltage gain of the amplifier is constant. The e"ect of the coupling capacitor
C2 in this frequency range is such as to maintain a constant voltage gain. Thus, as the frequency increases in this
range, the reactance of CC decreases, which tend to increase the gain.
However, at the same time, lower reactance means higher almost cancel each other, resulting in a uniform fair at
mid-frequency.
Common Emitter Amplifier analysis
The first step in AC analysis of Common Emitter amplifier circuit is to draw AC equivalent circuit by reducing all
DC sources to zero and shorting all the capacitors. Below figure shows the AC equivalent circuit.
AC Equivalent Circuit for CE Amplifier
The next step in the AC analysis is to draw h-parameter circuit by replacing the transistor in the AC equivalent
circuit with its h-parameter model. Below figure shows the h-parameter equivalent circuit for CE circuit.
h-Parameter Equivalent Circuit for Common Emitter Amplifier
The typical CE circuit performance is summarised below:
Device input impedance, Zb = hie
Circuit input impedance, Zi = R1 || R2 || Zb
Device output impedance, Zc= 1/hoe
Circuit output impedance, Zo = RC || ZC ≈ RC
Circuit voltage gain, Av = -hfe/hie*(Rc|| RL)
Circuit current gain, AI = hfe. RC. Rb/ (Rc+RL) (Rc+hie)
Circuit power gain, Ap = Av * Ai
Applications Of CE Amplifier
The common emitter circuit is popular because it’s well-suited for voltage amplification, especially at
low frequencies.
Common-emitter amplifiers are also used in radio frequency transceiver circuits.
Common emitter configuration commonly used in low-noise amplifiers.
This article discusses the working of the common emitter amplifier circuit and its applications. By reading the
above information you have got an idea about this concept. Furthermore, any queries regarding this or if you
want to implement Electronics and Electrical projects, please feel free to comment in the below section. Here is
the question for you, what is the function of the common emitter amplifier?
Manganin Shunt Common Collector Difference Between Transistor as an
Resistor - High Ampli=er or Emitter NPN and PNP Ampli=er : Common
Precision Low TCR Follower Circuit and Its Transistor Emitter Ampli=er
Value Applications Circuit & Its Working
Ad ctcores.com elprocus.com elprocus.com elprocus.com
Common Emitter Transistors - Major Transistor Different Types of
Ampli=er Circuit Difference between BJT Con=guration - Transistors and Their
Working and and MOSFET Common Base, Functions
Characteristics Collector and Emitter
elprocus.com elprocus.com elprocus.com elprocus.com
The 1 Mistake Almost Every Mac User Makes Daily
MacKeeper | Sponsored
How many ladoos are sold in India everyday? Book 2.5/3/4 BHK, SOBHA Winchester
Get passionate about data Chennai, 1.2 Cr Onwards
upGrad & IIIT Bangalore | Sponsored sobha.com | Sponsored
Indians Born Before 1968 Eligible For Hearing Aid Trial!
India Hearing Aid | Sponsored
India: These Hearing Aids Are Revolutionizing Ghee: 10 Reasons Why Everyone, Including
the Industry Diabetics And High Blood Pressure Patients,…
Soundrise | Sponsored NDTV | Sponsored
At 52, Salma Hayek Is Unrecognizable Today
Medical Matters | Sponsored
The 4 Sisters Took Photos Every Year For 40 They Took The Same Picture For 40 Years.
Years, You Won't Believe What Happened To… Don't Cry When You See The Last!
ezzin.com | Sponsored TopGentlemen.com | Sponsored
Cost of Hair Transplant in Coimbatore May Surprise You
Hair Transplant | Sponsored Links | Sponsored
Top 5 Best Scooty Below 30,000 Rs in India '0' Hiring Costs to Hire Sta! at WorkIndia
2018 - BestScooty.in WorkIndia | Sponsored
Best Scooty | Sponsored
What is the MOSFET: Basics, Working Principle 100+ Top Electrical (EEE) Projects Ideas for
and Applications Engineering Students 2019
Elprocus Elprocus
SHARE THIS POST:
Facebook Twitter Google+ LinkedIn Pinterest
‹ PREVIOUS NEXT ›
Tutorial On High Electron Mobility Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI)
Transistor (HEMT) and Its Functions
RELATED CONTENT
Ripple Carry Adder : Pulse Sensor : Working
Working, Types and Its Principle and Its
Applications Applications
Antenna Gain – Directivity, Active and Passive
Efficiency and Its Transducer and Their
Conversion Differences
4 Comments
Pavan Says: REPLY
at
Thank you for the clear explanation
Tarun Agarwal Says: REPLY
at
Hi Pavan
Thank you, and you’re welcome
Vivek Says: REPLY
at
sir very good article & useful Amplifier explain properly
Tarun Agarwal Says: REPLY
at
Hi Vivek
Thank you so much for your feedback
Add Comment
Comment:
Name *
Email *
Website
Post Comment
CATEGORIES RECENT COMMENTS FOLLOW ON FACEBOOK
Home Tarun Agarwal on Basics of Embedded C
Program and Programming Structure for
Popular posts
Beginners
Project Ideas
Tarun Agarwal on Different Types of Level
Electrical Sensors and their Workings
Electronics saiguptha on Basics of Embedded C
Program and Programming Structure for
Robotics Beginners
Technology Deviprasad a on Different Types of Level
Sensors and their Workings
Download Projects list
Tarun Agarwal on ECE Projects Ideas for
Electronics Engineering Students
Advertise With Us Disclaimer Report Violation Image Usage Policy Privacy Policy Contact Us
Copyright 2013 - 2019 © Elprocus
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Instrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualVon EverandInstrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Lab Report 04Dokument4 SeitenLab Report 04Mehmood Khan Marwat100% (1)
- AMDokument15 SeitenAMAnonymous oTwHSWV1NNoch keine Bewertungen
- AM Modulation Reception Tutorial QuestionsDokument3 SeitenAM Modulation Reception Tutorial QuestionsMohd Äwiw Vießar AvondrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulate and Compare CE Amp Frequency ResponseDokument3 SeitenSimulate and Compare CE Amp Frequency ResponsehimeshemraanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Properties of Radio WavesDokument5 SeitenOptical Properties of Radio WavesJOSHUA NEIL CARIGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Darlington Transistor: Electronics Bipolar Transistors Current GainDokument3 SeitenDarlington Transistor: Electronics Bipolar Transistors Current GainSrinath ArsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colpitts OscillatorDokument3 SeitenColpitts Oscillatorasra 10100% (2)
- Basic Electronics PowerpointDokument16 SeitenBasic Electronics PowerpointEarle Sean MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - Current Density, Conductors and CapacitanceDokument34 SeitenLecture 4 - Current Density, Conductors and CapacitanceHannahmhel MuanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransducersDokument9 SeitenTransducersRo#it100% (1)
- Transmission LinesDokument19 SeitenTransmission LinesSherwin CatolosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Tutorial ProblemsDokument63 SeitenDC Tutorial ProblemsKenneth Paul Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Circuit Analysis Lab ManualDokument51 SeitenElectronic Circuit Analysis Lab Manualppat2006Noch keine Bewertungen
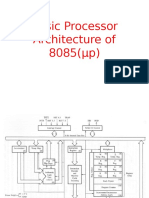
- Microprocessor 8085 ArchitectureDokument19 SeitenMicroprocessor 8085 ArchitectureSindhujaSindhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Emitter AmplifierDokument3 SeitenCommon Emitter AmplifierDaniel Tamisen100% (1)
- + sin 2 π f 1+ sin 2 π f: A=V V t V V t A=VDokument4 Seiten+ sin 2 π f 1+ sin 2 π f: A=V V t V V t A=VEunice Jane Bolgado-DoctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIA CIRCUITS QBDokument14 SeitenLIA CIRCUITS QBrkkumar07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yagi Uda Antenna EquationDokument9 SeitenYagi Uda Antenna EquationAshner Novilla100% (1)
- Laboratory Manual in Circuits 1 - DC Circuit AnalysisDokument35 SeitenLaboratory Manual in Circuits 1 - DC Circuit AnalysisMark Johnson0% (1)
- Direct Current Measurements GuideDokument2 SeitenDirect Current Measurements GuideErroll100% (1)
- Transmission Line Impedance Matching TechniquesDokument28 SeitenTransmission Line Impedance Matching TechniquesEm ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Noise AnalysisDokument32 Seiten2 - Noise AnalysisCheurnevee RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Fields & Waves (BEB20303) Chapter 1: Electrostatic FieldDokument32 SeitenElectromagnetic Fields & Waves (BEB20303) Chapter 1: Electrostatic FieldAFiqah Nazirah JailaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling Equations with the Telecoms-Trainer 101Dokument5 SeitenModeling Equations with the Telecoms-Trainer 101Ahmad RaheelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Modulation GuideDokument54 SeitenAngle Modulation GuideJan Nicholas TeorimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neets Module 10 SummaryDokument11 SeitenNeets Module 10 SummarySigmund VesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB Manual PHY 2 CircuitDokument12 SeitenLAB Manual PHY 2 CircuitMalvin Roix OrenseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noise and Its TypesDokument9 SeitenNoise and Its Typesnyma ahmdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 - Common Emitter AmplifierDokument6 SeitenExperiment 3 - Common Emitter AmplifierAsyraf Norahairuzan100% (1)
- PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA Experiment No.1Dokument12 SeitenPAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA Experiment No.1ManuelitoBorjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 WATTMETER ProblemsDokument1 Seite3 WATTMETER ProblemsDaneMauriceRovedilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Digital ElectronicsDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Digital ElectronicsBean SaladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To BJT Small SignalDokument35 SeitenIntro To BJT Small Signaldaserock83100% (1)
- BJT vs FET: Key Differences Between These Transistor TypesDokument2 SeitenBJT vs FET: Key Differences Between These Transistor TypeskanwaljiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabSheet Experiments - Giatutinhyeu14 - 2Dokument176 SeitenLabSheet Experiments - Giatutinhyeu14 - 2Nhi OtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter4 OscillatorsDokument36 SeitenChapter4 OscillatorsNabilah AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-2-DC MachineDokument83 SeitenCH-2-DC MachineÙm ØrthøbøyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three AM Modulator: Trainer Module: ETEK ACS-3000-02Dokument47 SeitenChapter Three AM Modulator: Trainer Module: ETEK ACS-3000-02Muhammed ÇağlarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Laplace Transform Is Conducted While Sending Signals Over Any TwoDokument2 SeitenA Simple Laplace Transform Is Conducted While Sending Signals Over Any TwohamryNoch keine Bewertungen
- D IODESDokument62 SeitenD IODESCllyan Reyes0% (1)
- Fiber Optic BlakeDokument4 SeitenFiber Optic BlakenicklingatongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utilization of Electrical Power: IlluminationDokument29 SeitenUtilization of Electrical Power: IlluminationHafsa AlhaddabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 4 MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIERDokument39 SeitenCHAPTER 4 MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIERÎQbãl HãikãmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op PPT 12Dokument16 SeitenOp PPT 12Jaymin PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block Diagram of Unregulated Power SupplyDokument3 SeitenBlock Diagram of Unregulated Power SupplyKunal MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier ExplainedDokument10 SeitenSilicon Controlled Rectifier ExplainedJenny MaristelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sig Cond Chap 3: Understand Purpose & Ops of Analog & Digital Sig CondDokument13 SeitenSig Cond Chap 3: Understand Purpose & Ops of Analog & Digital Sig CondAzrinshah Abu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 6. Thevenin's and Norton's TheoremDokument2 SeitenExperiment 6. Thevenin's and Norton's TheoremKennethCharlesYamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 9Dokument33 SeitenCH 9mugammad wasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Conclusion 1 - Opamp CharacteristicsDokument1 SeiteEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Conclusion 1 - Opamp Characteristicsdonatello840% (3)
- DC and AC Machines Lab ManualDokument68 SeitenDC and AC Machines Lab ManualGhilman HabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)Dokument4 SeitenBasic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)DARANoch keine Bewertungen
- DVD Mini Component System Troubleshooting and Repair GuideDokument69 SeitenDVD Mini Component System Troubleshooting and Repair GuideAlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common-Emitter Amplifier Biasing and Gain ExperimentDokument19 SeitenCommon-Emitter Amplifier Biasing and Gain ExperimentAdnan Khan0% (1)
- Transducer PDFDokument27 SeitenTransducer PDFGAJANAN M NAIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Components in A Transistor - Electrical4uDokument8 SeitenCurrent Components in A Transistor - Electrical4umanoj reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Noise Amplifier Lna DesignDokument9 SeitenLow Noise Amplifier Lna Designintissar abbesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em 6400Dokument4 SeitenEm 6400heri fauziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Devices CircuitsDokument1 SeiteElectronics Devices Circuitsarorabhavya27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Furniture and equipment rental price listDokument3 SeitenFurniture and equipment rental price listmamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLF-77 Servive ManualDokument26 SeitenPLF-77 Servive Manualapi-3711045100% (1)
- XT+ Releasing Control PanelDokument2 SeitenXT+ Releasing Control PanelCarlos CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Schedule 4 Exp 6Dokument9 SeitenSpecial Schedule 4 Exp 6Prìyañshú GuptãNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14pt3822 69 PhilipsDokument35 Seiten14pt3822 69 PhilipsHanif Rathore PrinceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtl7000 Series: Ultra-Slim Safety Barriers That Can Be Used Like TerminalsDokument13 SeitenMtl7000 Series: Ultra-Slim Safety Barriers That Can Be Used Like TerminalsDharmilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iis - Ignition System 4.1: Intelligent Ignition System With Microprozessor Controlled Auto TimingDokument1 SeiteIis - Ignition System 4.1: Intelligent Ignition System With Microprozessor Controlled Auto TimingBilal Nuraldin EltayebNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGCIL - C & R SPECIFICATION Rev - 4 PDFDokument80 SeitenPGCIL - C & R SPECIFICATION Rev - 4 PDFravindren_eee100% (1)
- Aion Phobos Tonebender Buzzaround DocumentationDokument9 SeitenAion Phobos Tonebender Buzzaround Documentationmichael higginsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Led Flood Light 120 W SCL - Factsheet r.0Dokument1 SeiteLed Flood Light 120 W SCL - Factsheet r.0Jellyn BaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Zener Diodes Voltage and Power SpecsDokument2 SeitenSilicon Zener Diodes Voltage and Power SpecsFabian BordaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upgrade the Performance and Lifespan of the Classic Yaesu FT-290R 2m TransceiverDokument8 SeitenUpgrade the Performance and Lifespan of the Classic Yaesu FT-290R 2m TransceiverRafa CidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Partes QAS 125VdDokument112 SeitenManual de Partes QAS 125VdLeandro ToledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step Motor M42SP-4 - Mitsumi PDFDokument2 SeitenStep Motor M42SP-4 - Mitsumi PDFHjac CarvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2000amp DC PanelDokument4 Seiten2000amp DC PanelAbdus SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vpa Public Address Amplifiers: Installation & Service ManualDokument22 SeitenVpa Public Address Amplifiers: Installation & Service ManualIlija GrozdanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Semiconductor Device MCQ PDFDokument3 SeitenPhysics Semiconductor Device MCQ PDFHR Debraj100% (1)
- Re22R1Mlmr: Product DatasheetDokument4 SeitenRe22R1Mlmr: Product DatasheetToto PotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 11: DC Transient AnalysisDokument81 SeitenLesson 11: DC Transient AnalysisJoshua JapitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2328a PDFDokument2 SeitenC2328a PDFVictorManuelBernalBlancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SERIES SC791 SINGLE POLE ROCKER SWITCH GUIDEDokument2 SeitenSERIES SC791 SINGLE POLE ROCKER SWITCH GUIDEaakritichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nord BU0500 - GB - 1013Dokument180 SeitenNord BU0500 - GB - 1013Carlos RodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD4027BMS: Pinout FeaturesDokument8 SeitenCD4027BMS: Pinout FeaturesShah WaqasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designer's Guide To Isolation CircuitsDokument70 SeitenDesigner's Guide To Isolation Circuitsrangerford100% (2)
- dn200m (Fuente)Dokument3 Seitendn200m (Fuente)piabNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR2117 ApplicationDokument24 SeitenIR2117 ApplicationBhaskar KharviNoch keine Bewertungen
- THree Phase To Single Phase TransformerDokument2 SeitenTHree Phase To Single Phase TransformerVamshi Kumar Reddy MNoch keine Bewertungen
- JFETsDokument78 SeitenJFETsLai Yon Peng100% (2)
- Talyvel SchematicDokument1 SeiteTalyvel SchematicChuck NorrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- HE Readboard: D E C E 1Dokument5 SeitenHE Readboard: D E C E 1Abdullah ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen