Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Adhf NCP
Hochgeladen von
kristine keen buan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
905 Ansichten3 SeitenNCP for acute decompensated heart failure
Originaltitel
ADHF-NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenNCP for acute decompensated heart failure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
905 Ansichten3 SeitenAdhf NCP
Hochgeladen von
kristine keen buanNCP for acute decompensated heart failure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
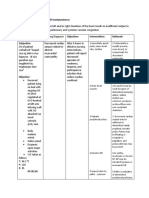
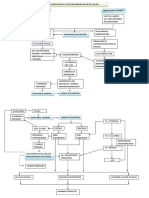
ASSESSMENT NSG. DIAGNOSIS PLANNING NSG.
INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: Independent STG:
Ineffective breathing STG: After 1hr of nursing Note heart sounds. S1 and S2 may be weak After 1 hr. of nursing
“Is very anxious pattern related to fatigue intervention the patient because of diminished intervention the patient
and ask, “Am I and decreased lung will be able demonstrate 3 pumping action. Gallop was able to demonstrate 3
going to die?” expansion and pulmonary out of 5 procedures to rythms are common(S3 out 5 ways to improve
Denies pain but congestion secondary to improve breathing pattern and S4), produced as breathing pattern.
says that he feels CHF. blood flows into
like he cannot get LTG: After 8hrs of nursing noncompliant chambers. GOAL MET
enough air intervention the Patient’s
Says that his heart respiratory pattern will Palpate peripheral pulses ↓CO may be reflected in LTG:
feels like it is decrease from 34 to 28 diminished radial, After 8 hrs. of nursing
“running away” cpm without exertion. popliteal, dorsalis pedis, intervention the patient’s
After being and post tibial pulses respiratory pattern was
weighed, he decreased from 34-28
reports, “that is Monitor BP In advanced HF, the body cpm without exertion.
more than I may no longer be able to
usually weigh” compensate, and GOAL MET
Reports that he is profound hypotension may
so exhausted he occur.
can’t eat or drink
by himself Inspect for pallor or Pallor is indicative of
Objective Data cyanosis diminished peripheral
Height: 175 cm perfusion secondary to
Weight: 95.5kg inadequate CO,
Temp: 37.6 vasoconstriction, and
HR: 34 anemia. Cyanosis may
118bpm develop in refractory HF.
BP: 90/60 Dependent area are often
blue or mottled as venous
Distant S1, S2,
congestion increases.
S3, S4 present,
Monitor UO Kidneys respond to
PMI at 6th ICS and
reduced CO by retaining
faint water and sodium
(+) atrial fibrillation Note changes in May indicate inadequate
sensorium, lethargy, cerebral perfuaion
with ventricular
confusion, disorientation, secondary to decreased
rate of 132pbm anxiety, and depression CO.
(+)crackles, Monitor oxygen saturation Provides information
↓breath sounds and ABGs. regarding the heart’s
ability to perfuse distal
RLL, +(frothy tubules with oxygenated
blood-tinged blood.
sputum) Encourage patient of rest Reduces cardiac workload
SpO2- 82% on and assist with all and minimizes myocardial
activities oxygen consumption
room air
(+) bowel sounds Assist the patient in Allows for better chest
assuming a high fowler’s expansion, thereby
Hepatomegaly position improving pulmonary
(4cm below costal capacity.
margin) Assist patient to use Identifies increased work
Bilateral JVD relaxation techniques of breathing
1+ peripheral Weigh patient daily and Body weight is a sensitive
compare to previous indicator of fluid balance
pulses and (+)
weights and an increase indicates
peripheral edema fluid volume excess.
Dependent:
Administer supplemental Increases available
oxygen as indicated oxygen for myocardial
uptake to combat effects
of hypoxia
Administer medications as To improve patient
indicated. condition
Interdependent:
Monitor laboratory results For early detection on
abnormal changes in body
function.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPDidith AbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP DobDokument3 SeitenNCP DobLester BuhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPWendy EscalanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarasoff CaseDokument2 SeitenTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Pleural EffusionDokument5 SeitenPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Failure NCPDokument1 SeiteRespiratory Failure NCPkyaw100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDokument3 SeitenNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Nursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainDokument3 SeitenNursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainAjay SupanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALDokument1 SeiteHemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP SEIZURE DISORDERDokument2 SeitenNCP SEIZURE DISORDERPatricia FaraonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As VerbalizedDokument2 SeitenAssessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalizedmayla_jordan3666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Disease NCPDokument5 SeitenCardiovascular Disease NCPShyla ManguiatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbed SleepDokument1 SeiteDisturbed Sleepmawel100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- NCP For CHFDokument2 SeitenNCP For CHFMayet De Castro Lejano100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDokument1 SeiteNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Weakness NCPDokument1 SeiteBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDokument5 SeitenNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- NCP HypertensionDokument1 SeiteNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPMark Benedict Ocampo VelardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDokument2 SeitenAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ch31 p991-992Dokument2 SeitenNCP Ch31 p991-992Ala'a Abd Mansor100% (2)
- NCP PTBDokument2 SeitenNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDokument4 Seiten2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDokument2 SeitenCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- NCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaDokument11 SeitenNCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaChristy Rose AgrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For HeadacheDokument1 SeiteNCP For HeadacheJohn MajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: DysrhythmiasDokument12 SeitenNCP: DysrhythmiasJavie100% (3)
- NCP For CTTDokument1 SeiteNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan ADokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDokument8 SeitenNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (1)
- NCP PTBDokument2 SeitenNCP PTBKath TalubanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver DiseaseDokument1 SeiteAssessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver Diseasehaniehaehae100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPJezza RequilmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Dokument6 SeitenRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockDokument7 SeitenIloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockAbie Jean BalbontinNoch keine Bewertungen
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDokument3 SeitenNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CopdDokument4 SeitenNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument5 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationArian May MarcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternDokument1 SeiteNursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternnikkilyceeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Anemia of PrematurityDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Anemia of PrematurityJARIEL L. CATACUTANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenStudent Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureAldrein GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Children With Cardiac DisordersDokument3 SeitenCase Study On Children With Cardiac DisordersAlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureDokument5 Seiten2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureLovely CacapitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afib NCPDokument3 SeitenAfib NCPGen RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF NCPDokument8 SeitenCHF NCPZy Hallasgo100% (1)
- Diana Kyla A. Punay Bsn-Dash-6: Subjective Data: Short Term: Short TermDokument3 SeitenDiana Kyla A. Punay Bsn-Dash-6: Subjective Data: Short Term: Short TermZoè AshtrönNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excess or Deficit in Oxygenation And/or Carbon Dioxide Elimination at The Alveolar-Capillary MembraneDokument6 SeitenExcess or Deficit in Oxygenation And/or Carbon Dioxide Elimination at The Alveolar-Capillary MembraneHazel MiraranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu 4Dokument7 SeitenIcu 4GemilleDaphneAndradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssessmentDokument2 SeitenAssessmentHazel MiraranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammation TASK 1. Briefly Discuss The Three Divisions of Immunity and Its Relationship To One AnotherDokument5 SeitenInflammation TASK 1. Briefly Discuss The Three Divisions of Immunity and Its Relationship To One Anotherkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 1. Concept Analysis and DiagramDokument4 SeitenTask 1. Concept Analysis and Diagramkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egypt PDFDokument66 SeitenEgypt PDFkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pancreatitis Case PresDokument29 SeitenAcute Pancreatitis Case Preskristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Femoral Neck and Intertrochanteric RegionDokument12 SeitenThe Femoral Neck and Intertrochanteric Regionkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adhf NCPDokument3 SeitenAdhf NCPkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIS 101-Presidents PDFDokument12 SeitenHIS 101-Presidents PDFkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1&2 PDFDokument8 SeitenChapter1&2 PDFkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IndonesiaDokument20 SeitenIndonesiakristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egypt PDFDokument66 SeitenEgypt PDFkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pancreatitis Case PresDokument29 SeitenAcute Pancreatitis Case Preskristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AfricaDokument22 SeitenAfricakristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suici DE: By: Kristine Keen BuanDokument57 SeitenSuici DE: By: Kristine Keen Buankristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amazing Facts About AfricaDokument19 SeitenAmazing Facts About Africakristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- However, If The Aneurysm Has Ruptured, The Treatment of Choice Is Immediate Surgical InterventionDokument4 SeitenHowever, If The Aneurysm Has Ruptured, The Treatment of Choice Is Immediate Surgical Interventionkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Ectopic PregnancyDokument10 SeitenCase Study - Ectopic Pregnancykristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of The Newborn 1219399928791425 9Dokument167 SeitenCare of The Newborn 1219399928791425 9kristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Ectopic PregnancyDokument10 SeitenCase Study - Ectopic Pregnancykristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Ilc - FinalDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Ilc - Finalkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypoglycaemiaDokument3 SeitenHypoglycaemiakristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adhf PathoDokument2 SeitenAdhf Pathokristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adhf PathoDokument2 SeitenAdhf Pathokristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MANAGING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE COMPLICATIONSDokument8 SeitenMANAGING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE COMPLICATIONSkristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DialysisDokument23 SeitenDialysiskristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightwave Maya 3D TutorialsDokument8 SeitenLightwave Maya 3D TutorialsrandfranNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDokument20 SeitenROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDan George IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Antonovsky (1979)Dokument280 SeitenAntonovsky (1979)M.Fakhrul Kurnia100% (1)
- DNB Paper - IDokument7 SeitenDNB Paper - Isushil chaudhari100% (7)
- Datasheet PDFDokument6 SeitenDatasheet PDFAhmed ElShoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antennas Since Hertz and MarconiDokument7 SeitenAntennas Since Hertz and MarconiTaiwo Ayodeji100% (1)
- Fraktur Dentoalevolar (Yayun)Dokument22 SeitenFraktur Dentoalevolar (Yayun)Gea RahmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare Blocks - ResultsDokument19 SeitenCompare Blocks - ResultsBramantika Aji PriambodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aleister Crowley and the SiriansDokument4 SeitenAleister Crowley and the SiriansJCMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of ClimateDokument18 SeitenElements of Climateእኔ እስጥፍNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lathe - Trainer ScriptDokument20 SeitenLathe - Trainer ScriptGulane, Patrick Eufran G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets: Etiology, Clinical Features and TreatmentDokument6 SeitenHypophosphatemic Rickets: Etiology, Clinical Features and TreatmentDeysi Blanco CohuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentDokument5 SeitenThe Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentGiovanni AlloccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Time ManagementDokument61 SeitenEffective Time ManagementTafadzwa94% (16)
- Monster of The Week Tome of Mysteries PlaybooksDokument10 SeitenMonster of The Week Tome of Mysteries PlaybooksHyperLanceite XNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient MesopotamiaDokument69 SeitenAncient MesopotamiaAlma CayapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec9-Rock Cutting ToolsDokument35 SeitenLec9-Rock Cutting ToolsAmraha NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gautam Samhita CHP 1 CHP 2 CHP 3 ColorDokument22 SeitenGautam Samhita CHP 1 CHP 2 CHP 3 ColorSaptarishisAstrology100% (1)
- Stability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelDokument7 SeitenStability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelSamwailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juan Martin Garcia System Dynamics ExercisesDokument294 SeitenJuan Martin Garcia System Dynamics ExercisesxumucleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Stones & TilesDokument41 SeitenProject On Stones & TilesMegha GolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Patents. 232467 - THE SYNERGISTIC MINERAL MIXTURE FOR INCREASING MILK YIELD IN CATTLEDokument9 SeitenIndian Patents. 232467 - THE SYNERGISTIC MINERAL MIXTURE FOR INCREASING MILK YIELD IN CATTLEHemlata LodhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsDokument1 SeiteJY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsAditya PrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevator Traction Machine CatalogDokument24 SeitenElevator Traction Machine CatalogRafif100% (1)
- 11 Baby Crochet Cocoon Patterns PDFDokument39 Seiten11 Baby Crochet Cocoon Patterns PDFIoanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ML AiDokument2 SeitenML AiSUYASH SHARTHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Phenomenological of in Church and TV WorshipDokument18 SeitenPhenomenological of in Church and TV WorshipCindy TirtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid Standards GuideDokument11 SeitenSmart Grid Standards GuideKeyboardMan19600% (1)
- Revolutionizing Energy Harvesting Harnessing Ambient Solar Energy For Enhanced Electric Power GenerationDokument14 SeitenRevolutionizing Energy Harvesting Harnessing Ambient Solar Energy For Enhanced Electric Power GenerationKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK 43 - Half-Past-TwoDokument2 SeitenWK 43 - Half-Past-TwoKulin RanaweeraNoch keine Bewertungen