Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Page 643
Hochgeladen von
panda biruOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Page 643
Hochgeladen von
panda biruCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
6.16.
Metal ions such as Zn2+ , Ni2+ , and Cu2+ enhance the rate of general base- 625
catalyzed enolization of 2-acetylpyridine by a several orders of magnitude.
PROBLEMS
Account for this effect.
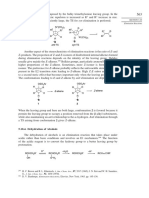
6.17. The C(2) equatorial hydrogen is selectively removed when 1,3-dithianes are
deprotonated. Furthermore, if the resulting carbanion is protonated, there is a
strong preference for equatorial protonation, even though it leads to the less stable
axial orientation for the 2-substituent. Discuss the relevance of these observations
to the structure of the sulfur-stabilized carbanion in MO terminology.
Hax
Hax – Hax
base CH3 *H+ CH3 S
CH3 S S *Heq
Heq S S
S CH3 CH3
CH3
6.18. a. It is found that when 2-methyl-2-butene is converted to a dianion, it first
gives the 2-methylbutadiene dianion 18-A, but this is converted to the more
stable anion 18-B, which can be referred to as a “methyltrimethylenemethane
dianion. Does simple HMO theory offer an explanation for this result?
H– H
CH3 CH3 H
H CH3
CH3 H –
CH3 –
– H H H
H H
18-A 18-B
b. The HMO diagrams of several conceivable dianions that might be formed
from double deprotonation of 2-methyl-1,5-hexadiene are given. On the basis
of these diagrams, which dianion would be expected to be most stable?
–
– 2–
– –
2 – CH3
CH3
C D E F
α – 1.8β α – 1.9β
α – 1.4β α – 1.7β α – 1.3β α – 1.2β
α–β α – 0.5β
α α
α α + 0.5β
α+β α + 1.2β
α + 1.4β α + 1.3β
α + 1.8β α + 1.9β
α + 1.7β
6.19. Which of the two possible structures for the dimer of methylketene is in best
accord with the observed pK of 2.8? Explain.
CH3CH CH3 CH3 OH
O
O O CH3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ib Chem Answers 20Dokument4 SeitenIb Chem Answers 20LE ZHAINoch keine Bewertungen
- TestFinal 350 v1 AnswersDokument8 SeitenTestFinal 350 v1 AnswersJabe KoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 9 KEYDokument3 SeitenProblem Set 9 KEYCARLOS ALBERTO OSORIO MARTINEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkana, Alkena Dan Alkuna Ok 1Dokument14 SeitenAlkana, Alkena Dan Alkuna Ok 1Niken LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes: 1.1 Classification of HydrocarbonDokument33 SeitenAlkanes: 1.1 Classification of HydrocarbonKhizra TehreemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Alkanes Tutorial Ans SchemeDokument14 Seiten2023 Alkanes Tutorial Ans SchemeJun JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6. Alkenes: Structure and Stability: or Add 1H To The Molecular Formula of Each HalogenDokument19 SeitenChapter 6. Alkenes: Structure and Stability: or Add 1H To The Molecular Formula of Each HalogenMarilyn Castro LaquindanumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem261, B2 Practice Questions For The Midterm Exam, AnswersDokument8 SeitenChem261, B2 Practice Questions For The Midterm Exam, Answerschemistry tutorialNoch keine Bewertungen
- DieneDokument11 SeitenDieneJen EscosesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5 MSCDokument10 SeitenLec 5 MSCCHEM_ENG_GALILNoch keine Bewertungen
- H BR H H 1 2 1 2 (A, E) Cis-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR H H BR H BR 1 2 1 2 (A, A) Trans-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR BR BR HDokument19 SeitenH BR H H 1 2 1 2 (A, E) Cis-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR H H BR H BR 1 2 1 2 (A, A) Trans-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane BR BR BR HVIGHNESH BALKRISHNA LOKARENoch keine Bewertungen
- G.O.C. Iws-1Dokument50 SeitenG.O.C. Iws-1Lakshya ChandakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkenes (Fasi)Dokument3 SeitenAlkenes (Fasi)kjjkimkmkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Sample-Midterm-SolutionsDokument12 SeitenChem Sample-Midterm-SolutionsScionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming Alkenes and Alkynes Rules PDFDokument2 SeitenNaming Alkenes and Alkynes Rules PDFMiguel RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Organic Chemistry 7Th Edition Brown Iverson Anslyn Foote 1133952844 9781133952848 Full Chapter PDFDokument36 SeitenSolution Manual For Organic Chemistry 7Th Edition Brown Iverson Anslyn Foote 1133952844 9781133952848 Full Chapter PDFrichard.parga191100% (14)
- Elimination ReactionDokument22 SeitenElimination ReactionSabitry YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- hw03 2017Dokument3 Seitenhw03 2017pNoch keine Bewertungen
- LKPD FixDokument6 SeitenLKPD FixNirmala DelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 321 Exam 2 Form 0Dokument8 SeitenCHE 321 Exam 2 Form 0Khadejah StewartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adisi AlkeneDokument15 SeitenAdisi Alkenekurniatriwijaya.2410Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Test-Ii: Part-I Section-I Single Correct Choice Type 1. (D)Dokument19 SeitenChemistry Test-Ii: Part-I Section-I Single Correct Choice Type 1. (D)aayushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al Kane:: (A) DefinitionDokument17 SeitenAl Kane:: (A) DefinitionsohamNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYdrocarbons PDFDokument24 SeitenHYdrocarbons PDFKumar PANKAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zumdahl Chemprin 6e CSM ch21 PDFDokument63 SeitenZumdahl Chemprin 6e CSM ch21 PDFMohit ShirpurkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry For Medicine Chapter 3Dokument39 SeitenOrganic Chemistry For Medicine Chapter 3أمال داودNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part A: Basicity of Amines: ChemactivityDokument9 SeitenPart A: Basicity of Amines: ChemactivityDORINA MANTUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Some New Pyridines, Thienopyridines and Pyrido (2,3:4',5') Thieno (3',2'-d) Pyrimidin-8-Ones From 2-AcetylbenzoimidazoleDokument8 SeitenSynthesis of Some New Pyridines, Thienopyridines and Pyrido (2,3:4',5') Thieno (3',2'-d) Pyrimidin-8-Ones From 2-AcetylbenzoimidazoleWalid EbaiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNP 4Dokument22 SeitenCNP 4Aregahagn NesruNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALKANE NAMES, Formulas, Properties (Memorize) (Sections 3.2,4)Dokument12 SeitenALKANE NAMES, Formulas, Properties (Memorize) (Sections 3.2,4)Jansenn PastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpp-Alkyl HalideDokument5 SeitenCpp-Alkyl Halidekrishnagamer565Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hcno C H H H C H H H C H H H: Remains +1 ThroughoutDokument4 SeitenHcno C H H H C H H H C H H H: Remains +1 ThroughoutpNoch keine Bewertungen
- AldeDokument2 SeitenAlde14.Hajjan MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elimination ReactionDokument6 SeitenElimination ReactionDxng 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Goc and Isomerism Notes - PMDDokument32 SeitenGoc and Isomerism Notes - PMDMahesh JagtapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbons Final Revision WorksheetDokument21 SeitenHydrocarbons Final Revision WorksheetMoonesh MKNoch keine Bewertungen
- 29 Cyclobutane SynthesisDokument10 Seiten29 Cyclobutane SynthesisEena BarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH-6 - Mains - Answers - ChemistryDokument17 SeitenPH-6 - Mains - Answers - Chemistrytanu15048Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chm258 Tutorial 2Dokument11 SeitenChm258 Tutorial 22022834672Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystals: Incidental Polymorphism, Non-Isomorphic and Isomorphic Substitution in Calcium-Valine Coordination PolymersDokument12 SeitenCrystals: Incidental Polymorphism, Non-Isomorphic and Isomorphic Substitution in Calcium-Valine Coordination Polymersmike7138Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Intro To Org Chem Tutorial Section B AnsDokument17 Seiten2022 Intro To Org Chem Tutorial Section B AnsLow Jia YingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krisna Dewi 1913031004Dokument33 SeitenKrisna Dewi 1913031004NOVAL TAUHIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios QO1-1Dokument3 SeitenEjercicios QO1-1hector juarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlkanDokument16 SeitenAlkanVerdinand VerbiestNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 AllDokument28 Seiten4 AllEtwo Xiao0% (1)
- Homework2 2017 KeyDokument8 SeitenHomework2 2017 KeysamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Alkane and CycloalkaneDokument3 SeitenQuestion Alkane and CycloalkaneFendi RohmawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANO4A-oxidation States-Nomenclatuur-2018 PDFDokument30 SeitenANO4A-oxidation States-Nomenclatuur-2018 PDFJelte de WitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry of SN Reactions PPT - Copy - Copy-1Dokument28 SeitenStereochemistry of SN Reactions PPT - Copy - Copy-1Vidya Rani100% (2)
- 3.15 Revision Guide NMRDokument5 Seiten3.15 Revision Guide NMRyimiyeh441Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Ii (Ecf 0024) : Tutorial 4Dokument3 SeitenChemistry Ii (Ecf 0024) : Tutorial 4utpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column Choices For Proteins - AgilentDokument48 SeitenColumn Choices For Proteins - Agilentlejla7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 - Carbon Compounds & Chemical Bonds: Tutorial: CHM125 - Basic Organic ChemistryDokument2 SeitenTopic 1 - Carbon Compounds & Chemical Bonds: Tutorial: CHM125 - Basic Organic ChemistryFarhana Mohd RazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neet Ug 2023 Chemistry Paper With AnswerDokument7 SeitenNeet Ug 2023 Chemistry Paper With Answervfg36579Noch keine Bewertungen
- AlkyneDokument25 SeitenAlkyneaditya.sachanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCI Lecture6-7Dokument18 SeitenOCI Lecture6-7Baga DagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Assignment 1Jimmy YungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringVon EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973Von EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973Noch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsVon EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 646Dokument1 Seite646panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Organik LanjutanDokument1 SeiteKimia Organik Lanjutanpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.2. Carbanion Character of Organometallic CompoundsDokument1 Seite6.2. Carbanion Character of Organometallic Compoundspanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Return Equilibrium Characterized by K: O O CH O CCH CO CH O O (CH) N O O PK 13.0 15.2 15.1 ODokument1 SeiteReturn Equilibrium Characterized by K: O O CH O CCH CO CH O O (CH) N O O PK 13.0 15.2 15.1 Opanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- O R C SR' O: Carbanions and Other Carbon NucleophilesDokument1 SeiteO R C SR' O: Carbanions and Other Carbon Nucleophilespanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- S O O O R' M O R S O O R' - O M X R: Carbanions As Nucleophiles in S 2 ReactionsDokument1 SeiteS O O O R' M O R S O O R' - O M X R: Carbanions As Nucleophiles in S 2 Reactionspanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem. Soc., 107, 3345 (1985) Helv. Chim. Acta, 64, 2617 (1981) J. Am. Chem. Soc.Dokument1 SeiteChem. Soc., 107, 3345 (1985) Helv. Chim. Acta, 64, 2617 (1981) J. Am. Chem. Soc.panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 594Dokument1 SeitePage 594panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronegative, As Viewed From The Proton Sharing An SP Hybrid Orbital, and HydrogensDokument1 SeiteElectronegative, As Viewed From The Proton Sharing An SP Hybrid Orbital, and Hydrogenspanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.2. Carbanion Character of Organometallic CompoundsDokument1 Seite6.2. Carbanion Character of Organometallic Compoundspanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH CH D D D: Compound K M S ×10 PKDokument1 SeiteCH CH D D D: Compound K M S ×10 PKpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem. Soc., 107, 3345 (1985) Helv. Chim. Acta, 64, 2617 (1981) J. Am. Chem. Soc.Dokument1 SeiteChem. Soc., 107, 3345 (1985) Helv. Chim. Acta, 64, 2617 (1981) J. Am. Chem. Soc.panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbanions and Other Carbon Nucleophiles: Tetrahedron Lett., 26, 1599 (1985)Dokument1 SeiteCarbanions and Other Carbon Nucleophiles: Tetrahedron Lett., 26, 1599 (1985)panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbanions and Other Carbon Nucleophiles: Table 6.9. Acidities of Some CyanohydrocarbonsDokument1 SeiteCarbanions and Other Carbon Nucleophiles: Table 6.9. Acidities of Some Cyanohydrocarbonspanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 610Dokument1 SeitePage 610panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti:37% Syn, For Methoxy. Discuss A Possible Mechanistic Basis For The CurvedDokument1 SeiteAnti:37% Syn, For Methoxy. Discuss A Possible Mechanistic Basis For The Curvedpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 615 PDFDokument1 SeitePage 615 PDFpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- General References: O H Dmpsi PH CH I OCH O H Dmpsi PH CH Dmpsi CO CH PH CHDokument1 SeiteGeneral References: O H Dmpsi PH CH I OCH O H Dmpsi PH CH Dmpsi CO CH PH CHpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 582 PDFDokument1 SeitePage 582 PDFpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 6.2. Acidity of Some Hydrocarbons: Entry Hydrocarbon Cs (CHA) Cs (THF) K (DMSO)Dokument1 SeiteTable 6.2. Acidity of Some Hydrocarbons: Entry Hydrocarbon Cs (CHA) Cs (THF) K (DMSO)panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems: Syn To The Methyl GroupDokument1 SeiteProblems: Syn To The Methyl Grouppanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 599 PDFDokument1 SeitePage 599 PDFpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 594Dokument1 SeitePage 594panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 590Dokument1 SeitePage 590panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 582Dokument1 SeitePage 582panda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- R CCHR' O H R CCHR' R R CCHR' + R R' R C C: 5.10.5. Eliminations Reactions Not Involving CDokument1 SeiteR CCHR' O H R CCHR' R R CCHR' + R R' R C C: 5.10.5. Eliminations Reactions Not Involving Cpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rco CH CH Si (CH) Rco Fsi (CH) + + + R N F CH CH: Elimination ReactionsDokument1 SeiteRco CH CH Si (CH) Rco Fsi (CH) + + + R N F CH CH: Elimination Reactionspanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si Si: Carbanions Stabilized by Functional GroupsDokument1 SeiteSi Si: Carbanions Stabilized by Functional Groupspanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Nama Barang Keluar Jumlah Harga Jual Total Tanggal KeteranganDokument4 SeitenNo Nama Barang Keluar Jumlah Harga Jual Total Tanggal Keteranganpanda biruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hew and Yang 1992 - Protein Interaction With IceDokument10 SeitenHew and Yang 1992 - Protein Interaction With IceRobert DowneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Proven Cleaner For Acetone ReplacementDokument4 SeitenA Proven Cleaner For Acetone ReplacementhuahmeduaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTP Brochure 020817Dokument12 SeitenWTP Brochure 020817Ravindra VemuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agua Purificada PH EurDokument2 SeitenAgua Purificada PH Eursarasa100% (1)
- Astm A514 1977Dokument6 SeitenAstm A514 1977Elumalai Srinivasan100% (1)
- Elastic: Abaqus Concrete Damaged Plasticity Parameters 1. Model 1: No Parameter ValueDokument5 SeitenElastic: Abaqus Concrete Damaged Plasticity Parameters 1. Model 1: No Parameter ValueMohcene BoukhezarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical TipDokument3 SeitenTechnical Tipkean.treylanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyrolysis of Waste Tires, A Modeling and Parameter Estimation Study Using Aspen Plus PDFDokument12 SeitenPyrolysis of Waste Tires, A Modeling and Parameter Estimation Study Using Aspen Plus PDFJosé Miguel GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Din en 1563Dokument2 SeitenDin en 1563Tayfun Tezanlar78% (9)
- Plate Hydraulic Design Procedure111Dokument17 SeitenPlate Hydraulic Design Procedure111Gebrekiros ArayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Care & Cosmetics: Oxarol C80Dokument1 SeitePersonal Care & Cosmetics: Oxarol C80Mohamed AdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- tmp2D3D TMPDokument7 Seitentmp2D3D TMPFrontiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 SM Chemistry English 2019 20 PDFDokument359 Seiten12 SM Chemistry English 2019 20 PDFMahi JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rheology Degradation Processing and Characterization of ReDokument261 SeitenThe Rheology Degradation Processing and Characterization of ReDeidra CadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Primer ANSWERSDokument81 SeitenChemistry Primer ANSWERSYazdan KelawalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facility Inspection Report Nitric Acid PlantDokument8 SeitenFacility Inspection Report Nitric Acid Plantlaoy aolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensor de Oxigeno Mercury MerdicalDokument2 SeitenSensor de Oxigeno Mercury MerdicalIrving MontesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopic Techniques For Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Industries - Unit 9 - Week 8 PDFDokument1 SeiteSpectroscopic Techniques For Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Industries - Unit 9 - Week 8 PDFantony bevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap. 2. Molecular Weight and Polymer SolutionsDokument66 SeitenChap. 2. Molecular Weight and Polymer SolutionsPembe HanimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 024Dokument40 Seiten08 024Hoang QuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citrus Bioflavanoids 60% (FEMAS) : Cambridge CommoditiesDokument16 SeitenCitrus Bioflavanoids 60% (FEMAS) : Cambridge Commoditiesibad muhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- AgrinosDokument19 SeitenAgrinosAgroteknologi umparNoch keine Bewertungen
- Re-Evaluation of The 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl Free Radical (DPPH) Assay For Antioxidant ActivityDokument10 SeitenRe-Evaluation of The 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl Free Radical (DPPH) Assay For Antioxidant Activitycentro surcolombiano de investigación en café uscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model M05 Non-Metallic Design Level 2: Service & Operating ManualDokument33 SeitenModel M05 Non-Metallic Design Level 2: Service & Operating ManualTrungGVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Gas Seminar ReportDokument49 SeitenBio Gas Seminar ReportLalitBisht100% (2)
- Welding For Design EngineersDokument518 SeitenWelding For Design EngineersHumberto Magno FukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Towards Recycling of Textile FibersDokument75 SeitenTowards Recycling of Textile FibersMusa EltayebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Class 12 Exemplar Questions and AnswersDokument39 SeitenChemistry Class 12 Exemplar Questions and AnswersBilly Jasneel SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instability of MetalsDokument44 SeitenInstability of MetalsBill AlbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- USP-43-NF - Zinc Acetate Oral SolutionDokument2 SeitenUSP-43-NF - Zinc Acetate Oral SolutionsyNoch keine Bewertungen