Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Attachment
Hochgeladen von
choudary garu0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten2 SeitenOperation research
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenOperation research
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten2 SeitenAttachment
Hochgeladen von
choudary garuOperation research
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
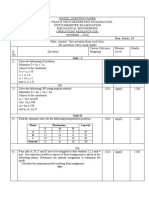
R.V.R. & J.C.
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, GUNTUR-522 019
III/IV B.Tech., ASSIGNMENT TEST # II Time:45 Mnts.
2019-2020 (1st Semester) Max.Marks: 12
ME 305 – OPERATIONS RESEARCH
1 a. Formulate assignment as a mathematical model CO3
b. Solve the following travelling salesman problem CO3
A B C D E
A ∞ 17 16 18 14
B 17 ∞ 18 15 16
C 16 18 ∞ 19 17
D 18 15 19 ∞ 18
E 14 16 17 18 ∞
2. a. Explain Bellman’s principle of optimality with an example? CO3
b. Solve the following linear programming problems by dynamic programming. CO3
Maximize z = 3x1 + 5x2
Subject to the constraints
X1 < 4
X2 < 6
3x1+ 2x2 < 18 ; x1 , x2 > 0
3. a. Explain the dominance rules CO4
b. Using dominance principle to simplify the rectangular game with the following pay of
matrix, and solve it graphically:
Player B
I II III IV
I 18 4 6 4
Player A II 6 2 13 7
III 11 5 17 3
IV 7 6 12 2
4. a. Explain the characteristics of queuing theory CO4
b. Cars arrive at a fast food drive through window according to poisson’s distribution with
the average rate of 1 car every 1min. the time each customer spends ordering and getting
food is exponential with the average time of 3min. when a customer is served , the other
arrived customer has to stay in line looking for their turn. Compute i) Expected number of
cars in the line at any time. ii). The probability that line is empty iii). The average time the
car spends in the system
5. a. What are the advantages and disadvantages of simulation CO5
b. In a single server queuing system inter arrival time distribution and service time CO5
distribution is as follows :
Inter arrival time Frequency Service time Frequency
(Min) (Min)
0 12 4 8
3 18 6 20
6 50 8 36
9 74 10 88
12 32 12 48
15 14
Consider the following random numbers for inter arrival time
58, 47, 23, 69, 35, 55, 69, 90, 86, 74
The following random numbers for service time
87, 39, 28, 97, 69, 87, 52, 52, 15, 85
Simulate the system for 10 arrivals and find average waiting of the customers
6. a. What is decision tree and explain the expected value criterian for taking decisions under CO5
risk with suitable example CO5
b. Mr. Sinha has to decide whether or not to drill a well on his farm. In his village, only 40%
of the wells drilled were successful at 200 feet of depth. Some of the farmers who did not get
water at 200 feet drilled further up to 250 feet but only 20% struck water at 250 feet. Cost of
drillings is Rs. 50/- per foot. Mr. Sinha estimated that he would pay Rs. 18000/- during a 5-
year period in the present value terms, if he continues to buy water from the neighbor rather
than go for the well which would have life of 5 years. Mr. Sinha has three decisions to make:
(a) Should he drill up to 200 feet? (b) If no water is found at 200 feet, should he drill up to
250 feet? (c) Should he continue to buy water from his neighbor? Draw up an appropriate
decision tree and determine its optimal decision.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- R.V.R. & J.C. College of Engineering (A), Guntur-522019 AY: 2023-2024 Semester V (Third Year) Max. Time: 135 Min. Max. Marks:12Dokument1 SeiteR.V.R. & J.C. College of Engineering (A), Guntur-522019 AY: 2023-2024 Semester V (Third Year) Max. Time: 135 Min. Max. Marks:12forallofus435Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer All QuestionsDokument3 SeitenAnswer All QuestionsDisha KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Internals - QTDokument3 Seiten2nd Internals - QTZiya KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMS College of Engineering, Bengaluru-560019Dokument3 SeitenBMS College of Engineering, Bengaluru-560019Sanketh SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityGiga KamaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokument25 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Saravana KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 SA Feb-19Dokument18 Seiten2019 SA Feb-19vishwas kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Research Model Paper 4Dokument4 SeitenOperation Research Model Paper 4Krishna MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus 320 DLM Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenBus 320 DLM Assignment 1PatriqKaruriKimbo0% (1)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityKALPESH MALINoch keine Bewertungen
- U.S.N.Iiiiiiiiii: BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019Dokument4 SeitenU.S.N.Iiiiiiiiii: BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument3 SeitenCase StudyVishnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Research-ORDokument3 SeitenOperations Research-ORSuthari AmbikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loyola College (Autonomous), Chennai - 600 034Dokument2 SeitenLoyola College (Autonomous), Chennai - 600 034Pooja PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- OR All GTU PapersDokument20 SeitenOR All GTU Papersdarshansabhani555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Buss 320 AssignmentDokument5 SeitenBuss 320 AssignmentCaroline MwikalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms Modeexam Qp-NbaDokument3 SeitenAlgorithms Modeexam Qp-NbaragunathNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPERATION RESEARCH External Model QP 2022Dokument3 SeitenOPERATION RESEARCH External Model QP 2022Divya SurendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- M. Tech. Semester - I: Concrete Construction Technology (MCEBT 105/IBMCEBT 905)Dokument40 SeitenM. Tech. Semester - I: Concrete Construction Technology (MCEBT 105/IBMCEBT 905)saurabh1116Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityChavda jayesh laljibhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTU BE Semester VII Operation Research exam questions solutionsDokument2 SeitenGTU BE Semester VII Operation Research exam questions solutionsyashesh vaidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2017 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsDokument4 SeitenBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2017 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsSanketh SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Research Model Paper 1Dokument3 SeitenOperation Research Model Paper 1Krishna MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Research March 2021Dokument8 SeitenOperations Research March 2021Rohith 344Noch keine Bewertungen
- Player B Player A I II III IV I II III IVDokument2 SeitenPlayer B Player A I II III IV I II III IVSharath RamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation ResearchDokument3 SeitenOperation ResearchHarshVavadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument4 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityTNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Operations Research exam questionsDokument4 SeitenMBA Operations Research exam questionsVishalatchi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iem 2103 (2022-2015)Dokument13 SeitenIem 2103 (2022-2015)ahnafmahbub05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization Techniques Question PaperDokument6 SeitenOptimization Techniques Question PaperZero SevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT 32031112016 QPDokument2 SeitenRT 32031112016 QPSai Charan BhogireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qar Makeup 17Dokument3 SeitenQar Makeup 17psychshetty439Noch keine Bewertungen
- Badruka College Managerial Economics Pre-Final Exams 2019Dokument2 SeitenBadruka College Managerial Economics Pre-Final Exams 2019Afreen Fathima100% (2)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument4 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityBandhu SakhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Question - Industrial Law - IIndDokument3 SeitenInternal Question - Industrial Law - IIndv75697609Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sub Code: 185TCS09 MIC18 B. Tech V Semester Regular Examinations, March - 2021 Optimization Techniques Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 70MDokument3 SeitenSub Code: 185TCS09 MIC18 B. Tech V Semester Regular Examinations, March - 2021 Optimization Techniques Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 70Mrajya lakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer All Questions. Three Marks Each.: Page 1 of 3Dokument3 SeitenAnswer All Questions. Three Marks Each.: Page 1 of 3Arjun RNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2016 Semester End Main ExaminationsDokument3 SeitenBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2016 Semester End Main ExaminationsahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sapthagiri College of Engineering Department of Computer Science and Engineering Internal Assessment Test - IIDokument3 SeitenSapthagiri College of Engineering Department of Computer Science and Engineering Internal Assessment Test - IIAasim InamdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- E SRKRPORTALuploadsSyllabus ModelPapersModel R17 B.tech MECH 69Dokument33 SeitenE SRKRPORTALuploadsSyllabus ModelPapersModel R17 B.tech MECH 69prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- r7410301 Operations ResearchDokument5 Seitenr7410301 Operations ResearchsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics: 17333 Seat Exam Question PaperDokument4 SeitenDigital Electronics: 17333 Seat Exam Question PaperYogesh KuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTU BE-SEMESTER 7 EXAM OPERATIONS RESEARCH QUESTIONSDokument3 SeitenGTU BE-SEMESTER 7 EXAM OPERATIONS RESEARCH QUESTIONSyashesh vaidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument4 SeitenGujarat Technological Universitysiddharth devnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Com Terminal Oct 2022Dokument4 Seiten12th Com Terminal Oct 2022george booksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Year Higher Secondary Model Examination: Lrac LRMCDokument2 SeitenSecond Year Higher Secondary Model Examination: Lrac LRMCBen MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat BOE-2023 PapersDokument9 SeitenGujarat BOE-2023 Papersramu naik malothNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Institute of Technology, Rourkela BTech/Dual 7th Sem, Mech Engg (End Sem, Autumn), Nov 2015 ExamDokument4 SeitenNational Institute of Technology, Rourkela BTech/Dual 7th Sem, Mech Engg (End Sem, Autumn), Nov 2015 ExamK Pushpendu PrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE10-R3: APPLIED OPERATIONS RESEARCH EXAMDokument4 SeitenBE10-R3: APPLIED OPERATIONS RESEARCH EXAMSougata ChattopadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3cs2 3it2 01 - Aem 8430Dokument4 Seiten3cs2 3it2 01 - Aem 8430rishabh pandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological Universitysiddharth devnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 BFT - V - Pom - QPDokument6 Seiten1 BFT - V - Pom - QPSalil SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Assessment Test - April 2018 ECE3002 VLSI System DesignDokument3 SeitenFinal Assessment Test - April 2018 ECE3002 VLSI System DesignNishant Panchal100% (1)
- DR Biniam B Quantitative Analysis AssignmentDokument5 SeitenDR Biniam B Quantitative Analysis AssignmentAmanuel MarkosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: - Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100Dokument3 SeitenFinal Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: - Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100ak164746Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityMaulik PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Migrants Reacton On CoronaDokument4 SeitenMigrants Reacton On CoronaApoorv TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Techniques: Roll NoDokument3 SeitenQuantitative Techniques: Roll NoHareg KidanemariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 QBDokument5 SeitenModule 3 QBVishnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorVon EverandAttainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 302 Quizz-IIDokument2 SeitenME 302 Quizz-IIchoudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia-Water PairDokument16 Seiten17 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia-Water PairPRASAD326100% (13)
- Institute Name: Delhi Technological University (IR-E-U-0098)Dokument2 SeitenInstitute Name: Delhi Technological University (IR-E-U-0098)Rob BowdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me309 HT At1 2019-20Dokument1 SeiteMe309 HT At1 2019-20choudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia-Water PairDokument16 Seiten17 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia-Water PairPRASAD326100% (13)
- ME302 Assignment Test-1 2019-20Dokument2 SeitenME302 Assignment Test-1 2019-20choudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic-06a 2009Dokument13 SeitenTopic-06a 2009lavanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me304 at Ii 2019-2020Dokument1 SeiteMe304 at Ii 2019-2020choudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Lab ManualDokument50 SeitenHeat Transfer Lab Manualchoudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional EthicsDokument184 SeitenProfessional Ethicsr_rame7678% (9)
- Ic Engines & Jet PropulsionsDokument11 SeitenIc Engines & Jet Propulsionschoudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AttachmentDokument1 SeiteAttachmentchoudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAC Lecture 10Dokument18 SeitenRAC Lecture 10api-373446667% (3)
- AttachmentDokument1 SeiteAttachmentchoudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 210 ATD Assign 1 2018 19Dokument1 SeiteME 210 ATD Assign 1 2018 19choudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elemen MesinDokument23 SeitenElemen MesinMonika NikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Gib and Cotter Joint 1Dokument17 SeitenDesign of Gib and Cotter Joint 1choudary garuNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.B.V.R.R.Women'S College (Autonomous) : Electromagnetic Theory and ApplicationsDokument2 SeitenR.B.V.R.R.Women'S College (Autonomous) : Electromagnetic Theory and ApplicationsAnil karelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Cbse Ix Sample Paper 19-20Dokument5 Seiten9th Cbse Ix Sample Paper 19-20dinesh lalwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Studies Descriptive Statistics Assessment 2012.09 Mark SchemeDokument5 SeitenIb Studies Descriptive Statistics Assessment 2012.09 Mark SchemeJohn RyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partitive Proportions Word ProblemsDokument2 SeitenPartitive Proportions Word Problemsxylaxander89% (18)
- Grade 5 MTAP Reviewer SolvedDokument3 SeitenGrade 5 MTAP Reviewer SolvedHaironisaMalaoMacagaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 0 - Review of Basic ConceptsDokument8 SeitenLecture 0 - Review of Basic ConceptsKismet100% (1)
- Coefficient of DeterminationDokument11 SeitenCoefficient of DeterminationKokKeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integers: CBSE Class 6 Mathematics WorksheetsDokument3 SeitenIntegers: CBSE Class 6 Mathematics WorksheetsIhtesham HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization - K. LangeDokument540 SeitenOptimization - K. Lange1600170100% (3)
- 53-Consolidation Exercise 3GDokument5 Seiten53-Consolidation Exercise 3G4D16 Lee Hoi Lam, Helen s190073Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fenet d3613 Dle Advanced Finite Element Contact BenchmarksDokument62 SeitenFenet d3613 Dle Advanced Finite Element Contact BenchmarkstonisugusNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP 1Dokument28 SeitenDSP 1Jayan GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parametric CurveDokument28 SeitenParametric Curveavi200894Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 Multiplication Table Missing NumberDokument10 SeitenGrade 3 Multiplication Table Missing NumberYondrizal KotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems Homework 1 SolutionDokument10 SeitenControl Systems Homework 1 SolutionpeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venn-Diagram by Total GadhaDokument41 SeitenVenn-Diagram by Total GadhaqwertyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics problem set explores quantum mechanicsDokument5 SeitenPhysics problem set explores quantum mechanicsDaljot Singh KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schools Division Office of Quirino Cabarroguis National School of Arts and TradesDokument3 SeitenSchools Division Office of Quirino Cabarroguis National School of Arts and TradesLeizel Jane LjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swarm Optimization Algorithms For Face Recognition: Juicy RayDokument40 SeitenSwarm Optimization Algorithms For Face Recognition: Juicy RayIshita VishnoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEAM LG Gr. 10 Module 2-Mathematics Linear Functions and Their GraphsDokument57 SeitenBEAM LG Gr. 10 Module 2-Mathematics Linear Functions and Their GraphsMarvin Go100% (1)
- Russell's Unpopular Essays Explore Philosophy, Politics and SocietyDokument30 SeitenRussell's Unpopular Essays Explore Philosophy, Politics and Societyzeeshan100% (1)
- Combinations and Permutations Notes-1Dokument3 SeitenCombinations and Permutations Notes-1Kevin KipropNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 2Dokument20 SeitenNcert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 2Rishabh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Engineering College Gandhinagar Maths PresentationDokument16 SeitenGovernment Engineering College Gandhinagar Maths PresentationParmar MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covariance and Correlation: Multiple Random VariablesDokument2 SeitenCovariance and Correlation: Multiple Random VariablesAhmed AlzaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10Dokument143 SeitenClass 10rajamohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is A Random Walk The Best ExchangeDokument13 SeitenIs A Random Walk The Best ExchangeÉlisabeth SoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Grade 1Dokument7 SeitenMathematics Grade 1IrqamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Specification Mathematics VI Second Periodical TestDokument3 SeitenTable of Specification Mathematics VI Second Periodical TestJessmiel LabisNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simplified Finite Element Solution For The Plates On Elastic FoundationDokument7 SeitenA Simplified Finite Element Solution For The Plates On Elastic Foundationiname11Noch keine Bewertungen