Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
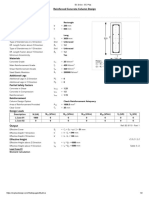
Reinforced Concrete Wall Design Report: Material and Design Data
Hochgeladen von
azwanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Reinforced Concrete Wall Design Report: Material and Design Data
Hochgeladen von
azwanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Reinforced Concrete Wall Design Report
MATERIAL AND DESIGN DATA
Load Allowance = 10 %
Code of Practice fcu (N/mm²) Ec, (N/mm²) fy (N/mm²) fyv (N/mm²) γc γs
BS8110 : 1997 30 24597 460 460 1.5 1.05
Cover (mm) Conc. Unit Weight (kN/m³) Steel Unit Weight (kg/m³)
25 24 7860
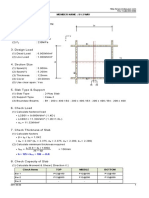
Design Calculation for RC Wall 1B (Core 1)
Wall Panel Thickness, t = 200 mm
Sub Panel 1 (Reg. 1)
Location in Panel: Wall Zone
Sub-Panel Length, b = 1850 mm | Gross Concrete Area, Ac = b × t = 370000 mm²
Design Status: Pass
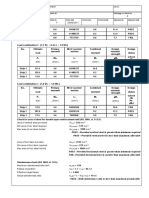
Reaction Table (3D) for RC Wall 1C/C-C1 Region 1
Reaction Edge Loading Source P Mx My Vx Vy X M
Dead Load 101.8 0.9 -1.6 -28.9 1.7 -753.2 -27.7
Top Edge
Live Load 26.1 0.4 -0.7 -16.0 0.8 -427.7 -15.6
Dead Load 135.6 0.5 3.9 -29.5 -2.4 1210.8 25.2
Bottom Edge
Live Load 20.1 0.0 1.7 -16.7 -0.7 1799.9 15.6
P - Axial Load (kN), Mx, My - Bending Moment About X-X / Y-Y Axis (kNm), Vx, Vy - Shear Force Along X-X / Y-Y Axis (kN)
X - Eccentricity of Axial Load from Left Reference of Section (mm), M - Moment by Eccentricity of Axial Load (kNm) where M = P × (Panel Length / 2 - X)
Sign of Top Edge Reactions have been reversed to be comparable to bottom edge
Loadings listed above does not consider load allowance of 10% specified by user
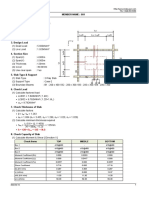
Sub-Frame 2D Analysis Result (Mx) for RC Wall 1C/C-C1Sub Panel 1 (Reg. 1)
Current Floor: 1B, Zone Length = 1850 mm
No. Floor Length Loc. D.L. L.L. Min. Max.
Top 0.27 0.11 0.55 0.69
1 1B 2050
Bot 0.76 0.21 1.40 1.40
Length - Distance of the first node to the last node of the 2D SubFrame Panel/Group Mesh (mm), Loc. - Location of Result (Top or Bottom of the Panel)
D.L., L.L. - Dead / Live Load Moment from Plan Sub-Frame Analysis (kNm)
Min., Max. - Minimum/Maximum Gravity Pattern Loading from Plan Sub-Frame Analysis (kNm)
Lower Floor: GB, Zone Length = 1850 mm
No. Floor Length Loc. D.L. L.L. Min. Max.
Top -0.07 -0.06 -0.20 -0.47
1 1B 2050
Bot -0.39 -0.34 -1.10 -1.72
Length - Distance of the first node to the last node of the 2D SubFrame Panel/Group Mesh (mm), Loc. - Location of Result (Top or Bottom of the Panel)
D.L., L.L. - Dead / Live Load Moment from Plan Sub-Frame Analysis (kNm)
Min., Max. - Minimum/Maximum Gravity Pattern Loading from Plan Sub-Frame Analysis (kNm)
Wall Panel 3D Analysis Result for Sub Panel 1 (Reg. 1)
Loading Reaction Load Mx
No P Mx My Vx Vy X M Process
Source Edge Comb. (Ecc)
1 G.L. B.E. LC1 244.3 -1.9 9.0 -74.8 -4.9 1296.2 66.2 2.4 Design
2 G.L. B.E. Min 149.2 -1.9 4.2 -32.5 -2.6 1210.8 27.7 1.5 Analysis
3 G.L. T.E. LC1 202.7 2.0 -3.7 -72.8 4.0 679.4 -70.1 2.0 Analysis
4 G.L. T.E. Min 112.0 1.0 -1.8 -31.8 1.9 753.2 -30.4 1.1 Analysis
Loading Source - G.L. for Gravity, W.L. for Wind Load, N.L. for Notional Load, S.L. for Seismic Load
Gravity Load Mx always uses greater of (3D, 2D Pattern Loading), Reaction Edge - Top Edge(T.E.) or Bottom Edge(B.E.)
Load Comb. - User Specified Load Combination in parameter, Min for minimum gravity load (1.0DL)
P - Axial Load (kN), Mx / My - Design Bending Moment About X-X / Y-Y Axis (kNm), Vx / Vy - Design Shear Force In X-X / Y-Y Axis (kN)
X - Eccentricity of Axial Load from Left Reference of Section (mm), M - Moment by Eccentricity of Axial Load (kNm) where M = P × (Panel Length / 2 - X)
Mx(Ecc) - Moment due to Minimum Eccentricity (emin) about wall minor axis (kNm)
Process - Process of Applied Loadings (Design/Analysis)
Load allowance of 10% has been added specified by user
Wall Zone Braced/Unbraced and Short/Slender Condition Table for RC Wall Sub Panel 1 (Reg. 1)
Wall Clear Height, lo = 3600 mm
Loading Braced/
No. P Vy ∆y Qy Short/ Slender
Source Unbraced
1 G.L. - - - - Braced Short
2 G.L.(Min) - - - - Braced Short
3 G.L. - - - - Braced Short
4 G.L.(Min) - - - - Braced Short
Loading Source - G.L. Gravity, W.L. for Wind Load, N.L. for Notional Load, S.L. for Seismic Load
P - Axial Force (kN), Vy - Shear Force in Wall Panel Local Y-Y Axis (kN)
∆y - RC. Wall Drift in Local Y-Y Axis (mm), Qy - RC. Wall Stability Index in Local Y-Y Axis (Q = P × ∆ / V × h)
Braced/Unbraced - RC. Wall Braced/Unbraced Condition in Local Y-Y Axis (mm), Limit Value = 0.05
Short/Slender - RC. Wall Short/Slender Condition in Local Y-Y Axis (mm)
All Gravity Load Cases Assigned as Braced regardless the Stability Index
Wall Zone Slenderness Limit Check
Wall Clear Height, lo = 3600 mm
Top Element Stiffness, KeTop = ∑KsTop + ∑KbTop + ∑KtwTop = 10659375.0 mm³
Bottom Element Stiffness, KeBot = ∑KsBot + ∑KbBot + ∑KtwBot = 7701358.7 mm³
Wall Stiffness, Kw = 4111111.1 mm³
Restraint Elements at the top part of wall zone
Elememt
No. Mark Width a, mm Depth b, mm Length L, mm Angle α, ° K
Type
1 Slab FS203:1 1025 150 1000 90.0 1729688
2 Slab FS257:1 1025 150 1000 90.0 1729688
3 Beam 1B39(230x600) - 1 230 600 6900 90.0 3600000
4 TWall C/1C-2A 200 3600 5000 90.0 933120000
5 TWall C1/1C-2A 200 3600 5000 90.0 933120000
K = 0 when the element is skipped from computation of restrain condition, please refer to the technical documentation
K = |Sin α| × [a × b³ / (12 × L)]
Restraint Elements at the bottom part of wall zone
Elememt
No. Mark Width a, mm Depth b, mm Length L, mm Angle α, ° K
Type
1 Slab FS191:1 2050 150 6900 90.0 501359
2 Beam GB33(230x600) - 1 230 600 6900 90.0 3600000
3 TWall C/1C-2A 200 4500 5000 90.0 1822500000
4 TWall C1/1C-2A 200 4500 5000 90.0 1822500000
K = 0 when the element is skipped from computation of restrain condition, please refer to the technical documentation
K = |Sin α| × [a × b³ / (12 × L)]
Effective Length Factor, β for Braced Condition
Relative Stiffness at Top of Element, αTop = 0.386
Relative Stiffness at Bottom of Element, αBot = 0.534
β1 = 0.7 + 0.05 × (αTop + αBot) = 0.75, β2 = 0.85 + 0.05 × Min (αTop, αBot) = 0.87
β = Min (β1, β2) = 0.75 < 1.0
Effective Length Factor, β for Unbraced Condition
Relative Stiffness at Top of Element, αTop = 0.386
Relative Stiffness at Bottom of Element, αBot = 0.534
β1 = 1.0 + 0.15 × (αTop + αBot) = 1.14, β2 = 2.0 + 0.3 × Min (αTop, αBot) = 2.12
β = Min (β1, β2) = 1.14
Wall Effective Height for Braced Condition, le = ßBraced × lo = 2700 mm
Wall Effective Height for Unbraced Condition, le = ßUnbraced × lo = 4104 mm
Clause 3.9.3.7.2 Limits of slenderness
Slenderness Ratio for braced condition le / h = 2700.0 / 200 = 13.5 ≤ 40 ← Checking for slenderness upper limit pass
Slenderness Result (Using Load Case Region 1 Load 1)
Lateral Force, V = 0, Use Stability Index Q = 0 for Gravity Load, The Element is Braced
Slenderness Ratio, sr = Leff / t = 2700.0 / 200 = 13.5 < 15 → The Wall is Short About X-X Axis
Design load selected is short (not slender), no slenderness iteration table and calculation will be shown
Loading Data
Design Loading Selected from Region 1 Load No. 1
Loading / Loadings from 3D Analysis Result
Loading Type Reaction Edge Load Comb. P Mx My Vx Vy X M
G.L. B.E. 1 244.3 -1.9 9.0 -74.8 -4.9 1296.2 66.2
Loading Type - Source of Loading (Gravity, Wind Load, Notional Load)
Reaction Edge - Top Edge(T.E.) or Bottom Edge(B.E.), Load Comb. - User Specified Load Combination
P - Axial Load (kN), Mx, My - Design Bending Moment About X-X / Y-Y Axis (kNm), Vx, Vy - Design Shear Force In X-X / Y-Y Axis (kN)
X - Eccentricity of Axial Load from Left Reference of Section (mm), M - Moment by Eccentricity of Axial Load (kNm) where M = P × (Panel Length / 2 - X)
Load allowance of 10% has been added specified by user
Sub-Panel Applied Axial Force, F = 244.3 kN
Sub-Panel Axial Force Capacity, FCap = 3615.2 kN
Sub-Panel Applied Moment About X-X Axis, Mx = 2.4 kNm
Sub-Panel Moment Capacity About X-X Axis, MxCap = 36.2 kNm
Sub-Panel Applied Moment About Y-Y Axis, My = 75.2 kNm
Sub-Panel Moment Capacity About Y-Y Axis, MyCap = 1113.6 kNm
Wall Sub-Panel Analysis/Design Passed
Vertical Reinforcement Provided: 14T12-300 (0.43%)
Shear Design and Checking Calculation
Basic Shear Design Data for Sub-Panel
H = 1850.0 mm, B = 200.0 mm, Concrete Cover, cov = 25 mm
Vertical Bar Diameter, ΦV = 12 mm, Horizontal Bar Diameter, ΦH = 10 mm
Effective Depth for Shear Design, d = H - cov - ΦH - ΦV / 2 = 1809.0 mm
Design Shear Force, V = 74.8 kN, Bending Moment, M = 2.0 kNm, Axial Force, N = 244.3 kN
Shear Stress, νss = V × 1000 / (b × d) = 74.8 × 1000 / (200.0 × 1809.0) = 0.21 N/mm²
Maximum Shear Stress Allowed, νMax = Min (0.8 × √30, 5) = 4.38 N/mm² - Clause 3.4.5.2
Shear Stress, νss = V × 1000 / (b × d) = 74.8 × 1000 / (200.0 × 1809.0) = 0.21 N/mm² ≤ νMax (4.38 N/mm²)
Checking for Maximum Shear Stress Allowed Pass
- Table 3.8: Values of νc, design concrete shear stress
Steel Percentage, 100 × As / (bv × d) = 0.15 % ≤ 3.0 %
0.15% of steel is used for calculation of compressive member
Effective Depth Ratio, edr = 400 / d = 400 / 1809.0 = 0.221
(400 / d)^ ¼ = 0.686 < 1, (400 / d)^ ¼ taken as 1
Minimum fcu, fcuMin = 25 N/mm², Concrete Grade Ratio, Min(fcu, 40) / fcuMin = 30 / 25 = 1.200
Concrete Shear Capacity, νc = 0.79 {100 As / (bv d)}⅓ (400 / d)¼ (fcu / 25)⅓ / γm
= 0.79 × {0.15}⅓ × 1.000 × (1.200)⅓ / 1.25 = 0.36 N/mm²
Clause 3.4.5.12: eqn. 6a
VhM Ratio = V × h / M = 74809 × 1850.0 / 2043431 = 67.73 > 1.00, VhM Ratio taken as 1.00
Design Shear Capacity, νc1' = νc + 0.60 × (N / Ac) × VhM = 0.357 + 0.60 × (244253.2 / 370000.0) × 1.00 = 0.753 N/mm²
Clause 3.4.5.12: eqn. 6b
Design Shear Capacity, νc2' = νc × SQRT[(1 + N / (Ac × νc)] = 0.357 × SQRT[(1 + 244253.2 / (370000.0) × 0.36] = 0.602 N/mm²
Select νc2' as νc' for design
Minimum Design Shear Stress, νMin = 0.40 N/mm²
νss = 0.207 < νc' + 0.4, Provides only minimum link
Design for minimum Shear Stress, νd = νmin = 0.40 N/mm²
Shear Link Area / Spacing Ratio, SAsv_Sv = (vd × b) / (fyy × fy) = (0.40 × 200) / (0.95 × 460) = 0.183 mm²/mm
Using link diameter ΦH = 10 mm (SAsv = 157.1 mm²) and spacing, Sv = 300 mm
SAsv_SvProv = SAsvProv / Sv = 157.1 / 300 = 0.524 mm²/mm ≥ SAsv_Sv (0.183 mm²/mm)
Provided 2 X 12T10-300, Shear Checking / Design Passed
Total horizontal steel area provided, AsProv(H) = 24 × 78.5 = 1885 mm²
Minimum steel percentage required, AsMin = 0.01 × 0.25 × (3600 × 200) = 1800 mm² <= 1885, OK
Checking for horizontal steel percentage passed
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ETABS Concrete Frame Design: IS 456:2000 Column Section DesignDokument2 SeitenETABS Concrete Frame Design: IS 456:2000 Column Section DesignSubhekshya ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure V Canopy DesignDokument6 SeitenAnnexure V Canopy DesignkrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trimdek DesignDokument10 SeitenTrimdek Designakgupta733779Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis: Tedds Calculation Version 1.0.23Dokument10 SeitenAnalysis: Tedds Calculation Version 1.0.23Sachin AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNYUDokument7 SeitenSNYUျမတ္ သူ ေအာင္Noch keine Bewertungen
- WL-2 1kpaDokument3 SeitenWL-2 1kpamuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- RCC31R Rigorous One-Way SlabsDokument148 SeitenRCC31R Rigorous One-Way SlabsMohammad Twaha JaumbocusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column DesignDokument2 SeitenColumn Designjohnstruct archNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC31R Rigorous One-Way SlabsDokument389 SeitenRCC31R Rigorous One-Way SlabsCioabla BogdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15m Brick Wall Frame 2021-08-21Dokument21 Seiten15m Brick Wall Frame 2021-08-21Jack WenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Structural CalculationsDokument2 SeitenCivil Structural Calculations3d arch viewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS Concrete Frame DesignDokument2 SeitenETABS Concrete Frame DesignRabi DhakalNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Floor RC Slab Design (EN1992)Dokument5 SeitenFirst Floor RC Slab Design (EN1992)Shingirai JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- WL-3 6kpaDokument3 SeitenWL-3 6kpamuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- BeamDokument10 SeitenBeamdoggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab DesignDokument4 SeitenSlab DesignAie BantuganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Design Design NoteDokument4 SeitenBearing Design Design Notearepelli madhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Job No.: U U Ua CR 4 U NDokument1 SeiteProject Job No.: U U Ua CR 4 U NAnonymous 0x2pwMCWgjNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.0.0 License # 18EMACAKL7JTANKDokument2 SeitenETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.0.0 License # 18EMACAKL7JTANKSanjeev SanjeevNoch keine Bewertungen
- LL1-0 89kNDokument6 SeitenLL1-0 89kNmuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- PS4dDokument7 SeitenPS4dgeethkumaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LL2-0 73kNperMDokument3 SeitenLL2-0 73kNperMmuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Compressive Stength For Channel With or Without Plate (As Per Is:800 2007)Dokument2 SeitenDesign Compressive Stength For Channel With or Without Plate (As Per Is:800 2007)K SrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: IS 456:2000 Column Section DesignDokument2 SeitenETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: IS 456:2000 Column Section DesignSamikshya ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Nail ReportDokument9 SeitenSoil Nail ReportUtsav ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Member Reinforced Concrete Column Design Report (AS-3600) PDFDokument13 SeitenMember Reinforced Concrete Column Design Report (AS-3600) PDFdongshengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Structural MemberDokument50 SeitenDesign of Structural Memberfrancis sebastian lagamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Calculation of Embed Balustrade-R2Dokument46 SeitenStructural Calculation of Embed Balustrade-R2vengadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Villa Assaf ReportDokument37 SeitenVilla Assaf ReportReda AtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aci 95Dokument14 SeitenAci 95Joseph AsfourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etabs Column Design MT CalculationDokument2 SeitenEtabs Column Design MT CalculationAung SoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- LL1-0 89kpaDokument3 SeitenLL1-0 89kpamuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Midasit: 1. General InformationDokument2 SeitenMidasit: 1. General InformationEng PhearumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Pile Design: Fspiii S275 Hot RolledDokument1 SeiteSheet Pile Design: Fspiii S275 Hot Rolledhessian123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 B&WDokument12 SeitenChapter 5 B&WPoshan DhunganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 2015 15.1.0-Design DetailsDokument2 SeitenETABS 2015 15.1.0-Design DetailsdenyfateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation PDFDokument126 SeitenCalculation PDFmohammed almahrooqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WL-1 75kpaDokument6 SeitenWL-1 75kpamuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Column Design (EN1993)Dokument8 SeitenSteel Column Design (EN1993)Bernard KiruiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 150x100x10UA STANDARD LINTEL 3.6mDokument9 Seiten150x100x10UA STANDARD LINTEL 3.6mTerry CheukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ang Residence (Flatdeck 1.0mm X 100mm THK Slab)Dokument6 SeitenAng Residence (Flatdeck 1.0mm X 100mm THK Slab)Pandaman227Noch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 19.0.0 License # 1AVSJX3S5D5WKQEDokument2 SeitenETABS Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 19.0.0 License # 1AVSJX3S5D5WKQEAastha AdhiakariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aashto LRFD Railway FlyoverDokument54 SeitenAashto LRFD Railway FlyoverShaileshRastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WL 2.1kpa (10 8)Dokument6 SeitenWL 2.1kpa (10 8)muralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 2015 15.1.0-Design DetailsDokument2 SeitenETABS 2015 15.1.0-Design DetailsdenyfateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Report PDFDokument10 SeitenDraft Report PDFSupun Aravinda JayawardhaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Twoway SlabDokument20 SeitenFinal Twoway Slabvishnumani3011Noch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.2.0 License # 1UARYUV5QA3ALLSDokument2 SeitenETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.2.0 License # 1UARYUV5QA3ALLSRakesh ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precast PlankDokument9 SeitenPrecast PlankKalpanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LL-0 73knpermDokument7 SeitenLL-0 73knpermmuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report 30 TonDokument10 SeitenReport 30 TonMARYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 30 TonDokument10 SeitenReport 30 TonMARYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation For 9 MM Fibrous Plaster CeilingDokument13 SeitenDesign Calculation For 9 MM Fibrous Plaster CeilingNur Fadzlini RamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- WL-1 2kpaDokument6 SeitenWL-1 2kpamuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7tc1 Top FixedDokument2 Seiten7tc1 Top FixedEmily ShumNoch keine Bewertungen
- WL-2 1kpaDokument6 SeitenWL-2 1kpamuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- WIND02 v2-21: Detailed Wind Load Analysis Per ASCE 7-16Dokument4 SeitenWIND02 v2-21: Detailed Wind Load Analysis Per ASCE 7-16Neil Checalla ApazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LL1-0 89kNDokument3 SeitenLL1-0 89kNmuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- WL 2.1 Kpa Top SupportDokument5 SeitenWL 2.1 Kpa Top Supportmuralidharan10901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- GEE - SW Hyraulic CalculationDokument2 SeitenGEE - SW Hyraulic CalculationazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision in Exclusion Clause For Your Medical Plan(s)Dokument10 SeitenRevision in Exclusion Clause For Your Medical Plan(s)thilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEE - SW PE Calculation (Rev01)Dokument7 SeitenGEE - SW PE Calculation (Rev01)azwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gee - SW Pe Calculation (Old)Dokument16 SeitenGee - SW Pe Calculation (Old)azwan100% (1)
- Gee - SW PeDokument7 SeitenGee - SW PeazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application For Top-Up Switching Valuation Oct2021Dokument6 SeitenApplication For Top-Up Switching Valuation Oct2021azwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Img 20210125 0001Dokument1 SeiteImg 20210125 0001azwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pilecap Design by Bending Theory To B.S 8110 & B.S 8004Dokument59 SeitenPilecap Design by Bending Theory To B.S 8110 & B.S 8004azwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Design - OkDokument35 SeitenSlab Design - OkazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esteem 8 Training 2011Dokument65 SeitenEsteem 8 Training 2011Asyraf Malik80% (5)
- Concrete Design and Construction Details For Tank Farms.Dokument23 SeitenConcrete Design and Construction Details For Tank Farms.António FontesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - 1BDokument16 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - 1BazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Retaining Structures To Bs 8007 and Bs 8110: Calculations OutputDokument93 SeitenWater Retaining Structures To Bs 8007 and Bs 8110: Calculations Outputazwan100% (2)
- Img 20210125 0003Dokument1 SeiteImg 20210125 0003azwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Summary Report - RBDokument4 SeitenSlab Summary Report - RBAnonymous yOTwy1XviJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Summary Report - RBDokument4 SeitenSlab Summary Report - RBAnonymous yOTwy1XviJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - RFDokument13 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - RFKavi MaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Summary Report - RBDokument4 SeitenSlab Summary Report - RBAnonymous yOTwy1XviJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - RFDokument13 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - RFKavi MaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - FBDokument20 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - FBazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Summary Report - RBDokument4 SeitenSlab Summary Report - RBAnonymous yOTwy1XviJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Summary Report - RBDokument4 SeitenSlab Summary Report - RBAnonymous yOTwy1XviJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Summary Report - RBDokument4 SeitenSlab Summary Report - RBAnonymous yOTwy1XviJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - FBDokument20 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - FBazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Summary Report - RFDokument11 SeitenSlab Summary Report - RFazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - 2BDokument17 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - 2BazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - 1BDokument16 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - 1BazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataDokument13 SeitenBeam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Key Plan Report - 2BDokument17 SeitenBeam Key Plan Report - 2BazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataDokument33 SeitenBeam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Modelling of A Direct Contact Condensation Experiment Using The AIAD FrameworkDokument25 SeitenNumerical Modelling of A Direct Contact Condensation Experiment Using The AIAD FrameworkAmin AlAhmadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collapse Dynamics of Super-Gaussian Beams: Taylor D. Grow, Amiel A. Ishaaya, Luat T. Vuong and Alexander L. GaetaDokument8 SeitenCollapse Dynamics of Super-Gaussian Beams: Taylor D. Grow, Amiel A. Ishaaya, Luat T. Vuong and Alexander L. GaetaVijay SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code - Aster: FDLV111 - Absorption of A Wave of Pressure in A Fluid ColumnDokument10 SeitenCode - Aster: FDLV111 - Absorption of A Wave of Pressure in A Fluid ColumnStefano MilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS 1893: 2002,2016 - CRITERIA For Earthquake Resistant Design of StructuresDokument29 SeitenIS 1893: 2002,2016 - CRITERIA For Earthquake Resistant Design of Structuresparam2189Noch keine Bewertungen
- Duct Design Rev2Dokument18 SeitenDuct Design Rev2AshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 11833 1 2019Dokument11 SeitenIso 11833 1 2019fNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Plasma Accelerators For Charged Particles PDFDokument105 SeitenLaser Plasma Accelerators For Charged Particles PDFAjit UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Transfer Function PDFDokument4 Seiten3 Transfer Function PDFisteboiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Creep Mechanics PDFDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Creep Mechanics PDFFaizanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Dokument10 SeitenLesson Plan in Science 7Maricel AlcoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 7 MAE 4333 Daniel Perez & Trevor KaaseDokument4 SeitenLAB 7 MAE 4333 Daniel Perez & Trevor Kaasedaniel perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRC201 Sdof JMWB PDFDokument99 SeitenSTRC201 Sdof JMWB PDFAkash ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stabilizing Slider-Crank Mechanism With Clearance JointsDokument13 SeitenStabilizing Slider-Crank Mechanism With Clearance JointsTomé GuenkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 05 ISM 8eDokument38 SeitenCH 05 ISM 8eevilgnsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Study of Transient and Steady State Natural Convection and Surface Thermal Radiation in A Horizontal Square Open CavityDokument19 SeitenNumerical Study of Transient and Steady State Natural Convection and Surface Thermal Radiation in A Horizontal Square Open CavitygovindNoch keine Bewertungen
- P11 Practice 7 SolnsDokument7 SeitenP11 Practice 7 SolnsajjagottuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyses and Use of Software Ansys and Franc2d For Fracture MechanicsDokument8 SeitenAnalyses and Use of Software Ansys and Franc2d For Fracture MechanicsPradeep KunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- SFG 3023 Chapter 1Dokument67 SeitenSFG 3023 Chapter 1Nik AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set A: Electrostatic FieldsDokument2 SeitenProblem Set A: Electrostatic FieldsfsfsfsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17-01-SEP-New Integral End Bent Pile Design ProcedureDokument17 Seiten17-01-SEP-New Integral End Bent Pile Design ProcedureMainulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Dokument8 SeitenPeperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Lee Li JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC MomentumDokument33 SeitenMC MomentumPuntos de periciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th STD Science I 1.gravitationDokument2 Seiten10th STD Science I 1.gravitationNarendra Jadhav100% (1)
- Training CourseDokument44 SeitenTraining CourseTugay ArıçNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure Analysis of High-Performance Surfaces Used For Transversal Stability of Ships (Bilge Keels)Dokument6 SeitenFailure Analysis of High-Performance Surfaces Used For Transversal Stability of Ships (Bilge Keels)Brizamar AguiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joule's Apparatus IPDokument31 SeitenJoule's Apparatus IP--MsKahokoHino--Noch keine Bewertungen
- Straw Rocket LabDokument4 SeitenStraw Rocket Labaaguiar1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Project Final1Dokument15 SeitenPhysics Project Final1sohamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys PZTDokument28 SeitenAnsys PZTQuoc LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis: Lecture SeriesDokument9 SeitenStructural Analysis: Lecture SeriesSourNoch keine Bewertungen