Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ASS
Hochgeladen von
Danniel Dizon LanggaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ASS
Hochgeladen von
Danniel Dizon LanggaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Define the following:
1. Budget - A budget is an estimation of revenue and expenses over a specified future period
of time and is usually compiled and re-evaluated on a periodic basis. Budgets can be made for
a person, a family, a group of people, a business, a government, a country, a multinational
organization or just about anything else that makes and spends money.
2. Budget Committee - A budget committee is a group of people that creates and maintains fiscal
responsibility for an entity or organization. In a company, this committee usually consists of the
top management and the CFO.
3. Master Budget – The master budget is the aggregation of all lower-level budgets produced
by a company's various functional areas, and also includes budgeted financial statements, a
cash forecast, and a financing plan. The master budget is typically presented in either a
monthly or quarterly format, and usually covers a company's entire fiscal year.
4. Continuous Budget – Continuous budgeting is the process of continually adding one more
month to the end of a multi-period budget as each month goes by. This approach has the
advantage of having someone constantly attend to the budget model and revise budget
assumptions for the last incremental period of the budget.
5. Fixed Budget – A fixed budget, also called a static budget, is financial plan based on the
assumption of selling specific amounts of goods during a period. In other words, fixed budgets
are based on a set volume of sales or revenues. This is an easy way for management to plan out
expenses and operations when they assume that sales volume and total revenues will be a set
amount during a period.
6. Flexible Budget – A flexible budget, also called a variable budget, is financial plan of estimated
revenues and expenses based on the current actual amount of output. In other words, a flexible
budget uses the revenues and expenses produced in the current production as a baseline and
estimates how the revenues and expenses will change based on changes in the output.
7. Incremental Budget – An incremental budget is a budget prepared using a previous period's
budget or actual performance as a basis with incremental amounts added for the new budget
period.
8. Zero-based Budgeting – Zero-based budgeting (ZBB) is a method of budgeting in which
all expenses must be justified for each new period. The process of zero-based budgeting starts
from a "zero base," and every function within an organization is analyzed for its needs and costs.
9. Life-Cycle Budgeting – A life-cycle budget is an estimate of the total amount
of sales and profits to be garnered from a product over its estimated life span. This estimate
includes the costs to develop, market, and service a product
10. Activity-Based Budgeting – Activity-based budgeting (ABB) is a system that records,
researches, and analyzes activities that lead to costs for a company. Every activity in an
organization that incurs a cost is scrutinized for potential ways to create efficiencies.
11. Kaizen Budgeting – Kaizen is the practice of continually improving processes and
reducing costs. The concept tends to yield gradual improvements over a long period of time.
12. Governmental Budget – Government budgeting is the critical exercise of allocating revenues
and borrowed funds to attain the economic and social goals of the country. It also entails the
management of government expenditures in such a way that will create the most economic impact
from the production and delivery of goods and services while supporting a healthy fiscal position.
13. Budget Manual – A budget manual is a set of rules and instructions used by large
organizations to prepare their budgets and related reports. As organizations become larger and
more complex, it is no longer possible for just one person to prepare a budget.
14. Budget Planning Calendar – A budget planning calendar is a schedule of activities that must
be completed to create and develop a budget. Budget planning calendars are necessary for the
creation of complex budgets used by large organizations.
15. Distribution Instructions – Items usually included in a budget manual are a planning calendar and
distribution instructions for all budget schedules. Distribution instructions are important because, once
a schedule is prepared, other departments within the organization will use the schedule to prepare their
own budgets.
16. Budget Report – A budget report is a comparison of the actual results of a business to a pre -
established budget. This report is issued to anyone responsible for a line item in the income
statement, which usually means the department managers.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Leganes - ComputationDokument18 SeitenLeganes - ComputationDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- China 2Dokument9 SeitenChina 2Danniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nia 02202023Dokument3 SeitenNia 02202023Danniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Should Jollibee Enter UK MarketDokument3 SeitenShould Jollibee Enter UK MarketDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Occupational Safety Health OSHADokument22 SeitenConstruction Occupational Safety Health OSHADanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeganesDokument18 SeitenLeganesDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accomplishment Report 2022Dokument23 SeitenAccomplishment Report 2022Danniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Occupational Safety Health OSHADokument22 SeitenConstruction Occupational Safety Health OSHADanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Guide For Docs PDFDokument2 SeitenUser Guide For Docs PDFNestor D. Mores, Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Risks AssociateDokument11 SeitenRisks AssociateDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNB OJT Portfolio for Herwin Mae M. BoclarasDokument12 SeitenPNB OJT Portfolio for Herwin Mae M. BoclarasDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 IntroDokument1 Seite1 IntroDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Weirs for Measuring Flow RatesDokument14 SeitenTypes of Weirs for Measuring Flow RatesDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Project Discount Rates Based on RiskDokument9 SeitenDetermine Project Discount Rates Based on RiskDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MASAMADokument9 SeitenMASAMADanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Project Discount Rates Based on RiskDokument9 SeitenDetermine Project Discount Rates Based on RiskDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions For Homework Accounting 311 CostDokument128 SeitenSolutions For Homework Accounting 311 Costblack272727Noch keine Bewertungen
- English 8Dokument15 SeitenEnglish 8Danniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Models ASSIGNMENTDokument5 SeitenQuantitative Models ASSIGNMENTDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
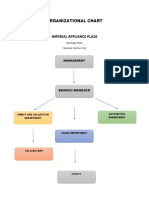
- Audit Flowchart and Org ChartDokument4 SeitenAudit Flowchart and Org ChartHerwin Mae Boclaras0% (1)
- English 8Dokument15 SeitenEnglish 8Danniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lay Outs BuildingDokument6 SeitenLay Outs BuildingDanniel Dizon Langga0% (1)
- The Balanced Scorecard Approach ExplainedDokument15 SeitenThe Balanced Scorecard Approach ExplainedSai KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Models ASSIGNMENTDokument5 SeitenQuantitative Models ASSIGNMENTDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Numerical DifferentiationDokument26 SeitenLecture 4 Numerical DifferentiationDanniel Dizon Langga100% (1)
- Data Structures Key to Organizing and Analyzing InformationDokument2 SeitenData Structures Key to Organizing and Analyzing InformationDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- James Building Wind Load AnalysisDokument7 SeitenJames Building Wind Load AnalysisJames HermoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imposition of A Specific TaxDokument2 SeitenImposition of A Specific TaxDanniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Term Planning Components 123Dokument15 SeitenLong Term Planning Components 123Danniel Dizon LanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Practices by KFCDokument17 SeitenPractices by KFCfariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HS AgroDokument42 SeitenHS AgroSHIVANSHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jio January Invoice Receipt-Arvind Kumar SharmaDokument4 SeitenJio January Invoice Receipt-Arvind Kumar SharmaArvind SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenText Vendor Invoice Management For SAP Solutions 7.5 SP4 - Administration Guide English (VIM070500-04-AGD-En-2)Dokument228 SeitenOpenText Vendor Invoice Management For SAP Solutions 7.5 SP4 - Administration Guide English (VIM070500-04-AGD-En-2)Goran Đurđić Đuka100% (3)
- International Financial Management Course OutlineDokument22 SeitenInternational Financial Management Course OutlineHOD MBA HOD MBANoch keine Bewertungen
- Extended Warranties-Scope As Insurance Under Indian Contract ActDokument4 SeitenExtended Warranties-Scope As Insurance Under Indian Contract ActPISAPATI VISHNUVARDHAN 1950221Noch keine Bewertungen
- RBM LFA Masyarakat KotaDokument18 SeitenRBM LFA Masyarakat KotaDeenar Tunas RancakNoch keine Bewertungen
- McKinsey 7s Framework Final (Draft 2)Dokument2 SeitenMcKinsey 7s Framework Final (Draft 2)Anshul Gautampurkar0% (1)
- Diagnostic Level 3 AccountingDokument17 SeitenDiagnostic Level 3 AccountingRobert CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google's Dominance and Continued Innovation in the Search Engine MarketDokument13 SeitenGoogle's Dominance and Continued Innovation in the Search Engine MarketMamta Singh RajpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ford Case StudyDokument2 SeitenFord Case StudyasrikalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ifrs 2: Share Based PaymentsDokument7 SeitenIfrs 2: Share Based PaymentsNomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Financial Management in Banking SectorDokument18 SeitenRole of Financial Management in Banking SectorAjit DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To Question Paper of TQM in MBA of Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University 2007Dokument5 SeitenAnswers To Question Paper of TQM in MBA of Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University 2007C P ChandrasekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breakfast is the Most Important Meal: Starting a Pancake House BusinessDokument28 SeitenBreakfast is the Most Important Meal: Starting a Pancake House BusinessChristian Lim100% (1)
- Case Study BookDokument106 SeitenCase Study BookshubhaomNoch keine Bewertungen
- # An - Je - 100k - 2-0 - 3-29-19 - v2Dokument5 Seiten# An - Je - 100k - 2-0 - 3-29-19 - v2Collblanc Seatours Srl Jose LahozNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM AssignmentDokument17 SeitenSM AssignmentElvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash PoolingDokument10 SeitenCash PoolingsavepageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Research Final PPT - OrangeDokument14 SeitenMarket Research Final PPT - OrangePrateek JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kavanagh4e PPT01Dokument24 SeitenKavanagh4e PPT01colin0% (1)
- Icaew Mi - WorkbookDokument452 SeitenIcaew Mi - WorkbookDương Ngọc100% (2)
- Assignment - Business Model Canvas Presentation - Fall - 2020Dokument2 SeitenAssignment - Business Model Canvas Presentation - Fall - 2020MattNoch keine Bewertungen
- The early days of risk management and derivatives marketsDokument8 SeitenThe early days of risk management and derivatives marketstuzemec19Noch keine Bewertungen
- EFFECTS OF ECONOMIC GROWTH AND GST RISEDokument41 SeitenEFFECTS OF ECONOMIC GROWTH AND GST RISESebastian ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Develop Business in Rural Areas With The Help of Digital PlatformsDokument30 SeitenDevelop Business in Rural Areas With The Help of Digital PlatformsMd Tasnim FerdousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tender Report For Construction Contracts - Designing BuildingsDokument5 SeitenTender Report For Construction Contracts - Designing BuildingsIsiaka Ozovehe SuleimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Banking Services in The Falkland IslandsDokument101 SeitenReview of Banking Services in The Falkland IslandsMercoPressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocean Carriers Assignment 1: Should Ms Linn purchase the $39M capsizeDokument6 SeitenOcean Carriers Assignment 1: Should Ms Linn purchase the $39M capsizeJayzie LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- COA 016 Audit Checklist For Coal Operation Health and Safety Management Systems PDFDokument43 SeitenCOA 016 Audit Checklist For Coal Operation Health and Safety Management Systems PDFMaia FitzgeraldNoch keine Bewertungen