Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
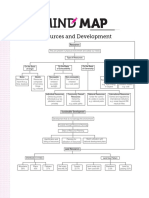
Mind Map
Hochgeladen von
Pramod JaiswalOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mind Map
Hochgeladen von
Pramod JaiswalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MIND
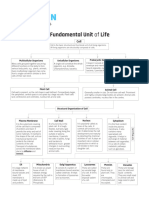
The Fundamental Unit of Life
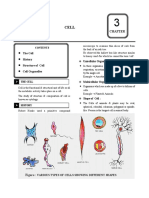
Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
All living organisms are structurally composed of cells.
Multicellular Organisms Unicellular Organisms Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell
Many cells group together and assume A single-cell constitutes the Nuclear envelope and Nucleus is well defined
different functions in the body to form whole organism, e.g. Amoeba, membrane-bound with nuclear envelope, and
various body parts, e.g. plants and Chlamydomonas and bacteria. organelles are absent, e.g. contains DNA in it, e.g.
animals. Every multicellular organism has bacteria and cyanobacteria. plant and animal cell.
come from a single cell which divides to
form many cells of its own kind.
Plant Cell Animal Cell
Cell wall is present, so the cell shape is well defined. Comparitively larger, Generally smaller in size. Do not have cell wall. Prominent
central space is occupied by a large vacuole. Plant cells lack centrosome and highly complex Golgi bodies are present. Animal cells
and centrioles and nucleus lies at one side of the cell. possess centrioles and nucleus lies in the centre.
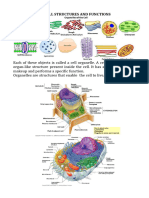
Structural Organisation of Cell
Plasma Membrane Cell Wall Nucleus Cytoplasm
It is the outermost covering It is found only in the It is popularly called as It is the fluid content
of the cell that is composed plant cell. It is tough, brain of the cells. It inside the plasma
Cell Organelles
of proteins and lipids. It non-living outer controls all functions of a membrane. It also
permits the entry and exit of covering lining the cell. It determines the cell contains many
some materials. It maintains outside of plasma development and maturity specialised cell
the shape of the cell, acts as membrane. It permits by directing the chemical organelles. It helps in
mechanical barrier and the cells of plants, fungi activities of cell. It plays an exchange of material
protects the internal and bacteria to important role in cellular between cell organelles.
contents of the cell. withstand much greater reproduction in which a It is a site of certain
Transport of substances changes in surrounding cell divides to form new metabolic pathways
across the membrane takes medium than the daughter cells. such as glycolysis.
place by diffusion or animal cells.
osmosis.
ER Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Plastids Vacuoles
It is large network They are known as It consists of a system of These are called These are These are storage
of membrane- power house of cell. It membrane-bound vesicles as suicidal bags found only in sacs for solid and
bound tubules and releases energy called cisternae. It helps of a cell. They plant cells. liquid contents.
sheets. ER required by the cell in in formation of lysosomes form the waste They are They are small sized
membrane is the form of ATP and in storing and disposal system chromoplast, in animal cells and
made up of lipids (Adenosine packging of various of a cell. chloroplast and large sized in plant
and proteins. Triphosphate). molecules in a cell. leucoplast. cells.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MindmapDokument1 SeiteMindmapSwapnil Tak25% (4)
- 12th Board Physics Paper July 21 2023Dokument8 Seiten12th Board Physics Paper July 21 2023Jibin star50% (2)
- ICSE Class 9 Biology Chapter 02 Cell The Unit of LifeDokument14 SeitenICSE Class 9 Biology Chapter 02 Cell The Unit of LifeTejas Singh Chaudhary100% (3)
- ICSE Class 10 Biology ProjectDokument38 SeitenICSE Class 10 Biology ProjectAbhisekh Razz Pandey100% (2)
- CLASS 9 SCIENCE HANDWRITTEN NOTES Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument30 SeitenCLASS 9 SCIENCE HANDWRITTEN NOTES Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Lifeaaravarora3010100% (1)
- Arihant History Class 12 Term 1 Sample PapersDokument189 SeitenArihant History Class 12 Term 1 Sample Papersavantika100% (2)
- Grade-9 Cbse Chapter-6 Plant TissuesDokument16 SeitenGrade-9 Cbse Chapter-6 Plant Tissuesniranjana75% (4)
- Revision-Map Chapter 5Dokument1 SeiteRevision-Map Chapter 5shinyy566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: by - NatalieDokument24 SeitenCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell PortfolioDokument7 SeitenCell PortfolioChhaya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CelsszDokument6 SeitenCelsszHITANSH NIJHAWANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Dokument21 SeitenAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONDokument48 SeitenThe Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONAlyssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDokument31 SeitenProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premidterms NotesDokument4 SeitenPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDokument28 SeitenAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology NotesDokument15 SeitenIGCSE Biology NotesMai YoussifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acp1 ActDokument6 SeitenAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell AnalogyDokument11 SeitenCell AnalogyMikaella Jayne CatanaoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDokument3 SeitenGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDokument19 SeitenLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Cell OrganellesDokument19 SeitenWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of Animal CellDokument27 SeitenParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Dokument14 SeitenDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology ReviewerDokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell and Cell Organelles 1Dokument4 SeitenThe Cell and Cell Organelles 1Wennie Fe MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Dokument34 SeitenCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DefinitionDokument14 SeitenCell DefinitionFarhan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26 03 2022 - 241421Dokument9 Seiten26 03 2022 - 241421Vedant SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio 2Dokument12 SeitenGen Bio 2Ma.Dulce ManalastasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal and Plant CellsDokument14 SeitenAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation - 1 RecapDokument15 SeitenFoundation - 1 RecapSonakshi ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany Full PDF EMDokument72 SeitenBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDokument6 SeitenCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Dokument3 SeitenAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e FunctionDokument14 Seiten2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e Functionwafa eliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Prelim NotesDokument47 SeitenBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableDokument5 SeitenWhat Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableChristopher BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Vocabulary: NameDokument3 SeitenCell Vocabulary: NameStephanie BannickNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDokument17 SeitenCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- Gen Bio Cell TypesDokument4 SeitenGen Bio Cell TypesRaeson Amir ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument23 SeitenCellridabatool151214Noch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument6 SeitenCellHONEYLYN CASINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11a Revision Pack T1Dokument36 Seiten11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDokument9 SeitenCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and FunctionDokument3 SeitenTerm 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and Functionprakashjoshi23aprilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Dokument11 SeitenInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology BasicsDokument23 SeitenCell Biology BasicsAbume DougyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDokument28 SeitenBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Cell VocabularyDokument3 SeitenCell Vocabularyapi-537617514Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Dokument5 SeitenCell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."shankaram shankaram100% (1)
- Found-1 Science NotesDokument15 SeitenFound-1 Science NotesSonakshi ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"Dokument12 SeitenBasic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"cbseiscNoch keine Bewertungen
- General BiologyDokument14 SeitenGeneral BiologyMason DeidriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and Functions of CellsDokument7 SeitenParts and Functions of CellsKate Aireen JerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are CellsHS PDFDokument12 SeitenWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument15 SeitenBiologyChit su su zawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal CellDokument23 SeitenPlant and Animal CellAnnisa Aulia100% (1)
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDokument8 SeitenCell - The Unit of Lifelpc4944Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- How To Convert Files To Binary FormatDokument1 SeiteHow To Convert Files To Binary FormatAhmed Riyadh100% (1)
- Not A Toy Sample PDFDokument37 SeitenNot A Toy Sample PDFMartha Paola CorralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Test Methods For Rheological Properties of Non-Newtonian Materials by Rotational (Brookfield Type) ViscometerDokument8 SeitenStandard Test Methods For Rheological Properties of Non-Newtonian Materials by Rotational (Brookfield Type) ViscometerRodrigo LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 788 ManualDokument16 Seiten788 Manualn0rdNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Iconic CPG Projects in SingaporeDokument2 SeitenList of Iconic CPG Projects in SingaporeKS LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Editan - Living English (CD Book)Dokument92 SeitenEditan - Living English (CD Book)M Luthfi Al QodryNoch keine Bewertungen
- SABRE MK-3 CFT Gel SpecDokument1 SeiteSABRE MK-3 CFT Gel Specseregio12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 19c Upgrade Oracle Database Manually From 12C To 19CDokument26 Seiten19c Upgrade Oracle Database Manually From 12C To 19Cjanmarkowski23Noch keine Bewertungen
- List of Some Common Surgical TermsDokument5 SeitenList of Some Common Surgical TermsShakil MahmodNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALE Manual For LaserScope Arc Lamp Power SupplyDokument34 SeitenALE Manual For LaserScope Arc Lamp Power SupplyKen DizzeruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item Analysis and Test BankingDokument23 SeitenItem Analysis and Test BankingElenita-lani Aguinaldo PastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTDokument42 SeitenFeasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTMyself IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implications of A Distributed Environment Part 2Dokument38 SeitenImplications of A Distributed Environment Part 2Joel wakhunguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frellwits Swedish Hosts FileDokument10 SeitenFrellwits Swedish Hosts FileAnonymous DsGzm0hQf5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Switching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Dokument3 SeitenSwitching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Jerry Fourier KemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative Network Letter Vol 7 No.1-Apr 1991-EQUATIONSDokument16 SeitenAlternative Network Letter Vol 7 No.1-Apr 1991-EQUATIONSEquitable Tourism Options (EQUATIONS)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Communications 05sept2023Dokument14 SeitenImportance of Communications 05sept2023Sajib BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosharaf HossainDokument2 SeitenMosharaf HossainRuhul RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Econometrics Questions and AnswersDokument3 SeitenBasic Econometrics Questions and AnswersRutendo TarabukuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction - Livspace - RenoDokument12 SeitenIntroduction - Livspace - RenoMêghnâ BîswâsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Modified Front Double Wishbone Suspension For A Three Wheel Hybrid VehicleDokument4 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Modified Front Double Wishbone Suspension For A Three Wheel Hybrid VehicleRima AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Dokument10 SeitenRoxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Rachele DolleteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ring and Johnson CounterDokument5 SeitenRing and Johnson CounterkrsekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNCITRAL Guide United Nations Commission On International Trade LawDokument56 SeitenUNCITRAL Guide United Nations Commission On International Trade Lawsabiont100% (2)
- Owners Manual Air Bike Unlimited Mag 402013Dokument28 SeitenOwners Manual Air Bike Unlimited Mag 402013David ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satish Gujral - FinalDokument23 SeitenSatish Gujral - Finalsatya madhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CiscoDokument6 SeitenCiscoNatalia Kogan0% (2)
- C4 Vectors - Vector Lines PDFDokument33 SeitenC4 Vectors - Vector Lines PDFMohsin NaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asterisk NowDokument82 SeitenAsterisk Nowkambojk100% (1)
- Exotic DVM 11 3 CompleteDokument12 SeitenExotic DVM 11 3 CompleteLuc CardNoch keine Bewertungen