Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mdm4u Fianl Exam Formula PDF
Hochgeladen von
Eliz SawOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mdm4u Fianl Exam Formula PDF
Hochgeladen von
Eliz SawCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
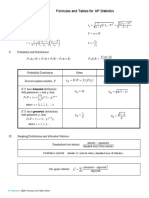
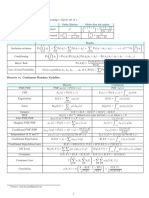
FORMULA SHEET
Central Angle = percent of the
population x 360º Factorial Notation: n! = n(n – 1)(n –
2)… (3)(2)(1)
n!
Permutations: P (n, r ) =
Sampling Interval = population size (n − r )!
sample size
Permutations with a, b, and c, Like
n!
range Objects =
a!b!c!
Bin Width = number of int ervals
n
xi n!
Mean: x = i =1 Combinations: C (n, r ) =
n r!(n − r )!
n
xi wi Odds in Favour of A : P( A) :1 − P( A)
Weighted mean: x = i =1
n
wi Expected Value of a Discrete Random
i =1 variable
Standard Deviation, (ungrouped data): n
n E ( x) = xi P ( X = xi )
(xi − x )2 i =1
σ= i =1
n n n n +1
Pascal’s Identity: + =
r r +1 r +1
Standard Deviation, (grouped data):
n
Binomial Probability Distribution:
f i ( xi − x )
2
n
σ= i =1
P( X = k ) = ( p )k (1 − q) n−k
n k
x−x Expected Value of Binomial Expansion:
Z-score: z = E(x) = np
σ
Experimental Probability: Normal Approximation of a Binomial
number of times the desired event occured Probability Distribution:
P( A) = x = np σ = np (1 − p )
number of trials
Hypergeometric Probabilty Distribution:
Theoretical Probability a b
n( A) k n−k
P( A) = Answer: P ( X = k ) =
n( S ) a+b
n
Probability of complimentary event:
P ( A′) = 1 − P ( A) where there are a elements of one type, b
elements of a second type, and we want
Additive Principle for the union of two to choose k of the first type from a draw
sets: of n.
n( A ∪ B ) = n( A) + n( B ) − n( A ∩ B )
P ( A ∪ B ) = P ( A) + P ( B ) − P ( A ∩ B ) Expected Value of Binomial Expansion:
na
E ( x) =
Conditional Probability: a+b
P( A ∩ B )
P ( B A) =
P( A)
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1
1 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1
1 9 36 84 126 126 84 36 9
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Exam Review 2 Q & A SamDokument5 SeitenExam Review 2 Q & A SamVishal Ponugoti0% (1)
- MDM4U Culminating Project RequirementsDokument2 SeitenMDM4U Culminating Project RequirementsAL Rajhi ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.2 Quiz SolutionsDokument1 Seite9.2 Quiz SolutionspicklebeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mdm4u Final ReviewsolutionDokument7 SeitenMdm4u Final Reviewsolutionchristian ursaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Els 2012Dokument124 SeitenCatalogo Els 2012prueba755Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reteach6 PDFDokument97 SeitenReteach6 PDFEryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Research Methods FinalDokument171 SeitenQualitative Research Methods Finaljennifer blackburnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Probability Practice TestDokument2 SeitenGrade 12 Probability Practice TestJonathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mdm4u Q7Dokument1 SeiteMdm4u Q7bigDinc100% (1)
- Materials SB: N) K X XDokument11 SeitenMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenFormula SheetJane Chun100% (1)
- Fe Engineering Probability StatisticsDokument9 SeitenFe Engineering Probability Statisticsvzimak2355Noch keine Bewertungen
- Helpful Formulas PDFDokument1 SeiteHelpful Formulas PDFziyingkangNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Statistics - Formulas and TablesDokument6 SeitenAP Statistics - Formulas and TablesJinhui ZhengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Formula SheetDokument3 SeitenMidterm Formula SheetShahd AlhamaydaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenFormula SheetSwarnabha RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- StatisticssheetDokument6 SeitenStatisticssheetmohNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PDokument2 SeitenAP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PRocket FireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics SymbolsDokument7 SeitenStatistics Symbolsapi-3857574100% (4)
- A 18-Page Statistics & Data Science Cheat SheetsDokument18 SeitenA 18-Page Statistics & Data Science Cheat SheetsAniket AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat SheetDokument7 SeitenCheat SheetChristos StiapisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook StatDokument2 SeitenHandbook Statmytu261105Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formulario Certamen 1Dokument2 SeitenFormulario Certamen 1Ignacia OlivaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Table CardDokument8 SeitenFormula Table Cardasif taj100% (1)
- AP Stat Free Response QuestionsDokument22 SeitenAP Stat Free Response QuestionsLOUELLA JADE SUAREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- σ p q ≤ n k x a n k p q np (1−p) : ĐÀO QUỐC THÁI - SE1508 - HE150059Dokument2 Seitenσ p q ≤ n k x a n k p q np (1−p) : ĐÀO QUỐC THÁI - SE1508 - HE150059Quốc Thái ĐàoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 1ching chauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulae SheetDokument11 SeitenFormulae Sheetthyanh.vuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2a 4 Ac B 4a: Quadratic Solution: VertexDokument5 Seiten2a 4 Ac B 4a: Quadratic Solution: VertexCheng Win-YarnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet STAT 2066Dokument4 SeitenFormula Sheet STAT 2066Shane TeddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap23 FRQ Statistics - Pdf#page 16Dokument25 SeitenAp23 FRQ Statistics - Pdf#page 16malvin.fedyanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityDokument2 SeitenAP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityKent BrouwerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics Formula Sheet and Tables 2020Dokument6 SeitenStatistics Formula Sheet and Tables 2020HafizNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAT202-homework2 HW21Dokument2 SeitenSTAT202-homework2 HW21Bao GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics Formula Sheet and Tables 2020Dokument6 SeitenStatistics Formula Sheet and Tables 2020bella lubbockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula PDFDokument3 SeitenFormula PDFWong Kai YiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SDokument2 SeitenLinear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SmichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stats Cheatsheet FinalDokument2 SeitenStats Cheatsheet FinalThulasi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat & Prob Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenStat & Prob Formula SheetBose Chan100% (1)
- Materials SB: 1+3.3log Log (N)Dokument10 SeitenMaterials SB: 1+3.3log Log (N)Tống DuyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1673852881544Dokument2 Seiten1673852881544Mohd. RahilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Formula Sheet: StatisticsDokument10 SeitenEngineering Formula Sheet: StatisticsManikandan SelvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Statistics Formulas and TablesDokument10 SeitenIntroductory Statistics Formulas and TablesP KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulario GEIDokument3 SeitenFormulario GEISergio Reinoso FuertesNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMOmath - Applications of CalculusDokument4 SeitenIMOmath - Applications of CalculusThang ThangNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMOmath - Applications of CalculusDokument4 SeitenIMOmath - Applications of CalculusThang ThangNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Erie de Fourier Da Sen Oide Retificada em Meia-OndaDokument3 SeitenS Erie de Fourier Da Sen Oide Retificada em Meia-OndaAndrei HolandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equation SheetDokument5 SeitenEquation SheetArisha BasheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet MDM4UDokument1 SeiteFormula Sheet MDM4UbigDinc100% (1)
- Stat 2500 Fomula Sheet For Final ExamDokument1 SeiteStat 2500 Fomula Sheet For Final Examamaka.iwu10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Probability NotesDokument2 SeitenApplied Probability NotesKalaivaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLTW Engineering Formula SheetsDokument5 SeitenPLTW Engineering Formula SheetsHugo BrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet STAT1301Dokument3 SeitenFormula Sheet STAT1301janeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula SheetDokument4 SeitenFormula SheetVien LaCroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mscds2022 SolutionsDokument23 SeitenMscds2022 SolutionsMohammad Faiz HashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- P (B !A) P (B) P (A!B) P (B) P (A!B) : 1 F (X) (X) DXDokument2 SeitenP (B !A) P (B) P (A!B) P (B) P (A!B) : 1 F (X) (X) DXFrancisco Javier Colli PintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics FormulasDokument2 SeitenStatistics FormulasJayson S. Verdeflor100% (1)
- (Last-Exercise) Lê Đ C Dũng - 2212340017Dokument4 Seiten(Last-Exercise) Lê Đ C Dũng - 2212340017Dung LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of FormulasDokument7 SeitenList of Formulastimeijkhout92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stat110 Cheatsheet PDFDokument2 SeitenStat110 Cheatsheet PDFMaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workplace EquipDokument34 SeitenWorkplace EquipEliz SawNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Adjustment Process: Prepaid. Unearned RevenueDokument10 SeitenThe Adjustment Process: Prepaid. Unearned RevenueEliz Saw0% (1)
- Part A: Readings: Eng4U Lee Tze Saw Module 4 Act 3Dokument3 SeitenPart A: Readings: Eng4U Lee Tze Saw Module 4 Act 3Eliz SawNoch keine Bewertungen
- m2 Act 5 Baf3mDokument2 Seitenm2 Act 5 Baf3mEliz SawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mdm4U Lee Tze Saw MODULE 1 Act 2Dokument2 SeitenMdm4U Lee Tze Saw MODULE 1 Act 2Eliz SawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lee Tze Saw Olc4O Module 3 Act 6: Global IssueDokument3 SeitenLee Tze Saw Olc4O Module 3 Act 6: Global IssueEliz SawNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - Playing With NumbersDokument20 Seiten01 - Playing With Numbersajay3518Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wardova Metoda Od WardaDokument10 SeitenWardova Metoda Od WardaStarý DonorNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathDokument3 SeitenMathBerlyn D. AlmandaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3Dokument15 SeitenModule 3Ann BombitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverse and Also Relations Questions PDFDokument3 SeitenInverse and Also Relations Questions PDFLiu FaYingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 13-Compass and Transit RuleDokument4 SeitenModule 13-Compass and Transit RuleGerovic ParinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Equations (MA 1150) : SukumarDokument42 SeitenDifferential Equations (MA 1150) : SukumarMansi NanavatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 ADP Nonlinear System Mismatched Disterbances 2Dokument8 Seiten2020 ADP Nonlinear System Mismatched Disterbances 2Khải VũNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan DivisionDokument12 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan DivisionDarlin Shane SanguirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Hazard AnalysisDokument103 SeitenSeismic Hazard AnalysisJohn MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math10.C5L2 - Multiplication and Addition PrinciplesDokument19 SeitenMath10.C5L2 - Multiplication and Addition PrinciplesmiggyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Code Check Theory EnuDokument117 SeitenConcrete Code Check Theory EnuNaida AdemovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors - 2D and 3D VectorsDokument50 SeitenVectors - 2D and 3D VectorsPo ToNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Image Noises Algorithms Explained and Manually ImplementationDokument5 SeitenMatlab Image Noises Algorithms Explained and Manually ImplementationSufiyan Ghori100% (8)
- Mathsprogint Y8a WBDokument27 SeitenMathsprogint Y8a WBTeacher Nwe NweNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - Mathematics 5Dokument9 SeitenDLL - Mathematics 5Donald Dann BuhayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 5.1bDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 5.1bNadia ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH1 Class 8 Foundation Cbse PDFDokument16 SeitenCH1 Class 8 Foundation Cbse PDFTechnical AkshayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refiners High School: MathematicsDokument5 SeitenRefiners High School: MathematicsGabriel OnalekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction Paper 2 0580 May 2024Dokument11 SeitenPrediction Paper 2 0580 May 2024minati0830100% (5)
- List of Books - PDFDokument335 SeitenList of Books - PDFLokendra Sahu100% (1)
- Brief Borwein IntegralsDokument11 SeitenBrief Borwein IntegralsTune LisNoch keine Bewertungen
- IA Notes Session 1Dokument29 SeitenIA Notes Session 1asalifew belachewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mood and Figure of SyllogismDokument9 SeitenMood and Figure of SyllogismwasimedupkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee 326 Lecture Notes 1Dokument38 SeitenEee 326 Lecture Notes 1Barış DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 5 Stat Inf b3 2022 2023 PDFDokument16 SeitenAssignment 5 Stat Inf b3 2022 2023 PDFMrinmoy BanikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metaheuristic Optimization: Algorithm Analysis and Open ProblemsDokument12 SeitenMetaheuristic Optimization: Algorithm Analysis and Open ProblemsOlivia brianneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zlib - Pub Computational InteractionDokument433 SeitenZlib - Pub Computational InteractionASDSADNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 16 Markov AnalysisDokument37 SeitenCH 16 Markov AnalysisRia Rahma PuspitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics IDokument5 SeitenEngineering Mathematics IAditya RaoNoch keine Bewertungen