Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A2 Edexcel and Cambridge Lecture Plan - Teacher's Material
Hochgeladen von
Milka Rahman0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten2 Seitenlecture plan
Originaltitel
A2 Edexcel and Cambridge Lecture Plan _ Teacher's Material
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenlecture plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten2 SeitenA2 Edexcel and Cambridge Lecture Plan - Teacher's Material
Hochgeladen von
Milka Rahmanlecture plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Introduction to Edexcel IAL Curriculum for Unit 4.
understand the overall reaction of photosynthesis as requiring energy from light
5.1 to split apart the strong bonds in water molecules, storing the hydrogen in a fuel
(glucose) by combining it with carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen into the
atmosphere
5.2 understand how photophosphorylation of ADP requires energy and that hydrolysis
of ATP provides an immediate supply of energy for biological processes
a) explain that energy transferred as ATP and reduced NADP from the light dependent stage
is used during the light independent stage (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis to produce
complex organic molecules
b) state the sites of the light dependent and the light independent stages in the chloroplast
5.3 understand the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, including how light
energy is trapped by exciting electrons in chlorophyll and the role of these
electrons in generating ATP, reducing NADP in cyclic and non-cyclic
photophosphorylation and producing oxygen through photolysis of water
f) describe the light dependent stage as the photoactivation of chlorophyll
resulting in the photolysis of water and the transfer of energy to ATP and
reduced NADP (cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation should be described
in outline only)
5.4 (i) understand the light-independent reactions as reduction of carbon dioxide
using the products of the light-dependent reactions (carbon fixation in the Calvin
cycle, the role of GP, GALP, RuBP and RUBISCO)
(ii) know that the products are simple sugars that are used by plants, animals and
other organisms in respiration and the synthesis of new biological molecules
(polysaccharides, amino acids, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids)
g) outline the three main stages of the Calvin cycle:
• fixation by rubisco of carbon dioxide by combination with ribulose bisphosphate
(RuBP), a 5C compound, to yield two molecules of GP (PGA), a 3C compound
• the reduction of GP to triose phosphate (TP) involving ATP and reduced NADP
• the regeneration of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) using ATP
h) describe, in outline, the conversion of Calvin cycle intermediates to
carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids and their uses in the plant cell
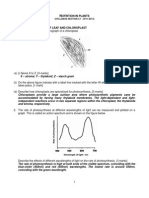
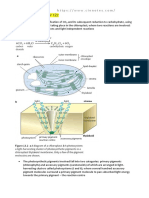
5.5 understand the structure of chloroplasts in relation to their role in photosynthesis
c) describe the role of chloroplast pigments (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene
and xanthophyll) in light absorption in the grana
5.6 understand what is meant by the terms absorption spectrum and action spectrum
d) interpret absorption and action spectra of chloroplast pigments
5.7 understand that chloroplast pigments can be separated using chromatography
and the pigments identified using Rf values
e) use chromatography to separate and identify chloroplast pigments and carry
out an investigation to compare the chloroplast pigments in different plants
(reference should be made to Rf values in identification)
13.2 Investigation of limiting a) explain the term limiting factor in relation to
factors photosynthesis
Environmental factors b) explain the effects of changes in light intensity, carbon
influence the rate of dioxide concentration and temperature on the rate of
photosynthesis. Investigating photosynthesis
these shows how they can
be managed in protected c) explain how an understanding of limiting factors is
environments used in crop used to increase crop yields in protected environments,
production. such as glasshouses
d) carry out an investigation to determine the effect of
light intensity or light wavelength on the rate of
photosynthesis using a redox indicator (e.g. DCPIP) and
a suspension of chloroplasts (the Hill reaction)
e) carry out investigations on the effects of light
intensity, carbon dioxide and temperature on the rate of
photosynthesis using whole plants, e.g. aquatic plants
such as Elodea and Cabomba
13.3 Adaptations for a) describe the relationship between structure and
photosynthesis function in the chloroplast using diagrams and electron
micrographs
All the stages of
photosynthesis occur in the b) explain how the anatomy and physiology of the leaves
chloroplast. Some tropical of C4 plants, such as maize or sorghum, are adapted for
crops have C4 metabolism high rates of carbon fixation at high temperatures in
and adaptations to maximise terms of:
carbon dioxide fixation. • the spatial separation of initial carbon fixation
from the light dependent stage (biochemical
details of the C4 pathway are required in outline
only)
the high optimum temperatures of the enzymes
involved
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ExpProInNeu (Ne PDFDokument299 SeitenExpProInNeu (Ne PDFanurag_kapila3901100% (1)
- AP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Dokument5 SeitenAP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Jakie Ubina0% (1)
- Mark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Pogil Track D - 5261224Dokument11 SeitenMark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Pogil Track D - 5261224api-544304176Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Photosynthesis and Respiration Revision Tutorial AnsDokument18 Seiten2015 Photosynthesis and Respiration Revision Tutorial Ansliveaq100% (1)
- The Global Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Scaling Ecological Energetics from Organism to the BiosphereVon EverandThe Global Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Scaling Ecological Energetics from Organism to the BiosphereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsDokument7 SeitenKami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsMaxwell Modeste0% (2)
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDokument17 SeitenPHOTOSYNTHESISDave Degaetano100% (3)
- 23 Cytogenetics 2 177 PDFDokument176 Seiten23 Cytogenetics 2 177 PDFfabilleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell CycleDokument2 SeitenDisorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell CycleAmelyn Lingbawan100% (2)
- Cell Cycle VocabularyDokument3 SeitenCell Cycle Vocabularyapi-328162824Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wednesday 20 January 2021: BiologyDokument40 SeitenWednesday 20 January 2021: BiologyMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wednesday 20 January 2021: BiologyDokument40 SeitenWednesday 20 January 2021: BiologyMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function of PhotosynthesisDokument58 SeitenFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Quiz MR ADokument4 SeitenPhotosynthesis Quiz MR Aapi-353447897100% (1)
- A Study Into The Cultivation of Algae - 2008Dokument71 SeitenA Study Into The Cultivation of Algae - 2008PatchworkFishNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET Biology Chapter Wise Mock Test - Biotechnology Principles and Its Applications - CBSE TutsDokument20 SeitenNEET Biology Chapter Wise Mock Test - Biotechnology Principles and Its Applications - CBSE Tutssreenandhan 2017Noch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Biology Past Year QuestionDokument8 SeitenSTPM Biology Past Year QuestionMc Donalds Ohl Ohlsen100% (2)
- Chapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PDokument7 SeitenChapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PShaira CogollodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review 3: Metabolism Unit - Respiration & Photosynthesis A. Top "10" - If You Learned Anything From This Unit, You Should Have LearnedDokument6 SeitenReview 3: Metabolism Unit - Respiration & Photosynthesis A. Top "10" - If You Learned Anything From This Unit, You Should Have LearnedNguyen Thi Thien MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis ACEDokument7 SeitenPhotosynthesis ACEZhiTing96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cuestionario Fisiotecnia en InglésDokument4 SeitenCuestionario Fisiotecnia en InglésMokr Guerrero EsperanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Notes For AGRO 102Dokument17 SeitenPhotosynthesis Notes For AGRO 102Misheck Chandiposha100% (1)
- Herculanum (Psicografia Wera Krijanowskaia - Espirito J. W. Rochester)Dokument52 SeitenHerculanum (Psicografia Wera Krijanowskaia - Espirito J. W. Rochester)Alexsandro ClaudinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology The Dynamic Science 4th Edition Russell Solutions Manual 1Dokument10 SeitenBiology The Dynamic Science 4th Edition Russell Solutions Manual 1matthew100% (30)
- Biology The Dynamic Science 4Th Edition Russell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument31 SeitenBiology The Dynamic Science 4Th Edition Russell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjason.collins370100% (14)
- CRPSCI 1100-Module5Dokument14 SeitenCRPSCI 1100-Module5carbonel.carlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pocket Biology, Card-1, Topic-5 (A2)Dokument2 SeitenPocket Biology, Card-1, Topic-5 (A2)Munavi ZamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- APBioCh10ReadingGuide10 11Dokument2 SeitenAPBioCh10ReadingGuide10 11Sergio LivingroomsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRespiration and Photosynthesis Review KeyDokument5 SeitenCRespiration and Photosynthesis Review Keyvictoire BadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPE Biology Unit 2 SyllabusDokument20 SeitenCAPE Biology Unit 2 Syllabussmithsashay74Noch keine Bewertungen
- CAPE Biology Syllabus With Specimen Papers - Split - 1Dokument5 SeitenCAPE Biology Syllabus With Specimen Papers - Split - 1Enz JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis (KEY)Dokument6 SeitenPhotosynthesis (KEY)kylevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fotosintesis PDFDokument6 SeitenFotosintesis PDFNorma YantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FotosintesisDokument6 SeitenFotosintesisNorma YantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiatomeasDokument17 SeitenDiatomeasbrandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Dokument6 SeitenAP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Gunnar OlsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Photosynthetic Response of The Microalga Scenedesmus Obtusiusculus To Light Intensity Perturbations (Cabello Et Al)Dokument8 SeitenDynamic Photosynthetic Response of The Microalga Scenedesmus Obtusiusculus To Light Intensity Perturbations (Cabello Et Al)Aline DassolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light-Independent Reactions: Water PhotolysisDokument5 SeitenLight-Independent Reactions: Water PhotolysisDharmendra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch. 8 Photosynthesis F17Dokument70 SeitenCh. 8 Photosynthesis F17bae loonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Reaction Center of Green Sulfur Bacteria: ReviewDokument18 SeitenThe Reaction Center of Green Sulfur Bacteria: ReviewMoisés ChávezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis 9700 CieDokument8 SeitenPhotosynthesis 9700 CietrinhcloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 El-Hendawy - Variation in The FTIR Spectra of A Biomass Under ImpregnationDokument8 Seiten2006 El-Hendawy - Variation in The FTIR Spectra of A Biomass Under ImpregnationHeri RustamajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Dokument5 SeitenDivision of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Jeston Mar BayogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis EllaDokument42 SeitenPhotosynthesis EllaElla AgyeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fotosintesis en Especies C4 No TipicasDokument31 SeitenFotosintesis en Especies C4 No TipicasFelipe MontejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 11 ch11 Class 11Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet 11 ch11 Class 11akilapaul17682Noch keine Bewertungen
- s10863 014 9545 0Dokument7 Seitens10863 014 9545 0Pablo PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-13: Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDokument8 SeitenChapter-13: Photosynthesis in Higher PlantssujushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulgaris Buitenzorg in Bubble Column PhotobioreactorDokument9 SeitenVulgaris Buitenzorg in Bubble Column PhotobioreactorRahmatika YaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis by Isolated ChloroplastsDokument9 SeitenPhotosynthesis by Isolated ChloroplastsFernando JarixNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7745 PDFDokument12 Seiten7745 PDFDiogomussumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors: C3: C4 Photosynthesis ResearchDokument4 SeitenFactors: C3: C4 Photosynthesis ResearchDharmendra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sbi 4u1photosynthesis Quiz2009Dokument4 SeitenSbi 4u1photosynthesis Quiz2009api-270880889Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4.applied Catalysis BDokument8 Seiten4.applied Catalysis BCristianAtanasiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Worksheet Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: StatementsDokument3 SeitenRevision Worksheet Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: StatementsKrishna Nilesh Lodhia G 11Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Shemesh JPCA Cyclohexanone PhotolysisDokument9 Seiten2016 Shemesh JPCA Cyclohexanone Photolysisdragon_hsome94Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Important Questions 2022-23Dokument13 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Important Questions 2022-23tytytfbfvhbvb dhbvNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology Chapter 10 Notes - PhotosynthesisDokument5 SeitenAP Biology Chapter 10 Notes - PhotosynthesisAustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 GiebelDokument17 Seiten3 GiebelfdfsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Requirement and Inhibition of C Photosynthesis: An Analysis of C Plants Deficient in The C and C CyclesDokument10 SeitenOxygen Requirement and Inhibition of C Photosynthesis: An Analysis of C Plants Deficient in The C and C CyclesjpmarocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity10answers PDFDokument6 SeitenActivity10answers PDFMuthu LakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Photosynthesis in and C4 Plants: A Molecular AppmachDokument11 SeitenRegulation of Photosynthesis in and C4 Plants: A Molecular AppmachM. Riyo Rizki RidwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 1 3 2025 Topic Test MsDokument5 SeitenC 1 3 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ba Sumata Ry 2015Dokument11 SeitenBa Sumata Ry 2015Xuân Sơn PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosyntesis Worksheet 3Dokument5 SeitenPhotosyntesis Worksheet 3Ryan De AlloNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUSY - Marcilla (2009) - Thermal and Catalytic Pyrolysis of Polyethylene Over HZSM5 and HUSY ZeolitesDokument9 SeitenHUSY - Marcilla (2009) - Thermal and Catalytic Pyrolysis of Polyethylene Over HZSM5 and HUSY ZeolitesKatiane MesquitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diurnal Photodegradation of Fluorinated Diketones (FDKS) by OH RadicalsDokument9 SeitenDiurnal Photodegradation of Fluorinated Diketones (FDKS) by OH RadicalsÁlvaro Gómez DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress in Phytochemistry: Volume 6Von EverandProgress in Phytochemistry: Volume 6L. ReinholdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Groundwater Remediation: A Practical Guide for Environmental Engineers and ScientistsVon EverandGroundwater Remediation: A Practical Guide for Environmental Engineers and ScientistsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2021Dokument25 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2021Milka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2021Dokument13 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2021Milka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 2021 Unit 4Dokument30 SeitenJanuary 2021 Unit 4mufrad muhtasibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jan21 (4) NewDokument32 SeitenJan21 (4) NewMonkey Lover0% (1)
- Friday 22 January 2021: BiologyDokument24 SeitenFriday 22 January 2021: BiologyMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meiosis: Milka Rahman Sr. Biology Instructor MastermindDokument47 SeitenMeiosis: Milka Rahman Sr. Biology Instructor MastermindMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS and A Level Biology B Core Practical 4 - Pollen Tube Growth (Student, Teacher, Technician Worksheets)Dokument7 SeitenAS and A Level Biology B Core Practical 4 - Pollen Tube Growth (Student, Teacher, Technician Worksheets)Md A RAZZAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4BI1 1BR Que 20201107Dokument24 Seiten4BI1 1BR Que 20201107Adeeba iqbal100% (5)
- Mark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRDokument16 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monday 1 June 2020: BiologyDokument20 SeitenMonday 1 June 2020: BiologyAdeeba iqbal100% (2)
- Mark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 1BRDokument24 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 1BRLittle WizardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monday 1 June 2020: BiologyDokument16 SeitenMonday 1 June 2020: BiologyAdeeba iqbal0% (2)
- Mark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BDokument19 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BLittle WizardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Igcse Jan 2020 MarkschemeDokument16 SeitenEdexcel Igcse Jan 2020 MarkschemeRose67% (3)
- 4BI1 1B Que 20201107Dokument28 Seiten4BI1 1B Que 20201107Adeeba iqbal78% (9)
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRDokument16 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRMilka Rahman100% (1)
- Tuesday 14 January 2020: BiologyDokument20 SeitenTuesday 14 January 2020: BiologyMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Ial Biology Jan 2020 Paper 1 MarkschemeDokument32 SeitenEdexcel Ial Biology Jan 2020 Paper 1 MarkschemeRose100% (2)
- Mark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 1BDokument25 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) November 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 1BLittle Wizard50% (2)
- Tuesday 14 January 2020: BiologyDokument24 SeitenTuesday 14 January 2020: Biologysham80% (5)
- Edexcel Igcse Jan 2020 MarkschemeDokument16 SeitenEdexcel Igcse Jan 2020 MarkschemeRose67% (3)
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRDokument16 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRMilka Rahman100% (1)
- 2020 Jan IGCSE Biology Paper 1BRDokument32 Seiten2020 Jan IGCSE Biology Paper 1BRNewtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2021Dokument25 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2021Milka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2021Dokument13 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2021Milka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 1BRDokument24 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 1BRMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friday 22 January 2021: BiologyDokument24 SeitenFriday 22 January 2021: BiologyMilka RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 2021 Unit 4Dokument30 SeitenJanuary 2021 Unit 4mufrad muhtasibNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC 2 Lab LU1. Introduction To EnzymologyDokument13 SeitenCC 2 Lab LU1. Introduction To EnzymologySophia Gail ChingNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeneticEngineering GizmoDokument4 SeitenGeneticEngineering GizmokallenbachcarterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Lab 6 GeneticsDokument10 Seiten2021 Lab 6 GeneticsGurleen KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Southern BlottingDokument5 SeitenSouthern BlottingSaba IkhlaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Bio DrawingsDokument2 SeitenIb Bio Drawings202484Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecure-5 The Origin of Biopotentials - 2Dokument34 SeitenLecure-5 The Origin of Biopotentials - 2Noor Ahmed100% (1)
- Long Test As Level Nucleic AcidDokument9 SeitenLong Test As Level Nucleic AcidPrisky Jofan SimbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHapter 14Dokument10 SeitenCHapter 14alaskamofoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of DNA Presentation in Colorful Retro Illustrative StyleDokument51 SeitenStructure and Function of DNA Presentation in Colorful Retro Illustrative Stylekimmymantos022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amboss - Enzymes and BiocatalysisDokument10 SeitenAmboss - Enzymes and BiocatalysisAllysahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crispr Poster 2021Dokument4 SeitenCrispr Poster 2021api-522847737Noch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewCorman Drosten Paper Final Version 10-3-Public FinalDokument30 SeitenReviewCorman Drosten Paper Final Version 10-3-Public Finalvigilancio153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorrhagic Disorders and Laboratory Assessment Part 2 - Study Guide With BlanksDokument7 SeitenHemorrhagic Disorders and Laboratory Assessment Part 2 - Study Guide With BlanksFaye AlmiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AGR514 Chapter 3Dokument60 SeitenAGR514 Chapter 3Muhamad Afif Abdul FatahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular and CellularDokument10 SeitenMolecular and CellularBAUTISTA TERRONES GILMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Cure of Hiv Using Crispr - Adlene Jenitta, Vikrant Thokchom, W. Jasmine Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, CoimbatoreDokument2 SeitenFunctional Cure of Hiv Using Crispr - Adlene Jenitta, Vikrant Thokchom, W. Jasmine Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, CoimbatoreRaj WillseeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Southern BlottingDokument4 SeitenSouthern Blottingumarlucky1819Noch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary Structure PredictionDokument43 SeitenSecondary Structure PredictionPallavi RamaswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fu2020 Article ExpressionsAndSignificancesOfTDokument10 SeitenFu2020 Article ExpressionsAndSignificancesOfTJosie ResendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROBLEM SETS For 7th Edition of Lehninger Chapter 10 17 21 23 MJ KrisingerDokument5 SeitenPROBLEM SETS For 7th Edition of Lehninger Chapter 10 17 21 23 MJ KrisingerMattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDokument4 SeitenBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carrier-Mediated Transport MechanismsDokument3 SeitenCarrier-Mediated Transport MechanismsShianne RacadioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease MarkersDokument91 SeitenDisease MarkersAlbertina MontenegroNoch keine Bewertungen