Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Primarysciencefpd
Hochgeladen von
api-399021565Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Primarysciencefpd
Hochgeladen von
api-399021565Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Primary Science FPD
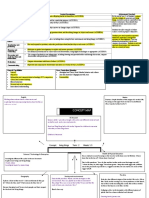
Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 5)
Sub-strands Content Descriptions Achievement Standard
Biological Living things have structural features and adaptations that help them to survive in By the end of Year 5,
sciences their environment (ACSSU043) students classify substances
according to their observable
Chemical Solids, liquids and gases have different observable properties and behave in properties and behaviours.
sciences different ways (ACSSU077)
They explain everyday
phenomena associated with
Earth and The Earth is part of a system of planets orbiting around a star (the sun)
(ACSSU078) the transfer of light. They
space sciences describe the key features of
Light from a source forms shadows and can be absorbed, reflected and refracted our solar system. They
Physical analyse how the form of
sciences (ACSSU080)
living things enables them to
Nature and Science involves testing predictions by gathering data and using evidence to function in their
development of develop explanations of events and phenomena environments. Students
science Important contributions to the advancement of science have been made by people from a discuss how scientific
range of cultures (ACSHE081) developments have affected
people’s lives and how
Use and Scientific understandings, discoveries and inventions are used to solve problems science knowledge develops
influence of that directly affect peoples’ lives (ACSHE083) from many people’s
science Scientific knowledge is used to inform personal and community decisions (ACSHE217) contributions.
Students follow instructions
to pose questions for
Questioning With guidance, pose questions to clarify practical problems or inform a scientific investigation, predict what
and predicting investigation, and predict what the findings of an investigation might be might happen when variables
(ACSIS231)
Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 5)
Sub-strands Content Descriptions Achievement Standard
Planning and With guidance, plan appropriate investigation methods to answer questions or are changed, and plan
conducting solve problems (ACSIS086) investigation methods. They
Decide which variable should be changed and measured in fair tests and accurately use equipment in ways that
observe, measure and record data, using digital technologies as appropriate are safe and improve the
(ACSIS087) accuracy of their
Use equipment and materials safely, identifying potential risks (ACSIS088) observations. Students
Processing and Construct and use a range of representations, including tables and graphs, to construct tables and graphs to
analysing data represent and describe observations, patterns or relationships in data using digital organise data and identify
and technologies as appropriate (ACSIS090) patterns. They use patterns in
information Compare data with predictions and use as evidence in developing explanations their data to suggest
(ACSIS218) explanations and refer to data
Evaluating Suggest improvements to the methods used to investigate a question or solve a when they report findings.
problem (ACSIS091) They describe ways to
improve the fairness of their
Communicating Communicate ideas, explanations and processes in a variety of ways, including
methods and communicate
multi-modal texts (ACSIS093)
their ideas, methods and
findings using a range of text
types.
General Capabilities Cross Curriculum Priorities Notes:
Literacy Aboriginal and Torres Strait
Numeracy
Islander histories and cultures
Information and communication
technology (ICT) competence Asia and Australia’s engagement
Critical and creative thinking
with Asia
Ethical behaviour
Personal and social competence Sustainability
Intercultural understanding
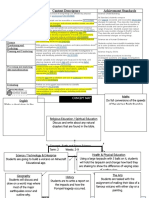
CONCEPT MAP
English
Literature: Technologies
Understand, interpret and Design and Technologies:
experiment with sound devices How people address competing considerations when designing products, services
and imagery, including simile, and environments (ACTDEK019)
metaphor and personification, in
narratives, shape poetry, songs, Identify available resources (WATPPS28)
anthems and odes (ACELT1611)
Develop and communicate alternative solutions, and follow design ideas, using
Literacy: annotated diagrams, storyboards and appropriate technical terms (WATPPS29)
Plan, rehearse and deliver
presentations for defined
audiences and purposes
incorporating accurate and The Arts
sequenced content and Concept: Physical Science, Light Term: Visual Arts:
multimodal elements 4 Weeks: 1-5 Use of techniques, art processes,
(ACELY1700) and experimentation with art
forms, such as digital imaging,
screen printing or illustration
Maths (ACAVAM115)
Measurement & Geometry:
Humanities & Social Sciences Describe translations, reflections and
Questioning & Researching Skills: Drama:
rotations of two-dimensional shapes. Experimentation and refinement
Record selected information and/or Identify line and rotational symmetries
data using a variety of methods (e.g. of ten (10) elements of drama
(ACMMG114) when creating improvised,
use graphic organisers, paraphrase,
summarise) (WAHASS53) devised or scripted drama
(ACADRM036)
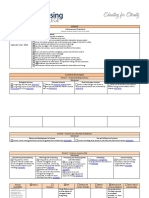
FORWARD PLANNING DOCUMENT
TERM/WEEKS: 4/1-5 YEAR LEVEL: 5 LEARNING AREA/TOPIC: Science
AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM
General Capabilities:
Literacy Numeracy ICT Critical and creative Ethical Behaviour Personal and social Intercultural Understanding
thinking Competence
Cross-curriculum priorities:
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and Cultures Asia and Australia’s engagement with Asia Sustainability
5E’s- ENGAGE (1-2 lessons)
To capture student interest and find out what they know about light
To elicit students’ questions/ prior knowledge about light
Diagnostic assessment used- in this lesson you will find out what the students already know about light. This will allow you to take account of students’ existing ideas when planning learning
experiences
WEEK/ AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM SPECIFIC LESSON ASSESSMENT TEACHING & LEARNING KEY RESOURCES
LESSON
LINKS OBJECTIVE (what & how) EXPERIENCES QUESTIONS
(include learner diversity)
Science Science as Science
Understand a Human Inquiry
ing Endeavour Skills
(ACSS (ACSIS2 Explain what light Introduction Why is light A2 paper
1 DIAGNOSTIC
U080) 31) is. Introduce the topic of light through the video important to
Sources of light. us?
Checklist using
Describe three https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d65mdT
the lesson
sources of light. What are
objectives. JaJTI
different
sources of
Body
light?
Students split into groups and brainstorm
what they know about light.
Pose the key questions too students.
Introduce the design brief “Year 5 Shadow
Puppet Show”.
Conclusion
Ask student what they now know about
light.
Ask students what they would like to learn
about light.
5E’s- EXPLORE (2-3 lessons)
To provide hands on, shared experiences of light
To support students to investigate and explore ideas about light
Formative assessment
WEEK/ AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM SPECIFIC LESSON ASSESSMENT TEACHING & LEARNING KEY RESOURCES
LESSON
LINKS OBJECTIVE (what & how) EXPERIENCES QUESTIONS
(include learner diversity)
Science Science as Science
Understand a Human Inquiry
ing Endeavour Skills
(ACSS Explain how a Introduction How did you Torches
22 FORMATIVE
U080) shadow is formed. Introduce key terminology for the topic: make the Blankets
Reflection, Refraction, Absorption and shadow? Camera/iPad
Checklist using
Describe how light Shadow. Mirrors
the lesson
from a torch How did the Black card
objectives.
interacts with Body mirror and List of Shapes
different materials. Activity 1: Shadow Puppets the black Worksheet
Students will go into forts made earlier. card interact
with the
Students will be given a list of shapes, light?
using their hands they will make each of the
shapes in the form of shadows.
Students take a photo of each shadow and
airdrop it to the teacher.
Activity 2: Observing Light
Students shine a torch onto a black piece of
paper, a mirror and another material of their
choosing.
Students write down what they observe and
draw what they see.
Conclusion
Ask students what they learnt from the
activities.
Explain what key terminology was used for
the activities.
5E’s- EXPLAIN (1 lesson)
To support students to develop explanations for experiences and make representations of developing conceptual understandings
Formative assessment
WEEK/ AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM SPECIFIC LESSON ASSESSMENT TEACHING & LEARNING KEY RESOURCES
LESSON
LINKS OBJECTIVE (what & how) EXPERIENCES QUESTIONS
(include learner diversity)
Science Science as Science
Understan a Human Inquiry
ding Endeavour Skills
(ACSS (ACSI Define and Introduction How are Glasses of
3 FORMATIVE
U080) S218) describe refraction. Introduce the topic of rainbows through the rainbows water
video “How do rainbows form”. created? White Paper
Explain how Checklist using https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= Torches
rainbows are the lesson What is light Periscope
formed. objectives. Body made up off?
Students work in pairs and each get a glass
What is a
of water.
wavelength?
Students use different light sources such as
torches or sun, and position the water in
different locations about a white piece of
paper.
Students must attempt to create a rainbow.
Extension
Students use a periscope they have
previously created.
Change the colour of the piece of paper.
Conclusion
Ask students why a rainbow was created,
pose the key questions.
5E’s- ELABORATE (1-2 lessons)
To challenge and extend students’ understandings in a new context or make connections to additional concepts through a student planned investigation
To use investigative/ inquiry skills
Summative assessment of science inquiry skills
WEEK/ AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM SPECIFIC LESSON ASSESSMENT TEACHING & LEARNING KEY RESOURCES
LESSON
LINKS OBJECTIVE (what & how) EXPERIENCES QUESTIONS
(include learner diversity)
Science Science as Science
Understand a Human Inquiry
ing Endeavour Skills
(ACSS (ACSI Identify the Introduction Coloured A2
4 SUMMATIVE
U080) S091) properties of Watch the video “How a camera works” paper
reflection of light. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7gmTY Scissors
(ACSI Science Inquiry Glue
R0QKqU
S086) Explain how light is Skills Rubric Does the size Tracing paper
used in the Body of the pinhole Cardboard
processing of Checklist using effect the Boxes
Students research the various designs of
images. the lesson image? Torches
objectives. pinhole cameras.
Tape
Students plan and build a pinhole camera How is an Juice cartons
of their own design (individual or pairs). image Investigation
Students use the camera to investigate created? worksheet
reflection of light.
Students observe and record their findings.
Extension
Sketch the light rays and depict how the
light creates the image.
Conclusion
Ask students what they found out from the
investigation.
5E’s- EVALUATE (1 lesson)
To provide opportunities to review and reflect on their learning about light and represent what they know about light
Summative assessment of science understanding
WEEK/ AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM SPECIFIC LESSON ASSESSMENT TEACHING & LEARNING KEY RESOURCES
LESSON
LINKS OBJECTIVE (what & how) EXPERIENCES QUESTIONS
(include learner diversity)
Science Science as Science
Understan a Human Inquiry
ding Endeavour Skills
(ACSS (ACSI Explain reflection, Introduction What is Posters
5 SUMMATIVE-
U080) S093) refraction, Reflect on the key terminology: Reflection, reflection? Mix and match
absorption and Science Worksheets
Refraction, Absorption and Shadow.
shadows. Understanding What is
Body refraction?
Explain what light Mark the review The teacher gives students a mix and
is made up off. sheet match key terminology game. In their What does it
mean when
groups students match the correct light
Checklist using light is
terminology with the correct definition. The absorbed?
the lesson
first group to match them together correctly
objectives.
gets a prize. How is a
Students create posters in groups about all shadow
they have learnt about light. created?
Students answer the review worksheet
individually.
Conclusion
Ask students what their favourite part of the
unit was.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Forward Planning DocumentDokument9 SeitenForward Planning Documentapi-427937246Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Argumentation in Biology: 30 Classroom ActivitiesVon EverandScientific Argumentation in Biology: 30 Classroom ActivitiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 Science-2Dokument1 SeiteYear 5 Science-2api-431986153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science FPDDokument12 SeitenScience FPDapi-395537786Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD With 5esDokument19 SeitenFPD With 5esapi-397898275Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sciencefpd 2Dokument12 SeitenSciencefpd 2api-397568836Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Forward Planning Document 2Dokument8 SeitenScience Forward Planning Document 2api-398148089Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum StrandsDokument3 SeitenCurriculum Strandsapi-459831554Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 6 Science FPDDokument10 SeitenYear 6 Science FPDapi-390074616Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)Dokument7 SeitenPrimary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)api-393907299Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD Yr3Dokument8 SeitenFPD Yr3api-430863841Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian CurriculumDokument2 SeitenAustralian Curriculumapi-450861338Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aus CurricDokument3 SeitenAus Curricapi-408957435Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science FPDDokument9 SeitenScience FPDapi-282280430Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science FPDDokument11 SeitenScience FPDapi-479604636Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPD 5esDokument13 SeitenPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-409145936Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptations FPDDokument16 SeitenAdaptations FPDapi-357270342Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian CurriculumDokument2 SeitenAustralian Curriculumapi-427927675Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science FPDDokument13 SeitenScience FPDapi-391256129Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Space Science-Fpd DwesterhoutfinalDokument15 SeitenEarth Space Science-Fpd Dwesterhoutfinalapi-347389851Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 Science UnitDokument13 SeitenYear 5 Science Unitapi-359063455Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anna Science FPDDokument18 SeitenAnna Science FPDapi-429838403Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science-Fpd - AdaptationsDokument21 SeitenScience-Fpd - Adaptationsapi-395538019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Planning Document University of Notre DameDokument15 SeitenScience: Planning Document University of Notre Dameapi-319889786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Curriculum - Year 3Dokument1 SeiteAustralian Curriculum - Year 3api-391225671Noch keine Bewertungen
- Forward Planning DocumentDokument11 SeitenForward Planning Documentapi-458392513Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Planning Document Primary & Secondary University ofDokument10 SeitenScience Planning Document Primary & Secondary University ofapi-443327549Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)Dokument17 SeitenFPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)api-475676181Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science-Forward-Planning-Document-Patrick FinalDokument8 SeitenScience-Forward-Planning-Document-Patrick Finalapi-450607837Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Curriculum DocumentDokument2 SeitenScience Curriculum Documentapi-360143529Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Unit OverviewDokument9 SeitenScience Unit Overviewapi-558955635Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2) : English MathsDokument15 SeitenAustralian Curriculum: Science (Year 2) : English Mathsapi-545623990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curric AssDokument2 SeitenCurric Assapi-389638207Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD Science 2019Dokument10 SeitenFPD Science 2019api-479357785Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPDDokument11 SeitenPrimary Science FPDapi-503017745Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example FPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 4)Dokument7 SeitenExample FPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 4)api-247482974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology and Chemistry 2022: Living Waters Lutheran CollegeDokument20 SeitenBiology and Chemistry 2022: Living Waters Lutheran Collegeapi-461267688Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science CurriculumDokument2 SeitenScience Curriculumapi-451039239Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Forward Planning DocumentDokument18 SeitenScience Forward Planning Documentapi-451266317Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Achievement Standard Year 4 Term: 3 Calendar Year: 2021Dokument10 SeitenScience Achievement Standard Year 4 Term: 3 Calendar Year: 2021api-359711783Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science FPD 1Dokument12 SeitenScience FPD 1api-350026931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)Dokument12 SeitenPrimary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)api-479877445Noch keine Bewertungen
- Forward Planning Document - Year 4Dokument12 SeitenForward Planning Document - Year 4api-476445675Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)Dokument14 SeitenFPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)api-397553972100% (1)
- Unit Plan Year 8 PhysicsDokument13 SeitenUnit Plan Year 8 Physicsapi-47919087850% (2)
- Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 5) : Sub-Strands Content Descriptions Achievement StandardDokument2 SeitenAustralian Curriculum: Science (Year 5) : Sub-Strands Content Descriptions Achievement Standardapi-483241012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPD 5esDokument11 SeitenPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-525582472Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 OverviewDokument2 SeitenYear 5 Overviewapi-451272629Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Plan Year 8 PhysicsDokument12 SeitenUnit Plan Year 8 Physicsapi-479190878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum LinksDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Linksapi-391216982Noch keine Bewertungen
- EDU421-717 Assignment 3: Unit Plan: Name: Brianna Howe ID: 1102336Dokument20 SeitenEDU421-717 Assignment 3: Unit Plan: Name: Brianna Howe ID: 1102336api-457440156100% (1)
- Overview FPDDokument2 SeitenOverview FPDapi-451063947Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Curriculum Year 3Dokument2 SeitenAustralian Curriculum Year 3api-432911874Noch keine Bewertungen
- Niamh Tosh Biology Year 2 FPDDokument8 SeitenNiamh Tosh Biology Year 2 FPDapi-458783343Noch keine Bewertungen
- My FPD PDFDokument7 SeitenMy FPD PDFapi-430999432Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptations FPD - Year 5 Biological SciencesDokument12 SeitenAdaptations FPD - Year 5 Biological Sciencesapi-395840685Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cover Page ScsaDokument1 SeiteCover Page Scsaapi-409530934Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solar System FPDDokument11 SeitenSolar System FPDapi-358863328Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Curriculum Science Year 5Dokument2 SeitenAustralian Curriculum Science Year 5api-481873722Noch keine Bewertungen
- Observing Light - Week 2Dokument3 SeitenObserving Light - Week 2api-399021565Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science of Light ChecklistDokument1 SeiteScience of Light Checklistapi-399021565Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science Design BriefDokument2 SeitenPrimary Science Design Briefapi-3990215650% (1)
- Ict Lesson 2Dokument2 SeitenIct Lesson 2api-399021565Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ict Lesson 1Dokument2 SeitenIct Lesson 1api-399021565Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tagore and CasteDokument14 SeitenTagore and CasteShiv kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 Fall 2018 Synthesis Matrix Analysis of LiteratureDokument38 SeitenPart 1 Fall 2018 Synthesis Matrix Analysis of Literatureapi-437184486Noch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Grade 6 Week-4Dokument12 SeitenDLL Grade 6 Week-4Marianne BatapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Values Vis A Vis Social JusticeDokument23 SeitenHuman Values Vis A Vis Social Justiceyesha rodasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annotated BibliographyDokument6 SeitenAnnotated Bibliographyapi-389874669Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - I (General Management) : HRM and Labour Welfare, Paper Code: 55, UGC NET Dec 2019Dokument3 SeitenUnit - I (General Management) : HRM and Labour Welfare, Paper Code: 55, UGC NET Dec 2019TarunPanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PDFsam CAE Sample 114 PDFsam SampleTest1167804-Cambridge-English-Advanced-handbookDokument4 Seiten1 PDFsam CAE Sample 114 PDFsam SampleTest1167804-Cambridge-English-Advanced-handbookandreea tuteleaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B-ARMY - Prayer Scriptures and GiftsDokument46 SeitenB-ARMY - Prayer Scriptures and GiftsChristopher FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Culture and Willingness To Share Knowledge: A Competing Values Perspective in Australian ContextDokument12 SeitenOrganizational Culture and Willingness To Share Knowledge: A Competing Values Perspective in Australian ContextGen ShuneiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Desing ThinkingDokument9 SeitenReview Desing ThinkingJessica GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Do You Know About Our Company?: Why Did You Apply For This PositionDokument6 SeitenWhat Do You Know About Our Company?: Why Did You Apply For This PositionWinda NurmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPhys Unit 03 CAPM Packet 2013Dokument12 SeitenHPhys Unit 03 CAPM Packet 2013Kelly O'Shea100% (3)
- Linda C. Mayes/ Donald Cohen: Children'S Developing Theory of MindDokument26 SeitenLinda C. Mayes/ Donald Cohen: Children'S Developing Theory of Mindcecilia martinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimber v. Bradshaw - Sanctions BriefingDokument166 SeitenKimber v. Bradshaw - Sanctions BriefingSarah BursteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts On DOMDokument10 SeitenHandouts On DOMGitanj ShethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1 - Working With Visual AidsDokument5 SeitenActivity 1 - Working With Visual AidsCecilia SepulvedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drishti YogaDokument26 SeitenDrishti Yogaphani1978100% (1)
- KrystalAegis144 PDFDokument144 SeitenKrystalAegis144 PDFTiahgee Dieson Daughtry100% (6)
- MADRID Syllabus Natural Science LT 6 EnglishDokument110 SeitenMADRID Syllabus Natural Science LT 6 EnglishAchraf HauachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Philo. SterbaDokument4 SeitenEnvironmental Philo. SterbaJanbert Rebosura100% (1)
- Resources Used in Abhidharmakośa-Bhā Ya: Biographical SourcesDokument2 SeitenResources Used in Abhidharmakośa-Bhā Ya: Biographical Sourcesdrago_rossoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enneagram Type 1Dokument16 SeitenEnneagram Type 1Marka KaticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 1 (25pts.) : Informative CommunicationDokument4 SeitenActivity No. 1 (25pts.) : Informative CommunicationGFJFFGGFD JNHUHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Transcendence As A Human Phenomenon Viktor E. FranklDokument10 SeitenSelf-Transcendence As A Human Phenomenon Viktor E. FranklremipedsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Tathagatagarbha Sutra: Siddhartha's Teaching On Buddha-NatureDokument6 SeitenThe Tathagatagarbha Sutra: Siddhartha's Teaching On Buddha-NatureBalingkangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanna-About The Soul Life of Plants-Gustav Theodor FechnerDokument47 SeitenNanna-About The Soul Life of Plants-Gustav Theodor Fechnergabriel brias buendia100% (1)
- Learning To Memories Script at SchoolDokument3 SeitenLearning To Memories Script at SchoolJen VenidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Related Literature: A. The Nature of ListeningDokument24 SeitenReview of Related Literature: A. The Nature of ListeningJayanti Putri PermataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educational LeadershipDokument13 SeitenEducational Leadershipha haNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contemporary Bildungsroman: A Study of Psycho-Sociological Aspects of Father-Son Relationship in Khaled Hosseini's The Kite RunnerDokument10 SeitenContemporary Bildungsroman: A Study of Psycho-Sociological Aspects of Father-Son Relationship in Khaled Hosseini's The Kite RunnerMarwa Bou HatoumNoch keine Bewertungen