Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Base Acid Conj. Acid Conj - Base
Hochgeladen von
rozOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Base Acid Conj. Acid Conj - Base
Hochgeladen von
rozCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
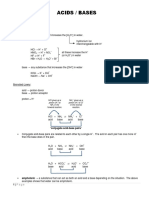
Week 8 Worksheet: Chapter 10 Acids and Bases
I. Identifying acid/base theories. For each molecule or ion in the table, identify whether it can act as
an acid or a base and put a checkmark under each theory or theories that describe it.
Molecule/Ion Acid or Base Arrhenius Bronsted-Lowry Lewis
Br- base x
CN- base x
H2CO3 acid x x
NH3 base x
HNO2 acid x x
Ba(OH)2 base x
HCl acid x x
AlCl3 acid x
Cl- base x
KOH base x
IO3- base x
CH3COOH acid x
HNO2 acid x
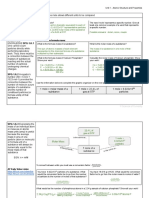
II. Conjugate Acids and Bases. In each reaction, identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and
conjugate base. Then, write which acid/base theory or theories describe the reaction.
(a) NH3 + H2O _ NH4+ + OH-
base acid conj. Acid conj.base
Theory: Bronsted
(b) NH4+ + H2O _ NH3 + H3O+
acid base conj.base conj acid
Theory: Bronsted
(c) 2NaOH + H2SO4 _ 2H2O + Na2SO4
base acid conj. Acid, base
Theory: Bronsted, Arrhenius
- - 2-
(d) HSO3 + CN _ HCN + SO3
acid base conj. Acid conj. base
Theory: Bronsted
(e) NH2- + H2O _ NH3 + OH-
base acid conj. Acid conj. base
Theory: Bronsted
(f) Draw Lewis structures depicting the reaction
AlCl3 + Cl- _ AlCl4-
and identify the acid/base theory that best describes the reaction.
Lewis acid/base theory
.. .. -
: Cl : :Cl:
.. .. .. - .. .. ..
Al : Cl : + : Cl : _ :Cl:Al:Cl:
.. .. .. .. .. ..
: Cl : :Cl:
.. ..
(g) Draw Lewis structures depicting the reaction
BBr3 + NH3 _ Br3B-NH3
and identify the acid/base theory that best describes the reaction.
Lewis acid/base theory
.. ..
: Br : H :Br: H
.. .. .. .. ..
B : Br : + : N : H _ :Br: B : N: H
.. .. .. .. ..
: Br : H :Br: H
.. ..
III. Acid/Base Strength
(a) What property do all strong acids and strong bases have in common? Write a
reaction for HCl and water to illustrate your explanation.
They dissociate completely in water
HCl_ H+ + Cl-
(b) Circle the stronger acid in each pair:
NH4+ NH3
H2O H3 O+
HXO HXO3 (X is an unknown element)
(c) Circle the weaker base in each pair:
NH4+ NH3
Cl- F-
NaOH NH4OH
NaOH NaHCO3
IV. Ternary Acids/Bases
Explain the order of increasing or decreasing acid strength and conjugate base strength for the
following groups:
(a) H2SO3, H2SO4 The more oxygens there are in an oxyacid, the more e- density is pulled from
(b) HNO2, HNO3 the protons, making them more likely to leave the molecule.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NS1Lec - Module 5 - NacionalesDokument5 SeitenNS1Lec - Module 5 - NacionalesWindere Marie NacionalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases Key ConceptsDokument8 SeitenAcids and Bases Key ConceptsAivan NovillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honors Chemistry QuizDokument4 SeitenHonors Chemistry QuizmariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid BaseDokument70 SeitenAcid BasevitrekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument259 SeitenChapter 7Hafizszul Feyzul100% (1)
- Ionic Equilibrium Lecture 9 (1st January 2023) Handout and HomeworkDokument402 SeitenIonic Equilibrium Lecture 9 (1st January 2023) Handout and Homeworktanishq yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMDokument3 SeitenActivity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMClarise CanANoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry Acids & Bases: Pauling'sDokument6 SeitenInorganic Chemistry Acids & Bases: Pauling'sAlmasriJosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS4. Lewis Bronsted-Lowry Acids Worksheet (HL)Dokument4 SeitenWS4. Lewis Bronsted-Lowry Acids Worksheet (HL)Yuvraj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 35 Titrimetry Acid BaseDokument46 SeitenCH 35 Titrimetry Acid BaseFarhan Muhammad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedDokument4 SeitenAcid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedMiasco Joy AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAcid-Base WorksheetMay LanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAcid Base WorksheetKirsten TroupeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAcid-Base WorksheetJoseph ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAcid Base WorksheetIyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study CheckDokument1 SeiteStudy CheckJenelyn Ponce AguiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and Base WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAcid and Base Worksheetapi-270967967Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1 Acids and Bases 22-23 PDFDokument143 Seiten7.1 Acids and Bases 22-23 PDFTomatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of Acids and Bases-Theory & ExerciseDokument53 SeitenConcepts of Acids and Bases-Theory & ExerciseRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in Acid-BasesDokument8 SeitenModule in Acid-BasesPenPen MalayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases: Key Theories and ConceptsDokument120 SeitenAcids and Bases: Key Theories and ConceptsAishaizlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap ChemDokument2 SeitenAp ChemEthan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 14 Study GuideDokument8 SeitenCH 14 Study Guide4b00d1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 09Dokument12 Seiten09ZenPhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 2Dokument8 SeitenProblem Set 2Katrina Louise GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 BiotechDokument74 Seiten2015 BiotechRosa DemlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titulaciones Acuosas y No AcuosasDokument27 SeitenTitulaciones Acuosas y No AcuosasMayerli LeónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedDokument4 SeitenAcid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedJoko SusiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equilibria and pH CalculationsDokument124 SeitenIonic Equilibria and pH CalculationsTasya KassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1c Worksheet Acids Bases With AnswersDokument4 Seiten1c Worksheet Acids Bases With Answersapi-369690183100% (1)
- Chapter Test B: Chapter: Acids and BasesDokument7 SeitenChapter Test B: Chapter: Acids and BasesWeng50% (2)
- Acids and Bases FundamentalsDokument6 SeitenAcids and Bases FundamentalsELAINE FAITH MEJOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exercise 5.1: Joana Lyn L. Torres BS Psych 1-BDokument5 SeitenPractice Exercise 5.1: Joana Lyn L. Torres BS Psych 1-BJoana Lyn Torres0% (1)
- Ionic EquilibriumDokument23 SeitenIonic EquilibriumjamzeethsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronsted Lowry+WorksheetDokument4 SeitenBronsted Lowry+WorksheetHo Hsiao JiunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Ionic EqulbrmDokument21 SeitenAcid Ionic EqulbrmsheenajerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equlibrium FinalDokument66 SeitenIonic Equlibrium Finalshreyas bulbuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Equilibria PDFDokument130 SeitenChemical Equilibria PDFLucienne IrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equilibrium (4 Marks)Dokument7 SeitenIonic Equilibrium (4 Marks)Nagesh NangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Practice Set 12 Chapters 1 11Dokument9 SeitenOrganic Practice Set 12 Chapters 1 11Jastine Ella Maxidel SimporiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Cha 4Dokument21 SeitenInorganic Cha 4Adugnaw BiksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic EquilibriumDokument39 SeitenIonic EquilibriumAnuragPandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NH 3 H 2 o Oh NH 4 Acid Base Concepts Chapter 15 H Conjugate Acid Base Pairs H Base AcidDokument12 SeitenNH 3 H 2 o Oh NH 4 Acid Base Concepts Chapter 15 H Conjugate Acid Base Pairs H Base AcidKhang TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM1280 Problem Set 1 Hybridization and StructuresDokument2 SeitenCHEM1280 Problem Set 1 Hybridization and StructuresLouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base Theories Explained: Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry & LewisDokument24 SeitenAcid-Base Theories Explained: Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry & Lewisfarooq shah shabbirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.8 Introduction To Acid-Base Reactions StudentDokument3 Seiten4.8 Introduction To Acid-Base Reactions StudentSyed RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (2094) Lecture Notes Ionic Equilibrium eDokument40 Seiten(2094) Lecture Notes Ionic Equilibrium eKartikey SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5-25102022Dokument49 SeitenLecture 5-25102022şevlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equilibrium Lecture NotesDokument40 SeitenIonic Equilibrium Lecture Noteskaushik2470% (1)
- Acid Base ConceptDokument20 SeitenAcid Base Conceptyadavamlesh045Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 2.docx Grade 12 Chemistry Note and WSDokument27 SeitenUNIT 2.docx Grade 12 Chemistry Note and WSmesfin yonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and BaseDokument3 SeitenAcid and BaseSeamus AlaricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equilibrium ConceptsDokument19 SeitenIonic Equilibrium ConceptsYogesh GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronst Acid Base QsDokument8 SeitenBronst Acid Base QsIsta EgbetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Acid and BaseDokument8 SeitenChapter 2 Acid and BaseKelsi Kyla PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base Equilibrium PPT UPDATED 2022Dokument96 SeitenAcid-Base Equilibrium PPT UPDATED 2022Sara Molinaro100% (1)
- BCHEM 2 - Lecture 2 - Organic Reaction MechanismDokument71 SeitenBCHEM 2 - Lecture 2 - Organic Reaction Mechanismaduashongsolomon06Noch keine Bewertungen
- 16.E__Acid___Base_Equilibria__Exercises____Chemistry_LibreTexts.pdfDokument2 Seiten16.E__Acid___Base_Equilibria__Exercises____Chemistry_LibreTexts.pdfgarciacLoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and BasesDokument30 SeitenAcids and BasesSwagata SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsVon EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TC Mwu 189Dokument108 SeitenTC Mwu 189rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME: A Clean Alternative FuelDokument14 SeitenDME: A Clean Alternative FuelrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- 單元操作PPT Chapter 21 Part 1 RevDokument87 Seiten單元操作PPT Chapter 21 Part 1 RevjahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice For Midterm$QUIZ2Dokument11 SeitenPractice For Midterm$QUIZ2rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument7 SeitenPresentation 1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1Dokument3 SeitenFigure 1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation Continuous PDFDokument27 SeitenDistillation Continuous PDFrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Calculations-1Dokument6 SeitenDetailed Calculations-1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant DesignDokument60 SeitenPlant DesignKaul PatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batch Distillation PDFDokument33 SeitenBatch Distillation PDFrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Distillatio II - pptx-1Dokument50 SeitenPractice Distillatio II - pptx-1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worked Example PDFDokument14 SeitenWorked Example PDFrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionsDokument4 SeitenQuestionsrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 22Dokument80 SeitenFinal 22rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week - 2 - EndDokument35 SeitenWeek - 2 - EndrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- WeeDokument34 SeitenWeerozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Energy TransformationsDokument16 SeitenThermodynamics Energy TransformationsrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eletrochemistry Last PDFDokument14 SeitenEletrochemistry Last PDFrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument1 Seite1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1Dokument3 SeitenFigure 1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionsDokument4 SeitenQuestionsrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALKANES ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Chapter - 1Dokument39 SeitenALKANES ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Chapter - 1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 10 2 PDFDokument24 SeitenLec 10 2 PDFrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALKANES ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Chapter - 1Dokument39 SeitenALKANES ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Chapter - 1rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC 300-Materials Science Chapter 3 and 4 Part 2 PDFDokument44 SeitenMEC 300-Materials Science Chapter 3 and 4 Part 2 PDFrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 11 2Dokument7 SeitenLec 11 2rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Objectives of This Report Are The Following:: What Is Meant by Green Chemistry?Dokument2 SeitenThe Objectives of This Report Are The Following:: What Is Meant by Green Chemistry?rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Acid Conj. Acid Conj - BaseDokument2 SeitenBase Acid Conj. Acid Conj - BaserozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6 2Dokument10 SeitenLec 6 2rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 11 2Dokument7 SeitenLec 11 2rozNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2.3. Molecules and Covalent Bonds PDFDokument3 Seiten3.2.3. Molecules and Covalent Bonds PDFClinton ChikengezhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibration Vulcan ExpertDokument6 SeitenCalibration Vulcan Expertsoufiane el khomssiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 InorgDokument15 SeitenChapter 3 InorgMauritiusFeliciano100% (2)
- PH and BufferDokument17 SeitenPH and Buffersima mhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material CodesDokument2 SeitenMaterial CodesUmair MumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CLEAPSS Recipe Book Introduction ToDokument128 SeitenThe CLEAPSS Recipe Book Introduction ToJsckson Jaden NtuliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section A Multiple Choice Questions (20 Marks)Dokument39 SeitenSection A Multiple Choice Questions (20 Marks)Timothy HandokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen Chemistry Class 10-Pages-45-55-CompressedDokument11 SeitenAllen Chemistry Class 10-Pages-45-55-CompressedSaismita ParidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 Quarter 2Dokument12 SeitenScience 9 Quarter 2Catherine Yorong PedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (H2 CHEM) Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDokument31 Seiten(H2 CHEM) Chapter 1 - Atomic StructurePriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akzo-3039 Akzo-3034 Acid Corrosion English Importante StimolazioneDokument4 SeitenAkzo-3039 Akzo-3034 Acid Corrosion English Importante StimolazioneFra Fra100% (1)
- Reactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesDokument24 SeitenReactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesCarl Agape DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM E415 15 Análisis de Carbono y Acero de Baja AleaciónDokument11 SeitenASTM E415 15 Análisis de Carbono y Acero de Baja AleaciónEacm McaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Progression Test: Science Paper 1Dokument16 SeitenCambridge Lower Secondary Progression Test: Science Paper 1mahdi hassan100% (4)
- Rev - Chemistry - AreasDokument7 SeitenRev - Chemistry - AreasUppu EshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDokument12 SeitenPaper 4 CIE Chemistry IGCSENovenda Ermina FatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 4 Quiz AnswerDokument8 SeitenChemistry Form 4 Quiz Answerkhangsiean89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla Periódica Dibujos PDFDokument1 SeiteTabla Periódica Dibujos PDFAngélica Bustamante RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 Electrochem A2Dokument9 SeitenTutorial 2 Electrochem A2Nur Dinah Alesha Mohd Ali ZarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Physical Chemical and Bact. Characteristics of WastewaterDokument6 Seiten2-Physical Chemical and Bact. Characteristics of WastewatermarkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Periodic TableDokument1 SeiteBest Periodic Tablemuxi rongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystalline Glaze NotesDokument5 SeitenCrystalline Glaze NotesTim Carlson100% (1)
- Ionic Equilibria Questions Set 2 2 PDFDokument4 SeitenIonic Equilibria Questions Set 2 2 PDFdanielmahsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges From Corrosion-Resistant Grid Alloys in Lead Acid Battery ManufacturingDokument10 SeitenChallenges From Corrosion-Resistant Grid Alloys in Lead Acid Battery ManufacturingDilfredo RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 & 8 Chem Study GuideDokument3 SeitenChapter 7 & 8 Chem Study GuideseabreezeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brainpop Periodic Table WsDokument1 SeiteBrainpop Periodic Table WsJen A. MacauleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEY Unit 1 AP Chemistery Review GuideDokument10 SeitenKEY Unit 1 AP Chemistery Review GuideMohammad AmmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorimetry and Turbidimetry: Indicated inDokument9 SeitenColorimetry and Turbidimetry: Indicated injycortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry Worksheet 3Dokument2 SeitenStoichiometry Worksheet 3Giorno GiovannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and BasesDokument70 SeitenAcids and BasesChery-an PletNoch keine Bewertungen