Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Diffusion
Hochgeladen von
Heherson CabreraCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Diffusion
Hochgeladen von
Heherson CabreraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
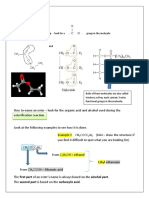
CRYSTALLIZATION
1. A saturated solution containing 1500 kg of potassium chloride at 360 K is cooled in
an open tank to 290 K. If the density of the solution is 1200 kg/m3, the solubility of
potassium chloride/100 parts of water by mass is 53.55 at 360 K and 34.5 at 290 K
calculate:
(a) the capacity of the tank required, and
(b) the mass of crystals obtained, neglecting any loss of water by evaporation.
2. Ten Mg of a solution containing 0.3 kg Na2CO3kg solution is cooled slowly to 293 K
to form crystals of Na2C03.lOHzO. What is the yield of crystals if the solubility of
Na2CO3 at 293 K is 21.5 kg/l00 kg water and during cooling 3 per cent of the original
solution is lost by evaporation?
3. The heat required when 1 kmol of MgS04.7H20 is dissolved isothermally at 291 K in
a large mass of water is 13.3 MJ. What is the heat of crystallization per unit mass of
the salt?
4. A solution of 500 kg of NazSO4 in 2500 kg water is cooled from 333 K to 283 K in an
agitated mild steel vessel of mass 750 kg. At 283 K, the solubility of the anhydrous salt
is 8.9 kg100 kg water and the stable crystalline phase is Na2S04.10H20. At 291 K, the
heat of solution is -78.5 M J h o l and the specific heat capacities of the solution and
mild steel are 3.6 and 0.5 H/kg deg K respectively. If, during cooling, 2 percent of the
water initially present is lost by evaporation, estimate the heat which must be removed.
5. A batch of 1500 kg of saturated potassium chloride solution is cooled from 360 K to
290 K in an unagitated tank. If the solubilities of KCI are 53 and 34 kg/100kg water
at 360 K and 290 K respectively and water losses due to evaporation may be neglected,
what is the yield of crystals?
6. Glauber’s salt, Na2S04.10H20, is to be produced in a Swenson-Walker crystallizer by
cooling to 290 K a solution of anhydrous Na2SO4 which saturates between 300 K and
290 K. If cooling water enters and leaves the unit at 280 K and 290 K respectively
and evaporation is negligible, how many sections of crystallizer, each 3 m long, will be
required to process 0.25 kg/s of the product? The solubilities of anhydrous Na2S04 in
water are 40 and 14 kgll00 kg water at 300 K and 290 K respectively, the mean heat
capacity of the liquor is 3.8 HkgK and the heat of crystallisation is 230 Hkg. For the
crystalliser, the available heat transfer area is 3 m2/m length, the overall coefficient of
heat transfer is 0.15 kW/m2 K and the molecular masses are NazSO4.10H2O = 322
kg/kmol and Na2SO4 = 142 kg/kmol.
7. A feed solution of 2268 kg at 327.6 K containing 48.2 kg MgSO4/100 kg total water is
cooled to 293.2 K, where MgSO4.7H2O crystals are removed. The solubility of the salt
is 35.5 kg MgSO4/100 k total water. The average heat capacity of the feed solution can
be assumed as 2.93 kJ/kg-K. The heat of solution at 291.2 K is -13.31 x 10^3 kJ/kgmol
MgSO4.7H2O. Calculate the yield of crystals and make a heat balance to determine the
total heat absorbed, assuming that no water is vaporized.
8. A hot solution of Ba(NO3)2 from an evaporator contains 30.6 kg Ba(NO3)2/kg H2O
and goes to a crystallizer where the solution is cooled and Ba(NO3)2 crystallizes. On
cooling, 10% of the original water present evaporates. For a feed solution of 100 kg
total, calculate the following.
a. The yield of crystals if the solution is cooled to 290 K, where the solubility is 8.6 kg
Ba(NO3)2/100 kg water.
b. The yield if cooled instead to 283 K, where the solubility is 7.0 kg Ba(NO3)2/100 kg
total water.
9. A batch of 1000 kg of KCL is dissolved in sufficient water to make a saturated
solution of 363 K, where the solubility is 35 wt % in water. The solution is cooled to 293
K, at which temperature its solubility is 25.4 wt%.
a. What is the weight of water required for solution and the weight of crystals of KCl
obtained?
b. What is the weight of crystals obtained if 5% of the original water evaporates on
cooling?
10. A hot solution containing 1000 kg of MgSO4 and water having a concentration of 30
wt% MgSO4 is cooled to 288.8 K, where the crystals of MgSO4.7H2O are precipitated.
The solubiliy at 288.8 K is 24.5 wt% anhydrous MgSO4 in the solution. Calculate the
yield of crystals obtained if 5% of the original water in the system evaporates on cooling.
11. A feed solution of 10000 lbm at 130 F containing 47.0 ln FeSO4/100 lb water is
cooled to 80 F, where FeSO4.7H2O crystals are removed. The solubility of the salt is
30.5 lb FeSO4/100 lb total water. The average heat capacity of the feed solution is 0.70
btu/lbm-F. The heat of solution at 18 F is -4.4 kcal/g-mol FeSO4.7H2O. Calculate the
yield of crystals and make a heat balance. Assume no water is vaporized.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ba(NO3)2 Crystallization Problem SetDokument2 SeitenBa(NO3)2 Crystallization Problem SetBea BacaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization Tutorial SolutionsDokument1 SeiteCrystallization Tutorial SolutionsjayaprinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization TutorialDokument2 SeitenCrystallization TutorialTshwarelo MahlakoaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CrystallizationDokument13 SeitenCrystallizationAnonymous P1iMib50% (2)
- ANSWER Tutorial CrystallizationDokument4 SeitenANSWER Tutorial CrystallizationAmalinaArouraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPS 370S - 2024 - Test 1 PreparationDokument1 SeiteSPS 370S - 2024 - Test 1 PreparationKhayakazi ZiweleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization Tutorial: Calculating Crystal Yields from Cooling SolutionsDokument1 SeiteCrystallization Tutorial: Calculating Crystal Yields from Cooling SolutionsHafiidz MalekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3 - CrystallizationDokument3 SeitenTutorial 3 - CrystallizationAhmad Muzammil25% (4)
- Tutorial Crystallization PDFDokument5 SeitenTutorial Crystallization PDFara_1909Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization ProblemsDokument1 SeiteCrystallization ProblemsAnonymous P1iMibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization 2013Dokument2 SeitenCrystallization 2013Peterter Paul100% (1)
- Crystallizations QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCrystallizations Questionsengr2021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization PrdasddaoblemsDokument4 SeitenCrystallization PrdasddaoblemsJim Laab100% (1)
- CrystallizationDokument18 SeitenCrystallizationNur AishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization Problems W/ AnswersDokument1 SeiteCrystallization Problems W/ AnswersMc Jason Laurete50% (2)
- FreeteeDokument14 SeitenFreeteemantascitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization 2Dokument48 SeitenCrystallization 2John Patrick Dagle67% (3)
- Thermochem Solved Practice Problems PDFDokument9 SeitenThermochem Solved Practice Problems PDFRez Balayo JanabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Chemistry ProblemsDokument1 SeiteSolving Chemistry ProblemsCharlene L. PulmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas ATK 2 1 2021Dokument1 SeiteTugas ATK 2 1 2021Monika Jelita SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Compilation of ProbSolvingDokument5 SeitenMy Compilation of ProbSolvingDianne VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry 1Dokument8 SeitenStoichiometry 1Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Solution-04 - Assignments (N)Dokument16 SeitenLiquid Solution-04 - Assignments (N)Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- numericals 2Dokument3 Seitennumericals 2nithinkumarin2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Revision On Heat (Calculation) : Water Ice F 5 V 6 Absorbed ReleasedDokument1 SeitePhysics Revision On Heat (Calculation) : Water Ice F 5 V 6 Absorbed ReleasedLim JingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Soal 1 2020Dokument1 SeiteLatihan Soal 1 2020aldo islamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Chemistry & General Chemistry Review QuestionsDokument3 SeitenAnalytical Chemistry & General Chemistry Review QuestionsMicahmae MorbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Competency Exam CrystallizationDokument1 SeiteTechnological Institute of The Philippines Competency Exam CrystallizationWinsletJoyDauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionDokument2 SeitenSolutionZuber SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On Clausius Clayperon EqnDokument5 SeitenProblems On Clausius Clayperon EqnAkshat RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On Clausius Clayperon EqnDokument5 SeitenProblems On Clausius Clayperon EqnAkshat RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Heat and Heat Capacity Worksheet SolutionsDokument3 SeitenSpecific Heat and Heat Capacity Worksheet SolutionsDigCity Digg100% (1)
- AaaaaDokument3 SeitenAaaaaAnonymous C3BD7OdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water of CrystallisationDokument3 SeitenWater of CrystallisationSreeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization With ProbsDokument5 SeitenCrystallization With ProbsEzekiel100% (1)
- Chemistry 30 Thermochemical Changes Practice 1Dokument9 SeitenChemistry 30 Thermochemical Changes Practice 1Alaa mohamed Shaat BANoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization Competency Exam (TIP)Dokument2 SeitenCrystallization Competency Exam (TIP)Kuo SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Heat Capacity WorksheetDokument3 SeitenSpecific Heat Capacity WorksheetMuhamad Zahwan AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions of Solids in LiquidsDokument16 SeitenSolutions of Solids in LiquidsNoorhalieza AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical changes, reactions, bonds, energy profilesDokument2 SeitenChemical changes, reactions, bonds, energy profilesLaurie-Ann 大丽花 Edwards-MurdockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problema 12Dokument5 SeitenProblema 12Lizeth CANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 12 Sem III Chap 2 Test 04042018Dokument2 SeitenChemistry 12 Sem III Chap 2 Test 04042018foryouonlinetutorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yield Crystallization ProblemDokument9 SeitenYield Crystallization ProblemRonald Angelo Lopez100% (1)
- CrystallizationDokument6 SeitenCrystallizationJemar Lim100% (1)
- Problem Set Flip CrystallizationDokument2 SeitenProblem Set Flip CrystallizationSam Denielle TugaoenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics exam questionsDokument3 SeitenThermodynamics exam questionsKhiara Claudine EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galaxy Chem Worksheet Chap 1,2,3,4.Dokument10 SeitenGalaxy Chem Worksheet Chap 1,2,3,4.Rahul MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole Concept & Stoich ProblemsDokument10 SeitenMole Concept & Stoich Problemssrinivas2111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization PDFDokument9 SeitenCrystallization PDFonly. starNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometric Calculations Made EasyeducationDokument13 SeitenStoichiometric Calculations Made Easyeducationandrew surajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystaliization FiltrationDokument12 SeitenCrystaliization FiltrationAsh YehiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry Problems SolvedDokument2 SeitenThermochemistry Problems SolvedHamzaHassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 U Thermo Lesson 2 Enthalpy Calculations WorksheetDokument2 Seiten12 U Thermo Lesson 2 Enthalpy Calculations WorksheethtyhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 1991 International Conference on Coal Science Proceedings: Proceedings of the International Conference on Coal Science, 16–20 September 1991, University of Newcastle-Upon-Tyne, United KingdomVon Everand1991 International Conference on Coal Science Proceedings: Proceedings of the International Conference on Coal Science, 16–20 September 1991, University of Newcastle-Upon-Tyne, United KingdomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry ExamDokument5 SeitenPhysical Chemistry ExamHeherson CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Multiple Choice ExamDokument6 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Multiple Choice ExamHeherson CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- General and Analytical ChemistryDokument8 SeitenGeneral and Analytical ChemistryHeherson CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Problems in Organic ChemistryDokument5 SeitenAdditional Problems in Organic ChemistryHeherson CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Himalaya GasesDokument4 SeitenHimalaya Gasesmitr_mmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio ScouringDokument14 SeitenBio ScouringPrachi GehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDTA Manganese Sodium (EDTA-MnNa2)Dokument2 SeitenEDTA Manganese Sodium (EDTA-MnNa2)8612106535Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is 2932 2003 PDFDokument22 SeitenIs 2932 2003 PDFSuyambu100% (1)
- SKF Industrial Shaft Seals (5300 EN) - CATALOGUE PDFDokument379 SeitenSKF Industrial Shaft Seals (5300 EN) - CATALOGUE PDFLily VyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Clariant Alemania 2003Dokument41 SeitenCatalogo Clariant Alemania 2003Carlo Pizarro100% (1)
- Final Report 3Dokument10 SeitenFinal Report 3TOBIRAMA SenkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study 3101 w1Dokument319 SeitenStudy 3101 w1Koray SimsekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Test A: Chemical BondingDokument4 SeitenChapter Test A: Chemical BondingPencils of PromiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy Way To Understand Stewart DR George Handbook 2015 PDFDokument48 SeitenEasy Way To Understand Stewart DR George Handbook 2015 PDFAnonymous SMLzNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Metals and Melting Practices: StructureDokument45 SeitenUnit 1 Metals and Melting Practices: StructureTapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Project Presentation SlidesDokument20 SeitenCorrosion Project Presentation SlidesIsmeth Amir Johari100% (1)
- An Experimental Verification of Saturated Salt Solution-Based Humidity Fixed PointsDokument17 SeitenAn Experimental Verification of Saturated Salt Solution-Based Humidity Fixed PointsRODRIGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Chemistry: Structure and Properties of PolyethyleneDokument19 SeitenPolymer Chemistry: Structure and Properties of PolyethyleneSumedha ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Solution PDFDokument5 SeitenChapter 2 Solution PDFツSoumya࿐100% (1)
- Introduction To Cost Estimating Lec 1Dokument146 SeitenIntroduction To Cost Estimating Lec 1Arwa HusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPTDokument28 SeitenPPTRaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esters Worksheet PDFDokument3 SeitenEsters Worksheet PDFAnonymous na314kKjOANoch keine Bewertungen
- Earl's Practical Test Part 2 (Lab Report Template) - Dk014Dokument5 SeitenEarl's Practical Test Part 2 (Lab Report Template) - Dk014MALIUS BIN SUNGGI MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AM of Ni-Base SuperalloysDokument31 SeitenAM of Ni-Base SuperalloysMahendra SukreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Behavior of Stainless Steel in Hydrochloric Acid and Nitric Acid SolutionsDokument5 SeitenCorrosion Behavior of Stainless Steel in Hydrochloric Acid and Nitric Acid SolutionsantonytechnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Bismuth in The SOHIO ProcessDokument39 SeitenThe Role of Bismuth in The SOHIO ProcessMarnel Roy MayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Producing A Novel Cold Mix Asphalt: University of Anbar College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDokument36 SeitenProducing A Novel Cold Mix Asphalt: University of Anbar College of Engineering Civil Engineering Departmentحميد مجيدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price List Brochure Klin'sDokument4 SeitenPrice List Brochure Klin'sAbdiyasa Dharma InovasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tack Welder Level 3 Question Bank I Fill in The BlanksDokument6 SeitenTack Welder Level 3 Question Bank I Fill in The BlanksVigneshwaran VijayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam ReformersDokument95 SeitenSteam Reformersassadeq100% (2)
- Ion Exchange Separation and Purification of AntibioticsDokument3 SeitenIon Exchange Separation and Purification of AntibioticsAnonymous k41BMGYDLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shieldmaster Brochure by Manuli HydraulicsDokument12 SeitenShieldmaster Brochure by Manuli HydraulicsPawan ChaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyester Properties, Preparation and Applications by Hina Yamashita, Yui Nakano PDFDokument259 SeitenPolyester Properties, Preparation and Applications by Hina Yamashita, Yui Nakano PDFVasile LeniucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coagulation / FlocculationDokument1 SeiteCoagulation / FlocculationElmaeen BagiohanonNoch keine Bewertungen