Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Plant Cells Are Eukaryotic Cells Present in Green Plants
Hochgeladen von
annOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Plant Cells Are Eukaryotic Cells Present in Green Plants
Hochgeladen von
annCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae
“Plant cells are eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out
certain specific functions.”
Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. They are eukaryotic cells, which have a true
nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. Plant cells have special
organelles called chloroplasts which create sugars via photosynthesis.
Plant Cell Types
There are five types of plant cells, each with different functions:
Parenchyma cells are the majority of cells in a plant. They are found in leaves and carry out photosynthesis and
cellular respiration, along with other metabolic processes. They also store substances like starches and proteins
and have a role in plant wound repair.
Collenchyma cells provide support to growing parts of a plant. They are elongated, have thick cell walls, and can
grow and change shape as a plant grows.
Sclerenchyma cells are hard cells that are the main supporting cells in the areas of a plant that have ceased
growing. Sclerenchyma cells are dead and have very thick cell walls.
Xylem cells transport mostly water and a few nutrients throughout a plant, from the roots to the stem and leaves.
Phloem cells transport nutrients made during photosynthesis to all parts of a plant. They transport sap, which is a
watery solution high in sugars.
Cell Wall
It is a rigid layer which is composed of cellulose, glycoproteins, lignin, pectin, and hemicellulose. It is located outside the
cell membrane. It comprises proteins, polysaccharides, and cellulose.
Cell membrane
It is the semi-permeable membrane that is present within the cell wall. It is composed of a thin layer of protein and fat.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that is present only in eukaryotic cells
Plastids
They are membrane-bound organelles that have their own DNA.
Leucoplasts
They are found in non-photosynthetic tissues of plants.
Chloroplasts
It is an elongated organelle enclosed by phospholipid membrane. The shape of the chloroplast is disk-shaped and the
stroma is the fluid within the chloroplast that comprises a circular DNA. Each chloroplast contains a green coloured
pigment called chlorophyll required for the process of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun
and uses it to transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Chromoplasts
They are heterogeneous, coloured plastids organelle
Central Vacuole
It occupies around thirty per cent of the cell’s volume in a mature plant cell. Tonoplast is a membrane that surrounds
central vacuole
Golgi Apparatus
They are found in all eukaryotic cells
Ribosomes
They are the smallest membrane-bound organelle which comprises RNA and protein. They are the sites for protein
synthesis, hence they are also referred to as the protein factories of the cell.
Mitochondria
They are the double-membraned organelles found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells.
Lysosome
Lysosomes are called as suicidal bags as they hold digestive enzymes in an enclosed membrane
All animals, including you and I, are made of the same basic building block called the animal cell. Animal cells are generally
smaller than plant cells and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; these are organelles pertinent to plant cells
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Paper Chromatography Is One of The Types of Chromatography Procedures Which Runs On A Piece of Specialized PaperDokument1 SeitePaper Chromatography Is One of The Types of Chromatography Procedures Which Runs On A Piece of Specialized PaperannNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Make Up GuyDokument2 SeitenThe Make Up GuyannNoch keine Bewertungen
- (DOC) Sample Questionnaire For Science Grade 7 First Quarter Exam - Docx - Enrique Delula II - Academia - EduDokument1 Seite(DOC) Sample Questionnaire For Science Grade 7 First Quarter Exam - Docx - Enrique Delula II - Academia - EduannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science TestDokument2 SeitenScience TestannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horror FilesDokument4 SeitenHorror FilesannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific MethodDokument1 SeiteScientific MethodannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Apparatuses and UsesDokument2 SeitenLaboratory Apparatuses and UsesDanielle Elish Goco88% (33)
- Science TestDokument2 SeitenScience TestannNoch keine Bewertungen
- 38Dokument2 Seiten38annNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A CompoundDokument4 SeitenParts of A CompoundannNoch keine Bewertungen
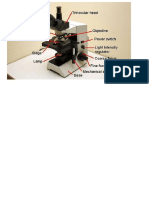
- When Moving Your Microscope, Always Carry It With Both Hands (Figure 1, at Left) - Grasp The Arm With One Hand and Place The Other Hand Under The Base For SupportDokument3 SeitenWhen Moving Your Microscope, Always Carry It With Both Hands (Figure 1, at Left) - Grasp The Arm With One Hand and Place The Other Hand Under The Base For SupportannNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ButterflyDokument1 SeiteThe ButterflyannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romeo and JulietDokument2 SeitenRomeo and JulietannNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ButterflyDokument1 SeiteThe ButterflyannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Pharmacognosy Introduction and TaxonomyDokument19 SeitenPharmacognosy Introduction and TaxonomytmleeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tissues - YTDokument94 SeitenTissues - YTRaima Sharma100% (3)
- Leaf ShapeDokument18 SeitenLeaf ShapeMohan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DISEASES OF FIELD AND HORTICULTURAL CROPS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT-II RevDokument36 SeitenDISEASES OF FIELD AND HORTICULTURAL CROPS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT-II RevTaushif AhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Tree Architecture To Tree Training - An Overview of Recent Concepts Developed in Apple in FranceDokument8 SeitenFrom Tree Architecture To Tree Training - An Overview of Recent Concepts Developed in Apple in FrancePutchong SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusDokument2 SeitenLycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusAbegail Bantilan ConiendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiosperms BookDokument278 SeitenAngiosperms BookShah RafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- PterisDokument12 SeitenPterisLINTA JOSEPH100% (2)
- Solanum Torvum PDFDokument2 SeitenSolanum Torvum PDFZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany Past Paper 2006Dokument9 SeitenBotany Past Paper 2006Tehzeeb ZubairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuperrosidsDokument10 SeitenSuperrosidsSebastian GhermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIRST QUARTER TEST IN TLE-Agriculture 6 (Ver3)Dokument3 SeitenFIRST QUARTER TEST IN TLE-Agriculture 6 (Ver3)ydel pascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationDokument7 SeitenI. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationBethymay EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pinophyta: 1 EvolutionDokument10 SeitenPinophyta: 1 EvolutionJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 2.5 - Plants Parts and Their FunctionsDokument16 SeitenLESSON 2.5 - Plants Parts and Their FunctionsJen TaniecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 OrnamentalDokument168 Seiten2 Ornamentalনাজমুল হক শাহিনNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Floral Morphology of Brinjal Genotypes in Gangetic-Alluvial Zone of West Bengal, IndiaDokument9 SeitenA Study On Floral Morphology of Brinjal Genotypes in Gangetic-Alluvial Zone of West Bengal, IndiaArindam DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pematahan Dormansi Benih Kelapa Sawit ElDokument15 SeitenPematahan Dormansi Benih Kelapa Sawit Elalius iyutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in Plants: Xylem and PhloemDokument2 SeitenTransport in Plants: Xylem and PhloemriyashreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 - Meristem Culture For Virus Free Plants - 2013 - Plant Tissue Cultur PDFDokument8 SeitenChapter 11 - Meristem Culture For Virus Free Plants - 2013 - Plant Tissue Cultur PDFLuis BermudezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Growth and Development. Botany. FinalDokument47 SeitenPlant Growth and Development. Botany. FinalMelanie Lequin CalamayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN6RC-IVc-3.2.5 - 2023-2024 - Day 1Dokument5 SeitenEN6RC-IVc-3.2.5 - 2023-2024 - Day 1Ma. Feliza SaliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gardening in DubaiDokument2 SeitenGardening in DubaiDUA TARIQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 11 AnswersDokument8 SeitenBiology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 11 AnswersFiveLimaRomeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrangea Bulletin HiDokument16 SeitenHydrangea Bulletin HiDan Danut100% (1)
- Anatomy in Flowering PlantsDokument5 SeitenAnatomy in Flowering PlantsDanish UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Element Stewardship Abstract For Ulex EuropaeusDokument22 SeitenElement Stewardship Abstract For Ulex EuropaeusCarlos AngaritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Oil Palm (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq.) Nursery in Bangun Bandar Estate, North SumateraDokument8 SeitenManagement Oil Palm (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq.) Nursery in Bangun Bandar Estate, North SumateraWendy JuliansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growing Plants Without SeedsDokument9 SeitenGrowing Plants Without Seedschristian capunongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reefertilizer Start Grow Bloom GuideDokument31 SeitenReefertilizer Start Grow Bloom GuideMichael DrouinNoch keine Bewertungen