Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Flower Whorls
Hochgeladen von
Milvy Faith C. SyjongtianCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Flower Whorls
Hochgeladen von
Milvy Faith C. SyjongtianCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
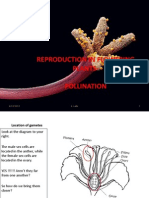
FLOWER WHORLS
- A whorl or verticil is the arrangement of sepals, petals, leaves, stipules (small leaflike
appendages) or branches that comes from a single part and surrounds the stem.
FOUR MAJOR WHORLS
1. Calyx, a whorl of Sepals
2. Corolla, a whorl of Petals
3. Androecium, a whorl of Stamen (contains Anther and Filament)
4. Gynoecium, a whorl of Carpels or female parts of the plant: the Pistil which consists
the Stigma, Style, and Ovary(Ovule)
The Calyx
- Outermost whorl
- is the leaf-like structures at the base of a flower that protects the flower during
development
- These leaf-like structures are individually called Sepals and sometimes there are as much
sepals as there are petals.
- function is to protect the flower at its early stages by closing it tightly as a bud
- The sepals are the outer covering of the flower as it forms. It protects the developing flower
and prevents it from drying out.
The Corolla
- second whorl that is composed of the flower's petals
- The petals serve two purposes: to protect the reproductive organs of the flower and to
attract pollinators.
- Because of this second purpose, they are usually brightly colored and scented so that
animals and insects will come close to them and move around the flower's pollen.
Perianth
- first two whorls of the flower -- the calyx and the corolla
Aestivation
- Arrangement of sepals or petals in a floral bud
o Valvate
the margin of the sepals/petals touch each other rather than overlap
o Twisted
the margin of the sepals/petals overlap
o Imbricate
the margin of the sepals/petals overlap in an irregular manner
o Vexillary
a mode of aestivation in which one larger upper petal folds over, and cover,
the other smaller petals
The Androecium
- third whorl of a flower that contain stamens, the male reproductive part
- The stamen is made of a thin vertical thread-like structure called a filament topped with a
circular or oblong structure called an anther.
- The anther is bi-lobed each lobe consists of 2 chambers called pollen sacs which produces
pollen.
o Staminode, sterile stamen
o Polyandrous, free stamen
o Monoadelphous, if the stamens are united in one bunch
o Diadelphous, if the stamens are united in 2 bunches
o Polyadelphous, if the stamens are united in 3 or more bunches
- If the stamen attaches to the petals they are called as Epipetalous stamen.
- If the stamen attaches to the perianth they are called as Epiphyllous stamen.
The Gynoecium
- At the center of the flower is the fourth whorl -- the carpels, which contain the pistil of the
flower.
- The pistil is the plant's female reproductive organ, which is composed of three parts: the
ovary, the style, and the stigma.
- The ovary contains the eggs, or ovules (which are attached to a flattened cushion-like
structure called a placenta), of the plant, and when the ovules are fertilized, the ovary
sometimes turns into a fruit to house the seed.
- The top of the ovary leads to a vertical structure called a style, which supports the stigma.
- The stigma catches grains of pollen that the wind or pollinators disperse, and the pollen
grains travel down the style to the ovary.
- If the carpels are free they are called Apocaprous.
- If the carpels are united they are called Syncarpous.
- After Fertilization these ovules develop into seeds and the ovary develops into a fruit.
TYPES OF FLOWERS BASED ON THE PRESENCE OF THE WHORLS
• Complete - A flower is called complete if all four floral organs are present in the same flower
structure.
• Incomplete - An incomplete flower lacks any one or more of these parts.
TYPES OF FLOWERS BASED ON THE PRESENCE OF REPRODUCTIVE WHORLS
• Perfect/Bisexual or Hermaphrodite - are flowers that contain both sexual floral organs
• Imperfect/Unisexual - contain either stamen or pistil only, regardless if the whorl their
missing is either the calyx or corolla or both
-Staminate flower
-Carpellate flower
All complete flowers are also perfect. But not all perfect flowers are complete flowers. (Example:
Rice)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Marcos MemeDokument2 SeitenMarcos MemeMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACET Pointers PDFDokument1 SeiteACET Pointers PDFMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ho 3 PDFDokument19 SeitenHo 3 PDFMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 18 Chemical Kinetics PDFDokument41 SeitenCHEM 18 Chemical Kinetics PDFMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument4 SeitenPresentation 1Milvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic DiagramDokument4 SeitenSchematic DiagramMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 18 Acid-Base EquilibriaDokument69 SeitenCHEM 18 Acid-Base EquilibriaMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument4 SeitenPresentation 1Milvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone, Joint and Muscle InjuriesDokument4 SeitenBone, Joint and Muscle InjuriesMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone, Joint and Muscle Injuries: Edward V. Ganggang, RN, LPTDokument22 SeitenBone, Joint and Muscle Injuries: Edward V. Ganggang, RN, LPTMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Readings 6Dokument15 SeitenReadings 6Milvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiosperms ReviewerDokument17 SeitenAngiosperms ReviewerMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z14 - Characteristics - Phylum Porifera & CnidariaDokument2 SeitenZ14 - Characteristics - Phylum Porifera & CnidariaMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- KIgdom ProtistaDokument64 SeitenKIgdom ProtistaMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veneration Without Understanding2Dokument10 SeitenVeneration Without Understanding2Katrina SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torrent Downloaded From ExtraTorrent - CCDokument1 SeiteTorrent Downloaded From ExtraTorrent - CCTalha HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 2 KorsgaardDokument5 SeitenReading 2 KorsgaardMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallurgy and Chemistry of Metals: Chem 18Dokument19 SeitenMetallurgy and Chemistry of Metals: Chem 18Milvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gamma RadiationDokument14 SeitenGamma RadiationMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downloaded From WWW - ETTV.tvDokument1 SeiteDownloaded From WWW - ETTV.tvAlwapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Updated TV Shows FromDokument1 SeiteDaily Updated TV Shows FromMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Please SupportDokument1 SeitePlease SupportMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Updated TV Shows FromDokument1 SeiteDaily Updated TV Shows FromMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPARISONNoli&El Fili 2019Dokument2 SeitenCOMPARISONNoli&El Fili 2019Milvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space ExplorationDokument1 SeiteSpace ExplorationMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- HD & BluRay Movies From TorrentCounter - ToDokument1 SeiteHD & BluRay Movies From TorrentCounter - ToMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dig GongDokument1 SeiteDig GongMilvy Faith C. SyjongtianNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- PollinationDokument18 SeitenPollinationapi-233236478Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology of Sweet Cherry FloweringDokument11 SeitenBiology of Sweet Cherry FloweringJohn SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power of Flowers JeopardyDokument22 SeitenPower of Flowers JeopardyCathie WoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Investigatory Project PDFDokument19 SeitenBiology Investigatory Project PDFAnargha BoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- AGP-312 Crop Improvement - I (Kharif Crops)Dokument50 SeitenAGP-312 Crop Improvement - I (Kharif Crops)kalulalupatidar00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kobukuro - SakuraDokument3 SeitenKobukuro - SakuraNurul Hani AziziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Species Biology - 2022 - Manrique Valderrama - First Report On Generalized Pollination Systems in Melastomataceae ForDokument13 SeitenPlant Species Biology - 2022 - Manrique Valderrama - First Report On Generalized Pollination Systems in Melastomataceae ForLuiz Fernando Lima CarvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3. PlantsDokument10 SeitenUnit 3. PlantsMartabm29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 5 - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKDokument16 SeitenGrade 5 - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKMeera Joy Deboma Blanco100% (1)
- Scientia Horticulturae: M.L. Alcaraz, J.I. HormazaDokument5 SeitenScientia Horticulturae: M.L. Alcaraz, J.I. HormazaCarlos CarvajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test-01 - SRFP and RIO - TestDokument5 SeitenTest-01 - SRFP and RIO - TestANUP MOHAPATRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Seed Formation and DevelopmentDokument12 SeitenSeed Formation and DevelopmentSabir Ahamed90% (20)
- 2017 Pollinationin Roses Elsevier Modulein Life Sciences 050703Dokument6 Seiten2017 Pollinationin Roses Elsevier Modulein Life Sciences 050703Cricket with AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Account of Genus DebregeasiaDokument21 SeitenAn Account of Genus DebregeasiaamitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2ND Chap QuizDokument33 Seiten2ND Chap QuizVidyut kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floret Fall Mini Course Dahlia Sources Updated 211012Dokument3 SeitenFloret Fall Mini Course Dahlia Sources Updated 211012Luthfian DaryonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity - EASYDokument1 SeiteActivity - EASYAmina Zeghar BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bee Movie ScriptDokument9 SeitenBee Movie ScriptMan reik medžiagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSAKINAH NAJWAH BT SUHAIMI (Dissection and Observation of Plant Reproductive Organs)Dokument9 SeitenNURSAKINAH NAJWAH BT SUHAIMI (Dissection and Observation of Plant Reproductive Organs)Nursakinah NajwahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domic 2017Dokument10 SeitenDomic 2017Brenda Leidy Orosco ArangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 AssignmentDokument7 SeitenCH 2 AssignmentRitu BarthwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ikimono Gakari - SAKURADokument3 SeitenIkimono Gakari - SAKURAapi-3799292100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension Test: Leaves, Flowers and SeedsDokument2 SeitenReading Comprehension Test: Leaves, Flowers and Seedsalex92sekulicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Plant - Oh Say Can You Seed PDFDokument20 Seiten1 Plant - Oh Say Can You Seed PDFGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductionDokument8 SeitenIntroductionIzuku MidoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 P5 Science Semestral Assessment 2 Henry ParkDokument37 Seiten2021 P5 Science Semestral Assessment 2 Henry ParkAkeil Hamza Mohamed Najeeb (Bsss)Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Year - Unit 4 TestDokument1 Seite1st Year - Unit 4 TestFannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table Rocks Curriculum: Pollination Partners ObjectiveDokument10 SeitenTable Rocks Curriculum: Pollination Partners ObjectiveMAXIMO AROCUTIPA CATACORANoch keine Bewertungen
- Floral Nectar Composition of An Outcrossing Bean Species Mucuna Sempervirens Hemsl. (Fabaceae)Dokument6 SeitenFloral Nectar Composition of An Outcrossing Bean Species Mucuna Sempervirens Hemsl. (Fabaceae)Santiago AristizábalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flower Notes Grade 5Dokument8 SeitenFlower Notes Grade 5Catherine JeaneNoch keine Bewertungen