Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Maximum Deflection. Recall Your Lessons in Determining The Deflection of Determinate Beams From Structural Theory Subject) (
Hochgeladen von
senior highOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Maximum Deflection. Recall Your Lessons in Determining The Deflection of Determinate Beams From Structural Theory Subject) (
Hochgeladen von
senior highCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CE 18 - TIMBER DESIGN
Prelim/ Midterm Take Home Examination
Part I: Discussion
1. Give 5 disadvantages and 5 advantages of wood as a construction material.
2. Give and discuss at least 5 factors affecting the strength of wood.
3. What is meant by anisotropic property of wood? Explain how this affects the strength of wood.
4. Give and describe five defects on wood.
Part II: Calculation
1. A masonry terrace of 75 mm concrete surface with 25 mm cement tiles on 75 mm x 200 mm lumber
spaced at 300 mm on centers acting as simple beam with effective span of 3.6 m. Weight of wood is 7.5
kN/m3 and masonry to be 24 kN/m3. Ew= 13800 MPa. The allowable stresses are 14 MPa for bending, 0.80
Mpa for shear parallel to the grain and deflection is 1/360 of span.
a. Which of the following gives the uniform load it could support if bending stress controls. (Ans: 3.49
kN/m)
b. Which of the following gives the uniform load it could support if shear controls. (Ans: 3.61 kN/m)
c. Which of the following gives the uniform load it could support if deflection controls. (Ans: 2.32 kN/m)
2. Wooden joists are used to support a floor load of 6.95 kPa exclusive of its own weight. The joists will
have an effective span of 4.25 m and be placed at 0.40 m on centers. Weight of wood is 7.5 kN/m3.
a. Design the wooden joists so as not to exceed the allowable bending stress of 10.35 MPa.
b. Design the wooden joists so as not to exceed the allowable shearing stress of 0.85 MPa.
c. Design the wooden joists so as not to exceed the allowable deflection of 10 mm. Es=12135 MPa.
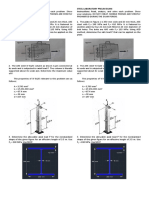
3. A wooden joist in a loading platform is 4 m. It has simple support at one end and at a point 1 m from
the other end. The supports are 3 m apart and the joists overhangs 1 m. The joist carry a load of 1200
N/m including its own weight.
a. Design the wooden joist so as not to exceed the allowable bending stress of 13.2 MPa. (Ans: 50 mm x
100 mm)
b. Design the wooden joist so as not to exceed the allowable shear stress of 0.65 MPa. (Ans: 50 mm x
100 mm)
c. Design the wooden joist so as not to exceed the allowable deflection of 20 mm. Assume E = 12300.
(Hint: Determine first the location where the maximum deflection occurs and solve for the value of
maximum deflection. Recall your lessons in determining the deflection of determinate beams from
Structural Theory subject) (Ans: 50 mm x 100 mm)
Part III: Designing
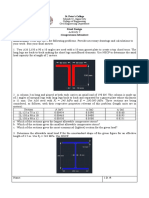
A wooden floor system is supported on four posts and measures 4.2 m x 3 m from center to center of
posts. It carries a live load of 4 kPa. Flooring is 25 mm x 400 mm in nominal dimensions. Joists are
supported by girders and spaced at 700 mm on centers along the 4.2 m side of the floor system. The
weight of wood is 6.8 kN/m3. Deflection I limited to 1/240 of the span of a member. The wood to be used
is Yakal @ 80% stress grade with the following design parameters: Bending and tension parallel to grain
= 24.5 MPa; Compression parallel to grain = 15.8 MPa; Compression perpendicular to grain = 6.27 MPa;
Shear parallel to grain = 2.49 MPa and E= 9.78 x 103 MPa.
Assuming the flooring and the joists to be simply supported and all adjustment factors for design stresses
are equal to 1.0, except for size and slenderness factors, investigate whether the spacing of the joists is
adequate. If adequate, design the floor joists using its given spacing. If not adequate, redesign the
spacing and design the joists using this new spacing.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ica ReviewerDokument23 SeitenIca ReviewerANGELO MARCO SERAPIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Requirements of Government Center and The Plaza Complex Plaza ComplexDokument7 SeitenDesign Requirements of Government Center and The Plaza Complex Plaza ComplexAdrian Emmanuel ValeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Plate 01: Proposed High-End Residential CondominiumDokument11 SeitenMajor Plate 01: Proposed High-End Residential CondominiumJan Adrian Atienza CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rule 7 8Dokument22 SeitenRule 7 8donna benitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 2 Lecture 5 LUMINAIRES (S)Dokument46 Seiten2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 2 Lecture 5 LUMINAIRES (S)Sophia Manila SillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIVISION 4 - Assignment Technical SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenDIVISION 4 - Assignment Technical SpecificationsPatrisha SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development Controls SolutionDokument17 SeitenDevelopment Controls Solutionart freakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design7 MP2 Triquetra ResearchDokument62 SeitenDesign7 MP2 Triquetra ResearchBenjamae MaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- BP 344 - Provisions Related To NBCDokument16 SeitenBP 344 - Provisions Related To NBCElison BaniquedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architect'S Schedule of Minimum Basic FeeDokument3 SeitenArchitect'S Schedule of Minimum Basic FeeMarlon NiduazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Considerations/Guidelines: A. Residential 1. Strictly Residential (Single Detached)Dokument5 SeitenDesign Considerations/Guidelines: A. Residential 1. Strictly Residential (Single Detached)James Phillip CustodioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm 01 - City ComfortsDokument122 SeitenMidterm 01 - City Comfortsjomarie apolinarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Quiz 2.1 Building Technology AR 390 ARCH32S3 Integregation Course For Architecture 1Dokument53 SeitenSuggested Quiz 2.1 Building Technology AR 390 ARCH32S3 Integregation Course For Architecture 1Mariane PadullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graduation Project ThesisDokument29 SeitenGraduation Project ThesismariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Architecture Thesis AbstractDokument1 SeiteSample Architecture Thesis AbstractJann MarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- GBDDokument17 SeitenGBDCristian CameroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foxell - 2003 - The Professionals' Choice The Future of The Built PDFDokument78 SeitenFoxell - 2003 - The Professionals' Choice The Future of The Built PDFmax marNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Building Code of The Philippines Chapter VII-IX SummaryDokument1 SeiteNational Building Code of The Philippines Chapter VII-IX SummaryJoshua CimanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProposalDokument11 SeitenProposaljhonggutaba67% (3)
- Bale Kultura: An Incorporation of Filipino Neo Vernacular Architecture On A World Class Multi-Use Convention CenterDokument9 SeitenBale Kultura: An Incorporation of Filipino Neo Vernacular Architecture On A World Class Multi-Use Convention CenterMary Alexien GamuacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1 3.2 Assign 1Dokument2 SeitenFigure 1 3.2 Assign 1piNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioclimaticDokument9 SeitenBioclimaticHaber HaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Redevelopment of Binirayan Sports Complex: Developing Adaptive Recreational Facilities For Sustainable Architecture" San Jose de Buenavista, AntiqueDokument12 Seiten"Redevelopment of Binirayan Sports Complex: Developing Adaptive Recreational Facilities For Sustainable Architecture" San Jose de Buenavista, AntiqueJohn Remmel Roga100% (1)
- A Challenge Faced by The Architecture and Construction IndustryDokument5 SeitenA Challenge Faced by The Architecture and Construction Industryem-tech100% (1)
- M2 Cw2a Attempt 2Dokument8 SeitenM2 Cw2a Attempt 2Ryan JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ica Reviewer ADokument13 SeitenIca Reviewer AqgbnarcisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toa 5 - Arkitektura MestizaDokument30 SeitenToa 5 - Arkitektura MestizaTricia InfanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binondo Case StudyDokument14 SeitenBinondo Case StudysamcaridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 2005 BLDGCONST1Dokument55 SeitenApril 2005 BLDGCONST1Markus Caraga NicartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of A Green Building Rating System For The PhilippinesDokument7 SeitenDevelopment of A Green Building Rating System For The PhilippinesChristopher Cruz de la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iloilo Convention CenterDokument14 SeitenIloilo Convention CenterMelissa de los SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Practice (Architecture Reviewer)Dokument6 SeitenProfessional Practice (Architecture Reviewer)Nicole De VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key-Ecommercial ExamDokument9 SeitenAnswer Key-Ecommercial ExamDonita Ginia AcuinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Design 10 Thesis Titles Bs Architecture 5-3Dokument2 SeitenArchitectural Design 10 Thesis Titles Bs Architecture 5-3Giannina PaglinawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parking and Loading Space RequirementsDokument2 SeitenParking and Loading Space Requirementsnanobots37Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 HousingDokument97 SeitenChapter 1 HousingMaDonna ZabalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.estimate Temp Bamboo BridgeDokument2 Seiten2.estimate Temp Bamboo Bridgejogesh moralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encouraging Use of Passive Cooling Ventilation and Atrium Architecture in Establishing Commercial and Housing Infrastructures in The Philippines Due To Limited Sources of Energy and Natural ResourcesDokument10 SeitenEncouraging Use of Passive Cooling Ventilation and Atrium Architecture in Establishing Commercial and Housing Infrastructures in The Philippines Due To Limited Sources of Energy and Natural ResourcesJohnBenedictRazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flyover Case StudyDokument12 SeitenFlyover Case Studyvrushankshah100% (1)
- Vol2 Zoning OrdinanceDokument118 SeitenVol2 Zoning OrdinanceJake BenliroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Views On Philippine Mining Service Cooperation in Pugalo, Alcoy, CebuDokument7 SeitenPublic Views On Philippine Mining Service Cooperation in Pugalo, Alcoy, CebuKimSon - baby SixteenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CITY OF LAS PIÑAS Basic ProfileDokument2 SeitenCITY OF LAS PIÑAS Basic Profilepepito manalotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rizal Technological University: Department of ArchitectureDokument1 SeiteRizal Technological University: Department of Architecturemaritthe moralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages, ProcedureDokument35 SeitenDefinition, Advantages, Disadvantages, ProcedureRica RegisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane Structure: Building TechnologyDokument10 SeitenMembrane Structure: Building Technologybernard louie abanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Basic Principles of Composition To Space Enclosing ElementsDokument12 Seiten7 Basic Principles of Composition To Space Enclosing ElementsElaiza Ann TaguseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rationale:: Basic Guideline For Chapter 7: Design FocusDokument2 SeitenRationale:: Basic Guideline For Chapter 7: Design FocusKaizer Khamomill T. MacatiagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Laws PDFDokument5 SeitenBuilding Laws PDFNikki Angela Lirio BercillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background Sample KineticDokument2 SeitenBackground Sample KineticMart Peeters CaledaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDokument4 SeitenTechnological Institute of The PhilippinesMel CoderesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis 1 Chapter 1Dokument19 SeitenThesis 1 Chapter 1Janissaries NivercaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV of Rudolph Villanueva - April 2016Dokument7 SeitenCV of Rudolph Villanueva - April 2016Rudolph Villanueva0% (1)
- Parking RequirementsDokument6 SeitenParking RequirementsRufina TiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction PaperDokument3 SeitenReaction PaperShania CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barangay Sta - AnaDokument90 SeitenBarangay Sta - AnaAbegail CaisedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entourage 5th Edition: A Tracing File and Color SourcebookVon EverandEntourage 5th Edition: A Tracing File and Color SourcebookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bending Stress and Shearing Stress in Timber BeamDokument98 SeitenBending Stress and Shearing Stress in Timber BeamCharizza Montarin CE100% (2)
- ProblemDokument3 SeitenProblemChrisneil DelosreyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Design ReviewDokument4 SeitenTimber Design ReviewRoben Casano78% (9)
- Enhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNDokument7 SeitenEnhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNChristian VillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Journal Lesson 13 - 23 - LisondraDokument5 SeitenStudy Journal Lesson 13 - 23 - Lisondrasenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics in Psychological TestingDokument27 SeitenBasics in Psychological Testingsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Journal Lesson 23-32 - LisondraDokument3 SeitenStudy Journal Lesson 23-32 - Lisondrasenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table MLZDokument1 SeitePeriodic Table MLZsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gantt Charts, Took Several Different Forms, Depending On TheirDokument5 SeitenGantt Charts, Took Several Different Forms, Depending On Theirsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literary Devices Elements TechniquesDokument38 SeitenLiterary Devices Elements Techniquessenior high100% (2)
- Butanol Proper Handling: Wash Thoroughly After Handling. Remove ContaminatedDokument3 SeitenButanol Proper Handling: Wash Thoroughly After Handling. Remove Contaminatedsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cryopreservation: Background/HistoryDokument3 SeitenCryopreservation: Background/Historysenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicomachean Ethics: Aristotle: Book 1: The Human GoodDokument4 SeitenNicomachean Ethics: Aristotle: Book 1: The Human Goodsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Running Head: DATA ANALYSIS 1Dokument4 SeitenRunning Head: DATA ANALYSIS 1senior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Summary of The Theology of The BodyDokument2 SeitenA Summary of The Theology of The Bodysenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Reflection On Genesis Chapters One To ThreeDokument1 SeiteA Reflection On Genesis Chapters One To Threesenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- DatusDokument3 SeitenDatussenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 2Dokument1 SeiteQuiz 2senior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil 1: γ, φ 3 3: K = 0.3 γ = 19.49 kN/mDokument1 SeiteSoil 1: γ, φ 3 3: K = 0.3 γ = 19.49 kN/msenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jota San JoaquinaDokument4 SeitenJota San Joaquinasenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- I MC S M F: Timber Advantages and Disadvantages of Wood Bending Stress in BeamsDokument4 SeitenI MC S M F: Timber Advantages and Disadvantages of Wood Bending Stress in Beamssenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinship, Marriage and The HouseholdDokument26 SeitenKinship, Marriage and The Householdsenior high100% (1)
- Steel Laboratory Prelim Exam PDFDokument1 SeiteSteel Laboratory Prelim Exam PDFsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Paulinian Values FrameworkDokument12 SeitenThe Paulinian Values Frameworksenior high100% (1)
- Term Paper CryotechnologyDokument14 SeitenTerm Paper Cryotechnologysenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21st LiteratureDokument14 Seiten21st Literaturesenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument3 SeitenLab 2senior high0% (2)
- Ucsp Family Tree FormatDokument1 SeiteUcsp Family Tree Formatsenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joseph Angelo Zerna: Dumaguete CityDokument2 SeitenJoseph Angelo Zerna: Dumaguete Citysenior highNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 - PDFsam - Conceptual Physics, Global EditionDokument13 Seiten8 - PDFsam - Conceptual Physics, Global EditionΒανικιώτης Νικήτας100% (1)
- Vehicle Aerodynamics PDFDokument15 SeitenVehicle Aerodynamics PDFRohit KoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Booklet 2012Dokument69 SeitenBooklet 2012Esteban RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SENIOR TWO PhysicsDokument7 SeitenSENIOR TWO PhysicsNdawula Isaac100% (1)
- History of Buckling of ColumnDokument10 SeitenHistory of Buckling of ColumnSorin Viorel CrainicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics NotesDokument3 SeitenThermodynamics Notesseema sahniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ampacity Calculation For Case # 05Dokument64 SeitenAmpacity Calculation For Case # 05Erfan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 07 23 JR.C 120 Jee Adv (2021 p1) Wta 03 Keysheet With SolutionsDokument10 Seiten02 07 23 JR.C 120 Jee Adv (2021 p1) Wta 03 Keysheet With SolutionsGururaj OmkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Response of A U Tube ManometerDokument8 SeitenDynamic Response of A U Tube ManometerRitikranjan YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Kertas 2 KimiaDokument9 SeitenSkema Kertas 2 KimiaariesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Report On Industrial Training (Siwes) by Fagorola Eniitan OlawoleDokument46 SeitenTechnical Report On Industrial Training (Siwes) by Fagorola Eniitan OlawoleOkorie Victor100% (2)
- Formation of Bubbles-2019Dokument68 SeitenFormation of Bubbles-201902indexchosenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testingcommissioning Blogspot QaDokument5 SeitenTestingcommissioning Blogspot QaratheeshkumardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear Strength and Dilatancy Behaviour of Sand - Tyre Chip MixturesDokument12 SeitenShear Strength and Dilatancy Behaviour of Sand - Tyre Chip MixturesHassan GhanemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromacnetic WavesDokument13 SeitenElectromacnetic WavesChaztan RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 17 Advent of Modern Physics PDFDokument8 SeitenChapter - 17 Advent of Modern Physics PDFsingoj.bhargava charyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 Chemistry Standardised Test For Science Stream (SPM)Dokument7 Seiten2018 Chemistry Standardised Test For Science Stream (SPM)carnationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument35 SeitenChapter 2younessinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Unit PlanDokument5 SeitenPhysics Unit Planapi-209389080Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6 MeteorologyDokument168 Seiten6 MeteorologyShann Xad100% (1)
- Inertial Navigation SystemDokument34 SeitenInertial Navigation Systemsameer7mohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Resistance To GroundDokument10 SeitenCalculation of Resistance To Groundalfonso.parker50% (2)
- Lesson 1 Exercises Problem No. 3-1Dokument2 SeitenLesson 1 Exercises Problem No. 3-1Prince BiscochoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/msDokument16 SeitenMultiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/mssliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fluencia e BookDokument141 SeitenThe Fluencia e Bookali noorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flashcards - Topic 7 Stars - Edexcel Physics GCSEDokument29 SeitenFlashcards - Topic 7 Stars - Edexcel Physics GCSEPhyo han kyaw PhillipNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Air Cycles PDFDokument18 SeitenAC Air Cycles PDFJoJa JoJa100% (1)
- UPMT 2015 BrochureDokument49 SeitenUPMT 2015 BrochureMota ChashmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 3 Rapidly Varied FlowDokument8 SeitenChapter - 3 Rapidly Varied FlowAbdulrasheed BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech Eng HeDokument12 SeitenMech Eng HeAtanasio PerezNoch keine Bewertungen