Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Charter Poster - Final
Hochgeladen von
api-485309489Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Charter Poster - Final
Hochgeladen von
api-485309489Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
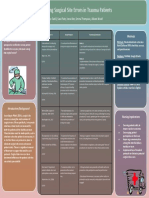
Reducing Falls Among Targeted Patients with Toileting Needs
Taylor Ballard, Shaila Ellis, Deisy Herrera, Brooke Roane, Tracey Tran
Bon Secours Memorial College of Nursing
Abstract Data and Analysis of the Issue Root Cause Proposed Solution
In-hospital falls are a critical problem to patient safety. Insufficient compliance by patient care staff
The prevalence of falls associated with toileting on ❑ On CVSU, patients fall rates are above Hypothesis: We predict that if targeted toileting
related to targeted toileting, as evidence by development is supported by staff nurses and
step-down care units range from 38% to 47% (Fridman, Magnet mean goal based on National
2019). On the Cardiovascular Services Unit (CVSU), fall NDNQI scores and nursing staff not patient care techs on the unit then fall rates will
Database of Nursing Quality Indicators
rates are above Magnet mean. To ensure the fall implementing the visual management board. decrease by 5% by Quarter 2 (2020).
(NDNQI)
prevention initiatives are optimized, consistent, and Contributing barriers:
❑ The average patient who suffers a fall is:
transformational, the current practice was ❑ Lack of communication ❑ Unit based council
investigated. The purpose of this project was to ▪ A&O x4
❑ Lack of awareness ❑ Toileting shift champion (PNAP points)
explore the gap between the current practice of ▪ Ambulating to or from the
targeted toileting and patient fall rates. Current
❑ Competing priorities ❑ Targeted toileting check off list outside of all
bathroom
targeting toileting guidelines are not being fully ❑ Staffing challenges targeted toileted patient rooms
❑ Variables contributing to falls include:
implemented consistently. We predict that if targeted
toileting development is supported by staff nurses and
▪ New medication regimens Logistics
▪ Immobility - audits - incentives - required education Evidence: According to Tzeng (2010), it is
patient care techs on the unit then fall rates will
decrease. ▪ Nurses and patient care techs - monthly unit meetings important to examine and understand barriers
report inconsistencies with - improved NDNQI and apply safety equipment to the patients at
Introduction and Description of the quarterly scores risk.
implementation of targeted Stakeholders
Issue toileting. - nurses - patient care technicians
Macro Description: ▪ Education with patients. - nurse manager - patients
-Toileted-related activities are associated with 38% to ▪ Unmotivated staff buy-in - hospital leadership - fall committee Conclusion
47% of patient falls (Fridman, 2019). Current targeted-toileting guidelines are not
-The prevalence of falls in acute care facilities range Potential Costs being implemented consistently. With improved
from 3.3 to 11.5 falls per 1000 patients days (Fridman, -dry erase markers - laminated check off list
- incentives - compensated meeting times engagement of CVSU staff, we hypothesize a
2019).
decrease in fall rates.
Micro Description:
-According to the NDNQI report, during the 8 quarters Timeline
from Quarter 2 (2017) to Quarter 1 (2019) patient fall - Nov 1, 2019: I-aspire module completion References
rates were above national Magnet hospital mean. - Dec 1, 2019: assign shift champion Fridman, V. (2019). Redesigning a Fall Prevention Program in
- Out of 8 quarters, CVSU outperformed the magnet - Jan 2020: evaluation of staff members Acute Care: Building on Evidence. Clinics in geriatric medicine,
- Mar 2020: evaluation of unit’s compliance
mean once (NDNQI). 35(2), 265-271. doi:10.1016/j.cger.2019.01.006
- Falls with injury: CVSU outperformed the magnet
Data Collection Tzeng, H. M. (2010). Understanding the prevalence of inpatient
mean 3 out of the 8 quarters (NDNQI).
- NDNQI quarterly scores falls associated with toileting in adult acute care settings.
- Reported falls Journal of Nursing Care Quality, 25(1), 22-30. doi:
10.1097/NCQ.0b013e3181afa321
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cert Nurse Assist Skills ChecklistDokument3 SeitenCert Nurse Assist Skills ChecklistnorthweststaffingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geriatric Anxiety Scale v2.0 FINALDokument2 SeitenGeriatric Anxiety Scale v2.0 FINALpujipurwaningsih67% (3)
- Modified Caregiver Strain Index assessment toolDokument2 SeitenModified Caregiver Strain Index assessment toolesbat07100% (1)
- Ontario Surgical and Diagnostic RecoveryDokument10 SeitenOntario Surgical and Diagnostic RecoveryIsaac Callan, Global NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step Guide To Protocol Based CareDokument19 SeitenStep Guide To Protocol Based CareAbdus Subhan A TakildarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMEA 2012 Fall PreventionDokument13 SeitenFMEA 2012 Fall PreventionBenny M Ikhwan H100% (2)
- Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy A Systematic Review 2011Dokument9 SeitenCerebral Amyloid Angiopathy A Systematic Review 2011Jaime Arevalo PanduroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument4 SeitenDecreased Cardiac OutputChristine MatasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Historical Perspective in Aging and GerontologyDokument22 SeitenA Historical Perspective in Aging and GerontologyMa Mayla Imelda LapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healing Gardens FinalDokument20 SeitenHealing Gardens FinalMohd Salahuddin100% (1)
- Charter Poster - FinalDokument1 SeiteCharter Poster - Finalapi-485309966Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qi Poster FinalDokument1 SeiteQi Poster Finalapi-475182877Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qi PosterDokument1 SeiteQi Posterapi-478583234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qi PosterDokument1 SeiteQi Posterapi-472233285Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qi Nur SynDokument1 SeiteQi Nur Synapi-508588133Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qi Project SaguarogroupDokument15 SeitenQi Project Saguarogroupapi-708256548Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCM118 Week11Dokument6 SeitenNCM118 Week11Loren SarigumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effectiveness-Matters-August-2014-Falls in HospitalsDokument4 SeitenEffectiveness-Matters-August-2014-Falls in HospitalsKibsJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cqi PresentationDokument17 SeitenCqi Presentationapi-580425291Noch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Taibah University Medical SciencesDokument9 SeitenJournal of Taibah University Medical SciencesrobertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 2011 Infusion Nursing Standards of PracticeDokument12 SeitenThe 2011 Infusion Nursing Standards of PracticeSugeng PrakosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruiting The Next Generation: Applying A Values-Based Approach To RecruitmentDokument6 SeitenRecruiting The Next Generation: Applying A Values-Based Approach To RecruitmentScribDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Improvement Case 1Dokument23 SeitenQuality Improvement Case 1api-534814911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nurs 390 Group 8 Project 2Dokument31 SeitenNurs 390 Group 8 Project 2api-621660715Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qi Project SaguarogroupDokument15 SeitenQi Project Saguarogroupapi-708278194Noch keine Bewertungen
- POMR Introduction Updates 2022Dokument35 SeitenPOMR Introduction Updates 2022WN ChokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triyana2017efek of CCT On Coverage and Quality of Atenalatal Care IndonesiaDokument10 SeitenTriyana2017efek of CCT On Coverage and Quality of Atenalatal Care IndonesiaMuhammad dzaky AdzhanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID 19 Stages InfographicDokument1 SeiteCOVID 19 Stages InfographicMika GrantozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Room Safer Transfer ofDokument8 SeitenEmergency Room Safer Transfer ofHerdy AdrianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Poster - 2Dokument1 SeiteResearch Poster - 2api-332714810Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4140 QI PosterDokument1 Seite4140 QI PosterZoe RaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP Project 2Dokument31 SeitenPP Project 2api-620262107Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ulcers 4Dokument5 SeitenUlcers 4Diego CastelblancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparison of Hand Hygiene Compliance and Attitudes of Health Care WorkersDokument1 SeiteA Comparison of Hand Hygiene Compliance and Attitudes of Health Care WorkersSarah JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRE-OPERATIVE SCREENING RECOMMENDATIONSDokument7 SeitenPRE-OPERATIVE SCREENING RECOMMENDATIONSBernice EbbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group A FinalDokument2 SeitenGroup A Finalapi-380281979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Incidence of In-Hospital Falls in Geriatric Patients Before and After The Introduction of An Interdisciplinary Team-Based Fall-Prevention InterventionDokument7 SeitenIncidence of In-Hospital Falls in Geriatric Patients Before and After The Introduction of An Interdisciplinary Team-Based Fall-Prevention InterventionDiego Quidequeo ReffersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-12 pp120-139 FINALDokument20 SeitenChapter-12 pp120-139 FINALRaghav SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bmjopen 2015 009650supp3 PDFDokument1 SeiteBmjopen 2015 009650supp3 PDFRodiani MoekroniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms. Andres - PHC Case StudyDokument48 SeitenMs. Andres - PHC Case StudyJBLMGH EMPLOYEESCLINICNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing the Patient Safety Incident Management System (DPSIMSDokument18 SeitenDeveloping the Patient Safety Incident Management System (DPSIMSDante820Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dessertation PresentationDokument9 SeitenDessertation PresentationKinjal VasavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7 Assignment-Capa Presentation LdatuDokument11 SeitenModule 7 Assignment-Capa Presentation Ldatuapi-682342806Noch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Surgical Safety and Nontechnical Skills in Variable-Resource Contexts: A Novel Educational CurriculumDokument8 SeitenImproving Surgical Safety and Nontechnical Skills in Variable-Resource Contexts: A Novel Educational CurriculumIsma WahyuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Situation, Background, AssessmentDokument25 SeitenSituation, Background, AssessmentFemtoson georgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of A Trauma Care BundleDokument7 SeitenDesign and Implementation of A Trauma Care BundleNi Nyoman AstriningsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feature Article: Use of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis To Improve Emergency Department Handoff ProcessesDokument10 SeitenFeature Article: Use of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis To Improve Emergency Department Handoff ProcessesAnatha ChrisciliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interventions To Improve The Quality of Cataract Services: Protocol For A Global Scoping ReviewDokument7 SeitenInterventions To Improve The Quality of Cataract Services: Protocol For A Global Scoping Reviewanita adrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PosterDokument3 SeitenPosterCamille ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SWOT Analysis of The Emergency ServiceDokument20 SeitenSWOT Analysis of The Emergency ServiceScribdTranslationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relationship Between General Practice Capitation Funding and The Quality of Primary Care in England: A Cross-Sectional, 3 - Year StudyDokument11 SeitenRelationship Between General Practice Capitation Funding and The Quality of Primary Care in England: A Cross-Sectional, 3 - Year Studyrizna rudiyaUchNoch keine Bewertungen
- BeneshsDokument17 SeitenBeneshsapi-708800698Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Care Toolkit 1 - HandoverDokument4 SeitenAcute Care Toolkit 1 - Handoveranurag katiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster TemplateDokument1 SeitePoster Templateapi-607378712Noch keine Bewertungen
- NURS FPX 6016 Assessment 2 Quality Improvement Initiative EvaluationDokument5 SeitenNURS FPX 6016 Assessment 2 Quality Improvement Initiative Evaluationlilykevin075Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gold Standard of Critical Care Nursing: Dr. Intan Idiana Hasan Universiti Sains MalaysiaDokument33 SeitenGold Standard of Critical Care Nursing: Dr. Intan Idiana Hasan Universiti Sains MalaysiaAlmaMickeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Patient HandlingDokument2 SeitenSafe Patient Handlingapi-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shift Report ProjectDokument1 SeiteShift Report Projectapi-347777703Noch keine Bewertungen
- A care bundle approach to falls preventionDokument3 SeitenA care bundle approach to falls preventionSheena CabrilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1502 Ce TestDokument4 Seiten1502 Ce TestGuswantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BHA4002 Presentation1Dokument8 SeitenBHA4002 Presentation1Pamela SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comprehensive Double Loop Activities For.12Dokument5 SeitenThe Comprehensive Double Loop Activities For.12Mishell TelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Implementation of Focus-Pdca Model To Decrease Patients' Length of Stay in Emergency DepartmentDokument5 SeitenEffects of Implementation of Focus-Pdca Model To Decrease Patients' Length of Stay in Emergency DepartmentMuhammad RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charisma Medical SoftwareDokument8 SeitenCharisma Medical SoftwareTotal SoftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Intent Quality Indicator (Qi) Criteria For Data MeasurementDokument4 SeitenSummary of Intent Quality Indicator (Qi) Criteria For Data Measurementapi-349641525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Using Tracking Tools To Improve Patient Flow in Hospitals: Executive SummaryDokument21 SeitenUsing Tracking Tools To Improve Patient Flow in Hospitals: Executive SummaryHughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weebly-Final AnalysisDokument4 SeitenWeebly-Final Analysisapi-485309489Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shaila Ellis Integrative ReviewDokument23 SeitenShaila Ellis Integrative Reviewapi-485309489Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shaila Ellis Resume For WeeblyDokument3 SeitenShaila Ellis Resume For Weeblyapi-485309489Noch keine Bewertungen
- Post-Practicum Reflection For Care-A-VanDokument4 SeitenPost-Practicum Reflection For Care-A-Vanapi-485309489Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advocacy MethodDokument2 SeitenAdvocacy Methodapi-485309489Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nur 4140-Shaila Ellis Philospohy of Nursing Paper RevisedDokument9 SeitenNur 4140-Shaila Ellis Philospohy of Nursing Paper Revisedapi-485309489Noch keine Bewertungen
- K Saz Resume 2021 - RNDokument1 SeiteK Saz Resume 2021 - RNapi-515998842Noch keine Bewertungen
- PM201428 (8) Brinkman StoppelenburgDokument27 SeitenPM201428 (8) Brinkman StoppelenburgAnanda Soraya B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Citalopram HydrobromideDokument2 SeitenCitalopram HydrobromideDiana PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Health Care of The Older AdultDokument30 SeitenChapter 12 Health Care of The Older AdultPearl DiBerardinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Health Status of Geriatric Populatio PDFDokument6 SeitenThe Health Status of Geriatric Populatio PDFMSKCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental enrichment boosts brain health for aging dogs and catsDokument4 SeitenEnvironmental enrichment boosts brain health for aging dogs and catsAntonio SessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epidemiologia Del Adulto MayorDokument17 SeitenEpidemiologia Del Adulto MayorDiana Milena Poveda Arias100% (1)
- PoCUS Program 1016Dokument3 SeitenPoCUS Program 1016Josh BurkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ClinicalOpiateWithdrawalScale PDFDokument2 SeitenClinicalOpiateWithdrawalScale PDFRajamanitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi PsychiatryDokument7 SeitenDelhi PsychiatryPrarthana SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cv. Dr. Saldy YusufDokument6 SeitenCv. Dr. Saldy YusufMuhammad FaturrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotic NursingDokument7 SeitenRobotic Nursingpramod kumawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- AgeFusionBook LoresDokument81 SeitenAgeFusionBook LoresSolentDesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Gerontologi 6Dokument3 SeitenJurnal Gerontologi 6HarfiMaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Management PlanDokument4 SeitenDaily Management PlanmirojsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of BedsoresDokument5 SeitenPrevention of BedsoresMadhu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Geriatric Medicine in MalaysiaDokument4 SeitenHistory of Geriatric Medicine in MalaysiaSarinahNoch keine Bewertungen
- HospisDokument9 SeitenHospiskevin94Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Dementia Care at HomeDokument18 SeitenA Guide To Dementia Care at Homehelping_hands100% (1)
- Gerontological Nursing History and RolesDokument5 SeitenGerontological Nursing History and RolesNjideka A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Collecting A Pediatric Urine SpecimenDokument2 SeitenCollecting A Pediatric Urine SpecimenLarry CornejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook Geriatric Psychiatry 09 PDFDokument23 SeitenTextbook Geriatric Psychiatry 09 PDFLydia AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Role Is Launched: Heather M. Monaghan, RN, MHSCDokument3 SeitenA New Role Is Launched: Heather M. Monaghan, RN, MHSCKimberly Bundley-JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen