Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
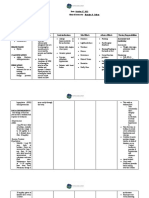
Presented By: Shaikh Yusuf Babu M.SC 2 Year (Industrial Automation) J.E.S College Jalna-431203
Hochgeladen von
aman lakherwal0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten20 SeitenThe document proposes a low-cost, wireless remote health monitoring system using sensors to measure vital signs like temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and lung capacity. The sensors transmit data to a personal monitoring device and then to an online server, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely. This reduces the need for frequent in-person visits and makes healthcare more accessible, especially for those in rural areas. The system aims to make monitoring simpler, more efficient, and affordable.
Originalbeschreibung:
nhi
Originaltitel
bh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document proposes a low-cost, wireless remote health monitoring system using sensors to measure vital signs like temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and lung capacity. The sensors transmit data to a personal monitoring device and then to an online server, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely. This reduces the need for frequent in-person visits and makes healthcare more accessible, especially for those in rural areas. The system aims to make monitoring simpler, more efficient, and affordable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten20 SeitenPresented By: Shaikh Yusuf Babu M.SC 2 Year (Industrial Automation) J.E.S College Jalna-431203
Hochgeladen von
aman lakherwalThe document proposes a low-cost, wireless remote health monitoring system using sensors to measure vital signs like temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and lung capacity. The sensors transmit data to a personal monitoring device and then to an online server, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely. This reduces the need for frequent in-person visits and makes healthcare more accessible, especially for those in rural areas. The system aims to make monitoring simpler, more efficient, and affordable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 20
Presented by: Shaikh Yusuf Babu
M.Sc 2nd Year (Industrial Automation)
J.E.S College Jalna-431203.
In today’s scenario, health care problems are increasing at
a very high pace like coronary heart diseases, obesity, lung
failures causing death rate of 7.2 million people per year
hence it is the need of the hour to overcome from all such
problems.
Our health care providers have developed an intelligent
and low cost health monitoring system to provide more
comfortable life for people suffering from such chronic
diseases using advanced technologies like wireless
communications, embedded computations, wearable and
portable remote health monitoring system. As a result need
for repetitive doctor visits are decreased as the
information reaches from everywhere. Implementation of
wireless communication technologies in monitoring systems
is now easier because of its patient friendly manner
Wireless technology is ruling worldwide and has invaded the
medical area with wide range of scope and capabilities.
To monitor continuous Medicare conditions of patient using
existing wireless technologies were quite convoluted.
To overcome this, we are proposing a change in wireless
sensor technology by designing a biomedical monitoring
device comprised of different sensors to acquire the
information regarding human body temperature, heart rate,
blood pressure, lung capacity which is sent to a personal
vitality measurement system and further transmit this
information on an IOT server which is user accessible over
the internet.
Various Biomedical sensors have been used as
AD8232 ECG sensor is used for remote ECG
monitoring by connecting ECG electrodes to the
recording unit with cables.
Blood pressure sensor (4811) is used to measure
systolic and diastolic pressure and pulse rate for
few seconds.
LM35 temperature sensor is used to measure skin
surface temperature as it is more accurate than a
thermistor and lung capacity is measured using an
arrangement of fan with motor like spirometry.
Current System Medical science is expanding by leaps and
bounds in the last couple of decades for their considerable
aim towards wireless and e-health monitoring systems
providing remote monitoring of patients. But the tools used
to deal with health conditions are tedious to maintain and
limited to specific number of parameters. The systems
being complex and laborious to operate also raise the cost
of health care services and hospital expenses which is not
affordable to economically challenged community.
In early 1960’s, Kadish used a system, which includes
several things namely glucose sensor, a processor and a
pump to control glycerin in patients with diabetes. To
manage complex situations, the pump will need several
MEMS based sensors to monitor more parameters like
glucose, heart rate, temperature and ECG etc.
BLOOD PRESSURE:-
Blood pressure is the pressure of the blood in the
arteries. The heart contracts and expands when
it beats. Contraction pushes the blood through
the arteries to body, and this force creates
pressure on the arteries. Blood pressure is
measured as high blood pressure and low blood
pressure which called systolic pressure (as the
heart beats) and the diastolic pressure (as the
heart relaxes between beats). The unit which
measures this is called Sphygmomanometer.
Systolic (mm Hg) Diastolic (mm Hg)
Hypotension < 90 < 60
Desired 90–119 60–79
Prehypertension 120–139 80–89
Stage 1 Hypertension 140–159 90–99
Stage 2 Hypertension 160–179 100–109
Hypertensive Crisis ≥ 180 ≥ 110
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the
process of recording the electrical activity of
the heart over a period of time using
electrodes placed on the skin.
These electrodes detect the tiny electrical
changes on the skin that arise from the heart
muscle's electro-physiologic pattern of
depolarizing during each heartbeat. It is a
very commonly performed cardiology test.
Lungcapacity is the amount of air your lungs
can hold or the combination of different lung
volumes.
The lung capacity is measured by blowing a
fan with the maximum strength one can, and
the power generated in voltage will help to
let us know that with how much strength the
one has blown the air fan. If the level
reaches out of the prior level set, then the
patient is having problem in lungs.
Programming languages for the visual arts which can
help any digital artist create complex animations and
interactive installations. Processing is a powerful and
fun to use programming language that was initially
created to help coding enthusiasts learn the basics of
programming but since then, it has evolved into
something much more elaborate.
Now it is an open source development tool which
emphasizes on the visual representation of the code,
targeting both advanced users and professionals. The
language builds on the Java language, but uses a
simplified syntax and graphics programming model. It
has User-friendly interface, it retains the advantages
of simplicity. The main window is comprised from
commonly 13 found elements in any code editor,
namely a toolbar, project tabs, text editor, message
area and a console.
The Internet of Things (IoT), also called internet
of everything. The network is formed by physical
objects or "things" which are implanted with
electronics, software, sensors. Things or the
Objects which are connect through IoT have
ability to connect with the things for data
exchange with the operator or any other
connected devices. IoT is a International's Global
Standards Initiative. The Internet of Things
allows the connected things or objects to be
identified and controlled remotely across the
network infrastructure. It helps in creating
opportunities for more direct integration
between the physical world and computer-based
systems.
Arduino is an open source physical computing
platform based on a simple input/output (I/O) board
and a development environment that implements the
Processing language. Arduino can be used to develop
standalone interactive objects or can be connected to
software on your computer. Arduino hardware is an
open-source circuit board with a microprocessor and
input/output (I/O) pins for communication and
controlling physical objects (LED, servos, buttons,
etc.). The board will typically be powered via USB or
an external power supply which in turn allows it to
power other hardware and sensors.
In the above mentioned system we have
proposed a health monitoring system which is
GSM based.
userfriendly and bridges gap between doctor
and patients.
The system is simple, Power efficient.
Practical application of the system is
superfine in rural areas as there would be no
need for the patients to get their continuous
follow-ups.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Arduino Based Wearable Health Care DevicesDokument20 SeitenArduino Based Wearable Health Care Devicesrock star100% (1)
- 11-06-2022-1654946434-6-.-6. ENGG - AN IOT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM (ECG, TEMPERATURE, HEARTBEAT, SKIN & SpO2) PDFDokument10 Seiten11-06-2022-1654946434-6-.-6. ENGG - AN IOT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM (ECG, TEMPERATURE, HEARTBEAT, SKIN & SpO2) PDFImpact JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Virtual Doctor System For Health Monitoring FinalDokument23 SeitenOn Virtual Doctor System For Health Monitoring FinalChetu ChethanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Sem ProjectDokument29 Seiten8th Sem ProjectRashmi B ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iot: Heart Rate Monitoring Tool Using Android With Alert Messanger Telegram SystemDokument7 SeitenIot: Heart Rate Monitoring Tool Using Android With Alert Messanger Telegram Systemriki capoeiristaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heartbeat and Temperature Monitoring SystemDokument7 SeitenHeartbeat and Temperature Monitoring SystemIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holy Mary Institute of Technology & ScienceDokument62 SeitenHoly Mary Institute of Technology & Sciencesiddharth raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Real Time Cardiac Arrhythmia Classification System With Wearable Sensor NetworksDokument27 SeitenA Real Time Cardiac Arrhythmia Classification System With Wearable Sensor NetworksSubash S VersatileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iot Based Android Health Care Management SystemDokument10 SeitenIot Based Android Health Care Management System2306 Karthick TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet of Things IoT Based Healthcare Monitoring System Using NodeMCU and Arduino UNODokument5 SeitenInternet of Things IoT Based Healthcare Monitoring System Using NodeMCU and Arduino UNOEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Health Monitoring System of Patient Using IoTDokument36 SeitenHealth Monitoring System of Patient Using IoTNaga Ananth100% (1)
- Research Paper 01Dokument11 SeitenResearch Paper 01esha imranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Patient Monitoring System Using Labview: IjarcceDokument3 SeitenReal Time Patient Monitoring System Using Labview: IjarcceHari KishorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutsvangwa ProjectDokument9 SeitenMutsvangwa ProjectmorelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Based Health Monitoring SystemDokument2 SeitenIOT Based Health Monitoring SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Based Health Monitoring System UsingDokument8 SeitenIOT Based Health Monitoring System UsingDoctor IggyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Based Health Monitoring System Using Arduino UNODokument8 SeitenIOT Based Health Monitoring System Using Arduino UNOIJRASETPublications100% (1)
- Ekg Mobile: Advanced Science and Technology Letters Vol.49 (Softtech 2014), Pp.95-100Dokument6 SeitenEkg Mobile: Advanced Science and Technology Letters Vol.49 (Softtech 2014), Pp.95-100RockyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IoT Based ECG Monitoring SystemDokument4 SeitenIoT Based ECG Monitoring SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An IoT Based Patient Health Monitoring S PDFDokument9 SeitenAn IoT Based Patient Health Monitoring S PDFJoko RifaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Health Care SystemDokument28 SeitenHuman Health Care SystemRethumon Baby100% (1)
- Heart Rate 2018Dokument5 SeitenHeart Rate 2018Subha ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM - DakshDokument17 SeitenIOT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM - DakshMohit MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time ECG and Saline Level Monitoring System Using Arduino UNO ProcessorDokument5 SeitenReal Time ECG and Saline Level Monitoring System Using Arduino UNO ProcessorstevebensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iaetsd-Mobile Icu Using AndroidDokument5 SeitenIaetsd-Mobile Icu Using AndroidiaetsdiaetsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Based Wearable Health Monitoring System For Pregnant LadiesDokument5 SeitenIOT Based Wearable Health Monitoring System For Pregnant LadiesPenrose LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase 1-1Dokument15 SeitenPhase 1-1Ammu Tanu Ammu TanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG2Dokument21 SeitenECG2spNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis: E-Ventilator (Emergency Ventilator) For Emergency SituationsDokument4 SeitenSynopsis: E-Ventilator (Emergency Ventilator) For Emergency SituationsDevika GhadageNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Patient Health Monitoring System: Ahmed Abdulkadir Ibrahim, Wang ZhuopengDokument4 SeitenIOT Patient Health Monitoring System: Ahmed Abdulkadir Ibrahim, Wang ZhuopengSung Yong JinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Health Tracker: Ishita, Mansi Kaushik & Palak KhareDokument6 SeitenPersonal Health Tracker: Ishita, Mansi Kaushik & Palak Khareiaset123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iot Based System For Heart Rate Monitoring IJERTV9IS070673Dokument9 SeitenIot Based System For Heart Rate Monitoring IJERTV9IS070673Penrose LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Rate Monitoring System Using FingeDokument4 SeitenHeart Rate Monitoring System Using FingeAndreea Ilie100% (1)
- Proposal Presentation Group BDokument20 SeitenProposal Presentation Group BRajkishor YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Health Monitoring System Using Iot and AndroidDokument3 SeitenPatient Health Monitoring System Using Iot and AndroidJournal 4 Research100% (3)
- A Secure Iot Based Modern Health Care System Using RpiDokument20 SeitenA Secure Iot Based Modern Health Care System Using RpiAnonymous F3JDwsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Bio-Medical Signal Monitoring SystemDokument4 SeitenSmart Bio-Medical Signal Monitoring SystemIJSTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijstev5i10015 2MDokument5 SeitenIjstev5i10015 2MHussien RaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Health Monitoring System Through Iot Using SensorsDokument6 SeitenReal Time Health Monitoring System Through Iot Using Sensorsقابوس الليثيNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument4 SeitenAbstractVaibhav GawandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paperv 2Dokument5 SeitenPaperv 2Smart ClasseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Self Health Monitoring System: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Omputer and Ommunication NgineeringDokument8 SeitenReal Time Self Health Monitoring System: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Omputer and Ommunication NgineeringJoy loboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Car Parking System Using IotDokument5 SeitenSmart Car Parking System Using IotAkbar aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advancement in Patient Monitoring SystemDokument23 SeitenAdvancement in Patient Monitoring SystemNawaz Sherif NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document - 2 - 6ob9 - 05042017 3Dokument4 SeitenDocument - 2 - 6ob9 - 05042017 3SEA163TANISHA POOJARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of The Project: Department of ECE, MRITS 1Dokument55 SeitenOverview of The Project: Department of ECE, MRITS 1dulipala alekya gupthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEMINAR1Dokument9 SeitenSEMINAR1SOMOSCONoch keine Bewertungen
- Pervasive ComputingDokument8 SeitenPervasive ComputingMadinah MiswakhNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeartBeat Rate and Temperature Monitoring Device 1 EDITEDDokument57 SeitenHeartBeat Rate and Temperature Monitoring Device 1 EDITEDFeddy Micheal FeddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Document 411Dokument60 SeitenProject Document 411PrudhviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vital Signs Monitoring in Human BodyDokument4 SeitenVital Signs Monitoring in Human BodyEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- nhịp tim iotDokument8 Seitennhịp tim iotxuanhoangmedisunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digicare System-Project PaperDokument6 SeitenDigicare System-Project PaperRichik SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Health Acquistion, Transmission & Monitoring SystemDokument4 SeitenE-Health Acquistion, Transmission & Monitoring SystemKethavath Sakrunaik KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of GSM Module in Wireless ECGDokument7 SeitenApplications of GSM Module in Wireless ECGAbd TashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9B Documentation (MAJOR)Dokument55 Seiten9B Documentation (MAJOR)dulipala alekya gupthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irjet V4i5119 PDFDokument7 SeitenIrjet V4i5119 PDFAnonymous plQ7aHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Physiological Parameter Monitoring and Recording SystemDokument11 SeitenWireless Physiological Parameter Monitoring and Recording SystemInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Health Monitoring System Using Iot Devices: Project Reference No.: 40S - Be - 1752Dokument4 SeitenPatient Health Monitoring System Using Iot Devices: Project Reference No.: 40S - Be - 1752Vignesh JayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 35, Urgent Care Imaging and InterpretationVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 35, Urgent Care Imaging and InterpretationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Research HypertensionDokument4 SeitenClinical Research HypertensionJay Linus Rante SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 47 YearDokument4 SeitenA 47 Yearwira rila zulmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood PressureDokument11 SeitenBlood PressureHilma NadzifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diadens-T & Diadens-Dt ManualDokument95 SeitenDiadens-T & Diadens-Dt ManuallopansNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP Preeclampsia RevisedDokument32 SeitenCP Preeclampsia RevisedTessa Grace PugonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Preeclampsia (A)Dokument6 SeitenNCP - Preeclampsia (A)Ronel ResurricionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Related Literary RiviewDokument6 SeitenRelated Literary RiviewShakira Louise BranzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endoscopy of GI TractDokument358 SeitenEndoscopy of GI TractEngin UçarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSNS 263 - Nursing - Pavithra SamaranayakeDokument9 SeitenHSNS 263 - Nursing - Pavithra SamaranayakeHarshana Sandaruwan SomarathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insel11e - ppt13 Effects Regular ExerciseDokument24 SeitenInsel11e - ppt13 Effects Regular ExerciseThalia SandersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti HypertensionDokument63 SeitenAnti HypertensionAngga CahyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac RehabilitationDokument510 SeitenCardiac RehabilitationDamir Celik100% (1)
- Terazosin Drug Study Group 4Dokument3 SeitenTerazosin Drug Study Group 4Michelle Dona MirallesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthy Foods Fact Versus Fiction-ManteshDokument320 SeitenHealthy Foods Fact Versus Fiction-ManteshRodrigo Durán Cuiñas100% (7)
- Hypertension NotesDokument5 SeitenHypertension NotesNkosi JupiterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge PlanningDokument2 SeitenDischarge PlanningsyifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems Associated With Chronic IllnessDokument8 SeitenProblems Associated With Chronic IllnessMeryville JacildoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambulatory Blood Pressure MonitoringDokument5 SeitenAmbulatory Blood Pressure Monitoringابو عبد الرحمنNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal MidtermDokument253 SeitenMaternal MidtermTrishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGLISHHALF YEARLY SAMPLE PAPER CLASS 12.docx 2Dokument9 SeitenENGLISHHALF YEARLY SAMPLE PAPER CLASS 12.docx 2kunalbestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doctors OET Writing Practice TestDokument3 SeitenDoctors OET Writing Practice Testanjali hansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eclampsia: Case Presentation Group ADokument56 SeitenEclampsia: Case Presentation Group AArah Momo67% (3)
- HYPERTENSION-WPS OfficeDokument4 SeitenHYPERTENSION-WPS OfficeAMOS MELINoch keine Bewertungen
- The Turkey Book - An Introductory Manual For The WardsDokument147 SeitenThe Turkey Book - An Introductory Manual For The WardsThe Physician Assistant LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pete Hanna - Mediterranean Diet Meal Prep - Easy and Healthy Mediterranean Diet Recipes To Prep, Grab and Go. 21-Day Fix Meal Plan To Lose Weight As Fast As Possible (2019)Dokument178 SeitenPete Hanna - Mediterranean Diet Meal Prep - Easy and Healthy Mediterranean Diet Recipes To Prep, Grab and Go. 21-Day Fix Meal Plan To Lose Weight As Fast As Possible (2019)adaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Effect of Raphanus Sativus (Radish) Taproot Ethanol Extract On Hypertension-Induced ALBINO Mus MusculusDokument57 SeitenAntihypertensive Effect of Raphanus Sativus (Radish) Taproot Ethanol Extract On Hypertension-Induced ALBINO Mus MusculusCai TabalocNoch keine Bewertungen
- English SbaDokument12 SeitenEnglish SbaCaden FahieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Nrcme Practice TestDokument19 Seiten17 Nrcme Practice Testdr_milan100% (1)
- HypertensionDokument9 SeitenHypertensionNader Smadi50% (4)