Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment of Gear
Hochgeladen von
Ahsan Shakeel100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
580 Ansichten4 SeitenGears are machine components that transmit mechanical power from one shaft to another through engaging teeth. There are many types of gears that can be used for different shaft arrangements and transmission requirements. Gears provide high transmission efficiency but can cause noise and vibration at high speeds. Common gear types include spur gears for parallel shafts, helical gears for quieter meshing, bevel gears for perpendicular shafts, and worm gears for transmitting power in one direction only.
Originalbeschreibung:
About gears and its types
Originaltitel
Assignment of gear
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenGears are machine components that transmit mechanical power from one shaft to another through engaging teeth. There are many types of gears that can be used for different shaft arrangements and transmission requirements. Gears provide high transmission efficiency but can cause noise and vibration at high speeds. Common gear types include spur gears for parallel shafts, helical gears for quieter meshing, bevel gears for perpendicular shafts, and worm gears for transmitting power in one direction only.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
580 Ansichten4 SeitenAssignment of Gear
Hochgeladen von
Ahsan ShakeelGears are machine components that transmit mechanical power from one shaft to another through engaging teeth. There are many types of gears that can be used for different shaft arrangements and transmission requirements. Gears provide high transmission efficiency but can cause noise and vibration at high speeds. Common gear types include spur gears for parallel shafts, helical gears for quieter meshing, bevel gears for perpendicular shafts, and worm gears for transmitting power in one direction only.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
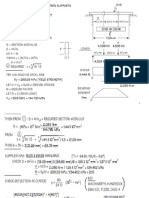
ASSIGNMENT
Gear | Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages, Types, Applications
GEAR:
A Gear is a machine component, which is used to transmit mechanical
power from one shaft to the other by successively engaging its teeth.
Gears are one of the most used method of mechanical power transmission
in the machines. Power transmission by the gears have almost 100%
efficiency.
ADVANTAGES OF GEAR DRIVE:
1) It is positive drive hence velocity remains constant
2) Provisions for changing velocity ratios can be made with the help of
gear box
3) Its efficiency is very high
4) It can be used even for low speeds
5) It can transmit high torque values
6) It is compact in construction
DISADVANTAGES OF GEAR DRIVE:
1) They are not suitable when shafts are distant
2) At high speeds noise and vibration happens
3) It requires lubrication
4) It has no flexibility
REASONS OF GEAR FAILURE:
There are following reasons of Gear failure;
1) Abrasive wear
2) Corrosive wear
3) Initial pitting
4) Destructive pitting
TYPES OF GEARS:
Depending on the requirement and place of use there are several types of
Gears.
1. Parallel Shafts:
This is the case when we have to transmit power between two parallel
shafts.
2. Spur Gears:
Spur Gears are used for the power transfer in the shafts which are parallel
to each other. They have straight teeth as shown in above image.
3. Spur Rack and Pinion:
The long bar shown in the image is known as rack and the gear is known
as pinion. We know that in a gear meshing, generally small Gear is known
as Pinion but why the single Gear used here is known as Pinion.
The reason is we consider the Rack as a very large Gear with infinite
diameter so that it looks almost straight and hence the other gear than rack
is known as pinion.
4. Helical Gears or Helical Spur Gears:
Helical gears are almost same as spur gears but they have inclined teeth
for uniform and silent teeth meshing. Power transmitting capacity of
helical spur gears is more than that of normal spur gears.
5. Double Helical Gears:
The the helical gears some unbalanced force remains in the system due to
inclined teeth so, to balance that unbalanced force we use double helical
gears which has inclined teeth in both the directions.
One should note that there is a gap between two sets of inclined teeth.
Power transfer capacity of double helical gear is more than simple helical
gear.
6. Herringbone Gears:
There is only one difference between double helical and Herringbone
gears. Herringbone gears do not have any gap between inclined teeth.
7. Intersecting Shafts:
This is the case when the shafts (between which the power is to be
transmitted) are mutually intersecting.
8. Spiral Bevel Gears:
Spiral bevel gears are used for power transmission in the shafts which are
perpendicular to each other. Due to spiral teeth they provide uniform and
silent teeth engagement. It has more power transmitting capacity than zero
bevel gears.
9. Zero Bevel Gears:
Zero bevel gears or simply Bevel gears have straight teeth. The teeth
engagement not as uniform and smooth as in spiral bevel gears.
10. Skew Shaft:
This is the case when the shafts (between which the power is to be
transmitted) are non-parallel and non-intersecting.
11. Cross Helical Gears:
Cross helical gears are used for non parallel and non intersecting shafts.
12. Worm Gears:
Sometimes this type of gear arrangement is also known as worm and
wheel. Here the long rod having spiral is the worm. We should note one
thing that worm can rotate the Gear but reverse is not true.
13. Hypoid Gears:
Hypoid gears as same as spiral bevel gears but the only difference is that
the center line of both the shafts do not intersect in Hypoid gears.
Alternatively we can say that there is some eccentricity in the center line
of the shafts in the Hypoid gear arrangement.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sample Minutes of MeetingDokument3 SeitenSample Minutes of MeetingMohamad AzmeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSE4610 DSE4620 Operators ManualDokument86 SeitenDSE4610 DSE4620 Operators ManualJorge Carrasco100% (6)
- TA35 & TA40 Articulated Dumptruck Maintenance Manual: Click Here For Table ofDokument488 SeitenTA35 & TA40 Articulated Dumptruck Maintenance Manual: Click Here For Table ofKot878100% (2)
- Fluid FrictionDokument18 SeitenFluid FrictionEdgar UbaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic V Mangotara DigestDokument3 SeitenRepublic V Mangotara DigestMickey Ortega100% (1)
- Experiment 7 (3D Equilibrium)Dokument3 SeitenExperiment 7 (3D Equilibrium)AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument14 SeitenHeat TreatmentAkhilesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Fans in Series and ParallelDokument3 SeitenUsing Fans in Series and Parallelvalentinlupascu33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wheel N AxleDokument11 SeitenWheel N AxleCarey FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-II-IC Engines-Lecture 1-IntroductionDokument47 SeitenUnit-II-IC Engines-Lecture 1-IntroductionarulNoch keine Bewertungen
- PA SystemDokument4 SeitenPA SystemSnehal DambhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Task 1st Quarter Poetry Writing WorkshopDokument3 SeitenPerformance Task 1st Quarter Poetry Writing WorkshopNicole john ZuluetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018Dokument62 SeitenWebinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Lab 2 Belt Friction Lab ReportDokument15 SeitenVibration Lab 2 Belt Friction Lab ReportYann YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 9: Aim: To Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of Simple andDokument2 SeitenExperiment No. 9: Aim: To Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of Simple andShiva Krishna Bhagavatula50% (2)
- Mechanics of Machinery 2 - Balancing of Rotating MassesDokument11 SeitenMechanics of Machinery 2 - Balancing of Rotating MassesAhmed Zawad ShovonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glimpse of Deformation Theory OssermanDokument10 SeitenGlimpse of Deformation Theory OssermanbhaumiksauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upto 2010 KomDokument36 SeitenUpto 2010 KomRajueswarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Assignment of MMCDokument9 Seiten1st Assignment of MMCAwais Asghar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 - Belt Friction Data PDFDokument10 Seiten13 - Belt Friction Data PDFMuhamad Amirul Amin AminnudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 3 - Rolling Disc and AxleDokument7 SeitenExp 3 - Rolling Disc and AxleCoco YapNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Shear-CentreDokument6 Seiten5 Shear-CentreRishNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 1 HOIST 2019Dokument22 SeitenCHP 1 HOIST 2019Max LuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lathe Machine Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenLathe Machine Lab ReportEdgar ThorpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cam and Follower: Omar Ahmad Ali Ayman Mohammad Alkhwiter Eid Sunhat AlharbiDokument17 SeitenCam and Follower: Omar Ahmad Ali Ayman Mohammad Alkhwiter Eid Sunhat AlharbiOmar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No - 1: AIM: Study of Various Types of Gear Boxes Such As Industrial Gear Box, SynchromeshDokument3 SeitenExperiment No - 1: AIM: Study of Various Types of Gear Boxes Such As Industrial Gear Box, SynchromeshParas KumbalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaping MachineDokument14 SeitenShaping MachineMohammad Javed IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Engineering Principles and UnitsDokument47 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Engineering Principles and Unitseng_yap_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 BeltDokument40 Seiten3.1 BeltLau Siong Kwong0% (1)
- Torsion of Bars Apparatus (A)Dokument4 SeitenTorsion of Bars Apparatus (A)Ram NiwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallography:: Steps To Reveal Microstructures of A SpecimenDokument7 SeitenMetallography:: Steps To Reveal Microstructures of A SpecimenJoyce Saddhu MeettooNoch keine Bewertungen
- L4 The Simple PendulumDokument13 SeitenL4 The Simple PendulumNur Syamiza ZamriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IDokument67 SeitenChapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IMohsin AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1A-Gear PDFDokument2 SeitenAssignment 1A-Gear PDFFattihiEkhmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Material Lab Report Angle of TwistDokument6 SeitenMechanics of Material Lab Report Angle of TwistAhsan MumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, RajshahiDokument9 SeitenRajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, RajshahiShakil Ahmed100% (1)
- MEC291 Mechanics and Materials Laboratory ManualDokument16 SeitenMEC291 Mechanics and Materials Laboratory ManualLAILATUL ATILA0% (1)
- Gear Design 2Dokument15 SeitenGear Design 2cracking khalifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory 1aDokument7 SeitenLaboratory 1aH2 MgZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Four Bar Mechanism of Sewing MachineDokument8 SeitenReport On Four Bar Mechanism of Sewing MachineshazedislamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT6501 (R-13) Notes PDFDokument131 SeitenAT6501 (R-13) Notes PDFAashiq NawinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smoke FlowDokument9 SeitenSmoke FlowArunSutharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 1Dokument19 SeitenLect 1Kong DuiDuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 10 - Shear CentreDokument4 SeitenPractical 10 - Shear CentreTbyTanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 29Dokument13 SeitenCHP 29Abhiram Reddy100% (1)
- Conservation of EnergyDokument7 SeitenConservation of EnergyJohn Nathaniel GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion AssignmentDokument30 SeitenCombustion AssignmentMichael AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assingment 1 MEC610Dokument14 SeitenAssingment 1 MEC610MUHAMMAD NURUDIN IMAN GHANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Governor NumericalsDokument14 SeitenGovernor NumericalsRohit Newar100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics Lab ManualDokument25 SeitenEngineering Mechanics Lab ManualShabbir AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsion TestDokument7 SeitenTorsion Testilya danisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laminar Flow Table: Name: Animesh Phatowali Roll No: 17AE30005 Group: 6 Experiment:7Dokument7 SeitenLaminar Flow Table: Name: Animesh Phatowali Roll No: 17AE30005 Group: 6 Experiment:7Animesh PhatowaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5Dokument6 SeitenTutorial 5Mohammad Asri ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Element II: Institute of TechnologyDokument39 SeitenMachine Element II: Institute of TechnologyAbiy Aliye100% (1)
- Lab Report 3 Flywheel ApparatusDokument7 SeitenLab Report 3 Flywheel ApparatusMansoob BukhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Lift: Subject: Topic: AimDokument3 SeitenHydraulic Lift: Subject: Topic: Aimamitk8045100% (2)
- Simple Machines RulesDokument2 SeitenSimple Machines Rulesapi-360547539Noch keine Bewertungen
- KOM ProjectDokument15 SeitenKOM ProjectArvene Binmer JesaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of VibrationDokument9 SeitenConcept of VibrationMuhammad ZikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 31701 GyroscopeDokument6 SeitenME 31701 GyroscopeHemanth Kumar ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Hoist 1-2Dokument9 SeitenHoist 1-2Wee Soon ChaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Report Motorized GyroscopeDokument4 SeitenLaboratory Report Motorized GyroscopeJeong Woo HyunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic JumpDokument5 SeitenHydraulic JumpKafeel Bichu0% (1)
- Lab 4 Pulley PDFDokument4 SeitenLab 4 Pulley PDFAngeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Job/Experiment No.: Me594/05 2.0 NAME OF EXPERIMENT: Angle Measurement Using Sine Bar & SlipDokument6 Seiten1.0 Job/Experiment No.: Me594/05 2.0 NAME OF EXPERIMENT: Angle Measurement Using Sine Bar & SlipHimanshu Vasistha0% (1)
- Differential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsVon EverandDifferential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 08Dokument77 SeitenCH 08abdallah ghannamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis ReportDokument72 SeitenThesis ReportMayur ShetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1778 3557 1 SM PDFDokument4 Seiten1778 3557 1 SM PDFjulio simanjuntakNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEP 33641012 Electrical Supply and Generation - Design and OperationDokument51 SeitenDEP 33641012 Electrical Supply and Generation - Design and Operationpeter wiltjerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lazard Levelized Cost of Storage v20Dokument46 SeitenLazard Levelized Cost of Storage v20macNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-Communication & NetworkingDokument70 SeitenChapter-Communication & NetworkingAfsar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionsManual NewDokument123 SeitenSolutionsManual NewManoj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- EASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanesDokument120 SeitenEASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanessnorrigNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE Sofware Lab Experiment 1, PDFDokument11 SeitenEEE Sofware Lab Experiment 1, PDF240 Sadman ShafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dragon Ball Z Project: R1 and R2J Dragon Boxes Merge: AcknowledgementsDokument11 SeitenDragon Ball Z Project: R1 and R2J Dragon Boxes Merge: Acknowledgements8ASergio GamarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 310 311 320 321 Toilet Warranty Codes PDFDokument11 Seiten310 311 320 321 Toilet Warranty Codes PDFTerri MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB PROGRAMMING An Engineering PerspectiveDokument129 SeitenMATLAB PROGRAMMING An Engineering PerspectivelolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case For Overhead and DistributionDokument2 SeitenCase For Overhead and DistributionBhargav D.S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Landis+Gyr Model EM5300 Class 0.5 Electricity Meter 14-2-63Dokument5 SeitenLandis+Gyr Model EM5300 Class 0.5 Electricity Meter 14-2-63kulukundunguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tes - 29 October 2021 UserUploadNetDokument120 SeitenTes - 29 October 2021 UserUploadNetTran Nhat QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLDokument12 SeitenPrishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLsudharaj86038Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report Liquid Detergent BreezeDokument12 SeitenReport Liquid Detergent BreezeDhiyyah Mardhiyyah100% (1)
- Ecological Consideration of Site AnalysisDokument20 SeitenEcological Consideration of Site AnalysisAUST BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 2 Online BPDokument98 SeitenLevel 2 Online BProbertduvallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall 2015 The Language of Anatomy PDFDokument14 SeitenFall 2015 The Language of Anatomy PDFpikminixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calling An Oracle Stored Proc in JasperDokument10 SeitenCalling An Oracle Stored Proc in Jasperlorenzofranchi6371Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIO SCI OsmosisDokument10 SeitenBIO SCI OsmosisJoy FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freeman Has Been A Partner in A Commercial Construction CompanyDokument1 SeiteFreeman Has Been A Partner in A Commercial Construction CompanyMuhammad ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrr2 Why The Future Doesnt Need UsDokument3 SeitenMrr2 Why The Future Doesnt Need UsSunshine Glory EgoniaNoch keine Bewertungen