Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Interior Design: Material Specification
Hochgeladen von
PoaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Interior Design: Material Specification
Hochgeladen von
PoaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PURPOSE OF SPECIFICATIONS :
INTERIOR DESIGN
1. Describe types and quantity of
Material Specification: product describe
root word ( S P E C I F I C ) 2. Requirement for fabrication.
synonym – exact definite Erection- application, installation
and finishing.
SWATCH – material specification & 3. Describing the quality of
architectural specification are different. workmanship necessary
4. Should include codes and standards
SWATCHES : 5. Description and procedures for
COLOR alternate materials
SIZE
QUANTITY TYPES
TEXTURE 1. Descriptive – extrinsic and intrusive
PATTERN properties.
OPERATION 2. Performance – how it works and
BRAND operates
SPECIFICATION – are the written 3. Reference Standard - ASTM, PNS,
requirement for a material product or etc
service for proposed project like building, 4. Proprietary – open ( equivalent
bridge or..(?) mean you have option) / close
(specific materials/description).
HOW WE SPECIFY: DRY WALL – ( wood without anything in
QUANTITY between)
SIZE *study vernacular terms = ex. Palstada,
PATTERN pinakuan, etc
MANNER OF OPERATIONS
GENERIC MATERIALS wall: vern concrete, dry wall, glass
COLOR curtain, aluminium..
BRAND NAME ( OPTIONAL)
NATURAL /ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING
IMPORTANCE Light - form of energy visible to the human
- protects the interests of both client and eye that is radiated by moving charged
architect particles
- basic for material estimates ( for - Sun is the Earth’s primary source of
contractors) light about 44%.
For architectural projects the specifications HOW LIGHT TRAVEL:
are part of the contract documents.(where - Light travel at very high speed
material specs are being included)
- The speed of light through empty SUNLIGHT- Solar radiation is absorbed,
spaces is about 186,000 miles per reflected, and scattered in the atmosphere
second. ( about 300,000 km per so that the visible.
second) - amount of daylight.
- Bundles of energy. The bundles are
3 BASIC CONDITION OF INCIDENT LIGHT
called Photons
are considered in design evolution,
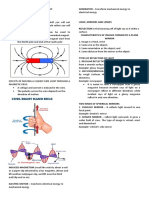
ABOUT LIGHT: depending on climatic and site.
- It travels in a straight line until it 1. Light from overcast sky only. – This
runs into something. varies with the density and
- Light bounces off. This is called uniformity of the overcast.
Reflection. 2. Light from a clear sky only.
- Opaque materials can also absorb or 3. Light from a clear sky plus direct
some or all of the colors that make sunlight. – the effect of direct
up light. This is why you can see sunlight on surface exposed to if is
color. added to clear sky condition.
- Refraction- bending of light
SOURCES OF ILLUMINATION
COLORS OF LIGHT:
- Kitchen - E
- A rainbow is called spectrum. - Living - S
- Violet has highest energy - Bedroom- NW NE SE SW
- Red has lower energy - Breakfast Area - E
In between of color red and violet - Service Area- E
that make the light is called visible
DIRECT SOLAR RADIATION NEEDS TO BE
light.
CONTROLLED
- Beyond violet is called ultraviolet
- Beyond red is called infrared. - Reduce heat gain through openings
during warm weather;
3 TYPES OF VISIBLE LIGHT SOURCE:
- Maximize heat gain when space
1. Natural phenomena – radiation of heating is required
the complete spectrum of light, - Reduce visual discomfort of glare or
from sun and stars; the reflection of sharp contrast and improve level
sunlight of the moon,sky..(?) and diffusion of illumination
2. Incandescence or temperature- as - Reduce visual discomfort radiation
an element is heated its molecule of the ground, water, snow or adjust
become increasingly active (heat vertical surface may cause glare.
reliant).
ORIENTATION
3. Luminescence- electric current
introduced through a gas or solid ( EAST:
electric reliant) - East-facing openings admits strong
sunlight early in the morning and
lose the sun sometime before noon. for the use of darker colors; used in
- BEDROOM, KITCHEN,BA,AREA carpets.
USED EARLY IN THE DAY SHADING DEVICES
BEDROOM – NE,NW,SE,SW - Louvers, overhangs, shades, blinds
WEST: ( with or without draperies), or
- West-facing windows receive the other devices can be applied
late afternoon creatively to control excessive
- western exposure can create illumination and luminance contrast
uncomfortable glare and heat in emitted from the sun.
some parts of the country. - Trees : natural sun shading devices
- shading devices such as overhangs
or blinds can prevent the heat going – we can use deciduous
inside. trees ( broad leaves ) on
NORTH: south side to prevent heat
- which never admit direct sun, and glare.
generally receive cool but consistent - Coniferous trees ( pointed
from the north sky. leaves) give a garden
SOUTH: guaranteed colour all year
- good orientation, ideally south round; when planted on the
with appropriate checking, make north side, they can block
difference in winter and summer. some of the piercing
- family room, living room, sewing northern winds in the colder
room. months of the year.
example : balsam fir, fraser
HOW TO CONTROL NATURAL LIGHT:
fir, douglas fir, red pine,
FINISHES white pine, scotch pine.
- the color and reflectivity of interior FURNITURE PLACEMENT
finishes are important in use of when placing furniture, it is
daylight and control luminous important to keep bright windows
ration. out of the field of vision of any
- light colored surface enlarge the person doing close up tasks like
perception of space and diffuse the reading or repair work. The
light distribution. traditional advice “light over the left
- THE CEILING is more effective shoulder” is still good, although light
surface for reflecting light and from the right is also satisfactory for
typically, it should be very light in most tasks and ideal for left-handed
color. people.
- THE FLOOR is one of the least MULTIPLE GLAZING.
significant, and it is here that the multiple glazing uses two,
designer has the greatest oppurnity sometimes three, sheets of glass
that are factory-assembled into a
sandwich. The dead air spaces maintenance and wattage;
between the layers minimize heat
loss or heat gain. Special glass tinted
to filter out unwanted heat energy
while permitting most light to pass
through can be obtained.
ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING
Illumination of the visual task is of premier
importantce:
- Provide adequate illumination at the plane
of work, on the object;
- Provide proper lighting for passages,
corridors, staircases and other means of
circulation;
- Ensure proper contrast of surround and
background
- Selection of lamp should be based on lamp
efficacy, lumen production, lumen
Select the light source with regard to
requirements of work or process,
psychological satisfaction, and
Illumination of the visual task is of premier
combination with natural light;
importance:
Be aware of color rendition for
Provide coordination with natural impact an environmental surfaces
lighting arrangements; - color in decorations, on machines
Provide auxiliary lighting as needed and equipment, emergency and
for safety, security, emergency, etc safety color identifications.
Correct color of lighting may be essential:
Indoor application - Focusing Attention
- Provision of security:
Flexibility of intended use of the
- Lighting can enhance visibility and
space is the biggest benefit of area
thereby engender a sense of
lighting, and it relies on uniform
security. Lighting can also be used to
illumination on the horizontal plane.
illuminate hazards, such as a
Uniform distribution can be
changing floor plane or moving
accomplished by using certain
objects.
arrangements of like-luminaire
systems or by combining different
types of systems
Office lighting can be satisfied with
recessed, surface-mounted,
pendant-mounted or portable
luminaires. It is often most effective
when combined with task lighting.
Typical area lighting seldom
provides sufficient luminance to
support growth of plants in interior
landscaping designs. Ground covers
and flowering plants typically
require substantial light
Indoor industrial task include a
variety of visual tasks often in one
large, open space. Building
definition can vary greatly and
movement of equipment and
material is constant.
Sports lighting typically requires
illumination beyong the limits of the
area of play.
FUNCTIONS OF LIGHTING
- Performance of tasks :
- Lighting to perform work, whether
it be reading assembling parts, or
seeing a blackboard referred to as
task lighting. Visual work is primary
reason for providing lighting
- Enhancement of space and
structure
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MODULE 12: BASICS OF LIGHTING (Terms and Concepts)Dokument7 SeitenMODULE 12: BASICS OF LIGHTING (Terms and Concepts)tarlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magbasa Sa InteriorDokument3 SeitenMagbasa Sa InteriorMark Justine GuevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIGHTINGDokument51 SeitenLIGHTING121915502011 gitamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Source WordDokument25 SeitenLight Source WordKEVIN JUGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 LightDokument5 SeitenChapter 2 LightDaniel ModestoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Indian Dessert Vernacular ArchDokument19 Seiten4 - Indian Dessert Vernacular ArchjashndeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arch 143 Module 2 (ELMCA Lighting Technologies)Dokument51 SeitenArch 143 Module 2 (ELMCA Lighting Technologies)Kyle Josef MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 5 - Light Sources - Written ReportDokument110 SeitenGroup 5 - Light Sources - Written ReportKEVIN JUGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Service Systems: Lighting, Intends To Light Up The Entire Room at ADokument2 SeitenBuilding Service Systems: Lighting, Intends To Light Up The Entire Room at ALea NarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1:light Subject: Building Sciences 2 Prepared By: Sampurna Maharjan Title: Sources of LightDokument3 SeitenChapter 1:light Subject: Building Sciences 2 Prepared By: Sampurna Maharjan Title: Sources of Lightgshakya_guita5355Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 11 LightingDokument4 SeitenWeek 11 LightingLyndryl ProvidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Paints With Infrared Radiation ReflDokument6 SeitenDevelopment of Paints With Infrared Radiation ReflGeorge FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Lighting: Sources and Types of Artificial LightingDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Lighting: Sources and Types of Artificial LightingAnmol ChughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daylighting: Design ConceptsDokument15 SeitenDaylighting: Design ConceptsAagney Alex RobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 (Introduction) PDFDokument29 SeitenLecture 1 (Introduction) PDFAachal PokharelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOURCES OF LIGHT Week 4 ReporterDokument4 SeitenSOURCES OF LIGHT Week 4 ReporterJustine Gabriel OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2.1 Properties of Light and Its Propagation SummaryDokument2 SeitenLesson 2.1 Properties of Light and Its Propagation SummaryJM OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 4int - Review 2nd TestDokument6 SeitenGrade 4int - Review 2nd TestHà NhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bu 5 - LightingDokument8 SeitenBu 5 - LightingSharmaine Danica MarceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy in The Earth System: How Do Radiation and Convection Currents Affect Phenomena On Earth?Dokument51 SeitenEnergy in The Earth System: How Do Radiation and Convection Currents Affect Phenomena On Earth?Noroña S.R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- F. L. Vargas College, Inc.: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The LessonDokument11 SeitenF. L. Vargas College, Inc.: Course Sem/AY Module No. Lesson Title Week Duration Date Description of The Lessonprincessp.pagaddu05Noch keine Bewertungen
- LightingDokument5 SeitenLightingapi-420899359Noch keine Bewertungen
- CW2 TermsDokument1 SeiteCW2 TermsKatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Illumination AdditionalDokument80 SeitenIllumination Additionalbutohpakang100% (1)
- Evs Presentation : Roof Form Fenestration Pattern External Colours and Textures Fenestration ControlsDokument14 SeitenEvs Presentation : Roof Form Fenestration Pattern External Colours and Textures Fenestration ControlsUtkarsh ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFLUENCE & CHROMATIC ENERGY ON ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN (History of Architecture 1 Lesson REVIEWER - Architecture)Dokument7 SeitenINFLUENCE & CHROMATIC ENERGY ON ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN (History of Architecture 1 Lesson REVIEWER - Architecture)Hanna ParenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate and Design ARC2030 Designing in Composite ClimateDokument39 SeitenClimate and Design ARC2030 Designing in Composite ClimateAlisha KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Int1014-L 6 - 2020Dokument51 SeitenInt1014-L 6 - 2020Enes YılmazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument30 SeitenUnit 1vignesh rulzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Design 1 FinalDokument1 SeiteProduct Design 1 FinalZeeshan SayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- RE200Dokument136 SeitenRE200Justine LedesmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot and Arid ClimateDokument50 SeitenHot and Arid ClimatePrashanthiniRajagopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Lecture 2Dokument42 SeitenNotes Lecture 2RHUTI NAIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Lighting 01Dokument2 SeitenElectrical Lighting 01Ybette Anorico VillamarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial LightDokument34 SeitenArtificial LightJohn KaruwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eu Reviewer CombinedDokument18 SeitenEu Reviewer Combineddritz tevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Experimental Study of A Specular and A 2019 Solar Energy MateriDokument7 SeitenPreliminary Experimental Study of A Specular and A 2019 Solar Energy MateriHARSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lighting: Lightning Artificial Light (Song) LightDokument15 SeitenLighting: Lightning Artificial Light (Song) LightPri N CENoch keine Bewertungen
- Landscape Lighting Landscape Lighting Landscape Lighting Landscape LightingDokument26 SeitenLandscape Lighting Landscape Lighting Landscape Lighting Landscape Lightingdemullu reddiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day Light FactorDokument24 SeitenDay Light FactorshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics and Lighting SystemsDokument5 SeitenAcoustics and Lighting SystemsGeri Adriana SonzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory 2Dokument5 SeitenTheory 2Camille CiokonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parans Light Guide 2.1-KomprimeradDokument27 SeitenParans Light Guide 2.1-Komprimeradatif_aman123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hotanddryclimatearchitecture 150720111730 Lva1 App6891 PDFDokument20 SeitenHotanddryclimatearchitecture 150720111730 Lva1 App6891 PDFSantript SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate: Sem. 3, Sec.B, B.arch 2014-19 SPA-PUDokument20 SeitenClimate: Sem. 3, Sec.B, B.arch 2014-19 SPA-PUArghyadip SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Landscape Design Site Planning ConsiderationsDokument9 SeitenLandscape Design Site Planning ConsiderationsYcen SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- L3-Lighting DesignDokument38 SeitenL3-Lighting DesignghaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in Comprehensive CourseDokument3 SeitenReviewer in Comprehensive CourseJohn Patrick ValinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 3 - LightingDokument10 SeitenUNIT 3 - LightingAanya BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSGN Joanne's NotesDokument2 SeitenDSGN Joanne's NotesGeraldine CanedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointers To Review 2nd QuarterDokument4 SeitenPointers To Review 2nd QuarterZaira Clarisse de GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letting The Research Grow: Needs of Researches Working On Wetlands by ProvidingDokument3 SeitenLetting The Research Grow: Needs of Researches Working On Wetlands by ProvidingBüddhì Chåthùränjèlì Dé SìlväNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesda AparriDokument21 SeitenTesda AparrijaimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Wells in Residential Building As A Complementary Daylight SourceDokument11 SeitenLight Wells in Residential Building As A Complementary Daylight SourcekautukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural and Artificial LightingDokument10 SeitenNatural and Artificial LightingRajat GandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Exam RevDokument4 Seiten3rd Exam RevErnest Mav Lorenz GolesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ILLUMINATIONLAWSDokument94 SeitenILLUMINATIONLAWSJemmuel MamintaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light: Light Light Light Light Light Light LightDokument16 SeitenLight: Light Light Light Light Light Light LightMechVfx ProgrammeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic Photography ModuleDokument47 SeitenForensic Photography ModuleKeith Wilson Vincent AndradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDokument27 SeitenRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsChikchikchat ChatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation PollutionDokument13 SeitenRadiation PollutionMuhammad YaqoobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research ArticleDokument14 SeitenResearch ArticleCarlos Daniel RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics CL10 WS 5Dokument7 SeitenPhysics CL10 WS 5vaibhave BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photo Electric EffectDokument8 SeitenPhoto Electric EffectRahul SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation Physics and Chemistry: Alejandra Tomac, María C. Cova, Patricia Narvaiz, María I. YeannesDokument6 SeitenRadiation Physics and Chemistry: Alejandra Tomac, María C. Cova, Patricia Narvaiz, María I. Yeannesarif yusuf julionartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Fiber OpticsDokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Fiber OpticsNida AjrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture5 B PETDokument26 SeitenLecture5 B PETYasir AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD 856Dokument66 SeitenPD 856Christine Lyza DinamlingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 2 Electromagnetic Waves Grade & SecDokument1 SeiteQuiz 2 Electromagnetic Waves Grade & SecLuis0% (1)
- Chapter - 26 Dual Nature of Radition and MatterDokument26 SeitenChapter - 26 Dual Nature of Radition and MatterTilahun ArfichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ TestDokument15 SeitenTest - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ Testsatish100% (1)
- Atmosphere Solar Energy and ClimateDokument14 SeitenAtmosphere Solar Energy and ClimateRoy MapingereNoch keine Bewertungen
- FTIR: Introdution and Application To ForensicsDokument23 SeitenFTIR: Introdution and Application To ForensicsLJ GicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiasi Benda HitamDokument20 SeitenRadiasi Benda HitamRifki AlgifahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Engineering-HazardsDokument20 SeitenMicrowave Engineering-HazardsKobid KarkeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpticsDokument29 SeitenOpticsVr MageshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Light As A Wave 20210126 - 1Dokument11 SeitenExploring Light As A Wave 20210126 - 1fjtambo25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rezalyn - 2 LASDokument18 SeitenRezalyn - 2 LASJonah Labine Jabulin-RadazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holography (Unit 1)Dokument19 SeitenHolography (Unit 1)Prince JunejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behic Ivy Detailed Lesson Plan Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument6 SeitenBehic Ivy Detailed Lesson Plan Electromagnetic SpectrumPhranxies Jean Loay BlayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dual Nature of LightDokument14 SeitenThe Dual Nature of LightABHISHEK SAININoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Is The Sky Blue - Google SearchDokument4 SeitenWhy Is The Sky Blue - Google SearchDarkmoonmothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Wave PropagationsDokument41 SeitenRadio Wave PropagationsKifaru Micro-electronics100% (2)
- Sanet - ST SynchrotronRadiationDokument52 SeitenSanet - ST SynchrotronRadiationijokyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beant College of Engineering & Technology, Gurdaspur Physics (Poly Wing)Dokument11 SeitenBeant College of Engineering & Technology, Gurdaspur Physics (Poly Wing)Debasish BeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lenses Ppt. Observation 2222Dokument33 SeitenLenses Ppt. Observation 2222bagasmarylord88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Normal Incidence of Waves at Interfaces: in This Lecture You Will LearnDokument11 SeitenNon-Normal Incidence of Waves at Interfaces: in This Lecture You Will LearnMukul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed /frequency / Wavelength: EquationDokument3 SeitenSpeed /frequency / Wavelength: Equationsansay cagaananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk AssessmentDokument3 SeitenRisk AssessmentJessica RileyNoch keine Bewertungen