Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exercise 02 - BKF1313 Chapter 2 Part 2
Hochgeladen von
Cornelius Philip0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
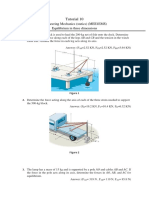
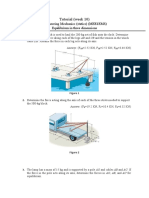
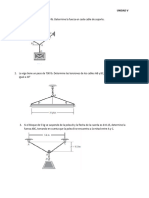
97 Ansichten2 SeitenThis document contains 9 questions about determining forces and other values needed for equilibrium of particles and objects. Question 1 asks to determine forces F1 and F2 for particle P in equilibrium. Question 2 asks to determine force magnitude and angle for force F1 for particle P in equilibrium. Question 3 asks to determine forces in cords AB and BC for equilibrium of a 200-kg crate.
Originalbeschreibung:
Engineering mechanic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document contains 9 questions about determining forces and other values needed for equilibrium of particles and objects. Question 1 asks to determine forces F1 and F2 for particle P in equilibrium. Question 2 asks to determine force magnitude and angle for force F1 for particle P in equilibrium. Question 3 asks to determine forces in cords AB and BC for equilibrium of a 200-kg crate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
97 Ansichten2 SeitenExercise 02 - BKF1313 Chapter 2 Part 2
Hochgeladen von
Cornelius PhilipThis document contains 9 questions about determining forces and other values needed for equilibrium of particles and objects. Question 1 asks to determine forces F1 and F2 for particle P in equilibrium. Question 2 asks to determine force magnitude and angle for force F1 for particle P in equilibrium. Question 3 asks to determine forces in cords AB and BC for equilibrium of a 200-kg crate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
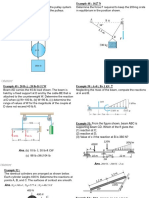
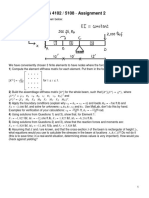
BKF1313 Chapter 2 – Equilibrium of Particles
Statics of Particles
Question 1
Determine the magnitudes of F1 and F2 so
that particle P is in equilibrium (F1 =435 lb
and F2 = 171 lb)
Question 4
If block B weighs 200 lb and block C
weighs 100 lb, determine the required
weight of block D and the angle θ for
equilibrium. (WD = 230 lb, θ = 64.3º)
Question 2
Determine the magnitude and angle θ of F1
so that particle P is in equilibrium (θ =
12.9º, F1 = 552 N)
Question 5
The unstretched length of spring AB is 2
m. If the block is held in the equilibrium
position shown, determine the mass of the
block at D. (m = 12.8 kg)
Question 3
Determine the force in each cord for
equilibrium of the 200-kg crate. Cord BC
remains horizontal due to the roller at C ,
and AB has a length of 1.5 m. Set y =
0.75 m . (FAB = 3924 N, FBC = 3398 N)
Question 8
Knowing that α =55° and that boom AC
exerts on pin C a force directed along line
AC, determine (a) the magnitude of that
force AC, (b) the tension in cable BC. (FAC
= 172.7 lb, TBC = 231 lb)
Question 6
The ball D has a mass of 20 kg. If a force
of F = 100 N is applied horizontally to the
ring at A, determine the dimension d so
that the force in cable AC is zero. (d =
2.42 m)
Question 9
Determine the stretch in springs AC and
AB for equilibrium of the 2-kg block. The
springs are shown in the equilibrium
position. (xAC = 0.793 m , xAB = 0.467 m)
Question 7
Knowing that α =20°, determine the
tension (a) in cable AC, (b) in rope BC.
(TAC = 1244 lb, TBC = 115.4 lb)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Equilibrium of Particle FBD of 2-D Systems: ObjectivesDokument20 SeitenEquilibrium of Particle FBD of 2-D Systems: ObjectivesMohamaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH3 Equilibrium Tutorial 3-1 PDFDokument2 SeitenCH3 Equilibrium Tutorial 3-1 PDFMax LuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGN 36 HomeworkDokument50 SeitenENGN 36 Homework082292fer67% (3)
- ENS161 Practice ProblemsDokument7 SeitenENS161 Practice ProblemsErl GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Chapter2 3552Dokument5 SeitenExercise Chapter2 3552Khuon RatanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cvle 210 - Assig 2Dokument2 SeitenCvle 210 - Assig 2bassamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVLE 210 Statics: Assignment (2) ProblemDokument2 SeitenCVLE 210 Statics: Assignment (2) ProblembassamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBVLDokument5 SeitenSBVLvuong100% (1)
- Week 7Dokument1 SeiteWeek 7Dang MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2Dokument6 SeitenTutorial 2A SкNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 QuestionsDokument2 SeitenTutorial 1 QuestionsNOUR ALGANAINYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2: Equilibrium of A Particle: All Problem Solutions Must Include FBDDokument2 SeitenTutorial 2: Equilibrium of A Particle: All Problem Solutions Must Include FBDIbrahim YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-3 Equilibrium ExamplesDokument30 SeitenCH-3 Equilibrium ExamplesHaftamu HilufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises: Ans. F = 1404.917 N; θ = 7.05ºDokument3 SeitenExercises: Ans. F = 1404.917 N; θ = 7.05ºRhey LuceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Engineering Mechanics 1 - QuestionsDokument4 Seiten1 - Engineering Mechanics 1 - Questionsskz linoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsDokument20 SeitenDAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsJM De Guzman TuzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starig 205 - Chapter 2 ProblemsDokument2 SeitenStarig 205 - Chapter 2 ProblemsNeil Anthony Pojas BlancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics & FluidsDokument9 SeitenStatics & FluidsShu RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Kuliah03 Equin2dDokument31 SeitenS Kuliah03 Equin2dMuhammad Fekrie Bin SarudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboard Problems FinalDokument5 SeitenPreboard Problems FinalAngel MarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- S - Kuliah03 - 28 Feb - Equ in 2d - 2Dokument23 SeitenS - Kuliah03 - 28 Feb - Equ in 2d - 2Fahmi FauziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium SystemsDokument12 SeitenEquilibrium SystemsEmilio Joaquin FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1,2,3Dokument8 SeitenTutorial 1,2,3RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Malaya Department of Mechanical Engineering Applied Mechanics (Kqe7005/Kxgm6105)Dokument2 SeitenUniversity of Malaya Department of Mechanical Engineering Applied Mechanics (Kqe7005/Kxgm6105)Zulfadzli RidzuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Dokument8 SeitenE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101Noch keine Bewertungen
- CVE10004 Tutorial02Dokument6 SeitenCVE10004 Tutorial02Evena FungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10 TutorialDokument2 SeitenWeek 10 TutorialbananaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Assignment No.6Dokument4 SeitenQuiz Assignment No.6CHA CHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch04-Axial Load (Autosaved)Dokument22 SeitenCh04-Axial Load (Autosaved)Mohammad RizkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (A) Week 10-TutorialDokument3 Seiten(A) Week 10-TutorialbananaNoch keine Bewertungen
- U5 Ep1 ProblemarioDokument4 SeitenU5 Ep1 ProblemarioIvan ARNoch keine Bewertungen
- TheoryLec01 Dec2019Dokument7 SeitenTheoryLec01 Dec2019cristina23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises in Chapter 3Dokument40 SeitenExercises in Chapter 3Lam TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 - Chapter 3Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 2 - Chapter 3Shaun KerouacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sheet 4.1 Chapter 4Dokument6 SeitenTutorial Sheet 4.1 Chapter 4schoolboy51Noch keine Bewertungen
- TM - Chapter 1 Exercises PDFDokument6 SeitenTM - Chapter 1 Exercises PDFVõ Văn VũNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take Home MidtermDokument2 SeitenTake Home MidtermEngr.PenguinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDokument11 SeitenStatics of Rigid Bodiesdonald escalanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCG 4102 / 5108 - Assignment 2: V V V M F M F M F M FDokument1 SeiteMCG 4102 / 5108 - Assignment 2: V V V M F M F M F M FInamNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 2024 - PSAD 1Dokument2 SeitenApril 2024 - PSAD 1rando12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Engineering MechanicsDokument5 Seiten2 Engineering MechanicsAdrianne CespedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exam Second TermDokument2 SeitenPhysics Exam Second TermsunliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- StaticsDokument5 SeitenStaticsJohn Joshua DavantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- SoRB - M2 23 24Dokument1 SeiteSoRB - M2 23 24Joel MiradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics I - Fall 2013 PDFDokument4 SeitenApplied Mechanics I - Fall 2013 PDFRajeshGupta100% (1)
- JEE 9 - 01 - 2019 - Slot - 2.pdf-98 PDFDokument13 SeitenJEE 9 - 01 - 2019 - Slot - 2.pdf-98 PDFAryan jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce Board May 2011Dokument3 SeitenCe Board May 2011DHANYL KHRISSNA MIJARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 2024 - PSAD 3Dokument2 SeitenApril 2024 - PSAD 3rando12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Dokument1 SeiteTopics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Levi John Corpin AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Theory - 1Dokument6 SeitenStructural Theory - 1jessa marie sayconNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM Assignment 2Dokument3 SeitenEM Assignment 2shreyashenoy03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statics of Rigid Bodies - First Term 2019: Y-AxisDokument11 SeitenStatics of Rigid Bodies - First Term 2019: Y-AxisLester John PrecillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani First Semester (2012-13) Assignment - Chapter 2Dokument4 SeitenBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani First Semester (2012-13) Assignment - Chapter 2Rohit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch2 44 50Dokument7 Seitench2 44 50Rafael Ohara NakagumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsVon EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesVon EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Von EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Bewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Solman PDFDokument71 SeitenSolman PDFdav00034Noch keine Bewertungen
- A320Dokument41 SeitenA320Varun Kapoor75% (4)
- Roles of A System AnalystDokument17 SeitenRoles of A System AnalystMohan William SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science of AstronomyDokument8 SeitenScience of AstronomyUyên Thi Trịnh NguyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- Srs TemplateDokument8 SeitenSrs Templateferrys37Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jaramogi Oginga Odinga University of Science and Technology, Kenya - BSC Computer Security & Forensics MSC IT Security & Audit, PHD IT Security & AuditDokument2 SeitenJaramogi Oginga Odinga University of Science and Technology, Kenya - BSC Computer Security & Forensics MSC IT Security & Audit, PHD IT Security & AuditKefa Rabah100% (1)
- Location Planning and AnalysisDokument22 SeitenLocation Planning and AnalysisEdCasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Marquis de SadeDokument10 SeitenThe Marquis de SadeAlexander100% (4)
- Short Biographical Sketch: Fundamental Considerations in Language Testing. Oxford University Press, 1990Dokument7 SeitenShort Biographical Sketch: Fundamental Considerations in Language Testing. Oxford University Press, 1990Douglas SpadottoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Study GuideDokument4 SeitenUnit 7 Study Guideapi-323808986Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Determinants of MoralityDokument10 SeitenThe Determinants of MoralityKaimi Ardee BorjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Reservoir Simulation in Optimal Reservoir ManagementDokument10 SeitenThe Role of Reservoir Simulation in Optimal Reservoir ManagementJaz MarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Training - DisysDokument12 SeitenJava Training - DisysArun KiliyaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- US National Design Policy Summit ReportDokument90 SeitenUS National Design Policy Summit Reportearthtomj100% (1)
- Issai 1530 PNDokument5 SeitenIssai 1530 PNMian Tahir WaseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotech - TimelineDokument9 SeitenRobotech - TimelineRobert BestNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReleaseNotes 30101R1 131015Dokument10 SeitenReleaseNotes 30101R1 131015pnh mcsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems 2012Dokument5 SeitenPractice Problems 2012Anonymous Fj3YPHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Computer Operation and ConceptsDokument3 SeitenBasic Computer Operation and ConceptsMaila Mejia TalamisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH Metru 913 MetrohmDokument8 SeitenPH Metru 913 MetrohmCorina StanculescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmulsionsDokument85 SeitenEmulsionsRamchandra Keny100% (2)
- Human Resources Management Practices in Modern WorldDokument7 SeitenHuman Resources Management Practices in Modern WorldMaheshkumar MohiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5 Standard Operations Research Models: Mathematical Modify ModelDokument2 Seiten3.5 Standard Operations Research Models: Mathematical Modify ModelAnonymous IjhB0kuFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vivek TiwariDokument4 SeitenVivek TiwariMehul ThakorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Air Bearing? 3. Why Air Bearing? 5. Working PrincipleDokument18 SeitenWhy Air Bearing? 3. Why Air Bearing? 5. Working PrinciplesachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIS Project ProposalDokument2 SeitenGIS Project ProposalKevin OdonnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS Speaking Study Planner For September-December - 2023Dokument2 SeitenIELTS Speaking Study Planner For September-December - 2023Althea Zhenya Antonio Claud100% (1)
- Fundamentals of ProbabilityDokument58 SeitenFundamentals of Probabilityhien05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy of Charlie Kaufman PDFDokument319 SeitenPhilosophy of Charlie Kaufman PDFCherey Peña RojasNoch keine Bewertungen