Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Banking Desire IAS Concept Counter Short Notes PDF
Hochgeladen von
Tarunkanti SatapathyOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Banking Desire IAS Concept Counter Short Notes PDF
Hochgeladen von
Tarunkanti SatapathyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Economy
Banking Series (Lecture-1 to 6)
www.DesireIAS.com
Plz Read Carefully and do not make laugh …
How to get maximum output from our notes ?
If you are a new aspirants or like a kid in UPSC journey boss we will say u should watch our
lectures First and read our notes
after that read Ramesh singh (bulky and written language is Mind blowing (aspirants cannot
understand in first reading what’s the author wants to make understand via this book
directly) hehehe) ( just joking)
Ramesh singh would be your primary resource, ( those coaching wala saying like Mere hi
Notes padho ..they are going to make u fool.. u cannot ignore books in upsc )
you can keep Desire IAS notes like a Revision notes or in desi style we can say Jugadu notes)
Just follow these 4 simple steps
Step-1 just watch our lectures on YouTube ( link Below) ( for countering the concept)
Step-2 read Economy Desire IAS notes ( for better understanding)
Step-3 Plz Avoid Grammar error becz we typed each and every word ( just joking) ( becz we
tried to write in HINGLISH language ) so even hindi medium aspirants can enjoy our notes (
offer limited only hehehhe)
Step -4 Read Any Economic Book ( Ramesh singh is good book .but read selective reading) on
Banking section (Serious Reading)
Ok apart of jokes let’s start it
for Lecture Playlist click this link -
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dWN88cvt4Xo&list=PLX2uHvzBJxOjdXovb49cMfYPPVY
LBkBGJ
TOPICS TO BE COVERED
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA
MINIMUM RESERVE SYSTEM
HISTORY OF BANKING IN INDIA
SCHEDULE AND NON SCHEDULE BANKS
REGIONAL RURAL BANKS
COOPERATIVE BANKS
NARASIMHAM COMMITTEE REPORT
PRIORITY SECTOR LENDING
NON BANKING FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
NON PERFORMING ASSETS
CIBIL
WILFULL DEFAULTER
TWIN BALANCESHEET PROBLEM
ARCS
CDR
S4A SCHEME
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
2
MISSION INDRADHANUSH
PROMPT CORRECTIVE ACTION
BANKING GUIDELINES
CORE BANKING SOLUTION
RTGS NEFT AND IMPS
UPI BHIM
BROWN AND WHITE LABEL ATMS
INSOLVENCY AND BANKRUPTCY CODE
Notes ( let’s start it ) .. (we assumed that u have already watched our economic lectures )( if not plz
watched it otherwise u r going to feel get bored here)
Reserve bank of India
In India RBI is the apex authority in the banking system.
RBI act 1934 and was setup on 1st April 1935
Earlier imperial bank of India used to perform its role.
In 1949 RBI (transfer to public ownership) act was passed and on 1 st Jan 1950 it was brought
under the control of GOI
Structure of RBI
RBI governor
4 deputy governors
1st RBI governor – sir Osborne smith
1st Indian rbi governor – cd deshmukh
At present – urjit patel
Functions of RBI
Traditional functions
Nontraditional functions
Traditional functions
Banker to the govt
The rbi is banker to the banks – lander of last resort
Control the entire banking system and some categories of nbfcs – scheduled banks have to
follow the guidelines given by rbi – 1/4th branch in rural areas etc.
Formulates monetary policy
Custodian of forex
Issues the currency above the denomination of Rs 1 that’s why Rs 1 note signed by finance
secretary. it can only issue notes.
Coins issued by goi but circulated by rbi.
Rbi can issue highest note of 10,000 and financial yearly 10000cr
For this minimum reserve system is used.
Minimum reserve system
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
3
In different countries different systems are used like proportional reserve system.
India uses MRS – 200cr(115 cr gold and 85 cr hard currency )
History of banking in india
• 1st – bank of hindustan – 1770 – alexander and company
• 3 banks by east india company at 3 presidencies –
1) 1806 – bank of bengal
2) 1840 – bank of bombay
3) 1843 – bank of madras
4) 1865 – allahabad bank – oldest bank surviving with same name – headquarter in calcutta
5) 1881 – oudh commercial bank – india’s 1st joint sector bank
6) 1894 - pnb – 1st bank with indian capital only
Imperial bank of india
Resulted into imperial bank of india in 1921.
Performed the functions of central bank till 1934
Sbi act was passed and it was brought under the goi in the year 1955
7 associates were also made.
• State bank of india
• Hyderabad
• Travancore
• Patiala
• Bikaner and jaipur
• Mysore
• Saurashtra
• Indore
In 2008 and in 2010 bank of saurashtra and indore were merged. On 1 st april 2017 even rest of
the 5 associates were merged. (narsimham committee recom.)
Bhartiya mahila bank is also merged which was setup in 2013
Nationalized banks
Meaning of Nationalization – converting a private sector company into a public sector
company.
Several acts were passed
1969 – banks with min deposit of 50cr – 14
1980 – banks with min deposit of 200cr – 6
Problems in banks
Private owned banks
Fraudlent activities
Most in urban areas
Reach to upper class only
Govt wish
To safeguard the interest of depositor
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
4
For benefits of masses
Government banks in india
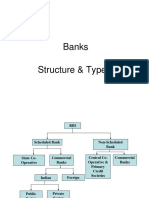
CLASSIFICATION OF BANKS
• 2 categories
• Scheduled – registered under 2nd schedule of rbi act ,1934 – list is dynamic – banks are
compelled to follow guidelines and in return they get monetary support of rbi.(guidelines to be
a bank will be covered later on)
• Non scheduled – opens and close everyday
•
Regional rural bank
Can be setup in rural part of a country only .
Responsibility – loan to agricultural farmers + small business
Earlier not established as a profit motive banks but now placed under it.
How they are opened –
Sponsored by psb’s only but work with different name
50% by central govt+35% by sponsored bank + 15% by state govt.
Problems
• Gradually number rose to 196 with 1000 of branches and most of them were running in losses
• Impacting sponsored banks
• Govt decided to merge them and number fall to 56
• Rrbs were opened in 1975 but act was passed in 1976
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
5
Cooperative Banks
• Based on mutual cooperation and no profit.
2 types –
1. State cooperative
2. Urban cooperative
• They have a dual regulation – banking part by rbi and management by state
State cooperative
• Registered under state cooperatives socities act
• Can operate in single state only
At 2 levels –
District – central cooperative
Village – primary agricultural credit socities (pacs)
Urban cooperative
Registered under multi state cooperative act
Can operate in more then 1 state
Narasimham committee report on banking sector reforms
No more nationalisation
Private and public sector to be treated equally
Complete computerisation
Weaker banks should’t be merged with big banks
Some banks to be promoted globally
Rationalisation of interest rates
Lower crr and slr
Profit banks to be listed
Asset reconstruction companies
Priority sector lending
Priority sector lending
Some sectors by rbi are considered most important for overall socio economic devn of the
country
Loans to them should be provided therefore put under priority sector.
But these sectors contribute highly to the npa therefore banks are reluctant
Therefore rbi has mandated the same and even there is subcategorisation for more focus.
E.g. 18% - agriculture and allied activities out of 40%
Rules for banks
40 % - banks with 20 or more branches – foreign + indian
Foreign banks with less then 20 branches – 32% with no sub category.
No action as by narasimham
Non banking financial companies
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
6
They are financial banks but not a complete bank – engaged in financial activities – known
as shadow bank
Nbfcs can be of several types including insurance companies even mutual funds but all not
regulated by rbi.
Nbfcs regulated by RBI
Non deposit taking
They cant take deposit , they have to work with their on capital.
Net owned fund – 100 cr
Deposit taking
Can accept deposit but it is termed
10 to 60 months
Cant issue debit and cheq book
Net owned fund – 200 cr
Deposit taking nbfcs
Rated
• Registered with credit rating agencies
• 4 times of net owned
Non rated
• Not registered with credit rating agencies
• 1.5 times only
Cant give interest rates Less then 3.5% and not More then 12.5%
NPA
THERE IS NO RECOVERY OF PRINCIPAL AND INTEREST FOR 90 DAYS
Procedure under NPA
• Against a type of npa – some amount has to be kept out of profit known as provision
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
7
CIBIL
It was constituted in aug 2000
It is an agency which maintains the database of all borrowers
These informations are provided by lender
On it a website is been made which gives a score to all borrower
It is out of 900
If anyone has lower 750 – cant get loan
Can be accesed by anyone
No borrowing - -1
Twin balance sheet problem
• Balance sheet refers to a document of a company which shows financial health of a company.
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
8
• If blnc sheet of company goes bad so it will impact the blnc sheet of other compnay as well
known as twin balance sheet problem.
How it happened in india
Solutions
Writing of the loan
Asset reconstruction companies
Corporate debt restructuring
Recapitalisation
Mission indradhanush
Prompt corrective action
Writing of the loan
Under this central banks can instruct the banks to clean their balance sheet by counting npas
as lost asset
Against them provision will be released and it could be used .
Meanwhile process of recovery can continue .
Asset reconstruction company
Sarfesi act 2002
can sell the secured assets
can sell to arcs
Accordingly 1st arc was established by sbi pnb idbi and icici known as arcil
Problems and solutions
Arcs but the npas of the banks at discounted price and recover them with the help of their
trained workers.
But problem kept on increasing as their npa have gone beyond a range e.g. pnb – 400000 cr
and even many were politically complex.
Solution by govt – bad bank
Bad bank and para
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
9
Bad bank was to be a bank backed by govt but came under tough resistance by
raguramrajan – transfering the problem , fiscal deficit problem in monetary policy
Govt came with new solution – para (public sector asset rehabilitation agency) raise fund
from public.
Corporate debt restructurring
Several loans defaulted were genuine due to market conditions hence rbi decided to give
chance to these corporates
Some guidelines were formed.
So they can pay back their loan
Guidelines
Cdr is not possible without permission of rbi
Possible iff borrowing is from more then 1 bank
Iff total borrowing is more then 10 cr
Banks and co both can apply for it.
Corporate can apply iff supported by 20 % loan and same goes with bank
Once application is accepted – joint lender forum
50% loan giver should get ready for further process – scheme will be decide
Plan should be certified by 75%
Schemes
5/25
Strategic debt restructuring
S4a
5/25
The loan of the company is restructured
Usually it was for infra comp and loan for them was 12-15 yrs
It was made to 25 yrs so the installments can be brought to low and as payment starts after
completion of project
Comp can borrow after 5 yrs of successful payment
Strategic debt restructurring
• If 5/25 fails
• Banks may forcefully acquire the ownership of the company (51%)
• Then banks are given time of 18 months to find a suitable buyer for it.
• If it finds a buyer who can start the repayment then loan wont be counted as a npa
• Banks still found a problem to get a buyer then it was done to 26% but he should be made a
single largest investor.
S4A
Loan should not be less then 500 cr
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
10
Even after a cash flow starts full payment is not possible due to low return
Therefore loan be divided into 2 including interest
Sustainable – to be paid
Non sustainable – to be converted into shares
Mission INDRADHANUSH
Also known as A TO G mission
A – APPOINTMENTS
B – BOARD OF DIRECTORS
C – CAPITALIZATION
D – DESTRESSING
E – EMPOWERMENT
F – FRAMEWORK OF ACCOUNTABILITY
G – GOVERNANCE – GYAN SANGAM – PM, FM , GOVERNOR (RBI), CMDS
PROMPT CORRECTIVE ACTION
Rbi keeps a close look on the health of banks as it violates rbi psychological range , it takes a
preventive action and puts them under the following 3 categories.
Rules to foreign investment in banking sector
In psbs – majority by govt – 51% , rbi asked it to go for 49% . Single buyer not more then 10%
and foreign investment not more then 20 %
Private sector indian banks – fdi – 74% but single not more then 10%
Foreign banks – 100%
On tap banking license guidelines
An interested investor with an experince of atleast 10 yrs in banking may apply
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
11
even an indian corporate owned by resident indian with a neat and clean history of atleast
10 yrs can apply and
even an existing nbfc can apply.
Group companies cant apply
License is valid for 18 months only if not worked it has to be surrender
Paid up capital – 500 cr
In 1st 5 yrs promoter to bring his sharing to 40% other investors cant take more then 10% ,
in these 5 yrs fdi cant be more then 49% ( indian in nature)
By the end of 15 yrs – promoter – 15% , fdi – 74% single buyer – 10%
25% branches in rural areas
6th year should be listed .
Core banking solution
It provides anywhere banking facility to the customers of the banks.
It connects each and every branch of the bank from the central server.
Money can be withdrawn and deposited at any branch of the bank with its customers.
E-kuber – rbi
Online fund transfer
RTGS – REAL TIME GROSS SETTLEMENT
NEFT – NATIONAL ELECTRONIC FUND TRANSFER
IMPS – IMMEDIATE PAYMENT SERVICES
UPI AND BHIM
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
12
INSOLVENCY AND BANKRUPCY CODE
It is considered to be a economic reform for ease of doing of business.
It will allow easy exit of business firms(why)
Bcuz of complex laws it is easy to enter but even it is more difficult to come out due to same
complex laws.
Insolvency refers to a financial condition in which person is not able to clear its debt and when
through legal procedure he allows himself to be declared as being called as bankrupt.
Procedure
Earlier complain could be filed in any tribunal or court like company law tribunal , h.c. etc but
now it is to be filed in nlt and it could be filed by banks also.
There is a proper mechanism to challenge like nclt – nclat – s.c.
Min amt – 1cr
Process wont be initiated at a point it will be evaluated by insolvency professionals under nclt
and to check over it there is a insolvency and bankruptcy board of india.
Fixed time limit – 180 days + 90 days ext
Msme – 90days + 45 days ext
After completion of bankruptcy liquidation will start and even liabilities order is fixed
Workers and secured lenders
Unsecured lenders
Dues of state
Preferential shareholders
Equity shareholders
Thanks for enyoing our notes ( it’s a party time..cheers )
Telegram link - https://t.me/DESIREIAS
www.DesireIAS.com E-Mail : caredesireias@gmail.com Banking Short Notes
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Banking Law Notes PDFDokument64 SeitenBanking Law Notes PDFsoumya100% (2)
- Regional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementVon EverandRegional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.19 FNB Relocation PolicyDokument5 Seiten2.19 FNB Relocation PolicyXbox FlashingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Banking System History and StructureDokument47 SeitenIndian Banking System History and StructureRahul SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Awarness Meritshine MaterialDokument162 SeitenBanking Awarness Meritshine MaterialRagavi JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFS Module 2Dokument47 SeitenIFS Module 2Dhrumi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banks in India: NbfcsDokument49 SeitenBanks in India: NbfcsVenkata Sai Reddy GarlapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regional Rural BankDokument26 SeitenRegional Rural BankVijayeta Nerurkar100% (1)
- Structure of Commercial Banking in IndiaDokument43 SeitenStructure of Commercial Banking in IndiaViral PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment Indian Banking System Part 2Dokument18 SeitenAttachment Indian Banking System Part 2nishant kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1627995243-Lecture - 1 HISTORY OF BANKING IN INDIADokument5 Seiten1627995243-Lecture - 1 HISTORY OF BANKING IN INDIAKhushraj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)Dokument14 SeitenIndian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)krunaldedehiya100% (1)
- Nationalization of Indian Commercial BanksDokument16 SeitenNationalization of Indian Commercial BanksAlbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- BankingDokument85 SeitenBankingZeel kachhiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Banking Sector For PresentationDokument23 SeitenOn Banking Sector For Presentationvaishali haritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banks in IndiaDokument13 SeitenBanks in IndiaSumedha TutejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Practice Unit 1Dokument13 SeitenBanking Practice Unit 1Nandhini VirgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDokument10 SeitenReserve Bank of IndiaPrathik_Shetty_204Noch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Structure in IndiaDokument5 SeitenBanking Structure in IndiaCharu Saxena16Noch keine Bewertungen
- L15 Scheduled BANKS PDFDokument14 SeitenL15 Scheduled BANKS PDFakshita raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Financial Services Management: Ms. Jebakerupa Roslin Amirtharajan St. Joseph S College of Engineering MBADokument82 SeitenBanking Financial Services Management: Ms. Jebakerupa Roslin Amirtharajan St. Joseph S College of Engineering MBASvijayakanthan SelvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDokument109 SeitenUnit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDr. S. Nellima KPRCAS-CommerceNoch keine Bewertungen
- SelvakumarDokument14 SeitenSelvakumarSelvakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Banking StructureDokument24 SeitenIndian Banking StructureRENUKA CHAUHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundDokument6 SeitenBanking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundRUPA GOELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Banking Sector: BY Siddhant Jain 9595637843Dokument66 SeitenIndian Banking Sector: BY Siddhant Jain 9595637843sh_09708Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 1Dokument93 SeitenUnit - 1Suji MbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking in India: An Introduction To The Banking System in The CountryDokument16 SeitenBanking in India: An Introduction To The Banking System in The CountryJayesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank ManagementDokument198 SeitenBank ManagementSooraj Kallooppara0% (1)
- Structure of Commercial Banks in India: Click To Edit Master Title StyleDokument10 SeitenStructure of Commercial Banks in India: Click To Edit Master Title StyleMamta KasodariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Commercial and Investment BankingDokument79 SeitenUnit 1 - Commercial and Investment BankingMd Rasool E FarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBI Project - Docx 1Dokument34 SeitenRBI Project - Docx 1Suraj changadev moteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mission Vission and ValuesDokument8 SeitenMission Vission and ValuesJiby JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intoduction To BankingDokument41 SeitenIntoduction To BankingAbhilash ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Banking SystemDokument45 SeitenOverview of Banking SystemShabri MayekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-Vii Types of BanksDokument18 SeitenUnit-Vii Types of Bankssheetal rajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibs F y B.com (H) Unit 1Dokument18 SeitenIbs F y B.com (H) Unit 1Nikunj PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devast IncDokument19 SeitenDevast IncPiyush SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercial Banks1Dokument16 SeitenMercial Banks1kanna1808Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)Dokument27 SeitenComparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)GUDDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBK Unit 3 (Ms. C. Yuvarani M.phil.,)Dokument9 SeitenMBK Unit 3 (Ms. C. Yuvarani M.phil.,)Edison paNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Banks IndiaDokument3 SeitenTypes of Banks India17-075 Upgna PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSDokument12 Seiten18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSramixudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Banking System in IndiaDokument37 SeitenHistory of Banking System in IndiaSrijan DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Management: Presented by C. KavyaDokument27 SeitenBanking Management: Presented by C. KavyaKaviya KaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking System of India: Presented By-Sohini MukherjeeDokument31 SeitenBanking System of India: Presented By-Sohini MukherjeeShivam AgarwalITF43Noch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Management Additional NotesDokument118 SeitenBanking Management Additional NotesLokesh ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Institutions & MarketsDokument62 SeitenFinancial Institutions & MarketsSaurav UchilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of BankDokument2 SeitenTypes of Bankashisghadai02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Origin & Kinds of BanksDokument21 SeitenOrigin & Kinds of BanksPriyankamohanant SumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BankingDokument4 SeitenBankingFirdaus PanthakyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Banks in IndiaDokument12 SeitenCommercial Banks in IndiaMamta KasodariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Banking System PDFDokument12 Seiten1 Banking System PDFNilu91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report Ms Word 15.7.2022Dokument44 SeitenProject Report Ms Word 15.7.2022Swathi JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial - Banks - in - India (Just For Reading)Dokument18 SeitenCommercial - Banks - in - India (Just For Reading)Nitya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Report On H.P. State Cooperative BankDokument61 SeitenSummer Report On H.P. State Cooperative BankVIKAS DOGRA71% (7)
- A Study On Loans and Advances at State Bank of India.Dokument83 SeitenA Study On Loans and Advances at State Bank of India.dikshapatil6789Noch keine Bewertungen
- History 2Dokument5 SeitenHistory 2bickyboom96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Banking IndustryDokument77 SeitenBanking Industryprashant mhatreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingVon EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wallstreetjournaleurope 20170503 TheWallStreetJournal-EuropeDokument22 SeitenWallstreetjournaleurope 20170503 TheWallStreetJournal-EuropestefanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Banking: 11/04/21 Om All Rights Reserved. 1Dokument180 SeitenCorporate Banking: 11/04/21 Om All Rights Reserved. 1Pravah ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Financial AppraisalDokument79 SeitenProject Financial AppraisalAmy MengistuNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Level 5 Practical ExerciseDokument4 SeitenIT Level 5 Practical Exerciseeyob awokeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 华尔街日报 2023 3 22Dokument31 Seiten华尔街日报 2023 3 22shichao.yuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nabil - Bank - Report - Final (Fianancial - Performance - Analysis) )Dokument45 SeitenNabil - Bank - Report - Final (Fianancial - Performance - Analysis) )Kishan SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Topics On Public PolicyDokument4 SeitenThesis Topics On Public Policyafknojbcf100% (2)
- Intermediate Examination: Suggested Answers To QuestionsDokument23 SeitenIntermediate Examination: Suggested Answers To QuestionsSannu VijayeendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samplepractice Exam 15 October 2020 Questions and AnswersDokument6 SeitenSamplepractice Exam 15 October 2020 Questions and AnswersMartha Nicole MaristelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law SyllabusDokument157 SeitenLaw SyllabusjiaorrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Account StatementDokument3 SeitenAccount StatementJobz ForuNoch keine Bewertungen
- INLIAS - Integrated Non-Life Insurance Application Solution - User ManualDokument30 SeitenINLIAS - Integrated Non-Life Insurance Application Solution - User Manualbirendra sonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBADokument128 SeitenRBACa Mehal DoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Bank of BarodaDokument49 SeitenIntroduction To Bank of BarodaVarun JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement of Uttara BankDokument30 SeitenFinancial Statement of Uttara BankRaqibul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Thesis On Investment BankingDokument4 SeitenPHD Thesis On Investment BankingSara Alvarez100% (2)
- Oceanic Bank International PLC Unaudited Financial Statement For Period Ended March 31, 2010Dokument1 SeiteOceanic Bank International PLC Unaudited Financial Statement For Period Ended March 31, 2010Oceanic Bank International PLCNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Report On Online BankingDokument18 SeitenA Project Report On Online BankingSourav PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Inclusion Policy - An Inclusive Financial Sector For AllDokument118 SeitenFinancial Inclusion Policy - An Inclusive Financial Sector For AllwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Issue ManagementDokument7 SeitenPublic Issue ManagementthensureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOI Small Compliance Guide.v1.1-FINALDokument57 SeitenBOI Small Compliance Guide.v1.1-FINALhernan garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-3-Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation - An AppraisalDokument32 SeitenChapter-3-Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation - An AppraisalRiti PaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citibank v. SabenianoDokument5 SeitenCitibank v. SabenianoBananaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 35863Dokument204 Seiten35863bhgthert100% (1)
- Research Paper On Debt RestructuringDokument7 SeitenResearch Paper On Debt Restructuringafnhfbgwoezeoj100% (1)
- Questionnaire For Bank (PNB)Dokument13 SeitenQuestionnaire For Bank (PNB)Abhishek PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Istisna V FinalDokument46 SeitenIstisna V FinalAlHuda Centre of Islamic Banking & Economics (CIBE)Noch keine Bewertungen
- StressDokument61 SeitenStressToufique Kazi100% (1)
- AC PaperDokument2 SeitenAC Paperpiyush kumarNoch keine Bewertungen