Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP Low Self Esteem Drei
Hochgeladen von
Ellenare Racion0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
3K Ansichten5 SeitenThe patient is experiencing low self-esteem related to the death of her embryo. The nursing interventions aim to help her recognize and verbalize her feelings, discuss her loss, and recognize how low self-esteem affects her. Within 8 hours, the patient will be able to verbalize her feelings and recognize the impact of low self-esteem. Within 24 hours, her mood will improve and she will be able to look toward the future. The long term goal is that within 24-48 hours, her mood will return to normal and she will think positively about the future.
Originalbeschreibung:
SAMPLE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe patient is experiencing low self-esteem related to the death of her embryo. The nursing interventions aim to help her recognize and verbalize her feelings, discuss her loss, and recognize how low self-esteem affects her. Within 8 hours, the patient will be able to verbalize her feelings and recognize the impact of low self-esteem. Within 24 hours, her mood will improve and she will be able to look toward the future. The long term goal is that within 24-48 hours, her mood will return to normal and she will think positively about the future.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
3K Ansichten5 SeitenNCP Low Self Esteem Drei
Hochgeladen von
Ellenare RacionThe patient is experiencing low self-esteem related to the death of her embryo. The nursing interventions aim to help her recognize and verbalize her feelings, discuss her loss, and recognize how low self-esteem affects her. Within 8 hours, the patient will be able to verbalize her feelings and recognize the impact of low self-esteem. Within 24 hours, her mood will improve and she will be able to look toward the future. The long term goal is that within 24-48 hours, her mood will return to normal and she will think positively about the future.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
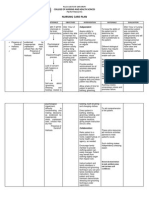
BSN 2 Sec 3 Grp B
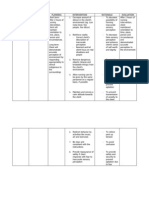
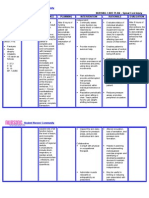
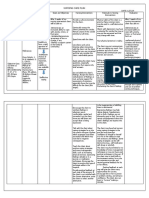
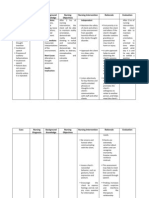
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
PROBLEM
Subjective: Self-esteem is defined STO: Dx: STO:
as the way an
"Sana magka anak individual thinks about Within 8 hours of Assess the patient’s Patients with self-esteem (Goal Met)
pa kami ". as himself or herself, and effective nursing feelings of comfort and issues may appear as
verbalized by interventions, the content with his or her though their actions are Within 8 hours of
how good he or she effective nursing
patient feels. Positive self- patient will be able to: own performance. not in keeping with their
own personal, moral, or interventions,
Objective: esteem develops
a) Will able to ethical values; they may the patient
when a person feels verbalize her recognized the
Mood is good and capable of also deny these
feelings impact/effect
dysphoric responding to b) Discuss any behaviors, project
blame, and rationalize of the low self
and tearful challenges and hard/angry
at times, but feelings about personal failure. esteem, able to
stressors. Nevertheless, verbalize her
client is the loss of her
when a person exhibits feelings and
responsive baby.
and mild to a c) Recognize the The patient may have inquire proper
remarkable shift in the Assess how competent
cooperative. impact/effect developed the ability to help.
Pre orbital view of himself or patients feel about their
of low self carry out personal
puffiness. herself such as esteem and ability to perform and
carry out their own and responsibilities despite
Staring negativity about self, inquire need for
distress help. others’ expectations. low self-esteem. This LTO:
low self-esteem may be a positive
develops. Low self- indicator of the (Goal Met)
Nursing Diagnosis: esteem can reduce patient’s potential for
the quality of a successful improvement Within 24 hours
Low self esteem person’s life in many LTO: of effective
of self-esteem.
related to death of different ways, nursing
an embryo as Within 24-48 hours of
including negative interventions,
evidenced by effective nursing
feelings, fear, the patient’s
Expressions of interventions, the
helplessness and relationship problems, patient will: mood will be
uselessness or low resilience. This back to normal,
change in self-esteem a) Patient reports Assess for presence of Ongoing grief may will think positive
progress in unfinished grief. hinder the patient’s
is a temporary phase about the future
in response to feeling current ability to move forward and reports
helpless to control the situation. in life. progress in
current situation. b) Look Tx: current
SOURCE: toward/plan for situation.
future, one at a Provide privacy. Private discussions need
https://nurseslabs.com time. to take place in a
/situational-low-self- c) Mood will back setting where the
esteem/ to normal patient is free to express
feelings without being
overheard.
Apply active listening and These communication
open-ended questions. methods permit the
patient to verbalize
interests, concerns,
worries, and thoughts
without interruption. This
technique will convey a
sense of respect for the
patient’s abilities and
strengths in addition to
recognizing problems
and concerns.
Spend time with the The patient needs to
patient; set aside enough explore options to
time so that the encounter improve self-esteem by
is calm and deliberate. substituting negative
behaviors with positive
Edx: actions.
Educate the patient to join The patient needs to
in activities anticipated to explore options to
result in healthy self- improve self-esteem by
esteem. substituting negative
behaviors with positive
actions.
Encourage the patient to
express if he or she is able The patient may be
to associate these knowledgeable of up-
changes to a specific to-date situations that
event in his or her life. negatively change his
or her self-concept.
Encouraged verbalization
of feelings Help the bereaved to
recognize, actualize,
and accept the loss
ASSESSMENT:
1. Focus on your Nursing Diagnosis (Subjective and Objective cues should ALL be align with your problem)
2. Subjective data (preferably verbalization from the patient and must be in an open and close quotation otherwise if it is coming from the mother
or any significant other, it must be categorize as subjective data from a secondary source or an objective data [if it can be perceived by the
senses, verified by another person observing the same patient, and tested against accepted standards or norms] from a secondary source).
3. Objective data (start with the most obvious observation that is related to your nursing diagnosis to the less obvious, followed by abnormal vital
signs that are related to your problem and any laboratory results that are relevant to your problem)
4. For Nursing Diagnosis, use the 3-Part Statement: PES Format (Problem + Etiology + Signs and Symptoms) Three parts are joined together by
“related to” or “associated with” and “as manifested by” or “as evidenced by”
EXPLANATION OF THE PROBLEM:
1. Should be in paragraph form, it’s just like doing your pathophysiology but explaining in detail how the problem arise in relation to your objective
data and other signs and symptoms manifested by the patient that are related to your problem.
2. DO NOT FORGET to indicate your source as a basis in coming up with your explanation of the problem.
OBJECTIVES:
1. Must follow the concept of SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Time bound).
2. STO (Short Term Goal). In theory it covers your acute care (till 6 months). But for our requirement we measure our STO within the shift (0 – 8 hours).
A better parameter would be using ranges of time depending on the planned activities.
3. LTO (Long Term Goal). In theory it covers your chronic care (6 months and above). But for our requirement we measure our LTO within the first day
to the third day or one rotation (24 – 72 hours). A better parameter would be using ranges of time depending on the planned activities.
NURSING INTERVENTION:
1. Dx (diagnostics) should be based on your SUBJECTIVE and OBJECTIVE DATA.
2. Tx (therapeutics) should be arrange as ICDS (Independent nursing function, Collaborative [other health-care professional aside from the
physician], Dependent nursing function [physician/doctor], Supportive [Significant others, clergy/priest, and non-health care professional]
3. Edx (educative) should be based on the most needed by the patient that is relevant to the nursing diagnosis. (you can also base it on your STO
and LTO if there are educative goal)
RATIONALE:
1. It must be aligned with your nursing intervention and relevant to the case of you patient.
2. For the administration of medication, your rationale should be the indication of the drug in relation with the patient’s case.
EVALUATION/ EXPECTED OUTCOMES:
1. Evaluation for ACTUAL PROBLEM and your NURSING INTERVENTION should be past tense.
2. EXPECTED OUTCOME for POTENTIAL PROBLEM and your NURSING INTERVENTION should be future tense.
3. Should evaluate (GOAL MET, GOAL NOT MET or GOAL PARTIALLY MET) accurately and should be supported by results from your STO and LTO.
4. For expected outcomes (GOAL MET IF, GOAL NOT MET IF or GOAL PARTIALLY MET IF), and give parameters for the IF.
5. Should discuss or make recommendation/s for goal not met and partially met.
Always remember that NURSING PROCESS is SYSTEMATIC, PATIENT-CENTERED, GOAL-ORIENTED AND DYNAMIC.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Situational Low Self-Esteem - NCPDokument3 SeitenSituational Low Self-Esteem - NCPLizzey YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - Fear NCPDokument2 SeitenAbnormal Uterine Bleeding - Fear NCPJasmine100% (1)
- NCP Self EsteemDokument4 SeitenNCP Self Esteemeinghel_24100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenNursing Care PlanJustine Suico100% (1)
- NCP Situational Low Self EsteemDokument1 SeiteNCP Situational Low Self EsteemMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (4)
- NCP - Situational Low Self-EsteemDokument1 SeiteNCP - Situational Low Self-EsteemJamal Agontong0% (1)
- Assessment Inference Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDokument1 SeiteAssessment Inference Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationJara Klaudette Tia67% (3)
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDokument2 SeitenDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDokument7 SeitenNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Social InteractionDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Social InteractionKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Social Interaction Related To Fear of Being Scrutinized and Embarrassed by OthersDokument9 SeitenImpaired Social Interaction Related To Fear of Being Scrutinized and Embarrassed by Othersnathalie cotengNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDokument2 SeitenNCP Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDayan CabrigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Violence - OtherDokument2 SeitenNCP Violence - OtherRosean Venus SilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Self EsteemDokument3 SeitenNCP Self EsteemAlfadz AsakilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Low SelfDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Low Selfmaimai32426394% (17)
- NCP Anxiety and PainDokument12 SeitenNCP Anxiety and PainCazze Sunio100% (1)
- NCP FinalDokument22 SeitenNCP FinalAlmira Ahamad100% (1)
- NCP GrievingDokument5 SeitenNCP GrievingEllenare Racion33% (3)
- NCP Sleep DisturbanceDokument1 SeiteNCP Sleep DisturbanceKrystel Cate DelaCruz DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP StressDokument2 SeitenNCP StressWaqas Javed100% (7)
- Anticipatory GrievingDokument2 SeitenAnticipatory GrievingKM100% (5)
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDokument4 SeitenDisturbed Thought ProcessJessieRamosAnicetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPChrisTine M. MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Care DeficitDokument1 SeiteSelf Care DeficitWilly EstacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument6 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationChristine Denise Venus ValentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective CopingDokument3 SeitenNCP Ineffective CopingAqua RentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Care NCPDokument2 SeitenSelf Care NCPMick De Leon100% (3)
- NCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To SchizophreniaDokument6 SeitenNCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To Schizophrenianaishel0% (1)
- NCP Depressive DisorderDokument3 SeitenNCP Depressive Disorderluthercarl cachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PowerlessnessDokument6 SeitenNCP PowerlessnessopxNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Psyche2Dokument6 SeitenNCP Psyche2Nica RTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDokument5 SeitenReadiness For Enhanced Hope NCPMarife Lipana ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP SelfMutilationDokument4 SeitenNCP SelfMutilationjhienelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chiari - Frommel Syndrome - Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Intercourse Discomfort & Loss of Sexual Desire Related To Dryness in The Vagina Secondary To Gal Actor RheaDokument3 SeitenChiari - Frommel Syndrome - Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Intercourse Discomfort & Loss of Sexual Desire Related To Dryness in The Vagina Secondary To Gal Actor RheaLoord Vie Lu MondigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardDokument9 SeitenNCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardMary Margarett BoadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Suicidal TendencyDokument2 SeitenNCP - Suicidal Tendencyяoxel яayмoи eитяeиa100% (5)
- NCP DepressionDokument2 SeitenNCP Depressionhollymadison80% (5)
- ND - Risk For SuicideDokument3 SeitenND - Risk For SuicideHu Dawi100% (2)
- Anxiety NCPDokument4 SeitenAnxiety NCPRey Tommy NaponeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anxiety Related To Stress HspitaiztionDokument1 SeiteAnxiety Related To Stress HspitaiztionEunice Lan Sandoval Ardiente100% (3)
- N C PDokument3 SeitenN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Dokument4 SeitenFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective CopingDokument5 SeitenNCP Ineffective CopingChiara Fajardo0% (3)
- Tuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Fear/AnxietyDokument3 SeitenTuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Fear/AnxietySALMA M. TUANO100% (1)
- NCP Self HarmDokument1 SeiteNCP Self HarmJoshua ArevaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Cre DeficitDokument3 SeitenSelf Cre DeficitSteph_Toinkz_240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cues / Evidences Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Objective Data: IndependentDokument6 SeitenCues / Evidences Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Objective Data: IndependentRiza Angela BarazanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: DATE: 6/27/19Dokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan: DATE: 6/27/19Maricris Tac-an Calising-PallarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMyrien BanaagNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP AnxietyDokument1 SeiteNCP AnxietyGrace MellaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP SchizophreniaDokument2 SeitenNCP Schizophreniajoshua canja100% (5)
- NCP SchizDokument12 SeitenNCP SchizKristine Reyes - MerleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Situational Low SelfDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Situational Low SelfChar Perea100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Mr. John E: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rational EvaluationDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan For Mr. John E: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rational EvaluationArnold Dickens JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- DELA CRUZ Postpartum Blues NCPDokument5 SeitenDELA CRUZ Postpartum Blues NCPRYAN CHRISTIAN DELA CRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hopelessness: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument6 SeitenHopelessness: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJasmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANGEL-NCP - CaseloadDokument7 SeitenANGEL-NCP - CaseloadNik Rose ElNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDokument4 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goalmark OrpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHN Non Communicable Diseases and OthersDokument90 SeitenCHN Non Communicable Diseases and OthersEllenare Racion100% (1)
- Unit 4 AppendixDokument54 SeitenUnit 4 AppendixEllenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument6 SeitenDrugsEllenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrapartum NCM 101Dokument92 SeitenIntrapartum NCM 101Ellenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Health PackagesDokument43 SeitenEssential Health PackagesEllenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family History: The Patients Stated That They Have No Family Health HistoryDokument4 SeitenFamily History: The Patients Stated That They Have No Family Health HistoryEllenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Risk For InfectionDokument6 SeitenNCP Risk For InfectionEllenare Racion100% (1)
- NCP GrievingDokument5 SeitenNCP GrievingEllenare Racion33% (3)
- I. Meal Plan For Elderly: Food Exchange No. of Exchange CHO G PRO G FAT G Energy Kcal B L D SNDokument2 SeitenI. Meal Plan For Elderly: Food Exchange No. of Exchange CHO G PRO G FAT G Energy Kcal B L D SNEllenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbed Sleeping PatternDokument5 SeitenDisturbed Sleeping PatternEllenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accountant: Joshua M. ToldingDokument2 SeitenAccountant: Joshua M. ToldingEllenare RacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Article Effects of PH On The Shape of Alginate Particles and Its Release BehaviorDokument10 SeitenResearch Article Effects of PH On The Shape of Alginate Particles and Its Release BehaviorAmalia HanifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa Food Technology Coursework Mark SchemeDokument7 SeitenAqa Food Technology Coursework Mark Schemeafjwdbaekycbaa100% (2)
- Reading Comprehension MaterialsDokument6 SeitenReading Comprehension MaterialsDiana PundavelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineering: ReactionDokument59 SeitenChemical Engineering: Reactionnluvwjm7275Noch keine Bewertungen
- TRAFFIC RULES PDF Project ReportDokument18 SeitenTRAFFIC RULES PDF Project ReportShweta SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abrams Clinical Drug Therapy Rationales For Nursing Practice 11th Edition Test BankDokument6 SeitenAbrams Clinical Drug Therapy Rationales For Nursing Practice 11th Edition Test BankWilliam Nakken100% (28)
- Cruz v. CA - G.R. No. 122445 - November 18, 1997 - DIGESTDokument2 SeitenCruz v. CA - G.R. No. 122445 - November 18, 1997 - DIGESTAaron Ariston80% (5)
- How Condensing Boilers WorkDokument1 SeiteHow Condensing Boilers WorkBrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parle G ReportDokument7 SeitenParle G ReportnikhilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.0.2 3.0.2 Thermax Inc.: Pressure Building Ambient Vaporizers For Bulk Storage TanksDokument2 Seiten3.0.2 3.0.2 Thermax Inc.: Pressure Building Ambient Vaporizers For Bulk Storage TanksSiDdu KalashettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set in Power System 2Dokument3 SeitenProblem Set in Power System 2Andrew AlterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burns Plastic Reconstructive Surgery MSCDokument4 SeitenBurns Plastic Reconstructive Surgery MSCCareer VoyageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methods - Print - QuizizzDokument5 SeitenResearch Methods - Print - QuizizzpecmbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clase No. 24 Nouns and Their Modifiers ExercisesDokument2 SeitenClase No. 24 Nouns and Their Modifiers ExercisesenriquefisicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incorporating Developmental Screening and Surveillance of Young Children in Office PracticeDokument9 SeitenIncorporating Developmental Screening and Surveillance of Young Children in Office PracticeakshayajainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Postpartum Hemorrhage and Third Stage of LaborDokument7 SeitenPathophysiology of Postpartum Hemorrhage and Third Stage of Labornouval_iqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saving AccountDokument9 SeitenSaving AccountpalkhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cvmmethod 101220131950 Phpapp02Dokument20 SeitenCvmmethod 101220131950 Phpapp02AlibabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDS-PE-102-UB5502H (Provisional) 2019Dokument2 SeitenTDS-PE-102-UB5502H (Provisional) 2019Oktaviandri SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Zombie in The Brain and The Woman Who Died LaughingDokument40 SeitenThe Zombie in The Brain and The Woman Who Died Laughingcory_ruda100% (1)
- Finding Clara: Establishing The Biographical Details of Clara Peeters (Ca. 1587-After 1636)Dokument15 SeitenFinding Clara: Establishing The Biographical Details of Clara Peeters (Ca. 1587-After 1636)victoriagalapedroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decommissioning HSE PDFDokument105 SeitenDecommissioning HSE PDFRafael Rocha100% (1)
- 9ha Power PlantsDokument2 Seiten9ha Power PlantsGaurav DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myasthenia Gravis DiseaseDokument14 SeitenMyasthenia Gravis Diseaseapi-482100632Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 GRADE 10 SYNCHRONOUS REVISED Fitness-Test-Score-CardDokument1 SeiteQ1 GRADE 10 SYNCHRONOUS REVISED Fitness-Test-Score-CardAlbert Ian CasugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peritoneal Dialysis Unit Renal Department SGH PD WPI 097 Workplace InstructionDokument10 SeitenPeritoneal Dialysis Unit Renal Department SGH PD WPI 097 Workplace InstructionAjeng SuparwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me22 M1a1Dokument2 SeitenMe22 M1a1Jihoo JungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reticular AbscessDokument4 SeitenReticular AbscessSasikala KaliapanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pamphlet InsideDokument1 SeitePamphlet Insideapi-2408549370% (1)
- Pharmacy Incharge JDDokument5 SeitenPharmacy Incharge JDUsman JamilNoch keine Bewertungen