Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
St. Teresita's Academy of Aritao, Inc
Hochgeladen von
Mauro UbungenOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
St. Teresita's Academy of Aritao, Inc
Hochgeladen von
Mauro UbungenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
St. Teresita’s Academy of Aritao, Inc.
Poblacion, Aritao, Nueva Vizcaya
SCI-MATH DEPARTMENT
MODULE 1.2
MICROSCOPE/ CELL THEORY/ CELL STRUCTURE
Microscope: “micro” - from Greek meaning small “scope” – from Greek meaning to look or see
By definition a microscope is:
1. An optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute
objects.
2. A non-optical instrument (as one using radiation or using vibrations) for making enlarged images of minute
objects.
3. An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye.
PARTS OF MICROSCOPE
Eyepiece or Ocular is what you look through at the top of the microscope. Typically, standard eyepieces have
a magnifying power of 10x. Optional eyepieces of varying powers are available, typically from 5x-30x.
Eyepiece Tube holds the eyepieces in place above the objective lens. Binocular microscope heads typically
incorporate a diopter adjustment ring that allows for the possible inconsistencies of our eyesight in one or both
eyes. The monocular (single eye usage) microscope does not need a diopter. Binocular microscopes also swivel
(Interpupillary Adjustment) to allow for different distances between the eyes of different individuals.
Objective Lenses are the primary optical lenses on a microscope. They range from 4x-100x and typically,
include, three, four or five on lens on most microscopes. Objectives can be forward or rear-facing.
Nosepiece houses the objectives. The objectives are exposed and are mounted on a rotating turret so that
different objectives can be conveniently selected. Standard objectives include 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x although
different power objectives are available.
Coarse and Fine Focus knobs are used to focus the microscope. Increasingly, they are coaxial knobs - that is
to say they are built on the same axis with the fine focus knob on the outside. Coaxial focus knobs are more
convenient since the viewer does not have to grope for a different knob.
Stage is where the specimen to be viewed is placed. A mechanical stage is used when working at higher
magnifications where delicate movements of the specimen slide are required.
Stage Clips are used when there is no mechanical stage. The viewer is required to move the slide manually to
view different sections of the specimen.
Aperture is the hole in the stage through which the base (transmitted) light reaches the stage.
Illuminator is the light source for a microscope, typically located in the base of the microscope. Most light
microscopes use low voltage, halogen bulbs with continuous variable lighting control located within the base.
Condenser is used to collect and focus the light from the illuminator on to the specimen. It is located under the
stage often in conjunction with an iris diaphragm.
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and
below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined,
they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
Condenser Focus Knob moves the condenser up or down to control the lighting focus on the specimen.
What are life functions?
Nutrition Excretion
Metabolism Homeostasis
Growth Reproduction.
Response
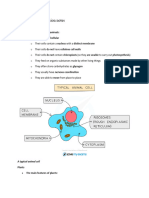
THE CELL THEORY
A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
Two Types of Cells
1. Prokaryotic
Do not have structures surrounded by
membranes
Few internal structures
One-celled organisms, Bacteria
2. Eukaryotic
Contain organelles surrounded by membranes
Most living organisms
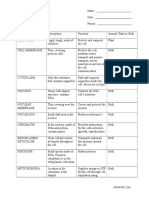
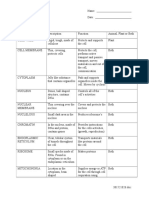
Parts of Cell
Organelles - Parts of Cell
A B
Nucleus Regulates all cell activities
Cell Membrane Is made out of phospholipids and proteins
Mitochondrion Site of cellular respiration "power house"
Lysosome Suicide Sacks that contain digestive enzymes
helps in food digestion of the cell
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Contains Ribosomes, transports proteins and other
materials
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Contains no ribosomes, stores proteins
Gogi complex (apparatus) Processes and packages proteins
Nucleuolus Dark spot of chromatin in the nucleous where
ribosomes are produced
Cytoplasm Colloid that contains water and nutrients and supports
the organelles
Organelles The parts of a cell with a particular function
Prokaryotic Cells with no true nucleus and no membrane bound
organelles
Eukaryotic Cells that contain a true nucleus and membrane bound
organelles
Centrioles Only in animal cells, aid in cell division
Ribosomes Produce Proteins
Chloroplast Found only in plants, site of photosynthesis
Vacuoles Large storage sacks found mainly in plants
Cell Wall Structure in plants made of cellulose that is outside of
the cell membrane
Chromatin Thin strands of DNA and proteins found in the
nucleus of a cell.
Cytoskeleton Long protein filaments in the cytosol that support the
cell. framework of the cell
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cells NatDokument62 SeitenCells NatErinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Cells & MicroscopeDokument31 SeitenUnit 2: Cells & MicroscopeSaisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sel PDFDokument32 SeitenSel PDFJeje DengiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell: The Unit of LifeDokument2 SeitenCell: The Unit of LifeLA RicanorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Sa BiologyDokument6 SeitenReviewer Sa BiologyKate ZuniegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDokument37 Seiten2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDokument5 Seiten2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology NotesDokument15 SeitenIGCSE Biology NotesMai YoussifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function ReviewerDokument4 SeitenCell Structure and Function ReviewerLeandre Jasmine ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDokument6 SeitenCell Organelles WorksheetAndi ImanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Bio Quiz 1Dokument3 SeitenCell Bio Quiz 1raphaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument8 SeitenCellsAnchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- #1 Cell Structure and FunctionDokument3 Seiten#1 Cell Structure and FunctionCharlene EpilepsiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDokument45 Seiten1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- B01 Cells and OrganellesDokument39 SeitenB01 Cells and OrganellesBobNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument30 SeitenCellNovita SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology: Science Explorer - Cells and HeredityDokument242 SeitenCell Biology: Science Explorer - Cells and HeredityZeinab ElkholyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDokument45 Seiten1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KEYDokument9 SeitenCell Organelles Worksheet KEYRonnieMaeMaullionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 2 Tingkatan 1Dokument58 SeitenBab 2 Tingkatan 1azizahembong84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesDokument39 SeitenCell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesNovanda D. PahleviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure: Structural Functional Unit: UnitDokument13 SeitenCell Structure: Structural Functional Unit: UnitHaya Attieh100% (1)
- PDF Cell Parts and Functions Table - CompressDokument5 SeitenPDF Cell Parts and Functions Table - CompressATHANYA RAKSAKANTONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - CellsDokument28 Seiten3 - CellsKat MicaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Theory ModifiedDokument33 SeitenCell Theory ModifiedNazish Altaf100% (1)
- As Chapter 1Dokument20 SeitenAs Chapter 1vt_greedhareeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions Topic 1.2 IB BiologyDokument4 SeitenPractice Questions Topic 1.2 IB BiologySamantha DAIRONoch keine Bewertungen
- IB 1 BIO UNIT1.2 Reading MaterialDokument3 SeitenIB 1 BIO UNIT1.2 Reading MaterialSaisriyaa PatroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal CellDokument31 SeitenAnimal CellAlyssa Sofia AlihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryDokument6 SeitenWeek 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDokument8 SeitenCell Organelles WorksheetVeer RamloghunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDokument8 SeitenCell Organelles Worksheet537777333% (3)
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDokument7 SeitenCell Organelles WorksheetKenneth ParungaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NGSS Cell Function Student Version EkDokument3 SeitenNGSS Cell Function Student Version EkLOUIE SOLMAYORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes: Intro To BioDokument4 SeitenBiology Notes: Intro To BioCorinne HooperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument16 SeitenChapter 1rida ikramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Y10 Ch2Dokument7 SeitenBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio 2Dokument4 SeitenGen Bio 2Melrhean GraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles ReviewDokument5 SeitenCell Organelles ReviewvictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDokument92 SeitenCell Structure and Functions PDFAishaizl100% (1)
- 2.1.1 Notes Ocr A BiologyDokument5 Seiten2.1.1 Notes Ocr A BiologyLuke BeaumontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Chapter 1Dokument13 SeitenScience Chapter 1Asia BibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDokument8 SeitenCell Organelles WorksheetErika Mae LibangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key - 2020 - Cell Organelles Worksheet ch2.2Dokument7 SeitenAnswer Key - 2020 - Cell Organelles Worksheet ch2.2Ria Cloe LavaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Organisation of Living ThingsDokument6 SeitenThe Organisation of Living ThingsFeRro ReniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Reviewer The CellDokument28 SeitenBiology Reviewer The CellAndrea Grace Bayot AdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: by - NatalieDokument24 SeitenCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal Cell WorksheetsDokument28 SeitenPlant and Animal Cell WorksheetsMarisol Leal PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDokument26 SeitenRganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationGasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDokument34 SeitenChapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationFHATIN AMIRA BINTI MUSA MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CellDokument24 SeitenThe CellCaren AdongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genbio Group 5Dokument1 SeiteGenbio Group 5lanceandreycafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)Dokument6 SeitenOrganelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)vscolegit shoppeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KeyDokument7 SeitenCell Organelles Worksheet KeyAngela ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1-2Dokument21 SeitenModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDokument7 SeitenLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Presentation Englsih VerDokument6 SeitenBio Presentation Englsih Verchristopherjohns0321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceVon EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Motivational Quotes For YouDokument1 SeiteMath Motivational Quotes For YouMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21stcenturylit q2 Mod2 Differentiating21stcentury v2Dokument19 Seiten21stcenturylit q2 Mod2 Differentiating21stcentury v2Mauro Ubungen100% (1)
- 21stcenturylit q2 Mod1 Writingacloseanalysis v2Dokument27 Seiten21stcenturylit q2 Mod1 Writingacloseanalysis v2Mauro Ubungen100% (6)
- Cot Demoteaching Stat & ProbabDokument22 SeitenCot Demoteaching Stat & ProbabMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21stcenturylit q2 Mod3 Creativeliteraryadaptation v2Dokument35 Seiten21stcenturylit q2 Mod3 Creativeliteraryadaptation v2Mauro Ubungen100% (2)
- 21stcenturylit q2 Mod4 Selfandpeerassessment v2Dokument27 Seiten21stcenturylit q2 Mod4 Selfandpeerassessment v2Mauro Ubungen100% (1)
- Practical Research 1 LAS Week 5Dokument63 SeitenPractical Research 1 LAS Week 5Mauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics: Learning Activity Sheet Simple and General AnnuitiesDokument14 SeitenGeneral Mathematics: Learning Activity Sheet Simple and General AnnuitiesMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Teresita's Academy of Aritao, Inc.: DepartmentDokument2 SeitenSt. Teresita's Academy of Aritao, Inc.: DepartmentMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- COT - DLL 4th QuarterrrDokument6 SeitenCOT - DLL 4th QuarterrrMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Importance of Maths in Everyday Life - : Amerigog, GuwahatiDokument3 SeitenThe Importance of Maths in Everyday Life - : Amerigog, GuwahatiMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orca Share Media1599498529868 6708783081823136821 PDFDokument78 SeitenOrca Share Media1599498529868 6708783081823136821 PDFMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Teresita's Academy of Aritao, IncDokument2 SeitenSt. Teresita's Academy of Aritao, IncMauro Ubungen100% (1)
- The Importance of Maths in Everyday Life - : Amerigog, GuwahatiDokument3 SeitenThe Importance of Maths in Everyday Life - : Amerigog, GuwahatiMauro UbungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Randomised Clinical Trial Comparing Myoinositol and Metformin in PCOSDokument7 SeitenA Randomised Clinical Trial Comparing Myoinositol and Metformin in PCOSAtika NajlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue of Palaearctic Coleoptera Vol.4 2007Dokument471 SeitenCatalogue of Palaearctic Coleoptera Vol.4 2007asmodeus822Noch keine Bewertungen
- Foundstone Hacme Bank User and Solution Guide v2.0Dokument60 SeitenFoundstone Hacme Bank User and Solution Guide v2.0Yeison MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7TH Maths F.a-1Dokument1 Seite7TH Maths F.a-1Marrivada SuryanarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Cutting 6Dokument71 SeitenPaper Cutting 6Vidya AdsuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conformational AnalysisDokument4 SeitenConformational AnalysisJinNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Industrial Policy 2010 (Bangla)Dokument46 SeitenNational Industrial Policy 2010 (Bangla)Md.Abdulla All Shafi0% (1)
- Dede - (2010) - Comparing Frameworks For 21st Century Skills PDFDokument16 SeitenDede - (2010) - Comparing Frameworks For 21st Century Skills PDFNaing Lynn HtunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFDokument10 Seiten2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFammarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sow and Learning ObjectivesDokument14 SeitenSow and Learning ObjectivesEhsan AzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GFN Cired PaperDokument8 SeitenGFN Cired PaperSukant BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irregular Verbs Lesson PlanDokument13 SeitenIrregular Verbs Lesson Planapi-311868026Noch keine Bewertungen
- Webinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018Dokument62 SeitenWebinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Iron in Water - SpectrophotometryDokument4 SeitenDetermination of Iron in Water - Spectrophotometryhanif ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesDokument10 SeitenZielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesPEDRO JOSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification For Neoprene Coating On The Riser CasingDokument17 SeitenSpecification For Neoprene Coating On The Riser CasingLambang AsmaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 04 - Motion and Force - DynamicsDokument24 SeitenChapter 04 - Motion and Force - DynamicsMohamad SyazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Paper 1 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Lower Secondary Sample Test For Use With Curriculum Published in September 2020Dokument11 SeitenEnglish Paper 1 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Lower Secondary Sample Test For Use With Curriculum Published in September 2020ABEER RATHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital BudgetingDokument24 SeitenCapital BudgetingHassaan NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monorail Hoist SystemDokument17 SeitenMonorail Hoist SystemypatelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The London SchoolDokument3 SeitenThe London SchoolKhawla Adnan100% (5)
- Ponce vs. Court of AppealsDokument7 SeitenPonce vs. Court of AppealsMp CasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Analysis of Concrete Frames Considering Joint FlexibilityDokument16 SeitenLinear Analysis of Concrete Frames Considering Joint FlexibilityluffiM13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Locomotive and Multi-Unit Fatigue Strength Considering The Results of Certifi Cation Tests in Ukraine and EU CountriesDokument8 SeitenAssessment of Locomotive and Multi-Unit Fatigue Strength Considering The Results of Certifi Cation Tests in Ukraine and EU CountriesLeonardo Antônio Pereira100% (1)
- Freeman Has Been A Partner in A Commercial Construction CompanyDokument1 SeiteFreeman Has Been A Partner in A Commercial Construction CompanyMuhammad ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Use of Power Tools Rev0Dokument92 SeitenSafe Use of Power Tools Rev0mohapatrarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise On Coordination and ResponseDokument8 SeitenExercise On Coordination and ResponseNorliyana AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ricoh Aficio SP C420DN PARTS CATALOGDokument82 SeitenRicoh Aficio SP C420DN PARTS CATALOGYury Kobzar100% (2)
- Australia Visa RequirementsDokument1 SeiteAustralia Visa RequirementsJoana DetomasNoch keine Bewertungen