Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Philosphies of Education
Hochgeladen von
Arianne Keh0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten5 SeitenOriginaltitel
PHILOSPHIES OF EDUCATION.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten5 SeitenPhilosphies of Education
Hochgeladen von
Arianne KehCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
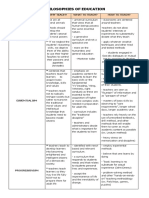
PHILOSOPHIES OF EDUCATION
PHILOSOPHY Why teach? What to teach? How to teach?
- learners to acquire basic - programs are - emphasize mastery of
Essentialism knowledge, skills and values. academically rigorous - the subject matter
- to transmit the traditional basic skill or the - teachers fountain of
moral values and intellectual fundamental r’s – reading, information and paragon of
knowledge that students need to ‘riting, ‘rithmetic, right virtue
become model citizens conduct needed in - teachers observe “core
preparation for adult life. requirements, longer school
- traditional discipline days and a longer academic
– Math, natural Science, year”
History, Foreign - rely heavily on the use of
Languages and Literature - prescribed textbooks
frown upon vocational - heavy stress on
courses -what is most memorization and
important and place little discipline.
emphasis on students
interest
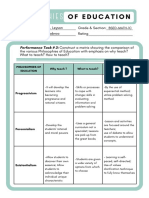
- to develop learners into - need-based and relevant - employ experiential
Progressivism becoming enlightened and curriculum - curriculum methods
intelligent citizens of a that respond to students’ - learns by doing
democratic society. need and relates to -John Dewey – advocate of
- teach learners so they may students’ lives and Progressivism - heavily rely
live life fully NOW experiences on the problem-solving
- accept the impermanence method (Scientific method)
of life and inevitability of - Hands-on-minds-on
change, everything else teaching method like field
change trips and thought-provoking
games.
-concerned with teaching
the learners the skill to
cope with change
- give focus to teaching of
skills or process in
gathering and evaluating
information and in problem
solving.
- give emphasis on natural
and social sciences
- we are all rational animals - curriculum is universal or - centered around teachers -
Perennialism - develop the students’ rational general students engaged in
and moral powers - heavy on the humanities, Socratic dialogues or
general education mutual inquiry sessions to
- less emphasis on develop an understanding
vocational and technical of history’s most timeless
education concepts.
- what the perennialist
teachers teach are lifted
from the Great Books
- to help students understand - students are given a wide - Focus on individual
Existentialism and appreciate themselves as variety of options from - learning is self-paced,
unique individual who accept which they to choose self directed.
complete responsibility for their -tremendous emphasis is - grate deal of individual
thoughts, feelings and action. given to Humanities to contact with the teacher
- to help students define their provide students with -employ values
own essence by exposing them vicarious experiences that clarification strategy
to various paths will help unleash their own
-education of the whole person creativity and self-
expression - vocational
education is regarded more
-encourage creativity and
imagination
- modification and shaping of - look people and other - ought to arrange
Behaviorism student’s behavior by providing animals as complex environment conditions
a favorable environment combination of matter that - ought to make the stimuli
act only in response to clear and interesting to
internally or externally capture and hold the
physical stimuli. - teach learners’ attention.
students to respond - ought to provide
favorably to various stimuli appropriate incentives to
in the environment. reinforce positive responses
to awaken or eliminate
negative ones.
- to develop the communication - learners should be taught - teach language and
Linguistic skills of the learners to communicate clearly communication through
- to develop in the learner the - Communication takes experiential way.
skill to send message clearly place in three ways: verbal, - make the classroom a
and receive messages correctly. nonverbal and paraverbal. place for the interplay of
Verbal – the content of our minds and hearts.
message, the choice and - facilitates dialogue among
arrangement of our words. learners because in the
This can be oral or written. exchange of words there is
Nonverbal – the message also an exchange of ideas.
we send through body
language.
Paraverbal – refers to how
we say what we say – tone,
pacing and volume of our
voices.
teach learners to use
language that is correct,
precise, grammatical,
coherent, accurate.
help student expand their
vocabularies
teach the learner how to
communicate clearly
caution the learners of
the verbal and non-verbal
barriers of communication
teach the learner to
speak as many languages
as you can.
-teaching philosophy 1. The human person, the -Teach philosophy in a way
Philosophy is important because a learner in particular and the that students also learn to
clear philosophy of teaching can educated person. formulate their own
lead to a change 2. what is true and good philosophy in life
in teaching behavior and foster and therefore must be particularly in teaching.
professional and personal taught.
growth. 3. how a learner must be
taught in order to come
close to the truth.
4. how learner must be
taught in order to come
close to the truth.
- to develop intrinsically - learners are taught how to - teacher provides students
Constructivism motivated and independent learn, learning processes with data or experiences
learners adequately equipped and skills that allow them to
with learning skills for them to hypothesize, predict,
be able to construct knowledge manipulate objects, pose
and make meaning of them. questions, research,
investigate, imagine and
invent.
- constructivist classroom is
interactive
- promotes dialogical
exchange of ideas among
learners and between
teachers and students.
- teacher’s role is to
facilitate the process.
o knowledge is
constructed by
learners through an
active, mental
process of
development.
o the minds are full of
ideas waiting to be
midwifed by the
teacher with his/her
skillful facilitating
skills.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Philosophies of EdDokument2 SeitenPhilosophies of EdJoefryQuanicoBarcebalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educational Philosophy Questionnaire: Statements 1 2 3 4Dokument6 SeitenEducational Philosophy Questionnaire: Statements 1 2 3 4JoefryQuanicoBarcebal100% (1)
- Module 3 Philosophies ActivityDokument4 SeitenModule 3 Philosophies ActivityFrancis KatigmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Teaching As A Vocation, Mission and ProfessionDokument15 SeitenLesson 4 Teaching As A Vocation, Mission and ProfessionElle HoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Let Review 2013 Prof - EdDokument318 SeitenLet Review 2013 Prof - EdbabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1Kim Carlo LampaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophies of Education Matrix 2Dokument3 SeitenPhilosophies of Education Matrix 2Rey Crtz II50% (2)
- Phil of Education Matrix PDFDokument2 SeitenPhil of Education Matrix PDFmarichu apilado100% (2)
- Jenny D. Napuran - Activity 1Dokument5 SeitenJenny D. Napuran - Activity 1Johnpaul Macapugas50% (2)
- Lesson 8 ReportDokument19 SeitenLesson 8 ReportMaam NikkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teaching Profession Chapter One: You, The Teacher, As A Person in The SocietyDokument4 SeitenThe Teaching Profession Chapter One: You, The Teacher, As A Person in The SocietyMargareth DaacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educational PhilosphyDokument11 SeitenEducational PhilosphyRhossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophies of EducationDokument2 SeitenPhilosophies of EducationKNoch keine Bewertungen
- STI - Explore - TasksDokument5 SeitenSTI - Explore - TasksSandra IsraelNoch keine Bewertungen
- President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityDokument8 SeitenPresident Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityJonel RazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: The Seven Philosophies of EducationDokument3 SeitenPhilosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: The Seven Philosophies of EducationJohn RaymondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaDokument3 SeitenSeven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaRocel NavajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTESDokument2 SeitenNOTESAlethea Zabdielle LaxamanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Dokument4 SeitenProf. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Mish LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Learning TheoriesDokument8 SeitenComparing Learning Theoriesfimmee2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- L FLCTDokument6 SeitenL FLCTJames Tyler BayalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Seven Philosophies of Education PhilDokument2 SeitenThe Seven Philosophies of Education PhilArnold C. LasitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismDokument2 SeitenWhy Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismSunako Claes0% (1)
- Philosophies of EducationDokument2 SeitenPhilosophies of EducationErica LeysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- You, The Teacher, As A PersonDokument59 SeitenYou, The Teacher, As A PersonGilbert AranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Seven Philosophies of Education PhilDokument2 SeitenThe Seven Philosophies of Education PhilJohn Patrick ArciteNoch keine Bewertungen
- with-Answers-TEACHING PROFESSION - MODULE1Dokument12 Seitenwith-Answers-TEACHING PROFESSION - MODULE1Aeron Chester DinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 You, The Teacher, As A Person in SocietyDokument53 Seiten1.0 You, The Teacher, As A Person in SocietyShandee Jeanne Magdaraog100% (2)
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDokument4 SeitenThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teacher As Person in The Society PDFDokument55 SeitenThe Teacher As Person in The Society PDFJohn Raymond80% (5)
- Philosophy in EducationDokument2 SeitenPhilosophy in EducationCherry Lynn NorcioNoch keine Bewertungen
- FS 1 Le16Dokument4 SeitenFS 1 Le16Jorebell W. QuiminoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum DevelopmentDokument85 SeitenCurriculum DevelopmentGen RabliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science RWDokument1 SeiteScience RWjesicaorbaneja101696Noch keine Bewertungen
- You, The Teacher, As A Person (Students' Copy)Dokument46 SeitenYou, The Teacher, As A Person (Students' Copy)Julius SalenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ED101Dokument2 SeitenED101Rodie lyn SueltoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophies of EducationDokument6 SeitenPhilosophies of EducationJake FundalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart of A Teacher PDFDokument33 SeitenHeart of A Teacher PDFLe-onoleu Ppa Sati Nem100% (1)
- Principles of TeachingDokument53 SeitenPrinciples of TeachingGlayza Marie ArcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching ProfessionDokument4 SeitenTeaching ProfessionNI C CANoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Profession AssignmentDokument2 SeitenTeaching Profession Assignmentjunjun gallosa100% (6)
- Explanation of TermsDokument12 SeitenExplanation of TermsIshanvi AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesDokument2 SeitenPrinciples of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesMaybza ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDokument25 SeitenThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Philosophical Heritage - Teaching ProfessionDokument2 SeitenThe Philosophical Heritage - Teaching ProfessionJessica Ruar Napoles76% (17)
- Module in TPDokument9 SeitenModule in TPQuenie De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study GuideDokument2 SeitenStudy Guideanthony100% (3)
- Philosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To TeachDokument4 SeitenPhilosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To TeachAMABELLE MITZI S. NO-OTNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDUC 105 Prelim DiscussionsDokument21 SeitenEDUC 105 Prelim DiscussionsChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Philosophies of EducationDokument2 Seiten5 Philosophies of EducationKuys Queng Cospeth83% (6)
- Different Type of Educ PhilosophyDokument6 SeitenDifferent Type of Educ PhilosophyThet SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Model Proponent/S Purpose/ Goal Concepts/ FeaturesDokument5 SeitenCurriculum Model Proponent/S Purpose/ Goal Concepts/ FeaturesJaja VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sdbecos Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenSdbecos Assignment 1Neliciwe MahlanguNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROF ED 9 UNIT 1 StudentsDokument12 SeitenPROF ED 9 UNIT 1 Studentsmelvin procianosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamDokument4 SeitenFinal ExamjhoerielNoch keine Bewertungen
- PERENNIALISMDokument6 SeitenPERENNIALISMJP PasionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carrera de Pedagogía en Idiomas Nacionales Y Extranjeros Course: C1Dokument7 SeitenCarrera de Pedagogía en Idiomas Nacionales Y Extranjeros Course: C1EVELYN JACQUELINE ESTRELLA SAILEMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: YOU, THE TEACHER, AS A PERSON IN SOCIETYDokument2 SeitenChapter 1: YOU, THE TEACHER, AS A PERSON IN SOCIETYMaitha Entia Cabezada0% (1)
- Unit 1Dokument13 SeitenUnit 1Adriana Ysabelle Mercado ArimangNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Ed. 2-YearsDokument114 SeitenM.Ed. 2-YearsMohanTnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL G6 Q2 WEEK 9 ALL SUBJECTS (Mam Inkay Peralta)Dokument79 SeitenDLL G6 Q2 WEEK 9 ALL SUBJECTS (Mam Inkay Peralta)Yvonne Karizza Mae Icuspit-TenedorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Criteria Wise Requirement 1 NBADokument47 SeitenCriteria Wise Requirement 1 NBAArun prasath100% (1)
- Motivating Project Based Learning Sustaining The Doing Supporting The LearningDokument31 SeitenMotivating Project Based Learning Sustaining The Doing Supporting The LearningCristina100% (1)
- Teaching ResumeDokument1 SeiteTeaching Resumeapi-473262254Noch keine Bewertungen
- English 101 Essay 2Dokument2 SeitenEnglish 101 Essay 2Nicole WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGPACM ProspectusDokument19 SeitenPGPACM Prospectusviratarun100% (1)
- Computer Grade 8 Curriculum Map 2021 2022Dokument4 SeitenComputer Grade 8 Curriculum Map 2021 2022ornopiakenneth07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Colegio Boston School Profile 2019Dokument8 SeitenColegio Boston School Profile 2019api-350863043Noch keine Bewertungen
- UZ Programmes PDFDokument52 SeitenUZ Programmes PDFApo ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mga AlamatDokument20 SeitenMga AlamatmarlonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Reading - 1Dokument4 SeitenProfessional Reading - 1api-508196283100% (2)
- Syllabus: PrimaryDokument39 SeitenSyllabus: PrimaryRedly SavarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridging The Gap Between Saudi Students Translator Training Programmes and The Needs of The Saudi Translation MarketDokument389 SeitenBridging The Gap Between Saudi Students Translator Training Programmes and The Needs of The Saudi Translation Marketahmed elnimeiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Learner Demonstrates Understanding Of... : GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDokument6 SeitenThe Learner Demonstrates Understanding Of... : GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Logric manalastasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum MappingDokument3 SeitenCurriculum MappingTrixie Mae RapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Log of M8Al-Ib-2 (Week 2 Day 3) : Can The Difference of Two Squares Be Applicable To 3 - 12 If No, Why?Dokument4 SeitenDaily Lesson Log of M8Al-Ib-2 (Week 2 Day 3) : Can The Difference of Two Squares Be Applicable To 3 - 12 If No, Why?zirconis10Noch keine Bewertungen
- UTSA 2012-14 CatalogDokument448 SeitenUTSA 2012-14 CatalogROBELLAANoch keine Bewertungen
- FTAD Implementing Guidelines On SBM Validation Final Version 21 APRIL 430PM 2Dokument51 SeitenFTAD Implementing Guidelines On SBM Validation Final Version 21 APRIL 430PM 2Ethel Paladin DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inclusive Education Task 2Dokument10 SeitenInclusive Education Task 2Sumaiya KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Implementation of The Senior High School Curriculum A Descriptive Analysis IJERTV8IS120084Dokument4 SeitenEffective Implementation of The Senior High School Curriculum A Descriptive Analysis IJERTV8IS120084Dhon ValeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof Ed Summative Exam Pdfca UbDokument53 SeitenProf Ed Summative Exam Pdfca UbCamela Rose CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 2 LESSON 1 The School Curriculum Definition, Nature and ScopeDokument6 SeitenMODULE 2 LESSON 1 The School Curriculum Definition, Nature and Scopeprincess pauline laiz0% (2)
- EMPLOYEES' PERCEPTION OF TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES IN AN ORGANIZATION: A CASE STUDY OF DELTA STEEL COMPANY (DSC) ALADJA, Nigeria.Dokument111 SeitenEMPLOYEES' PERCEPTION OF TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMMES IN AN ORGANIZATION: A CASE STUDY OF DELTA STEEL COMPANY (DSC) ALADJA, Nigeria.PROMISE CHIDI-AGBAI IROEGBUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Education Leader Visionary in Salt Lake City UT Resume Karen Smith-DellDokument2 SeitenExecutive Education Leader Visionary in Salt Lake City UT Resume Karen Smith-DellKarenSmithDellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology For Teaching and Learning 2Dokument9 SeitenTechnology For Teaching and Learning 2Jeneva Vistal100% (1)
- Music Education With Digital TechnologyDokument234 SeitenMusic Education With Digital Technologytotally_taz100% (1)
- Day1 Educational Management of InstitutionsDokument40 SeitenDay1 Educational Management of InstitutionsMilano Torres100% (1)
- Daily Curriculum Map Grade 9Dokument2 SeitenDaily Curriculum Map Grade 9Lea Cañolas BungcasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (2001) Textbooks, Contexts, and LearnersDokument19 Seiten(2001) Textbooks, Contexts, and LearnersMack MickNoch keine Bewertungen