Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP For Delivery Room
Hochgeladen von
Giselle Estoquia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
2K Ansichten4 Seitenj
Originaltitel
Ncp for Delivery Room
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
2K Ansichten4 SeitenNCP For Delivery Room
Hochgeladen von
Giselle Estoquiaj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
NCP FOR DELIVERY ROOM
RISK FOR DEFICIENT FLUID VOLUME AFTER PREGNANCY
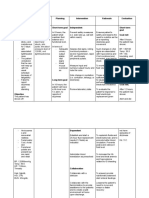
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS BACKGROUND GOALS AND NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
KNOWLEDGE OUTCOMES INTERVENTION
/ANALYSIS
Subjective Cues: Deficient Fluid Volume Deficient Fluid After 24 hours of 1. Assess vital signs and 1. Decreased fluid After the nursing
“Nakakaramdam po ako ng related to excessive blood Volume/Postpartum nursing intervention monitor for signs of volume will cause intervention has been
hilo” as verbalized by the loss and disseminated Hemorrhage is defined the patient will be shock. blood pressure to given, the goal is me
patient. intravascular coagulation, as any loss of blood able to: 2. Monitor blood loss drop and patient 1. Maternal
and uterine atony after from the uterus more 1. Prevented Site will go into shock. signs stab
Objective Cues: pregnancy as evidenced than 500mL within a from Type 2. Amount of blood 2. Bleeding
Pallor by blood loss more than 24-hour period. It may dysfuncti Amount – loss and presence diminishe
Soft Uterus 500 mL, heavy lochia be immediate or late onal should be nor of blood clots can stable.
Uterus not well flow, increased occurring from the first bleeding. more than 1 help determine 3. Assessme
contracted temperature due to 24 hours of delivery up 2. Improve perineal pad treatment. findings
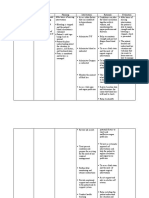
Blood loss of 500 mL per hour
infection predisposing to to the remaining days of fluid 3. If bleeding is due within no
Uncontrolled
uterine atony, elevation of the 6-week puerperium, volume. Presence of to vaginal limits
Bleeding
pulse rate indicating clots hematoma, rest
Heavy Lochia flow
Drop in hemoglobin
hypovolemia, decreased 3. Assess for vaginal and application of
laboratory results urine and sudden drop in hematoma an ice pack may be
Low Hemoglobin: blood pressure implying 4. Monitor intake and sufficient
10.0 g/dl (normal hemorrhage. output for 30mL – 50 treatment
range 12.0 g/dl) m/hr urine output; 4. Decreased urine
Uncontrolled may require output may be
Bleeding indwelling catheter assign of
V/S insertion for accurate hematomas that
Blood Pressure 90/70 measurement put pressure on the
mm/ hg 5. Monitor lab values to urethra, or may be
Temperature: 35.4℃ determine need for a late sign of
PR: 140 BPM transfusions ir signs of hypovolemic
RR: 20 complications shock
6. Watch hematocrit and
5. Administer IV clotting levels to know
fluids, medications if blood transfusion is
and blood necessary and for
products as signs and severity of
necessary DIC.
Oxytocin 7. Fluid replacement may
Antibiotics be necessary and
Analgesics depending on amount
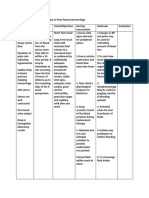
6. Perform uterine of blood lost and
massage to hematocrit level, a
stimulate blood transfusion may
contractions be required. Oxytocin
following delivery is sometimes given to
7. Monitor and initiate contractions
manage pain that will help stop
8. Place patient on bleeding.
bed rest with legs 8. Begin fundal massage
elevated and educate patient on
9. Prepare patient how to massage
for surgery if abdomen to stimulate
indicates; remain contractions. These
on NPO status contractions may help
stop bleeding
9. Continued, unrelieved
pain may be due to
hematomas or
lacerations within the
vagina
10. Rest and elevation of
legs helps venous
return and slows
bleeding.
11. If bleeding can’t
be managed
otherwise, surgery
may be required.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Final NCP For PostpartumDokument8 SeitenFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- NCP Post PartumDokument2 SeitenNCP Post PartumsteffiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDianne Mae100% (1)
- 5b - NCPDokument7 Seiten5b - NCPKelly Camero ÜNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDokument5 SeitenAbruptio Placenta NCPTinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP ObDokument2 SeitenNCP ObtimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PPHDokument2 SeitenNCP PPHmikee-berredo-9975Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Gestational HypertensionDokument2 SeitenNCP Gestational Hypertensionshila_glangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post-Partum Care Plan NCPDokument2 SeitenPost-Partum Care Plan NCPRap De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biographical Data - InfantDokument3 SeitenBiographical Data - Infantmitsuki_sylphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labor Nursing Care PlansDokument58 SeitenLabor Nursing Care PlansMuhamad AriNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLANDokument10 SeitenNURSING CARE PLANR-Chian Jose Germanp100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan 1Dokument12 SeitenNursing Care Plan 1Disyme Duron AzuresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Pain - OBDokument5 SeitenNCP Pain - OBSandra Guimaray50% (2)
- OB - NCP (Episiotomy)Dokument3 SeitenOB - NCP (Episiotomy)eosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PihDokument8 SeitenNCP PihReinell GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionMurugham DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Labor Stage 2 (Expulsion)Dokument15 SeitenNCP: Labor Stage 2 (Expulsion)Javie100% (1)
- Uterine Atony - NCPDokument17 SeitenUterine Atony - NCPMonica BorjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSVD Patient Sleep IssuesDokument3 SeitenNSVD Patient Sleep IssuesAlma Gobaleza100% (1)
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPJefferson ManasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum discharge plan vitamins exercise dietDokument2 SeitenPostpartum discharge plan vitamins exercise dietJude Labajo100% (1)
- Care Plan PostpartumDokument2 SeitenCare Plan Postpartumteokie082483% (6)
- NCP During LaborDokument6 SeitenNCP During LaborJamielyn BassigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDokument7 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDan Dan ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP EpisiotomyDokument1 SeiteNCP EpisiotomyKaye CeprianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Risk AssessmentDokument3 SeitenMaternal Risk AssessmentMark FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSVD Case Study FinalDokument60 SeitenNSVD Case Study Finaljints poterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorrhage NCPDokument4 SeitenHemorrhage NCPElishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum Hemorrhage ManagementDokument2 SeitenPostpartum Hemorrhage ManagementjsksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Preterm LaborDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan Preterm LaborAdriane Coma100% (1)
- N E E D S C O G N I T I V E P E R P E T U A L RationaleDokument14 SeitenN E E D S C O G N I T I V E P E R P E T U A L RationaleArianna Jasmine MabungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital SignsDokument3 SeitenAfter 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signsroma_elonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintaining Normal Body Temperature in NewbornsDokument2 SeitenMaintaining Normal Body Temperature in NewbornsErica Veluz LuyunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rle 107 Maternal and Child Health Nursing: University of The Assumption College of Nursing and PharmacyDokument6 SeitenRle 107 Maternal and Child Health Nursing: University of The Assumption College of Nursing and PharmacyEvangeline Anne Macanas100% (2)
- Retained Placental FragmentsDokument9 SeitenRetained Placental FragmentsHannah Laput100% (2)
- NCP Alterations in Normal LaborDokument9 SeitenNCP Alterations in Normal LaborCameron De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernandez NCP Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenHernandez NCP Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 Rle ActivityDokument3 SeitenWeek 2 Rle ActivityMICHELLE BIANCA PATRICE CRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection 1Dokument5 SeitenReflection 1api-400554289Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument6 SeitenNursing Care PlanAnthea ValinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Risk of InfectionDokument2 SeitenNCP For Risk of InfectionAdriane ComaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhageDokument3 SeitenFluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhagePatricia Franco100% (1)
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDokument2 SeitenGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- PRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDDokument8 SeitenPRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDAloha ItsmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing NURSING Care PlanDokument3 SeitenCollege of Nursing NURSING Care PlanToyour EternityNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Acute PainDokument4 SeitenNCP - Acute PainCharmin AlegreNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP On Ectopic PregnancyDokument5 SeitenNCP On Ectopic PregnancyDaisy Lui100% (1)
- NCP Case 1Dokument6 SeitenNCP Case 1boomer SeargeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Placenta PreviaDokument2 SeitenNCP Placenta PreviaCathy CnlsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Prenatal InfectionDokument10 SeitenNCP: Prenatal InfectionJavieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Abruptio PlacentaDokument2 SeitenNCP Abruptio PlacentaCarson Birth100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalDokument19 SeitenAbruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalTin100% (1)
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageDokument4 SeitenBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDokument9 SeitenNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFDokument2 SeitenPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFA sison100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Deficit PPHDokument3 SeitenFluid Volume Deficit PPHEllie GartungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceMelinda Cariño BallonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanDokument9 SeitenPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanElli SuñgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Postpartum HemorrhageDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Postpartum HemorrhageEvangeline Anne MacanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johari WindowDokument2 SeitenJohari WindowGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Dokument3 SeitenPATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Giselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- H E-DiabetesDokument41 SeitenH E-DiabetesGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRes1 Course Unit 5Dokument5 SeitenNRes1 Course Unit 5Giselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desirable Body Weight and Calorie RequirementsDokument12 SeitenDesirable Body Weight and Calorie RequirementsGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Visual ImpairmentDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Visual ImpairmentGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Management: Sedation, Headache, DepressionDokument2 SeitenMedical Management: Sedation, Headache, DepressionGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRes1 Course Unit 4Dokument5 SeitenNRes1 Course Unit 4Giselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology QuestionnaireDokument1 SeitePharmacology QuestionnaireGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Final 1 Ready To PrintDokument40 SeitenCase Study Final 1 Ready To PrintGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical ScenarioDokument3 SeitenClinical ScenarioGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol Literature Review UpdateDokument39 SeitenAlcohol Literature Review UpdateGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- POST NATAL FNCP - DotdotDokument1 SeitePOST NATAL FNCP - DotdotGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching PlanDokument2 SeitenTeaching PlanGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol Literature Review UpdateDokument39 SeitenAlcohol Literature Review UpdateGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Informatics: Bachelor of Science in NursingDokument5 SeitenNursing Informatics: Bachelor of Science in NursingGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desirable Body Weight and Calorie RequirementsDokument12 SeitenDesirable Body Weight and Calorie RequirementsGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching PlanDokument2 SeitenTeaching PlanGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 2 Perioperative Nursing PDFDokument171 SeitenWeek 1 2 Perioperative Nursing PDFGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PathophysioDokument1 SeitePathophysioGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- POST NATAL FNCP - DotdotDokument1 SeitePOST NATAL FNCP - DotdotGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PathophysioDokument1 SeitePathophysioGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unstable Blood Glucose Level: Criteria Computation Actual Score JustificationDokument5 SeitenUnstable Blood Glucose Level: Criteria Computation Actual Score JustificationGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Related LiteratureDokument12 SeitenReview of Related LiteratureGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ensuring Baby's Health After BirthDokument5 SeitenEnsuring Baby's Health After BirthGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital Information System World Wide WebDokument2 SeitenHospital Information System World Wide WebGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 2 Perioperative Nursing PDFDokument171 SeitenWeek 1 2 Perioperative Nursing PDFGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CU Task 6Dokument1 SeiteCU Task 6Giselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cu 4 Laboratory For Nutrient and Diet TherapyDokument11 SeitenCu 4 Laboratory For Nutrient and Diet TherapyGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cu Lab Week 2 Bmi, BBW, Ter, BMR, CPF Solutions For May, Mary and FreyDokument3 SeitenCu Lab Week 2 Bmi, BBW, Ter, BMR, CPF Solutions For May, Mary and FreyGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Banking QuestionsDokument18 SeitenBlood Banking QuestionsDefensor Pison Gringgo82% (45)
- Blood Transfusion - Hatem AlsrourDokument18 SeitenBlood Transfusion - Hatem Alsrourhatem alsrour100% (2)
- What Is A Blood TransfusionDokument6 SeitenWhat Is A Blood TransfusionCarlo TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mizoguchi 2016Dokument5 SeitenMizoguchi 2016Placido Rojas FrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC-Report RDokument1 SeiteCBC-Report Ryoutube premiumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Lab Report SummaryDokument6 SeitenPatient Lab Report SummaryDr. Omprakash SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygenation: Hematologic Pathophysiology: Allen Octaviano CudiamatDokument34 SeitenOxygenation: Hematologic Pathophysiology: Allen Octaviano Cudiamatᜀᜎ᜔ᜎᜒᜈ᜔ ᜃᜓᜇᜒᜀᜋᜆ᜔100% (1)
- HbA1c - I Chrome DuoDokument3 SeitenHbA1c - I Chrome DuoAnnisa Chaerani100% (1)
- Blood TransfusionDokument50 SeitenBlood TransfusionSerat Rahman100% (2)
- 18 Hematological Conditions in NewbornDokument25 Seiten18 Hematological Conditions in NewbornRana VandanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kell Blood Group System: Muhammad Asif Zeb Lecturer Hematology Ipms-Kmu PeshawarDokument11 SeitenKell Blood Group System: Muhammad Asif Zeb Lecturer Hematology Ipms-Kmu PeshawarMaaz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MLT Blood Bank Exam 2 FullDokument4 SeitenMLT Blood Bank Exam 2 Fullkasdf gre bbtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpreting Hematocrits: Critical Thinking QuestionsDokument4 SeitenInterpreting Hematocrits: Critical Thinking Questionsapi-400575655Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abo Incompatible Stem Cell Transplant - Laboratory Side BDokument28 SeitenAbo Incompatible Stem Cell Transplant - Laboratory Side BAlita PalpialyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationDokument9 SeitenEvaluation of The Performance of Sysmex XN-3100 Automated Hematology Analyzer Regarding The Sysmex XE-2100 and Microscopic ExaminationbalkisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Bank: Abo and RHDokument3 SeitenBlood Bank: Abo and RHGwynne VelasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cryoprecipitate The Current State of KnowledgeDokument12 SeitenCryoprecipitate The Current State of KnowledgeAngel Bernardo GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bloodservices PDF Sop Antibody IdentDokument13 SeitenBloodservices PDF Sop Antibody IdentChristoper BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- HELLP/Imitators of Severe Preeclampsia/EclampsiaDokument79 SeitenHELLP/Imitators of Severe Preeclampsia/Eclampsiakat_ghersiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology Unit: Complete Blood Picture (CBC)Dokument1 SeiteHematology Unit: Complete Blood Picture (CBC)Yousuf ShehabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal AnemiaDokument5 SeitenJurnal AnemiaRizki Nur Amalia100% (2)
- Jurnal Skripsi Evita OktaviaDokument10 SeitenJurnal Skripsi Evita OktaviaandiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Luxury Donor Couch: Making Blood Donation A Safe and Comfortable ExperienceDokument4 SeitenLuxury Donor Couch: Making Blood Donation A Safe and Comfortable ExperienceSajanan S S ChathannurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haematology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Dokument122 SeitenHaematology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Mohammed RisqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To The Child With AnemiaDokument13 SeitenApproach To The Child With AnemiavessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bruising OSCE History Taking PaediatricsDokument6 SeitenBruising OSCE History Taking PaediatricsJJ LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)Dokument1 SeiteCBC (Complete Blood Count)Roshan kumar giriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Laboratory Technology Journal ComparisonDokument6 SeitenMedical Laboratory Technology Journal ComparisonMuhammad RaihandNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC Arikod HoimaDokument37 SeitenCBC Arikod Hoimadaniel arikodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Terminology Blood Lymph SystemsDokument29 SeitenMedical Terminology Blood Lymph Systemsapi-268199514100% (1)